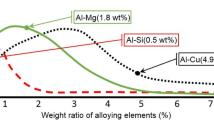
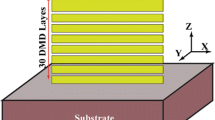
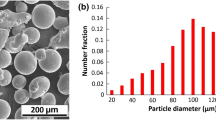
Abstract
Since scandium has a significant refining effect on aluminum alloys, the research on aluminum-scandium alloys has continued for decades. The development of Scalmalloy which has scandium element broadens the applications for additive manufacturing (AM) for scandium–aluminum alloys. In this research, Scalmalloy is processed by the laser-melting deposition (LMD) method. A fully equiaxed grain microstructure is identified and its formation related to the characteristics of LMD-processing method is discussed. The morphology and distribution of Al3Sc and Al3Zr after processing is observed and discussed, and the elemental distribution is analysed. The high mechanical properties are reached and their relation to the microstructure of the Scalmalloy processed is investigated. With compiled results and observations, this study provides a better understanding of microstructure formation and the mechanical performance of Scalmalloy fabricated by the LMD method which offers a good basis for any further research in the application of LMD for high-performance aluminum alloy.
Graphical abstract








Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets generated during and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Consent for publication
All authors participated in the study and agreed to the publication of this manuscript.
References
M. Vorel, S. Hinsch, M. Konopka, M. Scheerer, AlMgSc alloy 5028 status of maturation. In 7th European Conference for Aeronautics and Space Sciences (Eucass), Milan, Italy (2017)
N.Q. Tuan, A.C. Alves, F. Toptan, A.B. Lopes, A.M.P. Pinto, Effects of substituting ytterbium for scandium on corrosion behaviour of Al–Sc alloy. Mater. Corros. 66(12), 1504–1511 (2015)
Y. Sun, M. Song, Y. He, Effects of Sc content on the mechanical properties of Al–Sc alloys. Rare Met. 29(5), 451–455 (2010)
A.F. Norman, P.B. Prangnell, R.S. McEwen, The solidification behaviour of dilute aluminium–scandium alloys. Acta Mater. 46(16), 5715–5732 (1998)
Z. Yin, Q. Pan, Y. Zhang, F. Jiang, Effect of minor Sc and Zr on the microstructure and mechanical properties of Al–Mg based alloys. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 280(1), 151–155 (2000)
S. Lathabai, P.G. Lloyd, The effect of scandium on the microstructure, mechanical properties and weldability of a cast Al–Mg alloy. Acta Mater. 50(17), 4275–4292 (2002)
K. Venkateswarlu, L.C. Pathak, A.K. Ray, G. Das, P.K. Verma, M. Kumar, R.N. Ghosh, Microstructure, tensile strength and wear behaviour of Al–Sc alloy. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 383(2), 374–380 (2004)
Y. Shi, P. Rometsch, K. Yang, F. Palm, X. Wu, Characterisation of a novel Sc and Zr modified Al–Mg alloy fabricated by selective laser melting. Mater. Lett. 196, 347–350 (2017)
N. Blake, M.A. Hopkins, Constitution and age hardening of Al–Sc alloys. J. Mater. Sci. 20(8), 2861–2867 (1985)
R.R. Sawtell, C.L. Jensen, Mechanical properties and microstructures of Al–Mg–Sc alloys. Metall. Trans. A 21(1), 421–430 (1990)
L.S. Toropova, D.G. Eskin, M.L. Kharakterova, T.V. Dobatkina, Advanced Aluminum Alloys Containing Scandium: Structure and Properties (Routledge, London, 2017)
A.B. Spierings, K. Dawson, P. Dumitraschkewitz, S. Pogatscher, K. Wegener, Microstructure characterization of SLM-processed Al–Mg–Sc–Zr alloy in the heat treated and HIPed condition. Addit. Manuf. 20, 173–181 (2018)
A.B. Spierings, K. Dawson, P.J. Uggowitzer, K. Wegener, Influence of SLM scan-speed on microstructure, precipitation of Al3Sc particles and mechanical properties in Sc- and Zr-modified Al–Mg alloys. Mater. Des. 140, 134–143 (2018)
A.B. Spierings, K. Dawson, K. Kern, F. Palm, K. Wegener, SLM-processed Sc- and Zr-modified Al–Mg alloy: mechanical properties and microstructural effects of heat treatment. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 701, 264–273 (2017)
D. Koutny, D. Skulina, L. Pantělejev, D. Paloušek, B. Lenczowski, F. Palm, A. Nick, Processing of Al–Sc aluminum alloy using SLM technology. Procedia CIRP 74, 44–48 (2018)
C.N. Kuo, P.C. Peng, D.H. Liu, C.Y. Chao, Microstructure evolution and mechanical property response of 3D-Printed Scalmalloy with different heat-treatment times at 325 °C. Metals 11(4), 555 (2021)
I. Mingareev, N. Gehlich, T. Bonhoff, W. Meiners, I. Kelbassa, T. Biermann, M.C. Richardson, Post-processing of 3D-printed parts using femtosecond and picosecond laser radiation. In Laser 3D Manufacturing, March 2014, vol. 8970 (SPIE, 2014), pp. 86–92.
