Abstract
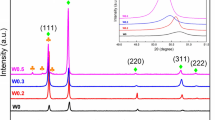
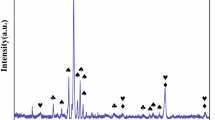
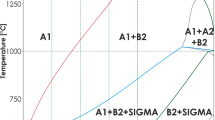
In this study, the effect of Al content on microstructure and high-temperature oxidation behavior of AlxMnCrCoFeNi (x = 0, 0.2, 0.4, 1) high-entropy alloys were investigated. High-entropy alloys with different compositions were synthesized by vacuum melting. Analysis of the microstructure and phase composition was performed by Backscatter Electron Microscopy and X-ray diffraction methods. The microstructures of the alloys were FCC for Al0 and FCC + BCC/B2 for other alloys. Cyclic oxidation tests were performed in an air atmosphere for 120 h at 1000 °C. The oxidation kinetics obeyed the parabolic law, and the main component of the oxide layer was Mn oxide. With increasing Al, a fine and dense Al2O3 oxide film was formed at the bottom of the oxide layer. The parabolic rate constant (Kp) decreased with Al content up to 8 at.%, whereas a further increase in Al concentration to 16 at.% revealed an inverse effect.
Graphical abstract










Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets generated during and analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
J.Y. He, H. Wang, H.L. Huang, X.D. Xu, M.W. Chen, Y. Wu, X.J. Liu, T.G. Nieh, K. An, Z.P. Lu, A precipitation-hardened high-entropy alloy with outstanding tensile properties. Acta Mater. 102, 187–196 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2015.08.076
Y. Zhang, T.T. Zuo, Z. Tang, M.C. Gao, K.A. Dahmen, P.K. Liaw, Z.P. Lu, Microstructures and properties of high-entropy alloys. Prog. Mater. Sci. 61, 1–93 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pmatsci.2013.10.001
M.H. Tsai, J.W. Yeh, High-entropy alloys: a critical review. Mater. Res. Lett. 2(3), 107–123 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1080/21663831.2014.912690
W. Yeh, S.K. Chen, S.J. Lin, J.Y. Gan, T.S. Chin, T.T. Shun, C.H. Tsau, S.Y. Chang, Nanostructured high-entropy alloys with multiple principal elements: novel alloy design concepts and outcomes. Adv. Eng. Mater. 6(5), 299–303 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1002/adem.200300567
G.L. Ma, LCh. Fu, J.Y. Tian, Recent progress in high-entropy alloys. Adv. Mater. Res. 631–632, 227–232 (2013). https://doi.org/10.4028/www.scientific.net/AMR.631-632.227
X. Wang, W. Guo, Y. Fu, High-entropy alloys: emerging materials for advanced functional applications. J. Mater. Chem. A 9(2), 663–701 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1039/d0ta09601f
D.B. Miracle, O.N. Senkov, A critical review of high entropy alloys and related concepts. Acta Mater. 122, 448–511 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2016.08.081
M.H. Tsai, R.C. Tsai, T. Chang, W.F. Huang, Intermetallic phases in high-entropy alloys: statistical analysis of their prevalence and structural inheritance. Metals (Basel) 9(2), 1–18 (2019). https://doi.org/10.3390/met9020247
E.J. Pickering, N.G. Jones, High-entropy alloys: a critical assessment of their founding principles and future prospects. Int. Mater. Rev. 61(3), 183–202 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1080/09506608.2016.1180020
X. Yang, Y. Zhang, Prediction of high-entropy stabilized solid-solution in multi-component alloys. Mater. Chem. Phys. 132(2–3), 233–238 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchemphys.2011.11.021
K.Y. Tsai, M.H. Tsai, J.W. Yeh, Sluggish diffusion in Co–Cr–Fe–Mn–Ni high-entropy alloys. Acta Mater. 6(13), 4887–4897 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2013.04.058
A. Mehta, Y. Sohn, High Entropy and sluggish diffusion ‘core’ effects in senary FCC Al–Co–Cr–Fe–Ni–Mn alloys. ACS Comb. Sci. 22(12), 757–767 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1021/acscombsci.0c00096
H.S. Grewal, R.M. Sanjiv, H.S. Arora, R. Kumar, A. Ayyagari, S. Mukherjee, H. Singh, Activation energy and high temperature oxidation behavior of multi-principal element alloy. Adv. Eng. Mater. 19(11), 1–5 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1002/adem.201700182
C. Lee, G. Song, M.C. Gao, R. Feng, P. Chen, J. Brechtl, Y. Chen, K. An, W. Guo, J.D. Poplawsky, Lattice distortion in a strong and ductile refractory high-entropy alloy. Acta Mater. 160, 158–172 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2018.08.053
Q. He, Y. Yang, On lattice distortion in high entropy alloys. Front. Mater. 5, 1–8 (2018). https://doi.org/10.3389/fmats.2018.00042
Y. Zhang, Y.J. Zhou, J.P. Lin, G.L. Chen, P.K. Liaw, Solid-solution phase formation rules for multi-component alloys. Adv. Eng. Mater. 10(6), 534–538 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1002/adem.200700240
