Abstract
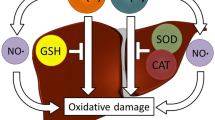
Iron saccharate complex ISC is an iron supplement used to optimize erythropoiesis in cases of iron deficiencies. Because of the lack of major mechanisms of iron excretion, excess iron unbound to protective molecules is believed to be involved in catalyzing the generation of reactive oxygen species and induction of oxidative stress. This study employed ISC for the purpose of inducing iron overload and hence investigating the consequent iron toxicity, lipid peroxidation and antioxidant extent in a murine species. Male Wistar rats were given iron as intraperitoneal injections of ISC in subacute (0.2 mg Fe kg−1 for 2 weeks) and subchronic (0.1 mg Fe kg−1 for 4 weeks) doses. In iron-overloaded rats, enhanced hepatic iron accumulation (P > 0.001) attended by increased serum concentrations of malondialdehyde (MDA) (P > 0.001) and activities of antioxidant enzymes (superoxide dismutase SOD, catalase CAT and glutathione peroxidase GPx) (P > 0.001) was pointed out. The demonstrated antioxidant boost is attributed to a sense of equilibrium prompted by the potential of iron-induced oxidative stress to modify antioxidant defense capacity and to modulate susceptibility to oxidative stress. Rats seemed to constantly suffer from oxidative stress based on the consistent rise in MDA that was not overwhelmed by the elevated antioxidant input. The current findings are of informative value in drawing attention to the health hazards of applying higher doses of the commercially used iron supplement ISC. Data are virtually significant in elucidating the higher magnitude of subchronic than subacute iron overload in initiating oxidative stress and antioxidant defense. Both pathways proceeded in a time-dependent rather than dose-dependent manner.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abd El-Baky A.E. 2011. Protective effect of Curcuma longa against iron overload on pancreatic B-cell function and sorbitol metabolism. Austr. J. Basic Appl. Sci. 5(2): 90–99.
Agarwal R., Vasavada N., Sachs N.G. & Chase S. 2004. Oxidative stress and renal injury with intravenous iron in patients with chronic kidney disease. Kidney Int. 65(6): 2279–2289. DOI: 10.1111/j.1523-1755.2004.00648.x
Andrews N.C. 1999. Disorders of iron metabolism, N. Engl. J. Med. 341(26): 1986–1995. DOI: 10.1056/NEJM199912233412607
Arpi T. & Tollerz G. 1965. Iron poisoning in piglets, autopsy findings in experimental and spontaneous cases. Acta Vet. Scand. 6(4): 360–373. PMID: 5892898
Auerbach M. & Ballard H. 2010. Clinical use of intravenous iron: administration, efficacy, and safety. Hematology American Society of Hematology Education Program 2010(1): 338–347. DOI: 10.1182/asheducation-2010.1.338
Bacon B.R. & Brown K.E. 1996. Iron metabolism and disorders of iron overload. Chapter 20, pp. 349–362. In: Kaplowitz N. (ed.), Liver and Biliary Diseases, Williams and Wilkins, Baltimore, 783 pp. ISBN: 0683045458, 9780683045451
Banerjee B.D., Seth V., Bhattacharya A., Pasha S.T. & Chakraborty A.K. 1999. Biochemical effects of some pesticides on lipid peroxidation and free radical scavengers, Toxicol. Lett. 107(1–3): 33–47. DOI: 10.1016/S0378-4274(99)00029-6
Bassett M.L., Halliday J.W. & Powell L.W. 1986. Value of hepatic iron measurements in early haemochromatosis and determination of the critical iron level associated with fibrosis. Hepatology 6(1): 24–29. DOI: 10.1002/hep.1840060106
Batts K.P. 2007. Iron overload syndromes and the liver. Modern Pathology 20(Suppl 1): S31–S39. DOI: 10.1038/modpathol.3800715
Bothwell T.H., Charlton R.W., Cook J.D. & Finch C.A. 1979. Iron Metabolism in Man. Blackwell Scientific, Oxford, England, 576 pp. ISBN: 0632002239, 9780632002238
