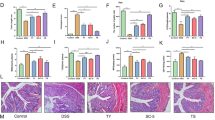
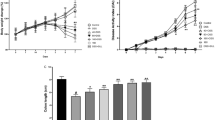
Abstract
Ulcerative colitis (UC) is a chronic and recurrent inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) that has become a major gastroenterologic problem during recent decades. Numerous complicating factors are involved in UC development such as oxidative stress, inflammation, and microbiota disorder. These factors exacerbate damage to the intestinal mucosal barrier. Spirulina platensis is a commercial alga with various biological activity that is widely used as a functional ingredient in food and beverage products. However, there have been few studies on the treatment of UC using S. platensis aqueous extracts (SP), and the underlying mechanism of action of SP against UC has not yet been elucidated. Herein, we aimed to investigate the modulatory effect of SP on microbiota disorders in UC mice and clarify the underlying mechanisms by which SP alleviates damage to the intestinal mucosal barrier. Dextran sulfate sodium (DSS) was used to establish a normal human colonic epithelial cell (NCM460) injury model and UC animal model. The mitochondrial membrane potential assay 3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide (MTT) and staining with Annexin V-fluorescein isothiocyanate (FITC)/propidium iodide (PI) and Hoechst 33258 were carried out to determine the effects of SP on the NCM460 cell injury model. Moreover, hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) staining, transmission electron microscopy (TEM), enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA), quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction (qPCR), western blot, and 16S ribosomal DNA (rDNA) sequencing were used to explore the effects and underlying mechanisms of action of SP on UC in C57BL/6 mice. In vitro studies showed that SP alleviated DSS-induced NCM460 cell injury. SP also significantly reduced the excessive generation of intracellular reactive oxygen species (ROS) and prevented mitochondrial membrane potential reduction after DSS challenge. In vivo studies indicated that SP administration could alleviate the severity of DSS-induced colonic mucosal damage compared with the control group. Inhibition of inflammation and oxidative stress was associated with increases in the activity of antioxidant enzymes and the expression of tight junction proteins (TJs) post-SP treatment. SP improved gut microbiota disorder mainly by increasing antioxidant enzyme activity and the expression of TJs in the colon. Our findings demonstrate that the protective effect of SP against UC is based on its inhibition of pro-inflammatory cytokine overproduction, inhibition of DSS-induced ROS production, and enhanced expression of antioxidant enzymes and TJs in the colonic mucosal barrier.
摘要
目的
探究钝顶螺旋藻水提取物(SP)对葡聚糖硫酸钠(DSS)诱导的溃疡性结肠炎(UC)小鼠肠道菌群紊乱的调节作用,并阐明其减轻结肠黏膜屏障损伤的潜在机制。
创新点
(1)成功鉴定出钝顶螺旋藻粉末及SP的化学成分;(2)研究结果证实SP可改善UC小鼠的结肠黏膜损伤,并能够调节肠道菌群,SP对UC的保护作用机制是减少炎症因子的过量产生、抑制氧化应激和增强结肠黏膜屏障中紧密连接蛋白(TJ)的表达。(3)SP可作为一种治疗UC、肠道菌群紊乱或氧化应激相关疾病的天然药物,并为该药物临床应用提供理论依据。
方法
采用DSS建立正常肠上皮细胞(NCM460)损伤模型和UC动物模型。采用噻唑兰法(MTT)、细胞凋亡染色法(AnnexinV-FITC/PI)、细胞染色法(Hoechst 33258)和线粒体膜电位法(MMP)测定SP对NCM460细胞损伤模型的影响。并采用苏木精&伊红染色法(H&E)、透射电镜(TEM)、酶联免疫吸附测定法(ELISA)、实时荧光定量聚合酶链式反应(qPCR)、蛋白质印迹法(Western blot)和16S rDNA测序等方法,探讨SP对UC小鼠的结肠黏膜损伤和肠道菌群的影响及其潜在作用机制。
结论
体外研究表明,SP可减轻DSS诱导的NCM460细胞损伤;SP还能显著减少该细胞内活性氧(ROS)的过度产生,并抑制DSS刺激后引起的细胞线粒体膜电位降低。体内研究表明,SP可减轻DSS诱导的结肠黏膜损伤程度。SP治疗后,炎症和氧化应激水平随着抗氧化酶和TJ表达的升高而降低。此外,SP主要通过增加抗氧化酶活性和结肠中TJ的表达来改善肠道菌群紊乱。综上所述,SP对UC的保护作用是基于抑制促炎细胞因子的过量产生、抑制ROS产生、增强结肠黏膜屏障中抗氧化酶和TJ的表达实现。
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akimoto T, Takasawa A, Murata M, et al., 2016. Analysis of the expression and localization of tight junction transmembrane proteins, claudin-1, -4, -7, occludin and JAM-A, in human cervical adenocarcinoma. Histol Histopathol, 31(8): 921–931. https://doi.org/10.14670/HH-11-729
