Abstract
Objective
To investigate the effects of body mass index (BMI) on the outcomes of in vitro fertilization (IVF) in Chinese patients with polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS).
Methods
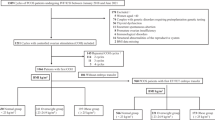
In the retrospective cohort study, a total of 1074 patients with PCOS undergoing IVF between April 2010 and May 2017 in two reproductive medicine centers, respectively in eastern China (Women’s Hospital, School of Medicine, Zhejiang University, Zhejiang Province) and in southern China (Maternal and Child Health Care Hospital of Liuzhou, Guangxi Province), were included. The patients were divided into four groups according to the recommended Chinese BMI cut-off points: underweight (BMI< 18.5 kg/m2), normal weight (18.5 kg/m2≤BMI<24.0 kg/m2), overweight (24.0 kg/m2≤BMI<28.0 kg/m2), and obese (BMI≥ 28.0 kg/m2). The basic characteristics of the PCOS patients, the details of IVF treatment, and the pregnancy outcomes were collected.
Main results
There were no significant differences among the normal weight, overweight, and obese PCOS patients undergoing IVF on the biochemical pregnancy rate, clinical pregnancy rate, miscarriage rate, live birth rate, or term delivery rate (P>0.05), although the overweight and obese PCOS patients required more gonadotropin (Gn) (P<0.001) as well as longer stimulation period (P<0.001), and got less retrieved oocytes (P<0.05) and fertilized oocytes (P<0.05). The underweight PCOS patients required less Gn (P<0.05) and achieved higher live birth rate and term delivery rate (P<0.05), compared with the normal weight PCOS patients.
Conclusions
High BMI had no negative effects on the outcomes of IVF in Chinese patients with PCOS; however, the conclusion may seem a little limited due to the retrospective design and the potential bias.
摘要
目的
探讨体重指数对中国多囊卵巢综合征(PCOS)患者体外受精胚胎移植结局的影响。
创新点
本研究是一项多中心大样本研究,纳入了华东、 华南两家生殖中心的患者;本研究根据中国体重指数(BMI)分界点进行分组,而非国际BMI分界点,得出的结论更加适合中国或者亚洲人 群。
方法
此项回顾性研究纳入2010 年4 月到2017 年5 月 分别在华东、华南两家生殖中心进行体外受精胚 胎移植的患者共1074 例。根据推荐的中国BMI 分界点,患者被分成四组:低体重组(BMI< 18.5 kg/m2),正常体重组(18.5 kg/m2≤BMI< 24.0 kg/m2),超重组(24.0 kg/m2≤BMI<28.0 kg/m2) 和肥胖组(BMI≥28.0 kg/m2)。比较各组间的基 本信息、体外受精情况和妊娠结局。
结论
高BMI 对中国PCOS 患者的体外受精胚胎移植结局没有不利影响。因为本研究是回顾性研究及一些潜在的偏差,所以此结论可能存在一定的局限性。
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anastasiou OE, Canbay A, Fuhrer D, et al., 2017. Metabolic and androgen profile in underweight women with polycystic ovary syndrome. Arch Gynecol Obstet, 296(2): 363–371. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00404-017-4422-9.
Bailey AP, Hawkins LK, Missmer SA, et al., 2014. Effect of body mass index on in vitro fertilization outcomes in women with polycystic ovary syndrome. Am J Obstet Gynecol, 211(2):63.e1–163.e6. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ajog.2014.03.035.
Balen AH, Morley LC, Misso M, et al., 2016. The management of anovulatory infertility in women with polycystic ovary syndrome: an analysis of the evidence to support the development of global WHO guidance. Hum Reprod Update, 22(6):687–708. https://doi.org/10.1093/humupd/dmw025.
Barba C, Sforza TC, Cutter J, et al., 2004. Appropriate bodymass index for Asian populations and its implications for policy and intervention strategies. Lancet, 363(9403): 157–163. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(03)15268-3.
Bentley-Lewis R, Seely E, Dunaif A, 2011. Ovarian hypertension: polycystic ovary syndrome. Endocrinol Metab Clin North Am, 40(2):433–449. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecl.2011.01.009.
Bergh CM, Moore M, Gundell C, 2016. Evidence-based management of infertility in women with polycystic ovary syndrome. J Obstet Gynecol Neonatal Nurs, 45(1): 111–122. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jogn.2015.10.001.
Bernardi LA, Carnethon MR, de Chavez PJ, et al., 2017. Relationship between obesity and anti-mullerian hormone in reproductive-aged african american women. Obesity, 25(1):229–235. https://doi.org/10.1002/oby.21681.
Beydoun HA, Stadtmauer L, Beydoun MA, et al., 2009. Polycystic ovary syndrome, body mass index and outcomes of assisted reproductive technologies. Reprod Biomed Online, 18(6):856–863. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1472-6483(10)60037-5.
