Abstract
Objective
The present study was to evaluate the feasibility of using the multi-biomarker strategy for the prediction of sepsis-induced myocardial dysfunction (SIMD) and mortality in septic patients.
Methods
Brain natriuretic peptide (BNP), cardiac troponin I (cTnI), and heart-type fatty acid-binding protein (h-FABP) in 147 septic patients were assayed within 6 h after admission. We also determined the plasma levels of myeloperoxidase (MPO) and pregnancy-associated plasma protein-A (PAPP-A). The receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve was used to assess the best cutoff values of various single-biomarkers for the diagnosis of SIMD and the prediction of mortality. Also, the ROC curve, net reclassification improvement (NRI), and integrated discrimination improvement (IDI) indices were used to evaluate the feasibility of using multi-biomarkers to predict SIMD and mortality.
Results
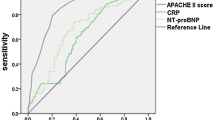
Our statistics revealed that only h-FABP independently predicted SIMD (P<0.05). The addition of MPO and cTnI to h-FABP for SIMD prediction provided an NRI of 18.7% (P=0.025) and IDI of 3.3% (P=0.033). However, the addition of MPO or cTnI to h-FABP did not significantly improve the predictive ability of h-FABP to SIMD, as evidenced by the area under the curve (AUC), NRI, and IDI (all P>0.05). A history of shock and MPO were independent predictors of mortality in septic patients (both P<0.05). The addition of PAPP-A and h-FABP to MPO resulted in a mortality prediction with NRI of 25.5% (P=0.013) and IDI of 2.9% (P=0.045). However, this study revealed that the addition of h-FABP or PAPP-A to MPO did not significantly improve the ability to predict mortality, as evidenced by the AUC, NRI, and IDI (all P>0.05).
Conclusions
The findings of this study indicate that a sensitive and specific strategy for early diagnosis of SIMD and mortality prediction in sepsis should incorporate three biomarkers.
概要
目 的
评估联合应用多种生物标记物以预测脓毒症患者早期心脏功能障碍及 28 天死亡率的可行性.
创新点
(1) 通过净重分类改善 (NRI) 和综合辨别改善 (IDI) 指标, 评估多种生物标志物策略相比单一生物标志物策略对脓毒症患者心脏功能障碍及 28 天死亡率的预测价值. (2) 评估心脏型脂肪酸结合蛋白(h-FABP)、 髓过氧化物酶 (MPO) 以及妊娠相关血浆蛋白A (PAPP-A) 等新型生物标记物在脓毒症中的临床预测价值.
方 法
检测 147 例脓毒症患者在入院后 6 小时内血浆中脑钠肽 (BNP)、 心肌肌钙蛋白 I(cTnI)、 h-FABP、 MPO 及 PAPP-A的水平. 使用受试者工作特征 (ROC) 曲线来评估各种单一生物标志物在脓毒症患者心脏功能障碍诊断和 28 天死亡率预测中的最佳截止值. 采用 ROC 曲线、 NRI 和 IDI 指标评估多种生物标志物策略相比单一生物标志物策略在预测脓毒症相关心脏功能障碍及 28 天死亡率中的价值.
结 论
MPO、 cTnI 和 h-FABP 联合应用显著提高了对脓毒症患者心脏功能障碍的预测能力, 同时 PAPP-A、MPO 和 h-FABP 联合应用显著提高了预测脓毒症患者 28 天死亡率的能力.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
ACCP/SCCM, 1992. American College of Chest Physicians/Society of Critical Care Medicine Consensus Conference: definitions for sepsis and organ failure and guidelines for the use of innovative therapies in sepsis. Crit Care Med, 20(6):864–874.
Alhadi HA, Fox KAA, 2010. Heart-type fatty acid-binding protein in the early diagnosis of acute myocardial infarction: the potential for influencing patient management. Sultan Qaboos Univ Med J, 10(1):41–49.
Annane D, Bellissant E, Cavaillon JM, 2005. Septic shock. Lancet, 365(9453):63–78. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0140-6736(04)17667-8
Arimoto T, Takeishi Y, Shiga R, et al., 2005. Prognostic value of elevated circulating heart-type fatty acid binding protein in patients with congestive heart failure. J Card Fail, 11(1):56–60. https://doi.org/10.1016/jxardfail.2004.03.005
Askari AT, Brennan ML, Zhou XR, et al., 2003. Myeloperoxidase and plasminogen activator inhibitor 1 play a central role in ventricular remodeling after myocardial infarction. J Exp Med, 197(5):615–624. https://doi.org/10.1084/jem.20021426
Avaliani T, Talakvadze T, Tabagari S, 2019. Prognostic value of plasma myeloperoxidase level’s and echocardiographic determinants in chronic heart failure patients. Georgian Med News, (288):55–60.
