Abstract
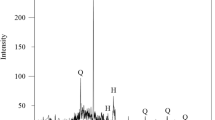
In this article, first, we present the characterization and the process of solidification/stabilization (S/S) of hazardous waste, industrial rejections of Algeria, by hydraulic binder CEM I, Second, we present the study on the influence of leaching tests and the amount of waste on the release of solidified/stabilized waste to the surrounding environment. S/S was performed at the laboratory using two types of formulations. The mechanical strength was evaluated at 7 days then at 28 days of cure. The results of mechanical strength show an increasing up to a maximum threshold, then a decrease due to the increasing of the amount of waste in the S/S materials. pH-dependence test showed two types of solubilization; chemical species that depends on pH (Ni2+, Pb2+, Cr3+, Ca2+) and others which are independent from pH (Na+, K+, Cl−). It was observed that the amounts of heavy metals released into the pH dependence, PW and MMF tests were very large compared to the amount released into the MLT test. XRD and SEM–EDX analysis show the presence of heavy metals within the structure of S/S materials which explains the effectiveness of the S/S process. Mortar showed better efficiency in trapping pollutants compared to cement paste.













Similar content being viewed by others
References
AFNOR (1996) Qualité des sols-Sols, sédiments-Mise en solution par attaque acide NF X31-147
AFNOR (2006) Méthodes d’essais des ciments: Partie 1: détermination des résistances mécaniques NF EN 196-1
AFNOR (2009) Méthodes d’essais des ciments: Partie 3: détermination du temps de prise et de la stabilité NF EN 196-3
AFNOR (2012) Caractérisation du déchet-Essai de lixiviation d’un déchet solide initialement massif ou généré par un procédé de solidification NF X31-211
Amini HR, Saeedi M, Baghvand A (2008) Solidification/stabilization of heavy metals from air heater washing wastewater treatment in thermal power plants. Int J Environ Res 2:297–306
Atahan HN, Oktar ON, Tasdemir MA (2009) Effects of water–cement ratio and curing time on the critical pore width of hardened cement paste. Constr Build Mater 23:1196–1200
Baeyens J, Van Puyvelde F (1994) Fluidized bed incineration of sewage sludge: a strategy for the design of the incinerator and the future for incinerator ash utilization. J Hazard Mater 37:179–190
Baur I, Keller P, Mavrocordatos D et al (2004) Dissolution-precipitation behaviour of ettringite, monosulfate, and calcium silicate hydrate. Cem Concr Res 34:341–348
Bozkurt S, Moreno L, Neretnieks I (2000) Long term processes in waste deposits. Sci Total Environ 250:101–121
Caucheteux A (2002) Evolution au cours de la lixiviation des propriétés physico-chimiques d’un REFIOM humide stabilisé aux liants hydrauliques. PhD thesis, The National school of mines of Saint-Etienne and National polytechnic institute of Gronoble, France
CEN (2005) CEN/TS 14429 Characterization of waste: leaching behaviour tests: influence of pH on leaching with initial acid/base addition
Chen QY, Hills CD, Tyrer M et al (2007) Characterisation of products of tricalcium silicate hydration in the presence of heavy metals. J Hazard Mater 147:817–825
Chen QY, Tyrer M, Hills CD et al (2009) Immobilisation of heavy metal in cement-based solidification/stabilization: a review. Waste Manag 29:390–403
Chen X, Wu S, Zhou J (2013) Influence of porosity on compressive and tensile strength of cement mortar. Constr Build Mater 40:869–874
Cheryl EH, Rose A, Donia B et al (2003) Evaluation the applicability of a modified toxicity characteristic leaching procedure (TCLP) for the classification of cementitious wastes containing lead and cadmium. J Hazard Mater B103:125–140
Chikhi M, Balaska F, Boudraa S et al (2012) Experimental study of stabilization of sludge containing toxic metal by hydraulic binders. Energy Proced 19:259–268
Conner JR (1990) Chemical fixation and solidification of hazardous wastes. Van Nostrand Reihold, New York
Cranck J (1975) The mathematics of diffusion, 2nd edn. Clarendon Press, Oxford
De Windt L, Badreddine R (2007) Modelling of long-term dynamic leaching tests applied to solidified/stabilized waste. Waste Manag 27:1638–1647
Engelsen CJ, Van der Sloot HA, Wibetoe G et al (2009) Release of major elements from recycled concrete aggregates and geochemical modelling. Cem Concr Res 39:446–459
Environment Agency EA (2005) EA NEN 7375:2004: leaching characteristics of moulded or monolithic building and waste materials: determination of leaching of inorganic components with the diffusion test ‘the tank test’ based on a translation of the Netherlands Normalisation Institute Standard, Version 1.0
Feng D, Aldrich C, Tan H (2000) Treatment of acid mine by use of heavy metal precipitation and ion exchange. Miner Eng 13:623–642