Brissot P., Ropert M., Le Lan C. & Loréal O. 2012. Nontransferrin bound iron: a key role in iron overload and iron toxicity, Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1820(3): 403–410. DOI: 10.1016/j.bbagen.2011.07.014
Britton R.S., Leicester K.L. & Bacon B.R. 2002. Iron toxicity and chelation therapy, Int. J. Hematol. 76(3): 219–228. DOI: 10.1007/BF02982791
Buege J. & Aust S. 1978. Microsomal lipid peroxidation. Method Enzymol. 52: 302–310. DOI: 10.1016/S0076-6879(78)52032-6
Charytan C., Levin N., Al-Saloum M., Hafeez T., Gagnon S. & Van Wyck D.B. 2001. Efficacy and safety of iron sucrose for iron deficiency in patients with dialysis-associated anemia: North American Clinical Trial. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 37(2): 300–307. DOI: 10.1053/ajkd.2001.21293 PMID:11157370
Cheeseman K.H. & Slater T.F. 1993. An introduction to free radical biochemistry. Br. Med. Bull. 49(3): 481–493. PMID: 8221017
Daba A., Gkouvatsos K., Sebastiani G. & Pantopoulos K. 2013. Differences in activation of mouse hepcidin by dietary iron and parenterally administered iron dextran: compartmentalization is critical for iron sensing. J. Mol. Med. (Berl.) 91(1): 95–102. DOI: 10.1007/s00109-012-0937-5
Devasagayam T.P.A., Tilak J.C., Boloor K.K., Sane K.S., Ghaskadbi S.S. & Lele R.D. 2004. Free radicals and antioxidants in human health: current status and future prospects. J. Assoc. Physicians India 52: 794–804. PMID: 15909857
de Valk B. & Marx J.J.M. 1999. Iron, atherosclerosis and ischemic heart disease. Arch. Intern. Med. 159(14): 1542–1548. DOI: 10.1001/archinte.159.14.1542.
Draper H. & Hadley M. 1990. Malondialdehyde determination as index of lipid peroxidation. Methods Enzymol. 186: 421–431. DOI: 10.1016/0076-6879(90)86135-I
Frankel E.N. 1980. Lipid oxidation. Prog. Lipid Res. 19: 1–22.
Fu Y., Cheng W.H., Ross D.A. & Lei X. 1999. Cellular glutathione peroxidase protects mice against lethal oxidative stress induced by various doses of diquat. Proc. Soc. Exp. Biol. Med. 222(2): 164–169. PMID: 10564541
Golberg L., Smith J.P. & Martin L.E. 1957. The effects of intensive and prolonged administration of iron parenterally in animals. Br. J. Exp. Pathol. 38(3): 297–311. PMID: 13436726
Halliwell B. & Gutteridge J.M.C. 1985. The chemistry of oxygen radicals and other oxygen-derived species, pp. 20–64. In: Halliwell B. & Gutteridge J.M.C. (eds), Free Radicals in Biology and Medicine, Oxford Science Publications, Clarendon Press, 346 pp. ISBN: 0198541376, 9780198541370
Halliwell B. & Gutteridge J.M.C. 1990. Role of free radicals and catalytic metal ions in human disease: An overview. Methods Enzymol. 186: 1–85. DOI: 10.1016/0076-6879(90)86093-B
Halpern B.N. & Pacaud A. 1951. Technique of obtaining blood samples from small laboratory animals by puncture of ophthalmic plexus., Comptes Rendus des Séances de la Société de Biologie et de ses Filiales 145(19–20): 1465–1466. PMID: 14926151
Herrera J., Nava M., Romero F. & Rodriguez-Iturbe B. 2001. Melatonin prevents oxidative stress resulting from iron and erythropoietin administration. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 37(4): 750–757. DOI: 10.1016/S0272-6386(01)80124-4
Hocken A.G. & Marwah P.K. 1971. Iatrogenic contribution to anaemia of chronic renal failure. Lancet 1(7691): 164–165. PMID: 4102187
Hou Y.J., Zhao Y.Y., Xiong B., Cui X.S., Kim N.H., Xu Y.X. & Sun S.C. 2013. Mycotoxin-containing diet causes oxidative stress in the mouse. PLoS ONE 8(3): e60374. DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0060374
Houglum K., Filip M., Witztum J.L. & Chojkier M. 1990. Malondialdehyde and 4-hydroxynonenal protein adducts in plasma and liver of rats with iron overload. J. Clin. Invest. 86(6): 1991–1998. PMID: 2123889
Howell D.C. 1987. Statistical Methods for Psychology. Second Edition. Duxbury Press. Boston, 636 pp.
