Abstract
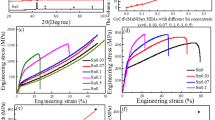
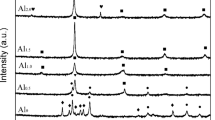
This study synthesized four kinds of CoCrMnFeNiX0.1 (X = Al, Cu, Mo, Ti) high-entropy alloys to investigate the alloying effect. We found the strengthening effect after aging thermal treatment can be sequenced as Ti > Mo > Cu > Al, of which the tensile strength was improved by 20 ~ 40% and the elongation to failure preserved (~ 50%) compared with the corresponding casting materials. Specifically, the CoCrMnFeNiTi0.1 alloy offered a yield strength of 435 MPa, an ultimate tensile strength of 900 MPa, and a fracture elongation of 40% is significantly higher than those of their conventional counterparts. Furthermore, the anti-corrosion ability of added secondary elements is in the following order: Ti > Mo > Al > Cu. Through microstructure observations, we discussed and analyzed the formation and evolution of second-phase particles, which play an important role due to the strong interactive effect among different elements. In general, adding a secondary trace Ti or Mo element improves strength and anti-corrosion properties.
Graphical abstract
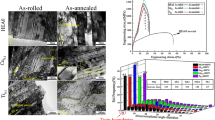
Enhanced tensile properties are shown in true stress–strain curves of the as-cast and as-aged CoCrMnFeNiX0.1 alloy; post-tensile fracture morphology and corrosion morphology of the as-aged CoCrMnFeNiTi0.1 alloy compare with the as-cast CoCrMnFeNi alloy, indicating that adding trace secondary Ti element benefits the outstanding improvement of strength and anti-corrosion properties.









Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Some data that could not be presented in this article is available as supplementary data (mentioned as online resource). Other data generated during this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
Code availability
Not applicable.
References
D.B. Miracle, O.N. Senkov, A critical review of high entropy alloys and related concepts. Acta Mater. 122, 448–511 (2017)
S.A. Firstov, V.F. Gorban’, N.A. Krapivka, M.V. Karpets, A.D. Kostenko, Wear resistance of high-entropy alloys. Powder Metall. Met. Ceram. 56(3–4), 158–164 (2017)
H.Z. Zhang, C.H. Li, Z.B. Zhu, H.F. Huang, Y.P. Lu, T.M. Wang, T.J. Li, Effects of He-ion irradiation on the microstructures and mechanical properties of the novel Co-free VxCrFeMnNiy high-entropy alloys. J. Nucl. Mater. 572, 154074 (2022)
J.C. Duan, M.L. Wang, R. Huang, J.W. Miao, Y.P. Lu, T.M. Wang, T.J. Li, A novel high-entropy alloy with an exceptional combination of soft magnetic properties and corrosion resistance. Sci. China Mater. 66(2), 772–779 (2022)
M.D. Zhang, L.J. Zhang, P.K. Liaw, G. Li, R.P. Liu, Effect of Nb content on thermal stability, mechanical and corrosion behaviors of hypoeutectic CoCrFeNiNbx high-entropy alloys. J. Mater. Res. 33(19), 1–11 (2018)
M.L. Wang, Y.P. Lu, J.G. Lan, T.M. Wang, C. Zhang, Z.Q. Cao, T.J. Li, P.K. Liaw, Lightweight, ultrastrong and high thermal-stable eutectic high-entropy alloys for elevated-temperature applications [J]. Acta Mater. 248, 118806 (2023)
M.L. Wang, Y.P. Lu, T.M. Wang, C. Zhang, Z.Q. Cao, T.J. Li, P.K. Liaw, A novel bulk eutectic high-entropy alloy with outstanding as-cast specific yield strengths at elevated temperatures. Scr. Mater. 204, 114132 (2021)
Z.Y. Lyu, X.S. Fan, C.H. Lee, S.Y. Wang, R. Feng, P.K. Liaw, Fundamental understanding of mechanical behavior of high-entropy alloys at low temperatures: a review. J. Mater. Res. 33(19), 1–13 (2018)
J.Y. He, W.H. Liu, H. Wang, Y. Wu, X.J. Liu, T.G. Nieh, Z.P. Lu, Effects of Al addition on structural evolution and tensile properties of the FeCoNiCrMn high-entropy alloy system. Acta Mater. 62, 105–113 (2014)
