Abstract
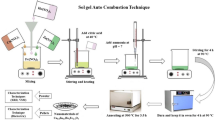
Sol–gel method has been used to synthesize copper substituted nickel ferrite CuxNi1−xFe2O4 nanoparticles with different concentration of copper as x = 0.0, 0.1, 0.2, 0.3, and 0.4. The crystallinity was confirmed through the powder X-ray diffraction method with single phase face-centred cubic structure for all CuxNi1−xFe2O4 samples having preferred orientation along (311) plane. The crystallite size was estimated through Scherrer’s formula and observed to be in the range from 21 to 38 nm. The microstructure of ferrite nanoparticles was characterized by the scanning electron microscopy. The existence of functional groups and copper substitution in CuxNi1−xFe2O4 nanoparticles was investigated by Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy. Impedance analyser was employed to investigate the dielectric properties of copper substituted nickel ferrites. The high value of dielectric constant at low frequency and low impedance at high frequency would make these nanoparticles a potential candidate for microwave device applications.
Graphical abstract







Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All necessary data is available in the manuscript in the form of figures and tables. There is no supplementary data available.
Change history
13 October 2023
A Correction to this paper has been published: https://doi.org/10.1557/s43578-023-01191-7
References
H. El-Sayed, Effect of induced magnetic anisotropy on the hysteresis parameters of Co-ferrite prepared from nano-sized particles. J. Alloys Compd. 474(1–2), 561 (2009)
S. Thakur, S. Katyal, A. Gupta, V. Reddy, M. Singh, Room temperature ferromagnetic ordering in indium substituted nano-nickel-zinc ferrite. J. Appl. Phys. 105(7), 07A521 (2009)
P. Mathur, A. Thakur, M. Singh, Effect of nanoparticles on the magnetic properties of Mn–Zn soft ferrite. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 320(7), 1364 (2008)
A. Dias, R.L. Moreira, N.D. Mohallem, A.C. Persiano, Microstructural dependence of the magnetic properties of sintered NiZn ferrites from hydrothermal powders. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 172(1–2), L9 (1997)
K. Roumaih, The transport properties of the mixed Ni–Cu ferrite. J. Alloys Compd. 465(1–2), 291 (2008)
F.S. Tehrani, V. Daadmehr, A. Rezakhani, R.H. Akbarnejad, S. Gholipour, Structural, magnetic, and optical properties of zinc- and copper-substituted nickel ferrite nanocrystals. J. Supercond. Nov. Magn. 25(7), 2443 (2012)
H. Dawoud, L. A-Ouda, S. Shaat, Investigation of the effect of Zn ions concentration on DC conductivity and Curie temperature of Ni-spinel ferrite. Am. J. Mater. Sci. Appl. 4(2), 11 (2016)
R. Sharma, P. Thakur, M. Kumar, P. Sharma, V. Sharma, Nanomaterials for high frequency device and photocatalytic applications: Mg–Zn–Ni ferrites. J. Alloys Compd. 746, 532 (2018)
M. Amiri, M. Salavati-Niasari, A. Akbari, Magnetic nanocarriers: evolution of spinel ferrites for medical applications. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cis.2019.01.003
R. Lebourgeois, C. Coillot, Mn–Zn ferrites for magnetic sensor in space applications. J. Appl. Phys. 103(7), 07E510 (2008)
C. Sujatha, K.V. Reddy, K.S. Babu, A.R.C. Reddy, M.B. Suresh, K. Rao, Effect of co substitution of Mg and Zn on electromagnetic properties of NiCuZn ferrites. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 74(7), 917 (2013)
B. Madhu, S. Ashwini, B. Shruthi, B. Divyashree, A. Manjunath, H. Jayanna, Structural, dielectric and electromagnetic shielding properties of Ni–Cu nanoferrite/PVP composites. Mater. Sci. Eng. B 186, 1 (2014)
S. Krupicka, P. Novak, Oxide Spinels Ferroelectric Materials, vol. 3 (North-Holland, Amsterdam, 1982)
S. Patil, S. Otari, V. Mahajan, M. Patil, A. Patil, M. Soudagar, B. Patil, S. Sawant, Structural, IR and magnetisation studies on La3+ substituted copper ferrite. Solid State Commun. 78(1), 39 (1991)
C. Upadhyay, D. Mishra, H. Verma, S. Anand, R. Das, Effect of preparation conditions on formation of nanophase Ni–Zn ferrites through hydrothermal technique. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 260(1–2), 188 (2003)