E. Brinksmeier, G. Levy, D. Meyer, A.B. Spierings, Surface integrity of selective-laser-melted components. CIRP Ann. 59(1), 601–606 (2010)
A. Fukuda, M. Takemoto, T. Saito, S. Fujibayashi, M. Neo, D.K. Pattanayak et al., Osteoinduction of porous Ti implants with a channel structure fabricated by selective laser melting. Acta Biomater. 7(5), 2327–2336 (2011)
S. Leuders, M. Thöne, A. Riemer, T. Niendorf, T. Tröster, H.A. Richard, H.J. Maier, On the mechanical behaviour of titanium alloy TiAl6V4 manufactured by selective laser melting: fatigue resistance and crack growth performance. Int. J. Fatigue 48, 300–307 (2013)
L.E. Murr, S.M. Gaytan, D.A. Ramirez, E. Martinez, J. Hernandez, K.N. Amato et al., Metal fabrication by additive manufacturing using laser and electron beam melting technologies. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 28(1), 1–14 (2012)
H. Attar, K.G. Prashanth, L.C. Zhang, M. Calin, I.V. Okulov, S. Scudino et al., Effect of powder particle shape on the properties of in situ Ti–TiB composite materials produced by selective laser melting. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 31(10), 1001–1005 (2015)
M. Ramoni, R. Shanmugam, N.S. Ross, M.K. Gupta, An experimental investigation of hybrid manufactured SLM based Al–Si10–Mg alloy under mist cooling conditions. J. Manuf. Process. 70, 225–235 (2021)
T. Wang, Y. Wang, C. Chen, H. Zhu, Relationships between the characteristics of porosity, melt pool and process parameters in laser powder bed fusion AlZn alloy. J. Manuf. Process. 68, 1236–1244 (2021)
A.D. Baghi, S. Nafisi, R. Hashemi, H. Ebendorff-Heidepriem, R. Ghomashchi, Effective post processing of SLM fabricated Ti–6Al–4V alloy: machining vs thermal treatment. J. Manuf. Process. 68, 1031–1046 (2021)
K. Schmidtke, F. Palm, A. Hawkins, C. Emmelmann, Process and mechanical properties: applicability of a scandium modified Al-alloy for laser additive manufacturing. Phys. Procedia 12, 369–374 (2011)
Z. Wang, X. Lin, Y. Tang, N. Kang, X. Gao, S. Shi, W. Huang, Laser-based directed energy deposition of novel Sc/Zr-modified Al–Mg alloys: columnar-to-equiaxed transition and aging hardening behavior. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 69, 168–179 (2021)
A.B. Spierings, K. Dawson, T. Heeling, P.J. Uggowitzer, R. Schäublin, F. Palm, K. Wegener, Microstructural features of Sc- and Zr-modified Al–Mg alloys processed by selective laser melting. Mater. Des. 115, 52–63 (2017)
Y. Zhang, A. Majeed, M. Muzamil, J. Lv, T. Peng, V. Patel, Investigation for macro mechanical behavior explicitly for thin-walled parts of AlSi10Mg alloy using selective laser melting technique. J. Manuf. Process. 66, 269–280 (2021)
C. Leyens, F. Brückner, E. Lopez, M. Riede, Successes and challenges of SLM and LMD for industrial production. In Laser additive manufacturing workshop, Schaumburg, IL, March 2017
J. Zhang, B. Song, Q. Wei, D. Bourell, Y. Shi, A review of selective laser melting of aluminum alloys: processing, microstructure, property and developing trends. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 35(2), 270–284 (2019)
B. Vayre, F. Vignat, F. Villeneuve, Designing for additive manufacturing. Procedia CIRP 3, 632–637 (2012)
M. Muhammad, P.D. Nezhadfar, S. Thompson, A. Saharan, N. Phan, N. Shamsaei, A comparative investigation on the microstructure and mechanical properties of additively manufactured aluminum alloys. Int. J. Fatigue 146, 106165 (2021)
M. Awd, J. Tenkamp, M. Hirtler, S. Siddique, M. Bambach, F. Walther, Comparison of microstructure and mechanical properties of Scalmalloy® produced by selective laser melting and laser metal deposition. Materials 11(1), 17 (2017)