F. Otto, A. Dlouhý, C. Somsen, H. Bei, G. Eggeler, E.P. George, The influences of temperature and microstructure on the tensile properties of a CoCrFeMnNi high-entropy alloy. Acta Mater. 61(15), 5743–5755 (2013)
Z. Wu, C.M. Parish, H. Bei, Nano-twin mediated plasticity in carbon-containing FeNiCoCrMn high entropy alloys. J. Alloys Compd. 647, 815–822 (2015)
A.J. Zaddach, R.O. Scattergood, C.C. Koch, Tensile properties of low-stacking fault energy high-entropy alloys. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 636, 373–378 (2015)
X.Z. Gao, W. Jiang, Y.P. Lu, Z.G. Ding, J.Z. Liu, W. Liu, G. Sha, T.M. Wang, T.J. Li, I.T.H. Chang, Y.H. Zhao, Excellent strength-ductility combination of Cr26Mn20Fe20Co20Ni14 high-entropy alloy at cryogenic temperatures. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 154, 166–177 (2023)
B. Gludovatz, A. Hohenwarter, D. Catoor, E.H. Chang, E.P. George, R.O. Ritchie, A fracture-resistant high-entropy alloy for cryogenic applications. Sci. 345(6201), 1153–1158 (2014)
S. Hu, T. Fu, Q.H. Liang, S.Y. Weng, X. Chen, Y.B. Zhao, X.H. Peng, Formation and anisotropic mechanical behavior of stacking fault tetrahedron in Ni and CoCrFeNiMn high-entropy alloy. Front. Mater. 8, 608 (2022)
M.S. Mehranpour, H. Shahmir, M. Nili-Ahmadabadi, CoCrFeNiMn high entropy alloy microstructure and mechanical properties after severe cold shape rolling and annealing. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 793, 139884 (2020)
S. Huang, W. Li, S. Lu, F.Y. Tian, J. Shen, E. Holmström, L. Vitos, Temperature dependent stacking fault energy of FeCrCoNiMn high entropy alloy. Scr. Mater. 108, 44–47 (2015)
S.H. Joo, H. Kato, M.J. Jang, J. Moon, C.W. Tsai, J.W. Yeh, H.S. Kim, Tensile deformation behavior and deformation twinning of an equimolar CoCrFeMnNi high-entropy alloy. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 689, 122–133 (2017)
J.W. Yeh, S.K. Chen, J.Y. Gan, Communication: formation of simple crystal structures in Cu-Co-Ni-Cr-Al-Fe-Ti-V alloys with multiprincipal metallic elements. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 35, 2533–2536 (2004)
D. Kong, J. Guo, R.W. Liu, X.H. Zhang, Y.P. Song, Z.X. Li, F.J. Guo, X.F. Xing, Y. Xu, W. Wang, Effect of remelting and annealing on the wear resistance of AlCoCrFeNiTi0.5 high entropy alloys. Intermetallics 114, 106560 (2019)
T.T. Shun, L.Y. Chang, M.H. Shiu, Microstructure and mechanical properties of multiprincipal component CoCrFeNiMox alloys. Mater. Charact. 70, 63–67 (2012)
ASTM, Standard Practice for Laborator Immersion Corrosion Testing of Metals (Academia, 2004)
B. Schuh, F. Mendez-Martin, B. Völker, E.P. George, H. Clemens, R. Pippan, A. Hohenwarter, Mechanical properties, microstructure and thermal stability of a nanocrystalline CoCrFeMnNi high-entropy alloy after severe plastic deformation. Acta Mater. 96, 258–268 (2015)
F. Otto, A. Dlouhý, K.G. Pradeep, M. Kuběnová, D. Raabe, G. Eggeler, E.P. George, Decomposition of the single-phase high-entropy alloy CrMnFeCoNi after prolonged anneals at intermediate temperatures. Acta Mater. 112, 40–52 (2016)
S.J. Sun, Y.Z. Tian, H.R. Lin, X.G. Dong, Y.H. Wang, Z.J. Zhang, Z.F. Zhang, Enhanced strength and ductility of bulk CoCrFeMnNi high entropy alloy having fully recrystallized ultrafine-grained structure. Mater. Des. 133, 122–127 (2017)
M.J. Yao, K.G. Pradeep, C.C. Tasan, D. Raabe, A novel, single phase, non-equiatomic FeMnNiCoCr high-entropy alloy with exceptional phase stability and tensile ductility. Scr. Mater. 72, 5–8 (2014)
G. Laplanche, A. Kostka, O.M. Horst, G. Eggeler, E.P. George, Microstructure evolution and critical stress for twinning in the CrMnFeCoNi high-entropy alloy. Acta Mater. 118, 152–163 (2016)