Baldus S, Heeschen C, Meinertz T, et al., 2003. Myeloperoxidase serum levels predict risk in patients with acute coronary syndromes. Circulation, 108(12):1440–1445. https://doi.org/10.1161/01.cir.0000090690.67322.51
Berdal JE, Stavem K, Omland T, et al., 2008. Prognostic merit of N-terminal-proBNP and N-terminal-proANP in mechanically ventilated critically ill patients. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand, 52(9):1265–1272. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1399-6576.2008.01737.x
Bessière F, Khenifer S, Dubourg J, et al., 2013. Prognostic value of troponins in sepsis: a meta-analysis. Intensive Care Med, 39(7):1181–1189. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00134-013-2902-3
Blanco J, Muriel-Bombín A, Sagredo V, et al., 2008. Incidence, organ dysfunction and mortality in severe sepsis: a Spanish multicentre study. Crit Care, 12(6):R158. https://doi.org/10.1186/cc7157
Charpentier J, Luyt CE, Fulla Y, et al., 2004. Brain natriuretic peptide: a marker of myocardial dysfunction and prognosis during severe sepsis. Crit Care Med, 32(3):660–665. https://doi.org/10.1097/01.ccm.0000114827.93410.d8
Consuegra-Sanchez L, Fredericks S, Kaski JC, 2009. Pregnancy-associated plasma protein-A (PAPP-A) and cardiovascular risk. Atherosclerosis, 203(2):346–352. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2008.07.042
Cook NR, Ridker PM, 2009. Advances in measuring the effect of individual predictors of cardiovascular risk: the role of reclassification measures. Ann Intern Med, 150(11):795–802. https://doi.org/10.7326/0003-4819-150-11-200906020-00007
Dellinger RP, Levy MM, Carlet JM, et al., 2008. Surviving sepsis campaign: international guidelines for management of severe sepsis and septic shock: 2008. Intensive Care Med, 34(1):17–60. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00134-007-0934-2
Fromm RE Jr, 2007. Cardiac troponins in the intensive care unit: common causes of increased levels and interpretation. Crit Care Med, 35(2):584–588. https://doi.org/10.1097/01.ccm.0000254349.10953.be
Fu XY, Kassim SY, Parks WC, et al., 2001. Hypochlorous acid oxygenates the cysteine switch domain of pro-matrilysin (MMP-7). A mechanism for matrix metalloproteinase activation and atherosclerotic plaque rupture by myeloperoxidase. J Biol Chem, 276(44):41279–41287. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M106958200
Funayama A, Shishido T, Netsu S, et al., 2011. Serum pregnancy-associated plasma protein a in patients with heart failure. J Card Fail, 17(10):819–826. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cardfail.2011.05.011
Glatz JFC, van Bilsen M, Paulussen RJA, et al., 1988. Release of fatty acid-binding protein from isolated rat heart subjected to ischemia and reperfusion or to the calcium paradox. Biochim Biophys Acta, 961(1):148–152. https://doi.org/10.1016/0005-2760(88)90141-5
Hanley JA, McNeil BJ, 1983. A method of comparing the areas under receiver operating characteristic curves derived from the same cases. Radiology, 148(3):839–843. https://doi.org/10.1148/radiology.148.3.6878708
Huber W, Mayr U, Umgelter A, et al., 2018. Mandatory criteria for the application of variability-based parameters of fluid responsiveness: a prospective study in different groups of ICU patients. J Zhejiang Univ-Sci B (Biomed & Biotechnol), 19(7):515–524. https://doi.org/10.1631/jzus.B1700243
Janes H, Pepe MS, Gu W, 2008. Assessing the value of risk predictions by using risk stratification tables. Ann Intern Med, 149(10):751–760. https://doi.org/10.7326/00034819-149-10-200811180-00009
Jardin F, Fourme T, Page B, et al., 1999. Persistent preload defect in severe sepsis despite fluid loading: a longitudinal echocardiographic study in patients with septic shock. Chest, 116(5):1354–1359. https://doi.org/10.1378/chest.116.5.1354
Jo YH, Kim K, Lee JH, et al., 2012. Heart-type fatty acid-binding protein as a prognostic factor in patients with severe sepsis and septic shock. Am J Emerg Med, 30(9): 1749–1755. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ajem.2012.02.005
Kadowaki S, Watanabe T, Otaki Y, et al., 2017. Combined assessment of myocardial damage and electrical disturbance in chronic heart failure. World J Cardiol, 9(5): 457–465. https://doi.org/10.4330/wjc.v9.i5.457
