Abstract
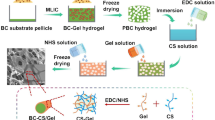
Lack of bioactivity limits the applications of bacterial cellulose (BC) in biomedical fields. In this study, we report the facile preparation of a macroporous BC (PBC)/chondroitin sulfate (CS) scaffold using the ex situ method by adding CS solution into the suspension of BC fragments followed by crosslinking with 1-ethyl-3(3-dimethyl aminopropyl) carbodiimide (EDC) and N-hydroxysuccinimide (NHS) and freeze drying. The PBC/CS scaffold was characterized for morphology, physicochemical properties, cell behavior, and capability of inducing mineral deposition. Results show that the PBC/CS scaffold presents improved mechanical properties, cell adhesion, and proliferation over the PBC scaffold. Moreover, the presence of CS greatly enhances the deposition of minerals on the PBC/CS scaffold, an indicator of bioactivity. The present study provides a simple methodology for improving the bioactivity of BC and the results of the present work suggest that the PBC/CS scaffold has potential for use in bone tissue engineering.
Graphical Abstract










Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Data will be made available on reasonable request.
References
J.D. Fontana, A. Souza, C.K. Fontana, I.L. Torriani, L. Farah, Acetobacter cellulose pellicle as a temporary skin substitute. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 24–25, 253–264 (1990)
D.A. Gregory, L. Tripathi, A.T.R. Fricker, E. Asare, I. Orlando, V. Raghavendran, I. Roy, Bacterial cellulose: a smart biomaterial with diverse applications. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 145, 100623 (2021)
R.A.N. Pertile, S. Moreira, R.M. Gil da Costa, A. Correia, L. Guardao, F. Gartner, M. Vilanova, M. Gama, Bacterial cellulose: long-term biocompatibility studies, J. Biomater. Sci. Polym. Ed. 23, 1339–1354 (2012).
H. Ullah, F. Wahid, H.A. Santos, T. Khan, Advances in biomedical and pharmaceutical applications of functional bacterial cellulose-based nanocomposites. Carbohydr. Polym. 150, 330–352 (2016)
A. Svensson, E. Nicklasson, T. Harrah, B. Panilaitis, D.L. Kaplan, M. Brittberg, P. Gatenholm, Bacterial cellulose as a potential scaffold for tissue engineering of cartilage. Biomaterials 26, 419–431 (2005)
S. Torgbo, P. Sukyai, Bacterial cellulose-based scaffold materials for bone tissue engineering. Appl. Mater. Today 11, 34–49 (2018)
M. Zaborowska, A. Bodin, H. Backdahl, J. Popp, A. Goldstein, P. Gatenholm, Microporous bacterial cellulose as a potential scaffold for bone regeneration. Acta Biomater. 6, 2540–2547 (2010)
C. Xu, J. Zhao, Q. Gong, S. Chen, Sustained release of vancomycin from bacterial cellulose membrane as dural substitutes for anti-inflammatory wound closure in rabbits. J. Biomater. Appl. 34, 1470–1478 (2020)
A.N. Frone, D.M. Panaitescu, C.A. Nicolae, A.R. Gabor, R. Trusca, A. Casarica, P.O. Stanescu, D.D. Baciu, A. Salageanu, Bacterial cellulose sponges obtained with green cross-linkers for tissue engineering. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 110, 110740 (2020)
N. Yin, M.D. Stilwell, T.M.A. Santos, H. Wang, D.B. Weibel, Agarose particle-templated porous bacterial cellulose and its application in cartilage growth in vitro. Acta Biomater. 12, 129–138 (2015)