Alwaleed EA, El-Sheekh M, Abdel-Daim MM, et al., 2021. Effects of Spirulina platensis and Amphora coffeaeformis as dietary supplements on blood biochemical parameters, intestinal microbial population, and productive performance in broiler chickens. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int, 28(2):1801–1811. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-10597-3
Berruien NNA, Smith CL, 2020. Emerging roles of melanocortin receptor accessory proteins (MRAP and MRAP2) in physiology and pathophysiology. Gene, 757:144949. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gene.2020.144949
Betanzos A, Javier-Reyna R, Garcia-Rivera G, et al., 2013. The EhCPADH112 complex of Entamoeba histolytica interacts with tight junction proteins occludin and claudin-1 to produce epithelial damage. PLoS ONE, 8(6):e65100. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0065100
Bradley PP, Priebat DA, Christensen RD, et al., 1982. Measurement of cutaneous inflammation: estimation of neutrophil content with an enzyme marker. J Invest Dermatol, 78(3):206–209. https://doi.org/10.1111/1523-1747.ep12506462
Cani PD, Possemiers S, van de Wiele T, et al., 2009. Changes in gut microbiota control inflammation in obese mice through a mechanism involving GLP-2-driven improvement of gut permeability. Gut, 58(8):1091–1103. https://doi.org/10.1136/gut.2008.165886
Castro-Ochoa KF, Vargas-Robles H, Chánez-Paredes S, et al., 2019. Homoectoine protects against colitis by preventing a claudin switch in epithelial tight junctions. Dig Dis Sci, 64(2):409–420. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10620-018-5309-8
Ciapetti G, Cenni E, Pratelli L, et al., 1993. In vitro evaluation of cell/biomaterial interaction by MTT assay. Biomaterials, 14(5):359–364. https://doi.org/10.1016/0142-9612(93)90055-7
da Cunha VP, Preisser TM, Santana MP, et al., 2020. Invasive Lactococcus lactis producing mycobacterial Hsp65 ameliorates intestinal inflammation in acute TNBS-induced colitis in mice by increasing the levels of the cytokine IL-10 and secretory IgA. J Appl Microbiol, 129(5):1389–1401. https://doi.org/10.1111/jam.14695
Davaatseren M, Hwang JT, Park JH, et al., 2014. Allyl isothiocyanate ameliorates angiogenesis and inflammation in dextran sulfate sodium-induced acute colitis. PLoS ONE, 9(7):e102975. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0102975
Ding SJ, Ma Y, Liu G, et al., 2019. Lactobacillus brevis alleviates DSS-induced colitis by reprograming intestinal microbiota and influencing serum metabolome in murine model. Front Physiol, 10:1152. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphys.2019.01152
Dobi A, Rosanaly S, Devin A, et al., 2021. Advanced glycation end-products disrupt brain microvascular endothelial cell barrier: the role of mitochondria and oxidative stress. Microvasc Res, 133:104098. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mvr.2020.104098
Eichele DD, Kharbanda KK, 2017. Dextran sodium sulfate colitis murine model: an indispensable tool for advancing our understanding of inflammatory bowel diseases pathogenesis. World J Gastroenterol, 23(33):6016–6029. https://doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v23.i33.6016
Emamie AD, Rajabpour M, Ghanavati R, et al., 2021. The effects of probiotics, prebiotics and synbiotics on the reduction of IBD complications, a periodic review during 2009–2020. J Appl Microbiol, 130(6):1823–1838. https://doi.org/10.1111/jam.14907
Eray M, Mättö M, Kaartinen M, et al., 2001. Flow cytometric analysis of apoptotic subpopulations with a combination of annexin V-FITC, propidium iodide, and SYTO 17. Cytometry, 43(2):134–142. https://doi.org/10.1002/1097-0320(20010201)43:2<134::AID-CYTO1028>3.0.CO;2-L
