Abstract
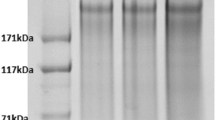
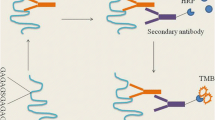
The degradation behavior of silk fibroin (SF) is a significant and intriguing subject in the area of archaeological ancient silk research. In the present study, the immunological detection techniques combined with traditional characterization methods, jointly studied the degradation process of SF from Bombyx mori (B. mori) and Antheraea pernyi (A. pernyi) through exposure to alkaline proteinase, α-chymotrypsin, pepsin, and trypsin. Spectroscopic analysis revealed that different enzymes showed similar hydrolysis effects on the secondary structure, but the changes of B. mori SF and A. pernyi SF were mainly reflected in the decrease of β-sheet and the reduction of α-helical structure, respectively. In further research of immunology, two diagnostic antibodies were prepared corresponding to SF of B. mori and A. pernyi, respectively. The enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) and western blot indicated the enzyme-treated SF proteins still exhibited higher immunoreactivity because the epitopes on the surface of SF molecules are retained. Although α-chymotrypsin possesses the most cleavage sites among these enzymes, the α-chymotrypsin-treated SF did not exhibit significant changes in secondary structures and high antibody binding capacity. The results deepen our understanding of the SF degradation process during enzymatic hydrolysis, and show far-reaching guiding significance in trace detection of SF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
J. Li, F. Cai, X. Ye, J. Liang, J. Li, M. Wu, D. Zhao, Z. Jiang, Z. You, and B. Zhong, J. Proteome Res., 2017, 16, 2495.
J. Glausiusz, Nature, 2009, 462, 574.
W. Patrick, S. Hans, and P. Angelika, J. Agric. Food Chem., 2009, 57, 8399.
H. Mai, Y. Yang, I. Abuduresule, W. Li, X. Hu, and C. Wang, Sci. Rep., 2016, 6, 18939.
E. Karpova, V. Vasiliev, V. Mamatyuk, N. Polosmak, and L. Kundo, J. Archaeol. Sci., 2016, 70, 15.
M. A. Koperska, D. Pawcenis, J. Bagniuk, M. M. Zaitz, M. Missori, T. Łojewski, and J. Łojewska, Polym. Degrad. Stabil., 2014, 105, 185.
M. E.-S. Osman, A. A. E.-N. El-Shaphy, D. A. Meligy, and M. M. Ayid, Int. J. Conserv. Sci., 2014, 5, 295.
K. Sterflinger and F. Pinzari, Environ. Microbiol., 2012, 14, 559.
Q. Lu, B. Zhang, M. Li, B. Zuo, D. L. Kaplan, Y. Huang, and H. Zhu, Biomacromolecules, 2011, 12, 1080.
R. You, Y. Xu, Y. Liu, X. Li, and M. Li, Biomed. Mater., 2014, 10, 015003.
T. Wongpinyochit, B. F. Johnston, and F. P. Seib, ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng., 2018, 4, 942.
K. Numata, P. Cebe, and D. L. Kaplan, Biomaterials, 2010, 31, 2926.
E. S. Sashina, A. M. Bochek, N. P. Novoselov, and D. A. Kirichenko, Russ. J. Appl. Chem., 2006, 79, 869.
Q. You, M. Liu, Y. Liu, H. Zheng, Z. Hu, Y. Zhou, and B. Wang, ACS Sens., 2017, 2, 569.
T. Tsumuraya, T. Sato, M. Hirama, and I. Fujii, Anal. Chem., 2018, 90, 7318.
J. Gu, C. Xu, M. Li, B. Chen, Y. Shang, H. Zheng, Y. Zhou, Z. Hu, Z. Peng, and B. Wang, Anal. Sci., 2019, 35, 175.
M. Timms, R. Steel, and J. Vine, Drug Test. Anal., 2016, 8, 164.
S. Ling, Z. Qi, D. P. Knight, Z. Shao, and X. Chen, Biomacromolecules, 2011, 12, 3344.
G. Fang, S. Sapru, S. Behera, J. Yao, Z. Shao, S. C. Kundu, and X. Chen, J. Mater. Chem. B, 2016, 4, 4337.
K. Tanaka, N. Kajiyama, K. Ishikura, S. Waga, A. Kikuchi, K. Ohtomo, T. Takagi, and S. Mizuno, Biochim. Biophys. Acta, 1999, 1432, 92.
S. Inoue, K. Tanaka, F. Arisaka, S. Kimura, K. Ohtomo, and S. Mizuno, J. Biol. Chem., 2000, 275, 40517.
Q. You, Q. Li, H. Zheng, Z. Hu, Y. Zhou, and B. Wang, J. Agric. Food Chem., 2017, 65, 7805.
L. Hedstrom, Chem. Rev., 2003, 34, 4501.
I. Siddiqui and Q. Husain, Colloid. Surf. B, 2019, 173, 733.
S. Ha, H. S. Gracz, A. E. Tonelli, and S. M. Hudson, Biomacromolecules, 2005, 6, 2563.
C. Guo, J. Zhang, J. S. Jordan, X. Wang, R. W. Henning, and J. L. Yarger, Biomacromolecules, 2018, 19, 906.
Y. Wang, J. Wen, B. Peng, B. Hu, X. Chen, and Z. Shao, Biomacromolecules, 2018, 19, 1999.
D. J. Barlow, M. S. Edwards, and J. M. Thornton, Nature, 1986, 322, 747.
T. Arai, G. Freddi, R. Innocenti, and M. Tsukada, J. Appl. Polym. Sci., 2004, 91, 2383.
Acknowledgments
Financial support was provided by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (51603188), the Public Technology Research Plan of Zhejiang Province, China (2016C33175), the Outstanding Young Research Program of Science and Technology for the Protection of Cultural Relics (2015-294), and the Special Funds from the Administration of Cultural Heritage of Zhejiang Province (2017014).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Electronic supplementary material
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, R., Zhou, L., Yang, H. et al. Degradation Behavior and Immunological Detection of Silk Fibroin Exposure to Enzymes. ANAL. SCI. 35, 1243–1249 (2019). https://doi.org/10.2116/analsci.19P222
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.2116/analsci.19P222