C. Gao, Y. Wan, C. Yang, K. Dai, T. Tang, H. Luo, J. Wang, Preparation and characterization of bacterial cellulose sponge with hierarchical pore structure as tissue engineering scaffold. J. Porous Mater. 18, 139–145 (2011)
P.M. Favi, S.P. Ospina, M. Kachole, M. Gao, L. Atehortua, T.J. Webster, Preparation and characterization of biodegradable nano hydroxyapatite-bacterial cellulose composites with well-defined honeycomb pore arrays for bone tissue engineering applications. Cellulose 23, 1263–1282 (2016)
Y. Hou, X. Wang, J. Yang, R. Zhu, Z. Zhang, Y. Li, Development and biocompatibility evaluation of biodegradable bacterial cellulose as a novel peripheral nerve scaffold. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. A 106, 1288–1298 (2018)
J. Li, Y. Wan, L. Li, H. Liang, J. Wang, Preparation and characterization of 2,3-dialdehyde bacterial cellulose for potential biodegradable tissue engineering scaffolds. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 29, 1635–1642 (2009)
H. Backdahl, M. Esguerra, D. Delbro, B. Risberg, P. Gatenholm, Engineering microporosity in bacterial cellulose scaffolds. J. Tissue Eng. Regener. Med. 2, 320–330 (2008)
E. Bayir, E. Bilgi, E.E. Hames, A. Sendemir, Production of hydroxyapatite-bacterial cellulose composite scaffolds with enhanced pore diameters for bone tissue engineering applications. Cellulose 26, 9803–9817 (2019)
G. Xiong, H. Luo, Y. Zhu, S. Raman, Y. Wan, Creation of macropores in three-dimensional bacterial cellulose scaffold for potential cancer cell culture. Carbohydr. Polym. 114, 553–557 (2014)
T.R. Stumpf, X. Yang, J. Zhang, X. Cao, In situ and ex situ modifications of bacterial cellulose for applications in tissue engineering. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 82, 372–383 (2018)
P. Cazon, M. Vazquez, Improving bacterial cellulose films by ex-situ and in-situ modifications: a review. Food Hydrocoll. 113, 106514 (2021)
G. Xiong, H. Luo, C. Zhang, Y. Zhu, Y. Wan, Enhanced biological behavior of bacterial cellulose scaffold by creation of macropores and surface immobilization of collagen. Macromol. Res. 23, 734–740 (2015)
J. Wang, Y.Z. Wan, H.L. Luo, C. Gao, Y. Huang, Immobilization of gelatin on bacterial cellulose nanofibers surface via crosslinking technique. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 32, 536–541 (2012)
L. Xu, F. Ma, F.K.L. Leung, C. Qin, W.W. Lu, B. Tang, Chitosan-strontium chondroitin sulfate scaffolds for reconstruction of bone defects in aged rats. Carbohydr. Polym. 273, 118532 (2021)
S. Yan, Q. Zhang, J. Wang, Y. Liu, S. Lu, M. Li, D. Kaplan, Silk fibroin/chondroitin sulfate/hyaluronic acid ternary scaffolds for dermal tissue reconstruction. Acta Biomater. 9, 6771–6782 (2013)
M. Pezeshki-Modaress, H. Mirzadeh, M. Zandi, S. Rajabi-Zeleti, N. Sodeifi, N. Aghdami, M.R.K. Mofrad, Gelatin/chondroitin sulfate nanofibrous scaffolds for stimulation of wound healing: In-vitro and in-vivo study. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 105, 2020–2034 (2017)
H. Cao, S.-Y. Xu, EDC/NHS-crosslinked type II collagen-chondroitin sulfate scaffold: characterization and in vitro evaluation, J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Med. 19, 567–575 (2008).