S. Guo, C. Ng, J. Lu, C.T. Liu, Effect of valence electron concentration on stability of fcc or bcc phase in high entropy alloys. J. Appl. Phys. 109(10), 1–5 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.3587228
B. Cantor, I.T.H. Chang, P. Knight, A.J.B. Vincent, Microstructural development in equiatomic multicomponent alloys Mater. Sci. Eng. A 375–377(1–2), 213–218 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2003.10.257
F. Otto, A. Dlouhý, C. Somsen, H. Bei, G. Eggeler, E.P. George, The influences of temperature and microstructure on the tensile properties of a CoCrFeMnNi high-entropy alloy. Acta Mater. 61(15), 5743–5755 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2013.06.018
T.M. Butler, M.L. Weaver, Oxidation behavior of arc melted AlCoCrFeNi multi-component high-entropy alloys. Alloys Compd. 674, 229–244 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2016.02.257
T.M. Butler, M.L. Weaver, Influence of annealing on the microstructures and oxidation behaviors of Al8(CoCrFeNi)92, Al15(CoCrFeNi)85, and Al30(CoCrFeNi)70 high-entropy alloys. Metals (Basel) 6(9), 222 (2016). https://doi.org/10.3390/met6090222
Z. Tang, L. Huang, W. He, P.K. Liaw, Alloying and processing effects on the aqueous corrosion behavior of high-entropy alloys. Entropy 16(2), 895–911 (2014). https://doi.org/10.3390/e16020895
T.M. Butler, J.P. Alfano, R.L. Martens, M.L. Weaver, High-temperature oxidation behavior of Al–Co–Cr–Ni–(Fe or Si) multicomponent high-entropy alloys. JOM 67(1), 246–259 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11837-014-1185-7
J. Dabrowa, G. Cieslak, M. Stygar, K. Mroczka, K. Berent, T. Kulik, M. Danielewski, Influence of Cu content on high temperature oxidation behavior of AlCoCrCuxFeNi high entropy alloys (x= 0; 0.5; 1). Intermetallics 84, 52–61 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.intermet.2016.12.015
E. Ananiadis, K. Lentzaris, E. Georgatis, C. Mathiou, A. Poulia, A.E. Karantzalis, AlNiCrFeMn equiatomic high entropy alloy: a further insight in its microstructural evolution, mechanical and surface degradation response. Met. Mater. Int. 26(6), 793–811 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12540-019-00401-4
Y.Y. Liu, Z. Chen, Y.Z. Chen, J.C. Shi, Z.Y. Wang, S. Wang, F. Liu, Effect of Al content on high temperature oxidation resistance of AlxCoCrCuFeNi high entropy alloys (x=0, 0.5, 1, 1.5, 2). Vacuum 169, 108837 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.vacuum.2019.108837
C.S. Giggins, F.S. Pettit, Oxidation of Ni–Cr–Al alloys between 1000° and 1200 °C. J. Electrochem. Soc. 118(11), 1782 (1971). https://doi.org/10.1149/1.2407837
C.J. Tong et al., Mechanical performance of the AlxCoCrCuFeNi high-entropy alloy system with multiprincipal elements. Metall. Mater. Trans. A Phys. Metall. Mater. Sci. 36(5), 1263–1271 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-005-0218-9
B.R. Anne, S. Shaik, M. Tanaka, A. Basu, A crucial review on recent updates of oxidation behavior in high entropy alloys. SN Appl. Sci. 3(3), 1–23 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42452-021-04374-1
G. Laplanche, U.F. Volkert, G. Eggeler, E.P. George, Oxidation behavior of the CrMnFeCoNi high-Entropy alloy. Oxid. Metals 85(5–6), 629–645 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11085-016-9616-1
K.R. Lim, K.S. Lee, J.S. Lee, J.Y. Kim, H.J. Chang, Y.S. Na, Dual-phase high-entropy alloys for high-temperature structural applications. J. Alloys Compd. 728, 1235–1238 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2017.09.089
Y.S. Huang, L. Chen, H.W. Lui, M.H. Cai, J.W. Yeh, Microstructure, hardness, resistivity and thermal stability of sputtered oxide films of AlCoCrCu0.5NiFe high-entropy alloy. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 457(1–2), 77–83 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2006.12.001
Y.Y. Chen, U.T. Hong, H.C. Shih, J.W. Yeh, T. Duval, Electrochemical kinetics of the high entropy alloys in aqueous environments—a comparison with type 304 stainless steel. Corros. Sci. 47(11), 2679–2699 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.corsci.2004.09.026
W.R. Wang, W.L. Wang, S.C. Wang, Y.C. Tsai, C.H. Lai, J.W. Yeh, Effects of Al addition on the microstructure and mechanical property of Al xCoCrFeNi high-entropy alloys. Intermetallics 26, 44–51 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.intermet.2012.03.005
S. Abbaszadeh, A. Pakseresht, H. Omidvar, A. Shafiei, Investigation of the high-temperature oxidation behavior of the Al0.5CoCrFeNi high entropy alloy. Surf. Interfaces 21, 100724 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.surfin.2020.100724