P. Kürnsteiner, P. Bajaj, A. Gupta, M.B. Wilms, A. Weisheit, X. Li et al., Control of thermally stable core–shell nano-precipitates in additively manufactured Al–Sc–Zr alloys. Addit. Manuf. 32, 100910 (2020)
S. Jiao, X. Cheng, S. Shen, X. Wang, B. He, D. Liu, H. Wang, Microstructure evolution and mechanical behavior of Al–Li alloy fabricated by laser melting deposition technique. J. Alloys Compd. 821, 153125 (2020)
G. Rolink, S. Vogt, L. Senčekova, A. Weisheit, R. Poprawe, M. Palm, Laser metal deposition and selective laser melting of Fe–28 at% Al. J. Mater. Res. 29(17), 2036–2043 (2014)
V.V. Zakharov, Effect of scandium on the structure and properties of aluminum alloys. Met. Sci. Heat Treat. 45(7), 246–253 (2003)
O.N. Senkov, R.B. Bhat, S.V. Senkova, J.D. Schloz, Microstructure and properties of cast ingots of Al–Zn–Mg–Cu alloys modified with Sc and Zr. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 36(8), 2115–2126 (2005)
V. Ocenasek, M. Slamova, Resistance to recrystallization due to Sc and Zr addition to Al–Mg alloys. Mater. Charact. 47(2), 157–162 (2001)
T. Wang, Q. Meng, S. Araby, G. Yang, P. Li, R. Cai et al., Non-oxidized graphene/metal composites by laser deposition additive manufacturing. J. Alloys Compd. 882, 160724 (2021)
J.Y. Zhang, Y.H. Gao, C. Yang, P. Zhang, J. Kuang, G. Liu, J. Sun, Microalloying Al alloys with Sc: a review. Rare Met. 39(6), 636–650 (2020)
A. Singh, A. Ramakrishnan, G.P. Dinda, Direct laser metal deposition of eutectic Al–Si alloy for automotive applications. In TMS 2017 146th Annual Meeting and Exhibition Supplemental Proceedings (Springer, Cham, 2017), pp. 71–80
T. Dorin, M. Ramajayam, S. Babaniaris, T.J. Langan, Micro-segregation and precipitates in as-solidified Al–Sc–Zr–(Mg)–(Si)–(Cu) alloys. Mater. Charact. 154, 353–362 (2019)
P.K. Farayibi, T.E. Abioye, A. Kennedy, A.T. Clare, Development of metal matrix composites by direct energy deposition of ‘satellited’ powders. J. Manuf. Process. 45, 429–437 (2019)
P. Li, R. Cai, G. Yang, T. Wang, S. Han, S. Zhang, Q. Meng, Mechanically strong, stiff, and yet ductile AlSi7Mg/graphene composites by laser metal deposition additive manufacturing. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 823, 141749 (2021)
Acknowledgments
Q. Meng would like to thank Sensen Han and Shuocheng Zhang for their advice during the research. Authors are responsible for correctness of the statements provided in the manuscript (Including experimental data and experimental pictures).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that no funds, grants, or other support were received during the preparation of this manuscript. The authors have no relevant financial or non-financial interests to disclose. The authors have no competing interests to declare that are relevant to the content of this article. All authors certify that they have no affiliations with or involvement in any organization or entity with any financial interest or non-financial interest in the subject matter or materials discussed in this manuscript. The authors have no financial or proprietary interests in any material discussed in this article.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, X., Cai, R., Chen, C. et al. High-performance aluminum alloy with fully equiaxed grain microstructure fabricated by laser metal deposition. Journal of Materials Research 37, 3658–3667 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1557/s43578-022-00738-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1557/s43578-022-00738-4