Kim JS, Kim M, Kim YJ, et al., 2019. Troponin testing for assessing sepsis-induced myocardial dysfunction in patients with septic shock. J Clin Med, 8(2):239. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm8020239
Klouche K, Pommet S, Amigues L, et al., 2014. Plasma brain natriuretic peptide and troponin levels in severe sepsis and septic shock: relationships with systolic myocardial dysfunction and intensive care unit mortality. J Intensive Care Med, 29(4):229–237. https://doi.org/10.1177/0885066612471621
Kolodziej AR, Abo-Aly M, Elsawalhy E, et al., 2019. Prognostic role of elevated myeloperoxidase in patients with acute coronary syndrome: a systemic review and metaanalysis. Mediat Inflamm, 2019:2872607. https://doi.org/10.1155/2019/2872607
Kothari N, Keshari RS, Bogra J, et al., 2011. Increased myeloperoxidase enzyme activity in plasma is an indicator of inflammation and onset of sepsis. J Crit Care, 26(4):435.e1–435.e7. https://doi.org/10.1016/jjcrc.2010.09.001
Levy MM, Fink MP, Marshall JC et al., 2003. 2001 SCCM/ESICM/ACCP/ATS/SIS International Sepsis Definitions Conference. Intensive Care Med, 29:530–538. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00134-003-1662-x
Mackinnon A, Mulligan R, 1998. Combining cognitive testing and informant report to increase accuracy in screening for dementia. Am J Psychiatry, 155(11):1529–1535. https://doi.org/10.1176/ajp.155.11.1529
Mehta NJ, Khan IA, Gupta V, et al., 2004. Cardiac troponin I predicts myocardial dysfunction and adverse outcome in septic shock. Int J Cardiol, 95(1):13–17. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijcard.2003.02.005
Melenovsky V, Hwang SJ, Lin G, et al., 2014. Right heart dysfunction in heart failure with preserved ejection fraction. Eur Heart J, 35(48):3452–3462. https://doi.org/10.1093/eurheartj/ehu193
Nakata T, Hashimoto A, Hase M, et al., 2003. Human heart-type fatty acid-binding protein as an early diagnostic and prognostic marker in acute coronary syndrome. Cardiology, 99(2):96–104. https://doi.org/10.1159/000069726
Ng LL, Pathik B, Loke IW, et al., 2006. Myeloperoxidase and C-reactive protein augment the specificity of B-type natriuretic peptide in community screening for systolic heart failure. Am Heart J, 152(1):94–101. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ahj.2005.09.020
O’Donoghue M, de Lemos JA, Morrow DA, et al., 2006. Prognostic utility of heart-type fatty acid binding protein in patients with acute coronary syndromes. Circulation, 114(6):550–557. https://doi.org/10.1161/circulationaha.106.641936
Papanikolaou J, Makris D, Mpaka M, et al., 2014. New insights into the mechanisms involved in B-type natriuretic peptide elevation and its prognostic value in septic patients. Crit Care, 18(3):R94. https://doi.org/10.1186/cc13864
Park KC, Gaze DC, Collinson PO, et al., 2017. Cardiac troponins: from myocardial infarction to chronic disease. Cardiovasc Res, 113(14):1708–1718. https://doi.org/10.1093/cvr/cvx183
Parker MM, Shelhamer JH, Bacharach SL, et al., 1984. Profound but reversible myocardial depression in patients with septic shock. Ann Intern Med, 100(4):483–490. https://doi.org/10.7326/0003-4819-100-4-483
Pellitero S, Reverter JL, Pizarro E, et al., 2007. Pregnancy-associated plasma protein-A levels are related to glycemic control but not to lipid profile or hemostatic parameters in type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care, 30(12):3083–3085. https://doi.org/10.2337/dc07-1092
Pencina MJ, D’Agostino RB, D’Agostino RB Jr, et al., 2008. Evaluating the added predictive ability of a new marker: from area under the ROC curve to reclassification and beyond. Stat Med, 27(2):157–172. https://doi.org/10.1002/sim.2929
Pepe MS, Janes H, Longton G, et al., 2004. Limitations of the odds ratio in gauging the performance of a diagnostic, prognostic, or screening marker. Am J Epidemiol, 159(9): 882–890. https://doi.org/10.1093/aje/kwh101
Perner A, Cecconi M, Cronhjort M, et al., 2018. Expert statement for the management of hypovolemia in sepsis. Intensive Care Med, 44(6):791–798. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00134-018-5177-x