Hundekari I.A., Suryakar A.N. & Rathi D.B. 2013. Acute organophosphorus pesticide poisoning in North Karnataka, India: oxidative damage, haemoglobin level and total leukocyte. Afr. Health Sci. 13(1): 129–136. DOI: 10.4314/ahs.v13i1.18.
IACUC 2008. Use of Animals in Research, Testing, and Teaching. Institutional Animal Care and Use Committees (IACUC) (412-383-2008). www.iacuc.pitt.edu/policies.asp
Inal M.E., Kanbak G. & Sunal E. 2001. Antioxidant enzyme activities and malondialdehyde levels related to aging. Clin. Chim. Acta 305(1–2): 75–80. DOI: 10.1016/S0009-8981(00)00422-8
Inman R.S. & Wessling-Resnick M. 1993. Characterization of transferrin-independent iron transport in K562 cells. Unique properties provide evidence for multiple pathways of iron uptake. J. Biol. Chem. 268(12): 8521–8528. PMID: 8473296
Jomova K. & Valko M. 2011. Advances in metal-induced oxidative stress and human disease. Toxicol. 283(2–3): 65–87. DOI: 10.1016/j.tox.2011.03.001
Kingston H.M. & Haswell S. (eds) 1997. Microwave Enhanced Chemistry. ACS Professional Reference Book Series. American Chemical Society, Washington, DC, 800 pp. ISBN: 9780841233751
Kushner J.P., Porter J.P. & Olivieri N.F. 2001. Secondary iron overload. Hematol. ASH Education Book 2001(1): 47–61. DOI: 10.1182/asheducation-2001.1.47
Kyle E., Brown M.D., Roy J. & Lucille A. 2003. Effect of iron overload and dietary fat on indices of oxidative stress and hepatic fibrogenesis in rats. Liver Int. 23(4): 232–242. PMID: 12895262
Lim P.S., Wei Y.H., Yu Y.L. & Kho B. 1999. Enhanced oxidative stress in haemodialysis patients receiving intravenous iron therapy. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 14: 2680–2687.
Malmström B.G., Andréasson L.E. & Reinhammer B. 1975. Copper-containing oxidases and superoxide dismutase. The Enzymes 12: 507–579. DOI: 10.1016/S1874-6047(08)60231-0
McCullough K.D. & Bartfay W.J. 2007. The dose-dependent effects of chronic iron overload on the production of oxygen free radicals and vitamin E concentrations in the liver of a murine model. Biol. Res. Nurs. 8(4): 300–304. DOI: 10.1177/109980040629873
Muir A.R. & Goldberg L. 1961. Observations on subcutaneous macrophages. Phagocytosis of iron-dextran and ferritin synthesis. Quart. J. Exp. Physiol. 46(4): 289–298.
Naithani R., Chandra J., Bhattacharjee J., Verma P. & Narayan S. 2006. Peroxidative stress and antioxidant enzymes in children with β-thalassemia major. Pediatr. Blood Cancer 46(7): 780–785. DOI: 10.1002/pbc.20669
Nielsen F., Mikkelsen B.B., Nielsen J.B., Andersen H.R. & Grandjean P. 1997. Plasma malondialdehyde as biomarker for oxidative stress: reference interval and effects of life-style factors. Clin. Chem. 43(7): 1209–1214. PMID: 9216458
Nyvad O., Danielsen H. & Madsen S. 1994. Intravenous iron sucrose complex to reduce epoietin demand in dialysis patients. Lancet 34(8932): 1305–1306. PMID: 7968018
Paglia D.E. & Valentine W.N. 1967. Studies on the quantitative and qualitative characterization of erythrocyte glutathione peroxidase. J. Lab. Clin. Med. 70(1): 158–169. PMID: 6066618
Pettit A. 1913. Simple method for drawing blood in small rodents. Compt. Rend. Soc. Biol. 74: 11–12.