Gollmann MAC, Da Silva MM, Masuero AB et al (2010) Stabilization and solidification of Pb in cement matrices. J Hazard Mater 179:507–514
Gougar MLD, Scheetz BE, Roy DM (1996) Ettringite and C–S–H Portland cement phases for waste ion immobilization: a review. Waste Manag 16:295–303
Hekal EE, Hegazi WS, Kishar EA et al (2011) Solidification/stabilization of Ni(II) by various cement pastes. Constr Build Mater 25:109–114
Hong S, Lim G, Lee B et al (1999) Mechanical strength enhancement of lower hydraulicity cementitious solid wastes using anhydrite and pozzolanic materials. Cem Concr Res 29:215–221
Imyim A (2000) Méthodologie d’évaluation environnementale des déchets stabilisés/solidifiés par liants hydrauliques. PhD thesis, National Institute of Applied Sciences of Lyon
Ivey DG, Heimann RB, Neuwirth M et al (1990) Electron microscopy of heavy metal waste in cement matrices. J Mater Sci 25:5055–5062
Kakali G, Tsivilis S, Tsialtas A (1998) Hydration of ordinary Portland cements made from raw mix containing transition oxides. Cem Concr Res 28:335–340
Laforest G, Duchesne J (2007) Investigation of stabilization/solidification of electric arc furnace dust: dynamic leaching of monolithic specimens. Cem Concr Res 37:1639–1646
Ligia R, Tiruta-Barna L, Barna R et al (2001) Modeling of solid/liquid/gas mass transfer for environmental evaluation of cement-based solidified wastes. Environ Sci Technol 35:149–156
Maltolack M, Howerton B, Atwood D (2002) Chemical precipitation of heavy metals from acid drainage. Water Res 36:4757–4764
Moussaceb K, Aït-Mokhtar A, Merabet D (2012) Influence of leaching conditions on the release kinetics of lead, chromium and nickel from solidified/stabilized cementitious materials. Environ Technol 33:2681–2690
Moussaceb K, Belebchouche Ch, Aït-Mokhtar A et al (2013) Evaluation of the impact of Ni, Cr and Pb contained in effluents of an industrial unit by the process of stabilization/solidification using hydraulic binders. Int J Environ Res 7(2):485–494
Omikrine O, Aït-Mokhtar A (2009) A proposed methodology for quantitative investigation of carbonation in polymer-modified mortars. Exp Tech 33:59–65
Planel D (2002) Les effets couplés de la précipitation d’espèces secondaires sur le comportement mécanique et la dégradation des bétons. PhD thesis, University of Marne La Vallée
Planel D, Sercombe J, Le Bescop P et al (2006) Long-term performance of cement paste during combined calcium leaching-sulfate attack: kinetics and size effect. Cem Concr Res 36:137–143
Qiao XC, Poon CS, Cheeseman CR (2007) Investigation into stabilization/solidification performance of Portland cement through cement clinker phases. J Hazard Mater B139:238–243
Richardson IG, Groves GW (1993) The incorporation of minor trace elements into calcium silicate hydrate gel in hardened cement pastes. Cem Concr Res 23:131–138
Sawai T, Yamazaki M, Shimokawa T et al (1990) Improvement of sedimentation and dewatering of municipal sludge by radiation. Int J Radiat Appl Instrum C Radiat Phys Chem 35:465–468
Sparrevik M, Eek E, Grini RS (2009) The importance of sulphide binding for leaching of heavy metals from contaminated Norwegian marine sediments treated by stabilization/solidification. Environ Technol 30:831–840
Ukrainczyk N, Vrbos N, Sipusic J (2012) Influence of metal chloride salts on calcium aluminate cement hydration. Adv Cem Res 25:249–262
Van der Sloot HA, Meeussen JCL, Van Zomeren A et al (2006) Developments in the characterisation of waste materials for environmental impact assessment purposes. J Geochem Explor 88:72–76
Van der Sloot HA, Van Zomeren A, Meeussen JCL et al (2007) Test method selection, validation against field data, and predictive modelling for impact evaluation of stabilised waste disposal. J Hazard Mater 141:354–369
Voglar GE, Lestan D (2013) Equilibrium leaching of toxic elements from cement stabilized soil. J Hazard Mater 246–247:18–25
Wang DX, Abriak N, Zentar R et al (2012) Solidification/stabilization of dredged marine sediments for road construction. Environ Technol 33:95–101
Zampori L, Gallo Stampino P, Dotelli G (2009) Long-term leaching test of organo-contaminated cement–clay pastes. J Hazard Mater 170:1041–1049
Zhao H, Poon CS, Ling TC (2013) Properties of mortar prepared with recycled cathode ray tube funnel glass sand at different mineral admixture. Constr Build Mater 40:951–960
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Belebchouche, C., Moussaceb, K., Tahakourt, A. et al. Parameters controlling the release of hazardous waste (Ni2+, Pb2+ and Cr3+) solidified/stabilized by cement-CEM I. Mater Struct 48, 2323–2338 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1617/s11527-014-0315-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1617/s11527-014-0315-6