Z.Ž Lazarević, Č Jovalekić, A. Milutinović, D. Sekulić, V.N. Ivanovski, A. Rečnik, B. Cekić, N.Ž Romčević, Nanodimensional spinel NiFe2O4 and ZnFe2O4 ferrites prepared by soft mechanochemical synthesis. J. Appl. Phys. 113(18), 187221 (2013)
L.B. de Mello, L.C. Varanda, F.A. Sigoli, I.O. Mazali, Co-precipitation synthesis of (Zn–Mn)-co-doped magnetite nanoparticles and their application in magnetic hyperthermia. J. Alloys Compd. 779, 698 (2019)
T. Tatarchuk, I. Mironyuk, V. Kotsyubynsky, A. Shyichuk, M. Myslin, V. Boychuk, Structure, morphology and adsorption properties of titania shell immobilized onto cobalt ferrite nanoparticle core. J. Mol. Liq. 297, 111757 (2020)
S.B. Somvanshi, M.V. Khedkar, P.B. Kharat, K. Jadhav, Influential diamagnetic magnesium (Mg2+) ion substitution in nano-spinel zinc ferrite (ZnFe2O4): thermal, structural, spectral, optical and physisorption analysis. Ceram. Int. 46(7), 8640 (2020)
M.A. Yousuf, S. Jabeen, M.N. Shahi, M.A. Khan, I. Shakir, M.F. Warsi, Magnetic and electrical properties of yttrium substituted manganese ferrite nanoparticles prepared via micro-emulsion route. Results Phys. 16, 102973 (2020)
J.D. Wright, N.A. Sommerdijk, Sol–Gel Materials: Chemistry and Applications (CRC Press, Boca Raton, 2000)
M.P. Reddy, R. Shakoor, A. Mohamed, Auto combustion synthesis, microstructural and magnetic characteristics of nickel ferrite nanoparticles. Indian J. Sci. Technol. 10(13), 1 (2017)
M. Kurian, D.S. Nair, Effect of preparation conditions on nickel zinc ferrite nanoparticles: a comparison between sol–gel auto combustion and co-precipitation methods. J. Saudi Chem. Soc. 20, S517 (2016)
O. Kamigaito, What can be improved by nanometer composites? J. Jpn. Soc. Powder Powder Metall. 38(3), 315 (1991)
F. Song, X. Shen, M. Liu, J. Xiang, Preparation and magnetic properties of SrFe12O19/Ni0.5Zn0.5Fe2O4 nanocomposite ferrite microfibers via sol–gel process. Mater. Chem. Phys. 126(3), 791 (2011)
K.V. Babu, G.S. Kumar, G. Satyanarayana, B. Sailaja, C.C.S. Lakshmi, Microstructural and magnetic properties of Ni1−xCuxFe2O4 (x = 0.05, 0.1 and 0.15) nano-crystalline ferrites. J. Sci.: Adv. Mater. Devices 3(2), 236 (2018)
S.B. Khan, S. Irfan, S.-L. Lee, Influence of Zn2+ doping on Ni-based nanoferrites; (Ni1−xZnxFe2O4). Nanomaterials 9(7), 1024 (2019)
R. Lahouli, J. Massoudi, M. Smari, H. Rahmouni, K. Khirouni, E. Dhahri, L. Bessais, Investigation of annealing effects on the physical properties of Ni0.6Zn0.4Fe1.5Al0.5O4 ferrite. RSC Adv. 9(35), 19949 (2019)
I. Toqeer, M. Naz, Y. Khan, M. Azam, M. Alkanhal, R. Meer, Morphological and magnetic response of copper-substituted nickel ferrite nanoparticles. Philos. Mag. Lett. 99(2), 67 (2019)
S. Singhal, S. Jauhar, J. Singh, K. Chandra, S. Bansal, Investigation of structural, magnetic, electrical and optical properties of chromium substituted cobalt ferrites (CoCrxFe2−xO4, 0 ≤ x ≤ 1) synthesized using sol gel auto combustion method. J. Mol. Struct. 1012, 182 (2012)
A. Yadav, D. Varshney, Structural and dielectric properties of copper-substituted Mg–Zn spinel ferrites. J. Supercond. Nov. Magn. 30, 1297 (2017)
K. Naz, J.K. Khan, M. Khalid, M.S. Akhtar, Z.A. Gilani, G.A. Mersal, M.M. Ibrahim, A. Muhammad, M. Ashiq, Structural, dielectric, impedance and electric modulus analysis of Ni substituted copper spinel ferrites nanoparticles for microwave device applications. Mater. Chem. Phys. 285, 126091 (2022)
K.M. Batoo, M.S. Ansari, Low temperature-fired Ni–Cu–Zn ferrite nanoparticles through auto-combustion method for multilayer chip inductor applications. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 7(1), 112 (2012)
D. Paramesh, K.V. Kumar, P.V. Reddy, Influence of nickel addition on structural and magnetic properties of aluminium substituted Ni–Zn ferrite nanoparticles. Process. Appl. Ceram. 10(3), 161 (2016)