Guinane CM, Cotter PD, 2013. Role of the gut microbiota in health and chronic gastrointestinal disease: understanding a hidden metabolic organ. Therap Adv Gastroenterol, 6(4): 295–308. https://doi.org/10.1177/1756283X13482996
Halfvarson J, Brislawn CJ, Lamendella R, et al., 2017. Dynamics of the human gut microbiome in inflammatory bowel disease. Nat Microbiol, 2(5):17004. https://doi.org/10.1038/nmicrobiol.2017.4
Hayes CL, Dong J, Galipeau HJ, et al., 2018. Commensal microbiota induces colonic barrier structure and functions that contribute to homeostasis. Sci Rep, 8:14184. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-32366-6
Ida N, Hartmann T, Pantel J, et al., 1996. Analysis of heterogeneous βA4 peptides in human cerebrospinal fluid and blood by a newly developed sensitive western blot assay. J Biol Chem, 271(37):22908–22914. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.271.37.22908
Kaplan GG, 2015. The global burden of IBD: from 2015 to 2025. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol, 12(12):720–727. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrgastro.2015.150
Kariyil BJ, Ayyappan UPT, Gopalakrishnan A, et al., 2021. Chloroform fraction of methanolic extract of seeds of Annona muricata induce S phase arrest and ROS dependent caspase activated mitochondria-mediated apoptosis in triple-negative breast cancer. Anticancer Agents Med Chem, 21(10):1250–1265. https://doi.org/10.2174/1871520620666200918101448
Kose A, Ozen MO, Elibol M, et al., 2017. Investigation of in vitro digestibility of dietary microalga Chlorella vulgaris and cyanobacterium Spirulina platensis as a nutritional supplement. 3 Biotech, 7(3):170. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13205-017-0832-4
Kruidenier L, Kuiper I, Lamers CB, et al., 2003. Intestinal oxidative damage in inflammatory bowel disease: semi-quantification, localization, and association with mucosal antioxidants. J Pathol, 201(1):28–36. https://doi.org/10.1002/path.1409
Laparra JM, Sanz Y, 2010. Interactions of gut microbiota with functional food components and nutraceuticals. Pharmacol Res, 61(3):219–225. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phrs.2009.11.001
Li LH, Yang F, Jia RJ, et al., 2020. Velvet antler polypeptide prevents the disruption of hepatic tight junctions via inhibiting oxidative stress in cholestatic mice and liver cell lines. Food Funct, 11(11):9752–9763. https://doi.org/10.1039/d0fo01899f
Liu QQ, Zeng XL, Guan YL, et al., 2020. Verticillin A inhibits colon cancer cell migration and invasion by targeting c-Met. J Zhejiang Univ-Sci B (Biomed & Biotechnol), 21(10):779–795. https://doi.org/10.1631/jzus.B2000190
Lu J, Chen XN, Xu XH, et al., 2019. Active polypeptides from Hirudo inhibit endothelial cell inflammation and macrophage foam cell formation by regulating the LOX-1/LXR-α/ABCA1 pathway. Biomed Pharmacother, 115: 108840. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2019.108840
Luo M, Luo Y, 2021. Imperatorin relieved ulcerative colitis by regulating the Nrf-2/ARE/HO-1 pathway in rats. Inflammation, 44(2):558–569. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10753-020-01353-3
Mishra SK, Kang JH, Kim DK, et al., 2012. Orally administered aqueous extract of Inonotus obliquus ameliorates acute inflammation in dextran sulfate sodium (DSS)-induced colitis in mice. J Ethnopharmacol, 143(2):524–532. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jep.2012.07.008
Nielsen TS, Fredborg M, Theil PK, et al., 2020. Dietary red meat adversely affects disease severity in a pig model of DSS-induced colitis despite reduction in colonic pro-inflammatory gene expression. Nutrients, 12(6):1728. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12061728
Pardhasaradhi BVV, Ali AM, Kumari AL, et al., 2003. Phycocyanin-mediated apoptosis in AK-5 tumor cells involves down-regulation of Bcl-2 and generation of ROS. Mol Cancer Ther, 2(11):1165–1170.