Podrez EA, Febbraio M, Sheibani N, et al., 2000. Macrophage scavenger receptor CD36 is the major receptor for LDL modified by monocyte-generated reactive nitrogen species. J Clin Invest, 105(8):1095–1108. https://doi.org/10.1172/jci8574
Post F, Weilemann LS, Messow CM, et al., 2008. B-type natriuretic peptide as a marker for sepsis-induced myocardial depression in intensive care patients. Crit Care Med, 36(11):3030–3037. https://doi.org/10.1097/CCM.0b013e31818b9153
Riedemann NC, Guo RF, Ward PA, 2003. Novel strategies for the treatment of sepsis. Nat Med, 9(5):517–524. https://doi.org/10.1038/nm0503-517
Sato R, Nasu M, 2015. A review of sepsis-induced cardiomyopathy. J Intensive Care, 3:48. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40560-015-0112-5
Schrijver IT, Kemperman H, Roest M, et al., 2017. Myeloperoxidase can differentiate between sepsis and noninfectious SIRS and predicts mortality in intensive care patients with SIRS. Intensive Care Med Exp, 5:43. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40635-017-0157-y
Singer M, Deutschman CS, Seymour CW, et al., 2016. The third international consensus definitions for sepsis and septic shock (sepsis-3). JAMA, 315(8):801–810. https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.2016.0287
Wittfooth S, Tertti R, Lepäntalo M, et al., 2011. Studies on the effects of heparin products on pregnancy-associated plasma protein A. Clin Chim Acta, 412(3–4):376–381. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cca.2010.11.024
Witthaut R, Busch C, Fraunberger P, et al., 2003. Plasma atrial natriuretic peptide and brain natriuretic peptide are increased in septic shock: impact of interleukin-6 and sepsis-associated left ventricular dysfunction. Intensive Care Med, 29(10):1696–1702. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00134-003-1910-0
Yan GT, Lin J, Hao XH, et al., 2009. Heart-type fatty acid-binding protein is a useful marker for organ dysfunction and leptin alleviates sepsis-induced organ injuries by restraining its tissue levels. Eur J Pharmacol, 616(1–3): 244–250. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejphar.2009.06.039
Yucel T, Memiş, D, Karamanlioglu B, et al., 2008. The prognostic value of atrial and brain natriuretic peptides, troponin I and C-reactive protein in patients with sepsis. Exp Clin Cardiol, 13(4):183–188.
Zhang ZC, Dai HW, Yu YH, et al., 2012. Usefulness of heart-type fatty acid-binding protein in patients with severe sepsis. J Crit Care, 27(4):415.e13–415.e18. https://doi.org/10.1016/jocrc.2012.01.004
Zhang ZC, Dai HW, Yu YH, et al., 2014. Elevated pregnancy-associated plasma protein A predicts myocardial dysfunction and death in severe sepsis. Ann Clin Biochem, 51(1):22–29. https://doi.org/10.1177/0004563213489275
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Fa-chao CHEN performed the experimental research and data analysis, and wrote and edited the manuscript. Yin-chuan XU and Zhao-cai ZHANG participated in the study design, data analysis, and writing and editing of the manuscript. All authors have read and approved the final manuscript and, therefore, have full access to all the data in the study and take responsibility for the integrity and security of the data.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Fa-chao CHEN, Yin-chuan XU, and Zhao-cai ZHANG declare that they have no conflict of interest.
All procedures followed were in accordance with the ethical standards of the responsible committee on human experimentation (institutional and national) and with the Helsinki Declaration of 1975, as revised in 2008 (5). Written informed consent was required from all participants or their legal proxies before registration for being included in the study.
Additional information
Project supported by the Zhejiang Provincial Natural Science Foundation of China (No. LQ16H020003) and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 81971860 and 81772110)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, Fc., Xu, Yc. & Zhang, Zc. Multi-biomarker strategy for prediction of myocardial dysfunction and mortality in sepsis. J. Zhejiang Univ. Sci. B 21, 537–548 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1631/jzus.B2000049
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1631/jzus.B2000049