S. Chen, W. Chen, Y. Chen, X. Mo, C. Fan, Chondroitin sulfate modified 3D porous electrospun nanofiber scaffolds promote cartilage regeneration. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 118, 11312 (2021)
J.Y. Lai, Y.T. Li, C.H. Cho, T.C. Yu, Nanoscale modification of porous gelatin scaffolds with chondroitin sulfate for corneal stromal tissue engineering. Int. J. Nanomed. 7, 1101–1114 (2012)
A. Sadeghi, M. Zandi, M. Pezeshki-Modaress, S. Rajabi, Tough, hybrid chondroitin sulfate nanofibers as a promising scaffold for skin tissue engineering. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 132, 63–75 (2019)
K. Xu, Z. Wang, J.A. Copland, R. Chakrabarti, S.J. Florczyk, 3D porous chitosan-chondroitin sulfate scaffolds promote epithelial to mesenchymal transition in prostate cancer cells. Biomaterials 254, 120126 (2020)
G. M. de Olyveira, P. Basmaji, L. M. Manzine Costa, M.L. dos Santos, C. d. S. Riccardi, F. P. Semeghini Guastaldi, R.M. Scarel-Caminaga, T. S. de Oliveira Capote, E. Pizoni, A. C. Guastaldi, Surface physical chemistry properties in coated bacterial cellulose membranes with calcium phosphate, Mater. Sci. Eng. C 75, 1359–1365 (2017).
G. M. de Olyveira, M.L. dos Santos, C. d. S. Riccardi, L. M. Manzine Costa, P. B. Daltro, P. Basmaji, G. d. C. Daltro, A. C. Guastaldi, Physically Modified Bacterial Cellulose Biocomposites for Guided Tissue Regeneration, Sci. Adv. Mater. 7, 1657–1664 (2015).
G. Helenius, H. Bäckdahl, A. Bodin, U. Nannmark, P. Gatenholm, B. Risberg, In vivo biocompatibility of bacterial cellulose. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. A 76A, 431–438 (2006)
K.J. Burg, S. Porter, J.F. Kellam, Biomaterial developments for bone tissue engineering. Biomaterials 21, 2347–2359 (2000)
L. Liang, T. Hou, Q. Ouyang, L. Xie, S. Zhong, P. Li, S. Li, C. Li, Antimicrobial sodium alginate dressing immobilized with polydopamine-silver composite nanospheres. Compos. Part B 188, 107877 (2020)
L. Gu, T. Li, X. Song, X. Yang, S. Li, L. Chen, P. Liu, X. Gong, C. Chen, L. Sun, Preparation and characterization of methacrylated gelatin/bacterial cellulose composite hydrogels for cartilage tissue engineering. Regener. Biomater. 7, 1–8 (2019)
J. Wu, N. Yin, S. Chen, D. Weibel, H. Wang, Simultaneous 3D cell distribution and bioactivity enhancement of bacterial cellulose (BC) scaffold for articular cartilage tissue engineering. Cellulose 26, 1–16 (2019)
C. Castro, A. Vesterinen, R. Zuluaga, G. Caro, I. Filpponen, O.J. Rojas, G. Kortaberria, P. Ganan, In situ production of nanocomposites of poly(vinyl alcohol) and cellulose nanofibrils from gluconacetobacter bacteria: effect of chemical crosslinking. Cellulose 21, 1745–1756 (2014)
G. Zhu, H. Wang, H. Xu, L. Zhang, Enhanced capacitive deionization by nitrogen-doped porous carbon nanofiber aerogel derived from bacterial-cellulose. J. Electroanal. Chem. 822, 1–37 (2018)
Y. Liu, H. Lv, L. Ren, G. Xue, Y. Wang, Improving the moisturizing properties of collagen film by surface grafting of chondroitin sulfate for corneal tissue engineering. J. Biomater. Sci. Polym. Ed. 27, 758–772 (2016)
T. Fan, J. Chen, P. Pan, Y. Zhang, Y. Hu, X. Liu, X. Shi, Q. Zhang, Bioinspired double polysaccharides-based nanohybrid scaffold for bone tissue engineering. Colloids Surf. B 147, 217–223 (2016)
Y. Gong, Y. Zhu, Y. Liu, Z. Ma, C. Gao, J. Shen, Layer-by-layer assembly of chondroitin sulfate and collagen on aminolyzed poly(l-lactic acid) porous scaffolds to enhance their chondrogenesis. Acta Biomater. 3, 677–685 (2007)