Park JH, Lee SI, Kim IH, 2018. Effect of dietary Spirulina (Arthrospira) platensis on the growth performance, antioxidant enzyme activity, nutrient digestibility, cecal microflora, excreta noxious gas emission, and breast meat quality of broiler chickens. Poult Sci, 97(7):2451–2459. https://doi.org/10.3382/ps/pey093
Payne CM, Weber C, Crowley-Skillicorn C, et al., 2007. Deoxycholate induces mitochondrial oxidative stress and activates NF-kB through multiple mechanisms in HCT-116 colon epithelial cells. Carcinogenesis, 28(1):215–222. https://doi.org/10.1093/carcin/bgl139
Prasad A, Pospisil P, Tada M, 2019. Editorial: reactive oxygen species (ROS) detection methods in biological system. Front Physiol, 10:1316. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphys.2019.01316
Rao XY, Huang XL, Zhou ZC, et al., 2013. An improvement of the 2^(−delta delta CT) method for quantitative realtime polymerase chain reaction data analysis. Biostat Bioinforma Biomath, 3(3):71–85.
Reers M, Smiley ST, Mottola-Hartshorn C, et al., 1995. Mitochondrial membrane potential monitored by JC-1 dye. Methods Enzymol, 260:406–414, IN1–IN3, 415–417. https://doi.org/10.1016/0076-6879(95)60154-6
Siddiqui H, Nederbragt AJ, Lagesen K, et al., 2011. Assessing diversity of the female urine microbiota by high throughput sequencing of 16S rDNA amplicons. BMC Microbiol, 11:244. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2180-11-244
Sokol H, Beaugerie L, 2010. Body mass index and disease activity at treatment initiation: potential new predictors of response to azathioprine therapy in IBD. Inflamm Bowel Dis, 16(4):714–715. https://doi.org/10.1002/ibd.21102
Speckmann B, Steinbrenner H, 2014. Selenium and selenoproteins in inflammatory bowel diseases and experimental colitis. Inflamm Bowel Dis, 20(6): 1110–1119. https://doi.org/10.1097/MIB.0000000000000020
Sun Y, Ge X, Li X, et al., 2020a. High-fat diet promotes renal injury by inducing oxidative stress and mitochondrial dysfunction. Cell Death Dis, 11(10):914. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41419-020-03122-4
Sun Y, Li LW, Lai AY, et al., 2020b. Does ulcerative colitis influence the inter-individual heterogeneity of the human intestinal mucosal microbiome? Evol Bioinform, 16: 1176934320948848. https://doi.org/10.1177/1176934320948848
Szulinska M, Gibas-Dorna M, Miller-Kasprzak E, et al., 2017. Spirulina maxima improves insulin sensitivity, lipid profile, and total antioxidant status in obese patients with well-treated hypertension: a randomized double–blind placebo-controlled study. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci, 21(10):2473–2481.
Taghipour N, Mosaffa N, Aghdaei HA, et al., 2019. Immunomodulatory effect of Syphacia obvelata in treatment of experimental DSS-induced colitis in mouse model. Sci Rep, 9:19127. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-019-55552-6
Takagi T, Naito Y, Uchiyama K, et al., 2011. Carbon monoxide liberated from carbon monoxide-releasing molecule exerts an anti-inflammatory effect on dextran sulfate sodium-induced colitis in mice. Dig Dis Sci, 56(6):1663–1671. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10620-010-1484-y
Tsang L, Banerjee N, Tabibian JH, 2019. Bloody diarrhea and weight loss in a patient in remission from ulcerative colitis. Gastroenterology, 157(5):1207–1209. https://doi.org/10.1053/j.gastro.2019.01.272
Unno N, Wang H, Menconi MJ, et al., 1997. Inhibition of inducible nitric oxide synthase ameliorates endotoxin-induced gut mucosal barrier dysfunction in rats. Gastroenterology, 113(4):1246–1257. https://doi.org/10.1053/gast.1997.v113.pm9322519
Vinolo MAR, Rodrigues HG, Nachbar RT, et al., 2011. Regulation of inflammation by short chain fatty acids. Nutrients, 3(10):858–876. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu3100858
Wargo JA, 2020. Modulating gut microbes. Science, 369(6509): 1302–1303. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.abc3965
Xu LL, Liu T, Wang L, et al., 2018. 3-(1H-Benzo[d]imidazol-6-yl)-5-(4-fluorophenyl)-1,2,4-oxadiazole (DDO7232), a novel potent Nrf2/ARE inducer, ameliorates DSS-induced murine colitis and protects NCM460 cells against oxidative stress via ERK1/2 phosphorylation. Oxid Med Cell Longev, 2018:3271617. https://doi.org/10.1155/2018/3271617
