Abstract
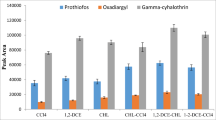
The excessive application of organophosphate pesticides (OPPs) in crop fields close to hives and its application in beekeeping practices are potential sources of contamination of propolis. Pesticides were extracted from raw propolis by matrix solid-phase dispersion. Because of the complex chemical composition of propolis, binary solvent mixtures based on acetonitrile and a relatively non-polar solvent in different proportions were tested for the selective elution of OPPs. The effect of mixed solvents on clean-up was evaluated by GC-MS and the main interfering compounds co-eluted with pesticides were identified. In addition, three volumes of the solvent mixture and the volume of the sample were evaluated in an experimental factorial design. The final experimental conditions were 1 mL of dissolved propolis and 8 mL of acetonitrile/dichloromethane (g4 r = 25: 75). Mean recoveries ranged from 55 % to 96 % (relative standard deviation < 8 %) with an inter-day precision lower than 24 %. The proposed method was applied to the analysis of real samples obtained from local beekeepers.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Acosta-Tejada, G. M., Medina-Peralta, S., Moguel-Ordóñez, Y. B., & Muñoz-Rodríguez, D. (2011). Matrix solid-phase dispersion extraction of organophosphorus pesticides from propolis extracts and recovery evaluation by GC-MS. Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry, 400, 885–891. DOI: 10.1007/s00216-011-4828-3.
Anastassiades, M., Lehotay, S. J., Stajnbaher, D., & Shenk, F. J. (2003). Fast and easy multiresidue method employing acetonitrile extraction/partitioning and “dispersive solid-phase extraction” for the determination of pesticide residues in produce. Journal of AOAC International, 86, 412–431.
Bogdanov, S. (2006). Contaminants of bee products. Apidologie, 37, 1–18. DOI: 10.1051/apido:2005043.
Chen, F., Che, L. Z., Wang, Q., Zhou, J. H., Xue, X. F., & Zhao, J. (2009). Determination of organochlorine pesticides in propolis by gas chromatography-electron capture detection using double column series solid-phase extraction. Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry, 393, 1073–1079. DOI: 10.1007/s00216-008-2474-1.
Dove, H., & Mayes, R. W. (2006). Protocol for the analysis of nalkanes and other plant-wax compounds and for their use as markers for quantifying the nutrient supply of large mammalian herbivores. Nature Protocols, 1, 1680–1697. DOI: 10.1038/nprot.2006.225.
Hercegová, A., Dömötörová, M., & Matisová, E. (2007). Sample preparation methods in the analysis of pesticide residues in baby food with subsequent chromatographic determination. Journal of Chromatography A, 1153, 54–73. DOI: 10.1016/j.chroma.2007.01.008.
Hill, A. R. C., & Reynolds, S. L. (1999). Guidelines for inhouse validation of analytical methods for pesticide residues in food and animal feeds. Analyst, 124, 953–958. DOI: 10.1039/a900603f.
Kazemi, M., Tahmasbi, A. M., Valizadeh, R., Nazerian, A. A., Soni, A., & Moheghi, M. M. (2012). Importance and toxicological effects of organophosphorus pesticides: A comprehensive review. Journal of Agricultural Science and Review, 1, 43–57.
Lambropoulou, D. A., & Albanis, T. A. (2007). Methods of sample preparation for determination of pesticide residues in food matrices by chromatography-mass spectrometry-based techniques: a review. Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry, 389, 1663–1683. DOI: 10.1007/s00216-007-1348-2.
Marcucci, M. C. (1995). Propolis: chemical composition, biological properties and therapeutic activity. Apidologie, 23, 83–89. DOI: 10.1051/apido:19950202.
Melliou, E., Stratis, E., & Chinou, I. (2007). Volatile constituents of propolis from various regions of Greece-antimicrobial activity. Food Chemistry, 103, 375–380. DOI: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2006.07.033.
Mohammadzadeh, S., Shariatpanahi, M., Hamedi, M., Ahmadkhaniha, R., Samadi, N., & Ostad, S. N. (2007). Chemical composition, oral toxicity and antimicrobial activity of Iranian propolis. Food Chemistry, 103, 1097–1103. DOI: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2006.10.006.
Montgomery, D. (2004). Diseño y análisis de experimentos (2nd ed.). Mexico City, Mexico: Editorial Limusa. (in Spanish)
Oldroyd, B. P. (2007). What’s killing American honey bees? PLoS Biology, 5, 1195–1199. DOI: 10.1371/journal.pbio. 0050168.
Pérez-Parada, A., Colazzo, M., Besil, N., Geis-Asteggiante., L., Rey, F., & Heinzen, H. (2011). Determination of coumaphos, chlorpyrifos and ethion residues in propolis tinctures by matrix solid-phase dispersion and gas chromatography coupled to flame photometric and mass spectrometric detection. Journal of Chromatography A, 1218, 5852–5857. DOI: 10.1016/j.chroma.2011.06.097.
Pope, C. N. (1999). Organophosphorus pesticides: Do they all have the same mechanism of toxicity? Journal of Toxicology and Environmental Health, Part B, 2, 161–181. DOI: 10.1080/109374099281205.
Sahinler, N., & Kaftanoglu, O. (2005). Natural product propolis: chemical composition. Natural Product Research, 19, 183–188. DOI: 10.1080/14786410410001704877.
dos Santos, T. F. S., Aquino, A., Dórea, H. S., & Navickiene, S. (2008). MSPD procedure for determining buprofezin, tetradifon, vinclozolin, and bifenthrin residues in propolis by gas chromatography-mass spectrometry. Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry, 390, 1425–1430. DOI: 10.1007/s00216-007-1813-y.
Shimelis, O., Yang, Y. H., Stenerson, K., Kaneco, T., & Ye, M. (2007). Evaluation of a solid-phase extraction dual-layer carbon/primary secondary amine for clean-up of fatty acid matrix components from food extracts in multiresidue pesticide analysis. Journal of Chromatograpgy A, 1165, 18–25. DOI: 10.1016/j.chroma.2007.07.037.
Viuda-Martos, M., Ruiz-Navajas, Y., Fernández-López, J., & Pérez-álvarez, J. A. (2008). Functional properties of honey, propolis, and royal jelly. Journal of Food Science, 73, R117–R124. DOI: 10.1111/j.1750-3841.2008.00966.x.
Walker, P., & Crane, E. (1987). Constituents of propolis. Apidologie, 18, 327–334. DOI: 10.1051/apido:2000102.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Medina-Dzul, K., Muñoz-Rodríguez, D., Moguel-Ordoñez, Y. et al. Application of mixed solvents for elution of organophosphate pesticides extracted from raw propolis by matrix solid-phase dispersion and analysis by GC-MS. Chem. Pap. 68, 1474–1481 (2014). https://doi.org/10.2478/s11696-014-0600-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.2478/s11696-014-0600-4