Y. Wan, S. Yang, M. Peng, M. Gama, Z. Yang, X. Deng, J. Zhou, C. Ouyang, H. Luo, Controllable synthesis of biomimetic nano/submicro-fibrous tubes for potential small-diameter vascular grafts. J. Mater. Chem. B 8, 5694–5706 (2020)
H. Luo, J. Dong, X. Xu, J. Wang, Z. Yang, Y. Wan, Exploring excellent dispersion of graphene nanosheets in three-dimensional bacterial cellulose for ultra-strong nanocomposite hydrogels. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 109, 290–297 (2018)
X. Yang, K. Shi, I. Zhitomirsky, E.D. Cranston, Cellulose nanocrystal aerogels as universal 3D lightweight substrates for supercapacitor materials. Adv. Mater. 27, 6104–6109 (2015)
H. Sehaqui, M. Salajkova, Q. Zhou, L.A. Berglund, Mechanical performance tailoring of tough ultra-high porosity foams prepared from cellulose I nanofiber suspensions. Soft Matter 6, 1824–1832 (2010)
R. T. Olsson, M. A. S. Azizi Samir, G. Salazar Alvarez, L. Belova, V. Strom, L. A. Berglund, O. Ikkala, J. Nogues, U. W. Gedde, Making flexible magnetic aerogels and stiff magnetic nanopaper using cellulose nanofibrils as templates, Nat. Nanotechnol. 5, 584–588 (2010).
H. Luo, Y. Zhang, G. Li, J. Tu, Z. Yang, G. Xiong, Z. Wang, Y. Huang, Y. Wan, Sacrificial template method for the synthesis of three-dimensional nanofibrous 58S bioglass scaffold and its invitro bioactivity and cell responses. J. Biomater. Appl. 32, 265–275 (2017)
H. Luo, Y. Zhang, Z. Wang, Z. Yang, J. Tu, Z. Liu, F. Yao, G. Xiong, Y. Wan, Constructing three-dimensional nanofibrous bioglass/gelatin nanocomposite scaffold for enhanced mechanical and biological performance. Chem. Eng. J. 326, 210–221 (2017)
J. Ran, P. Jiang, S. Liu, G. Sun, P. Yan, X. Shen, H. Tong, Constructing multi-component organic/inorganic composite bacterial cellulose-gelatin/hydroxyapatite double-network scaffold platform for stem cell-mediated bone tissue engineering. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 78, 130–140 (2017)
P. Jiang, J. Ran, P. Yan, L. Zheng, X. Shen, H. Tong, Rational design of a high-strength bone scaffold platform based on in situ hybridization of bacterial cellulose/nano-hydroxyapatite framework and silk fibroin reinforcing phase. J. Biomater. Sci. Polym. Ed. 29, 107–124 (2018)
P. Basu, N. Saha, R. Alexandrova, P. Saha, Calcium phosphate incorporated bacterial cellulose-polyvinylpyrrolidone based hydrogel scaffold: structural property and cell viability study for bone regeneration application. Polymers (Basel) 11(11), 1821 (2019)
Y. Li, X. Xun, Y. Xu, A. Zhan, E. Gao, F. Yu, Y. Wang, H. Luo, C. Yang, Hierarchical porous bacterial cellulose scaffolds with natural biomimetic nanofibrous structure and a cartilage tissue-specific microenvironment for cartilage regeneration and repair. Carbohydr. Polym. 276, 118790 (2022)
X. Xun, Y. Li, X. Zhu, Q. Zhang, Y. Lu, Z. Yang, Y. Wan, F. Yao, X. Deng, H. Luo, Fabrication of robust, shape recoverable, macroporous bacterial cellulose scaffolds for cartilage tissue engineering. Macromol Biosci 21, e2100167 (2021)
M. Kouhi, J. Varshosaz, B. Hashemibeni, A. Sarmadi, Injectable gellan gum/lignocellulose nanofibrils hydrogels enriched with melatonin loaded forsterite nanoparticles for cartilage tissue engineering: fabrication, characterization and cell culture studies. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 115, 111114 (2020)
B. Zhang, J. Huang, R.J. Narayan, Gradient scaffolds for osteochondral tissue engineering and regeneration. J. Mater. Chem. B 8, 8149–8170 (2020)