A. Gali, E.P. George, Tensile properties of high- and medium-entropy alloys. Intermetallics 39, 74–78 (2013)
H. Shahmir, A. Derakhshandeh, B. Hallstedt, M. Nili-Ahmadabadi, Microstructural evolution and mechanical properties of CoCrFeNiMnTix high-entropy alloys. Materialwiss. Werkstofftech. 52(4), 441–451 (2021)
J. Moon, O. Bouaziz, H.S. Kim, Y. Estrin, Twinning engineering of a CoCrFeMnNi high-entropy alloy. Scr. Mater. 197, 113808 (2021)
W.H. Liu, Z.P. Lu, J.Y. He, J.H. Luan, Z.J. Wang, B. Liu, Y. Liu, M.W. Chen, C.T. Liu, Ductile CoCrFeNiMox high entropy alloys strengthened by hard intermetallic phases. Acta Mater. 116, 332–342 (2016)
C.D. Dai, Y. Fu, Y. Pan, Y.P. Yin, C.W. Du, Z.Y. Liu, Microstructure and mechanical properties of FeCoCrNiMo0.1 high-entropy alloy with various annealing treatments. Mater. Charact. 179, 111313 (2021)
W.Q. Wu, L. Guo, B. Liu, S. Ni, Y. Liu, M. Song, Effects of torsional deformation on the microstructures and mechanical properties of a CoCrFeNiMo0.15 high-entropy alloy. Philos. Mag. 97(34), 3229–3245 (2017)
J.L. Yuan, Y.C. Wu, P.K. Liaw, J.H. Luan, Z.B. Jiao, J. Li, P.D. Han, J.W. Qiao, Remarkable cryogenic strengthening and toughening in nano-coherent CoCrFeNiTi0.2 high-entropy alloys via energetically-tuning polymorphous precipitates. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 842, 143111 (2022)
J.X. Hou, J.W. Qiao, J.H. Lian, P.K. Liaw, Revealing the relationship between microstructures, textures, and mechanical behaviors of cold-rolled Al0.1CoCrFeNi high-entropy alloys. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 804, 140752 (2021)
G. Ma, Y. Zhao, H. Cui, X. Song, M. Wang, K. Lee, X. Gao, Q. Song, C. Wang, Addition Al and/or Ti induced modifications of microstructures, mechanical properties, and corrosion properties in CoCrFeNi high-entropy alloy coatings. Acta Metall. Sin. (Engl. Lett.) 34(8), 1087–1102 (2021)
Y.Z. Shi, B. Yang, X. Xie, J. Brechtl, K.A. Dahmen, P.K. Liaw, Corrosion of AlCoCrFeNi high-entropy alloys: Al-content and potential scan-rate dependent pitting behavior. Corros. Sci. 119, 33–45 (2017)
Y.J. Hsu, W.C. Chiang, J.K. Wu, Corrosion behavior of FeCoNiCrCux high-entropy alloys in 3.5% sodium chloride solution. Mater. Chem. Phys. 92(1), 112–117 (2005)
W. Wang, J. Wang, H. Yi, W. Qi, Q. Peng, Effect of molybdenum additives on corrosion behavior of (CoCrFeNi)(100–x)Mo(x) high-entropy alloys. Entropy 20(12), 908 (2018)
W.H. Guo, J.Y. Li, M.F. Qi, Y.Z. Xu, H.R. Ezatpour, Effects of heat treatment on the microstructure, mechanical properties and corrosion resistance of AlCoCrFeNiTi0.5 high-entropy alloy. J. Alloys Compd. 884, 161026 (2021)
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to acknowledge the financial support of the National Natural Science Foundation of China (NO. 51801072, NO. 51805219), and China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (2019TQ0126).
Funding
The financial support was provided by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (NO. 51801072, NO. 51805219), and China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (2019TQ0126).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no relevant financial or non-financial interests to disclose.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Tang, L., Guo, M., Zhou, Y. et al. Effects of trace secondary elements on microstructure and properties in CoCrMnFeNiX0.1 alloys. Journal of Materials Research 38, 3110–3123 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1557/s43578-023-01031-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1557/s43578-023-01031-8