Buyuk E, Asemota OA, Merhi Z, et al., 2017. Serum and follicular fluid monocyte chemotactic protein-1 levels are elevated in obese women and are associated with poorer clinical pregnancy rate after in vitro fertilization: a pilot study. Fertil Steril, 107(3):632–640 e3. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fertnstert.2016.12.023.
Cakiroglu Y, Vural F, Vural B, 2016. The inflammatory markers in polycystic ovary syndrome: association with obesity and IVF outcomes. J Endocrinol Invest, 39(8): 899–907. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40618-016-0446-4.
Chang J, Azziz R, Legro R, et al., 2004. Revised 2003 consensus on diagnostic criteria and long-term health risks related to polycystic ovary syndrome. Fertil Steril, 81(1):19–25. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fertnstert.2003.10.004.
Chen X, Ni R, Mo Y, et al., 2010. Appropriate BMI levels for PCOS patients in southern China. Hum Reprod, 25(5): 1295–1302. https://doi.org/10.1093/humrep/deq028.
Cui N, Wang H, Wang W, et al., 2016. Impact of body mass index on outcomes of in vitro fertilization/intracytoplasmic sperm injection among polycystic ovarian syndrome patients. Cell Physiol Biochem, 39(5):1723–1734. https://doi.org/10.1159/000447873.
Deshmukh VL, Jadhav M, Yelikar K, 2016. Impact of high BMI on pregnancy: maternal and foetal outcome. J Obstet Gynaecol India, 66(Suppl 1):192–197. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13224-015-0825-3.
Fleming R, Fairbairn C, Blaney C, et al., 2013. Stability of AMH measurement in blood and avoidance of proteolytic changes. Reprod Biomed Online, 26(2):130–132. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rbmo.2012.11.005.
Hoellen F, Hornemann A, Haertel C, et al., 2014. Does maternal underweight prior to conception influence pregnancy risks and outcome? In Vivo, 28(6):1165–1170.
Huang K, Liao X, Dong X, et al., 2014. Effect of overweight/obesity on IVF-ET outcomes in Chinese patients with polycystic ovary syndrome. Int J Clin Exp Med, 7(12): 5872–5876.
Joham AE, Boyle JA, Zoungas S, et al., 2015. Hypertension in reproductive-aged women with polycystic ovary syndrome and association with obesity. Am J Hypertens, 28(7):847–851. https://doi.org/10.1093/ajh/hpu251.
Jungheim ES, Lanzendorf SE, Odem RR, et al., 2009. Morbid obesity is associated with lower clinical pregnancy rates after in vitro fertilization in women with polycystic ovary syndrome. Fertil Steril, 92(1):256–261. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fertnstert.2008.04.063.
Kalem MN, Kalem Z, Sari T, et al., 2016. Effect of body mass index and age on in vitro fertilization in polycystic ovary syndrome. J Turk Ger Gynecol Assoc, 17(2):83–90. https://doi.org/10.5152/jtgga.2016.15235.
Lefebvre T, Dumont A, Pigny P, et al., 2017. Effect of obesity and its related metabolic factors on serum anti-mullerian hormone concentrations in women with and without polycystic ovaries. Reprod Biomed Online, 35(3):325–330. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rbmo.2017.05.013.
Mantakas A, Farrell T, 2010. The influence of increasing BMI in nulliparous women on pregnancy outcome. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol, 153(1):43–46. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejogrb.2010.06.021.
Martin KE, Grivell RM, Yelland LN, et al., 2015. The influence of maternal BMI and gestational diabetes on pregnancy outcome. Diabetes Res Clin Pract, 108(3):508–513. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.diabres.2014.12.015.
McCormick B, Thomas M, Maxwell R, et al., 2008. Effects of polycystic ovarian syndrome on in vitro fertilizationembryo transfer outcomes are influenced by body mass index. Fertil Steril, 90(6):2304–2309. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fertnstert.2007.10.077.
Meenakshi, Srivastava R, Sharma NR, et al., 2012. Obstetric behavior and pregnancy outcome in overweight and obese women: maternal and fetal complications and risks in relation to maternal overweight and obesity. J Obstet Gynaecol India, 62(3):276–280. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13224-012-0215-z.
Merhi Z, Polotsky AJ, Bradford AP, et al., 2015. Adiposity alters genes important in inflammation and cell cycle division in human cumulus granulosa cell. Reprod Sci, 22(10):1220–1228. https://doi.org/10.1177/1933719115572484.
Mulders AG, Laven JS, Imani B, et al., 2003. IVF outcome in anovulatory infertility (WHO group 2)—including polycystic ovary syndrome—following previous unsuccessful ovulation induction. Reprod Biomed Online, 7(1):50–58. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1472-6483(10)61728-2.