E.S. Lima, L.S. Costa, G.R. Sampaio, E.S. Oliveira, E.B. Silva, H.O. Nascimento, R.F. Nascimento, K.O. Moura, M. Bastos-Neto, A.R. Loiola, Zinc ferrite nanoparticles via coprecipitation modified method: glycerol as structure directing and stabilizing agent. J. Braz. Chem. Soc. 30(4), 882 (2019)
A. Ghoneim, T. Meaz, H. Aboelkhir, Structural, thermal and ferrimagnetic studies of the as-fabricated La3+-doped Co-nano-spinels. J. Phys.: Conf. Ser. 1253, 012020 (2019)
M. Zaid, D. Hemeda, S.A. Kader, G. Farag, Structural, electrical and infrared studies of Ni0.7Cd0.3SmxFe2−xO4 ferrite. Turk. J. Phys. 31(1), 41–50 (2007)
S.E. Shirsath, M.L. Mane, Y. Yasukawa, X. Liu, A. Morisako, Self-ignited high temperature synthesis and enhanced super-exchange interactions of Ho3+–Mn2+–Fe3+–O2− ferromagnetic nanoparticles. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 16(6), 2347 (2014)
N. Channa, M. Khalid, A.D. Chandio, G. Mustafa, M.S. Akhtar, J.K. Khan, J. Ahmad, K.A. Kalhoro, Nickel-substituted manganese spinel ferrite nanoparticles for high-frequency applications. J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electron. 31, 1661 (2020)
R. Gimenes, M.R. Baldissera, M. Da Silva, C. Da Silveira, D. Soares, L.A. Perazolli, M. Da Silva, M. Zaghete, Structural and magnetic characterization of MnxZn1−xFe2O4 (x = 0.2; 0.35; 0.65; 0.8; 1.0) ferrites obtained by the citrate precursor method. Ceram. Int. 38(1), 741 (2012)
A. Volkov, A. Prokhorov, Broadband dielectric spectroscopy of solids. Radiophys. Quantum Electron. 46(8–9), 657 (2003)
T.K. Bromho, K. Ibrahim, H. Kabir, M.M. Rahman, K. Hasan, T. Ferdous, H. Taha, M. Altarawneh, Z.-T. Jiang, Understanding the impacts of Al3+-substitutions on the enhancement of magnetic, dielectric and electrical behaviors of ceramic processed nickel–zinc mixed ferrites: FTIR assisted studies. Mater. Res. Bull. 97, 444 (2018)
K. Wagner, Dissipation of energy under AC. Ann. Phys. 40, 817 (1913)
K.W. Wagner, Zur theorie der unvollkommenen dielektrika. Ann. Phys. 345(5), 817 (1913)
A.A. Hossain, T. Biswas, T. Yanagida, H. Tanaka, H. Tabata, T. Kawai, Investigation of structural and magnetic properties of polycrystalline Ni0.50Zn0.50−xMgxFe2O4 spinel ferrites. Mater. Chem. Phys. 120(2–3), 461 (2010)
F. Kremer, A. Schönhals, Broadband Dielectric Spectroscopy (Springer Science & Business Media, Berlin, 2002)
J. Li, H. Yuan, G. Li, Y. Liu, J. Leng, Cation distribution dependence of magnetic properties of sol–gel prepared MnFe2O4 spinel ferrite nanoparticles. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 322(21), 3396 (2010)
I. Gul, E. Pervaiz, Comparative study of NiFe2−xAlxO4 ferrite nanoparticles synthesized by chemical co-precipitation and sol–gel combustion techniques. Mater. Res. Bull. 47(6), 1353 (2012)
M. Hashim, S. Kumar, S. Ali, B. Koo, H. Chung, R. Kumar, Structural, magnetic and electrical properties of Al3+ substituted Ni–Zn ferrite nanoparticles. J. Alloys Compd. 511(1), 107 (2012)
S. Li, W. Yang, M. Chen, J. Gao, J. Kang, Y. Qi, Preparation of PbO nanoparticles by microwave irradiation and their application to Pb(II)-selective electrode based on cellulose acetate. Mater. Chem. Phys. 90(2–3), 262 (2005)
N. Velinov, T. Petrova, R. Ivanova, T. Tsoncheva, D. Kovacheva, I. Mitov, Synthesis and characterization of copper–nickel ferrite catalysts for ethyl acetate oxidation. Hyperfine Interact. 241(1), 1 (2020)
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by King Khalid University through a Grant (KKU/RCAMS/22) under the Research Centre for Advanced Materials Science (RCAMS) at King Khalid University, Saudi Arabia.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
On behalf of all the authors of manuscript entitled “Sol–Gel Synthesis and Physical Properties of Ni–Cu based Spinel Ferrites Nanoparticles”, I would like to declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Kalhoro, K.A., Khalid, M., Naz, K. et al. Sol–gel synthesis and physical properties of Ni–Cu based spinel ferrites nanoparticles. Journal of Materials Research 38, 3764–3775 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1557/s43578-023-01098-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1557/s43578-023-01098-3