Y. Zhang, X. Liu, L. Zeng, J. Zhang, J. Zuo, J. Zou, J. Ding, X. Chen, Polymer fiber scaffolds for bone and cartilage tissue engineering. Adv. Funct. Mater. 29, 1903279 (2019)
F. Hejazi, S. Bagheri-Khoulenjani, N. Olov, D. Zeini, A. Solouk, H. Mirzadeh, Fabrication of nanocomposite/nanofibrous functionally graded biomimetic scaffolds for osteochondral tissue regeneration. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. A 109, 1657–1669 (2021)
H. Luo, G. Xiong, C. Zhang, D. Li, Y. Zhu, R. Guo, Y. Wan, Surface controlled calcium phosphate formation on three-dimensional bacterial cellulose-based nanofibers. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 49, 526–533 (2015)
N.V. Lukasheva, D.A. Tolmachev, Cellulose nanofibrils and mechanism of their mineralization in biomimetic synthesis of hydroxyapatite/native bacterial cellulose nanocomposites: molecular dynamics simulations. Langmuir 32, 125–134 (2016)
F. Nurlidar, E. Budianto, D. Darwis, Hydroxyapatite deposition on modified bacterial cellulose matrix. Macromol. Symp. 353, 128–132 (2015)
B. Sun, F. Wei, W. Li, X. Xu, H. Zhang, M. Liu, J. Lin, B. Ma, C. Chen, D. Sun, Macroporous bacterial cellulose grafted by oligopeptides induces biomimetic mineralization via interfacial wettability. Colloids Surf. B 183, 110457 (2019)
Y.Z. Wan, Y. Huang, C.D. Yuan, S. Raman, Y. Zhu, H.J. Jiang, F. He, C. Gao, Biomimetic synthesis of hydroxyapatite/bacterial cellulose nanocomposites for biomedical applications. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 27, 855–864 (2007)
Y. Wan, Z. Lin, Q. Zhang, D. Gan, M. Gama, J. Tu, H. Luo, Incorporating graphene oxide into biomimetic nano-microfibrous cellulose scaffolds for enhanced breast cancer cell behavior. Cellulose 27, 4471–4485 (2020)
H. Luo, D. Gan, M. Gama, J. Tu, F. Yao, Q. Zhang, H. Ao, Z. Yang, J. Li, Y. Wan, Interpenetrated nano-and submicro-fibrous biomimetic scaffolds towards enhanced mechanical and biological performances. Mater. Sci. Eng. C: Mater. Biol. Appl. 108, 110416 (2020)
Z. Wang, Y. Cui, J. Wang, X. Yang, Y. Wu, K. Wang, X. Gao, D. Li, Y. Li, X.-L. Zheng, The effect of thick fibers and large pores of electrospun poly (ε-caprolactone) vascular grafts on macrophage polarization and arterial regeneration. Biomaterials 35, 5700–5710 (2014)
A. H. Aparecida, M. V. L. Fook, A. C. Guastaldi, Biomimetic apatite formation on Ultra-High Molecular Weight Polyethylene (UHMWPE) using modified biomimetic solution, J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Med. 20, 1215–1222 (2009).
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 31870963, 51973058, and 32160229), the Key Research and Development Program of Jiangxi Province (Grant No. 20192ACB80008), the Key Project of Natural Science Foundation of Jiangxi Province (Grant No. 20202ACBL204013), and the Science and Technology Research Project of Jiangxi Education Department (GJJ200663).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
On behalf of all authors, the corresponding author states that there is no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, Q., Zhong, B., Zhang, Y. et al. Incorporation of chondroitin sulfate into macroporous bacterial cellulose scaffold for improved bioactivity. Journal of Materials Research 38, 2213–2224 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1557/s43578-023-00951-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1557/s43578-023-00951-9