Oteng-Ntim E, Varma R, Croker H, et al., 2012. Lifestyle interventions for overweight and obese pregnant women to improve pregnancy outcome: systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Med, 10:47. https://doi.org/10.1186/1741-7015-10-47.
Ozgun MT, Uludag S, Oner G, et al., 2011. The influence of obesity on ICSI outcomes in women with polycystic ovary syndrome. J Obstet Gynaecol, 31(3):245–249. https://doi.org/10.3109/01443615.2010.546906.
Qiao J, Feng HL, 2011. Extra-and intra-ovarian factors in polycystic ovary syndrome: impact on oocyte maturation and embryo developmental competence. Hum Reprod Update, 17(1):17–33. https://doi.org/10.1093/humupd/dmq032.
Qu F, Wang FF, Wu Y, et al., 2017a. Transcutaneous electrical acupoint stimulation improves the outcomes of in vitro fertilization: a prospective, randomized and controlled study. Explore (NY), 13(5):306–312. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.explore.2017.06.004.
Qu F, Li R, Sun W, et al., 2017b. Use of electroacupuncture and transcutaneous electrical acupoint stimulation in reproductive medicine: a group consensus. J Zhejiang Univ-Sci B (Biomed & Biotechnol), 18(3):186–193. https://doi.org/10.1631/jzus.B1600437.
Robinson N, 2017. Integrating acupuncture: are there positive health outcomes for women? J Zhejiang Univ-Sci B (Biomed & Biotechnol), 18(3):233–238. https://doi.org/10.1631/jzus.B1600260.
Salmassi A, Mettler L, Hedderich J, et al., 2015. Cut-off levels of anti-mullerian hormone for the prediction of ovarian response, in vitro fertilization outcome and ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome. Int J Fertil Steril, 9(2):157–167. https://doi.org/10.22074/ijfs.2015.4236.
Sebire NJ, Jolly M, Harris J, et al., 2001. Is maternal underweight really a risk factor for adverse pregnancy outcome? A population-based study in London. BJOG, 108(1):61–66. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1471-0528.2001.00021.x.
Stepto NK, Cassar S, Joham AE, et al., 2013. Women with polycystic ovary syndrome have intrinsic insulin resistance on euglycaemic-hyperinsulaemic clamp. Hum Reprod, 28(3):777–784. https://doi.org/10.1093/humrep/des463.
Szydlarska D, Macha M, Jakimiuk A, 2017. History of discovery of polycystic ovary syndrome. Adv Clin Exp Med, 26(3):555–558. https://doi.org/10.17219/acem/61987.
Teede HJ, Misso ML, Deeks AA, et al., 2011. Assessment and management of polycystic ovary syndrome: summary of an evidence-based guideline. Med J Aust, 195(6):S65–S112. https://doi.org/10.5694/mja11.10915.
Valckx SD, de Pauw I, de Neubourg D, et al., 2012. BMIrelated metabolic composition of the follicular fluid of women undergoing assisted reproductive treatment and the consequences for oocyte and embryo quality. Hum Reprod, 27(12):3531–3539. https://doi.org/10.1093/humrep/des350.
Wang FF, Pan JX, Wu Y, et al., 2018. American, European, and Chinese practice guidelines or consensuses of polycystic ovary syndrome: a comparative analysis. J Zhejiang Univ-Sci B (Biomed & Biotechnol), 19(5):354–363. https://doi.org/10.1631/jzus.B1700074.
Wu Y, Robinson N, Hardiman PJ, et al., 2016. Acupuncture for treating polycystic ovary syndrome: guidance for future randomized controlled trials. J Zhejiang Univ-Sci B (Biomed & Biotechnol), 17(3):169–180. https://doi.org/10.1631/jzus.B1500301.
Xie X, Gou W, 2013. Obstetrics and Gynecology, 8th Ed. People’s Medical Publishing House, Beijing, China, p.120 (in Chinese).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Project supported by the Zhejiang Provincial Natural Science Foundation for Distinguished Young Scholars (No. LR16H040001), the Key Project of Science and Technology Department of Zhejiang Province (No. 2018C03010), the Zhejiang Provincial & Ministry of Health Research Fund for Medical Sciences (Nos. WKJ-ZJ-1522 and WKJ-ZJ-1722), the National Key Technology R & D Program of China (No. 2014BAI05B04), the Guangxi Natural Science Foundation (Nos. 2015GXNSFBA139177, 2017GXNSFAA198199, and 2017 GXNSFAA198193), China
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pan, Xm., Lin, Z., Li, N. et al. Effects of body mass index on the outcomes of in vitro fertilization in Chinese patients with polycystic ovary syndrome: a retrospective cohort study. J. Zhejiang Univ. Sci. B 19, 490–496 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1631/jzus.B1800113
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1631/jzus.B1800113