Xue PP, Wang LF, Xu JW, et al., 2020. Temperature-sensitive hydrogel for rectal perfusion improved the therapeutic effect of Kangfuxin liquid on DSS-induced ulcerative colitis mice: the inflammation alleviation and the colonic mucosal barriers repair. Int J Pharm, 589:119846. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijpharm.2020.119846
Ye ZH, Ning K, Ander BP, et al., 2020. Therapeutic effect of methane and its mechanism in disease treatment. J Zhejiang Univ-Sci B (Biomed & Biotechnol), 21(8):593–602. https://doi.org/10.1631/jzus.B1900629
Yousefi R, Saidpour A, Mottaghi A, 2019. The effects of Spirulina supplementation on metabolic syndrome components, its liver manifestation and related inflammatory markers: a systematic review. Complement Ther Med, 42:137–144. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ctim.2018.11.013
Yusuf MS, Hassan MA, Abdel-Daim MM, et al., 2016. Value added by Spirulina platensis in two different diets on growth performance, gut microbiota, and meat quality of Japanese quails. Vet World, 9(11):1287–1293. https://doi.org/10.14202/vetworld.2016.1287-1293
Zarepoor L, Lu JT, Zhang C, et al., 2014. Dietary flaxseed intake exacerbates acute colonic mucosal injury and inflammation induced by dextran sodium sulfate. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol, 306(12):G1042–G1055. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpgi.00253.2013
Zhang FX, Wu WM, Deng ZY, et al., 2015. High altitude increases the expression of hypoxia-inducible factor 1α and inducible nitric oxide synthase with intestinal mucosal barrier failure in rats. Int J Clin Exp Pathol, 8(5):5189–5195.
Zhang L, Gui SQ, Liang ZB, et al., 2019. Musca domestica cecropin (Mdc) alleviates Salmonella typhimurium-induced colonic mucosal barrier impairment: associating with inflammatory and oxidative stress response, tight junction as well as intestinal flora. Front Microbiol, 10:522. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2019.00522
Zhang L, Gui SQ, Xu YH, et al., 2021. Colon tissue-accumulating mesoporous carbon nanoparticles loaded with Musca domestica cecropin for ulcerative colitis therapy. Theranostics, 11(7):3417–3438. https://doi.org/10.7150/thno.53105
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Key R&D Program of China (No. 2018YFC1603900), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 32070509 and 31501894), and the Guangdong Basic and Applied Basic Research Foundation (No. 2021A1515220119), China.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Jian WANG and Liqian SU performed the experimental research and data analysis. Jian WANG wrote and edited the manuscript. Lun ZHANG, Jiali ZENG, Qingru CHEN, Rui DENG, Ziyan WANG, and Weidong KUANG established the animal models. Xiaobao JIN, Shuiqing GUI, Yinghua XU, and Xuemei LU contributed to the study design, data analysis, and article revision. All authors have read and approved the final manuscript, and therefore, have full access to all the data in the study and take responsibility for the integrity and security of the data.
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Compliance with ethics guidelines
Jian WANG, Liqian SU, Lun ZHANG, Jiali ZENG, Qingru CHEN, Rui DENG, Ziyan WANG, Weidong KUANG, Xiaobao JIN, Shuiqing GUI, Yinghua XU, and Xuemei LU declare that they have no conflict of interest.
All institutional and national guidelines for the care and use of laboratory animals were followed. The study complied with the Guidelines for the Care and Use of Experimental Animals, Guangdong Pharmaceutical University (No. SYXK (Yue) 2012-0125) and was approved by the Guangdong Pharmaceutical University Animal Care and Use Committee, China.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, J., Su, L., Zhang, L. et al. Spirulina platensis aqueous extracts ameliorate colonic mucosal damage and modulate gut microbiota disorder in mice with ulcerative colitis by inhibiting inflammation and oxidative stress. J. Zhejiang Univ. Sci. B 23, 481–501 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1631/jzus.B2100988
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1631/jzus.B2100988
Key words
- Spirulina platensis aqueous extracts
- Ulcerative colitis
- Oxidative stress
- Inflammation
- Antioxidant
- Gut microbiota