A. Ostovari Moghaddama, N.A. Shaburovab, M.V. Sudarikovc, S.N. Veselkovb, O.V. Samoilova, E.A. Trofimovb, High temperature oxidation resistance of Al0.25CoCrFeNiMn and Al0.45CoCrFeNiSi0.45 high entropy alloys. Vacuum 192, 110412 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.vacuum.2021.110412
Y.C. Hsu, C.L. Li, C.H. Hsueh, Effects of Al addition on microstructures and mechanical properties of CoCrFeMnNiAlx high entropy alloy films. Entropy 22(1), 2 (2020). https://doi.org/10.3390/e22010002
F. Ye, Z. Jiao, S. Yan, L. Guo, L. Feng, J. Yu, Microbeam plasma arc remanufacturing: effects of Al on microstructure, wear resistance, corrosion resistance and high temperature oxidation resistance of AlxCoCrFeMnNi high-entropy alloy cladding layer. Vacuum 174, 109178 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.vacuum.2020.109178
S. Guo, C.T. Liu, Phase stability in high entropy alloys: formation of solid-solution phase or amorphous phase. Prog. Nat. Sci. Mater. Int. 21(6), 433–446 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1016/S1002-0071(12)60080-X
J.C. Rao, H.Y. Diao, V. Ocelík, D. Vainchtein, C. Zhang, C. Kuo, Z. Tang, W. Guo, J.D. Poplawsky, Secondary phases in AlxCoCrFeNi high-entropy alloys: an in-situ TEM heating study and thermodynamic appraisal. Acta Mater. 131, 206–220 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2017.03.066
Y.F. Kao, T.J. Chen, S.K. Chen, J.W. Yeh, Microstructure and mechanical property of as-cast, -homogenized, and -deformed AlxCoCrFeNi (0 ≤ x ≤ 2) high-entropy alloys. J. Alloys Compd. 488(1), 57–64 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2009.08.090
L. Lijing, X. Xin, Z. Zhihong, W. Yucheng, P.K. Liaw, Microstructure stability and its influence on the mechanical properties of CrMnFeCoNiAl0.25 high entropy alloy. Metals Mater. Int. 26, 1192–1199 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12540-019-00542-6
L.C. Tsao, C.S. Chen, C.P. Chu, Age hardening reaction of the Al0.3CrFe1.5MnNi0.5 high entropy alloy. Mater. Des. 36, 854–858 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matdes.2011.04.067
D.G. Shaysultanov, N.D. Stepanov, A.V. Kuznetsov, G.A. Salishchev, O.N. Senkov, Phase composition and superplastic behavior of a wrought AlCoCrCuFeNi high-entropy alloy. JOM 65(12), 1815–1828 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11837-013-0754-5
S. Singh, N. Wanderka, B.S. Murty, U. Glatzel, J. Banhart, Decomposition in multi-component AlCoCrCuFeNi high-entropy alloy. Acta Mater. 59(1), 182–190 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2010.09.023
C.C. Tung, J.W. Yeh, T.-t Shun, S.K. Chen, Y.S. Huang, H.C. Chen, On the elemental effect of AlCoCrCuFeNi high-entropy alloy system. Mater. Lett. 61(1), 1–5 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matlet.2006.03.140
Y.K. Kim, Y.A. Joo, H.S. Kim, K.A. Lee, High temperature oxidation behavior of Cr–Mn–Fe–Co–Ni high entropy alloy. Intermetallics 98, 45–53 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.intermet.2018.04.006
F. Ye, Z. Jiao, Y. Yang, Effect of medium temperature precipitation phase and Mn element diffusion mechanism on high temperature oxidation process of repair and remanufacture CoCrFeMnNi high-entropy alloy cladding. Mater. Res. Express 6(5), 056521 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1088/2053-1591/ab01be
J. Dąbrowa, M. Danielewski, State-of-the-art diffusion studies in the high entropy alloys. Metals (Basel) 10(3), 347 (2020). https://doi.org/10.3390/met10030347
P.R.S. Jackson, G.R. Wallwork, High temperature oxidation of iron-manganese-aluminum based alloys. Oxid. Metals 21(3–4), 135–170 (1984). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00741468
X. Chen, Y. Sui, J. Qi, Y. He, F. Wei, Q. Meng, Zh. Sun, Microstructure of Al1.3CrFeNi eutectic high entropy alloy and oxidation behavior at 1000 °C. J. Mater. 32, 2109–20116 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1557/jmr.2017.10
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by Iran National Science Foundation (INSF) (Grant No. 98002224).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
On behalf of all authors, the corresponding author states that there is no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Familifard, A., Amadeh, A.A., Raygan, S. et al. The role of Al on microstructure and high-temperature oxidation behavior of AlxMnCrCoFeNi (x = 0, 0.2, 0.4, 1) high-entropy alloys. Journal of Materials Research 38, 1197–1210 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1557/s43578-022-00876-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1557/s43578-022-00876-9