Ranjbar A., Solhi H., Mashayekhi F.J., Susanabdi A., Rezaie A. & Abdollahi M. 2005. Oxidative stress in acute human poisoning with organophosphorus insecticides: a case control study. Env. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 20(1): 88–91. DOI: 10.1016/j.etap.2004.10.007
Richter G.W. 1978. The iron-loaded cell-the cytopathology of iron storage. A review. Am. J. Pathol. 91(2): 362–404. PMID: 2018208
Roob J.M., Khoschsorur G., Tiran A., Horina J.H., Holzer H. & Winklhofer-Roob B.M. 2000. Vitamin E attenuates oxidative stress induced by intravenous iron in patients on hemodialysis. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 11(3): 539–549. PMID: 10703678
Tavill A.S., Bipin K.S. & Bacon B.R. 1990. Iron and the liver: genetic hemochromatosis and other hepatic iron overload disorders. Prog. Liver Dis. 9: 281–305.
Udipi S., Ghugre P. & Gokhale C. 2012. Oxidative Stress and Health, pp. 147–148. In: Lushchak V. & Semchyshyn H.M. (eds), Oxidative Stress Molecular Mechanisms and biological effects, Open Access: INTECH, 374 pp. ISBN: 9535105541, 9789535105541
USEPA 1996. “Method 3052. Microwave Assisted Digestion of Siliceous and Organically Based Matrices.” Revision 0 (December 1996).” In Test Methods for Evaluating Solid Wastes: Physical/Chemical Methods, EPA SW-846, Third Ed., Vol. I, Section A, Chapter 3 (Inorganic Analytes), pp. 3052-1–3052-20, U.S. Environmental Protection Agency, Office of Solid Waste and Emergency Response, Washington, D.C. http://www.epa.gov/epaoswer/hazwaste/test/pdfs/3052.pdf (accessed 15.01.2014)
Valerio L.G. & Petersen D.R. 1998. Formation of liver microsomal MDA-protein adducts in mice with chronic dietary iron overload. Toxicol. Lett. 98(1–2): 31–39. DOI: 10.1016/S0378-4274(98)00100-3
van Herck H., Baumans V., Brandt C.J.W.M., Boere H.A.G., Hesp A.P.M., van Lith H.A., Schurink M. & Beynen A.C. 2001. Blood sampling from the retro-orbital plexus, the saphenous vein and the tail vein in rats: comparative effects on selected behavioural and blood variables. Lab. Anim. 35(2): 131–139. PMID: 11315161
Welz B. & Sperling M. 1999. Atomic Absorption Spectrometry. 3rd edition. Wiley-VcH, Weinheim, Germany, 965 pp. ISBN: 978-3-527-28571-6
Wheeler C.R., Salzman J.A., Elsayed N.M., Omaye S.T. & Korte D.W. Jr., 1990. Automated assays for superoxide dismutase, catalase, glutathione peroxidase, and glutathione reductase activity. Anal. Biochem. 184(2): 193–199. DOI: 10.1016/0003-2697(90)90668-Y
Yessayan L., Sandhu A., Besarab A., Yessayan A., Frinak S., Zasuwa G. & Yee J. 2013. Intravenous iron dextran as a component of anemia management in chronic kidney disease: a report of safety and efficacy. Int. J. Nephrol. 2013: article ID 703038, 9 pp. DOI: 10.1155/2013/703038.
Zhang Y., Huang Y., Deng X., Xu Y., Gao Z. & Li H. 2012. Iron overload induced rat liver injury: Involvement of protein tyrosine nitration and the effect of baicalin. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 680(1–3): 95–101. DOI: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2012.01.010
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Adham, K.G., Alkhalifa, A.A., Farhood, M.H. et al. Oxidative stress and antioxidant response to subacute and subchronic iron overload in Wistar rat. Biologia 69, 817–824 (2014). https://doi.org/10.2478/s11756-014-0364-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.2478/s11756-014-0364-x