Abstract
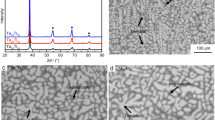
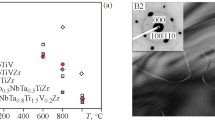
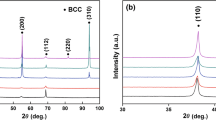
In this work, novel WNbMoTaVZrx (x = 0.1, 0.25, 0.5, 0.75, 1.0) refractory high entropy alloys (RHEAs) were developed, and the corresponding phase formation, microstructure and mechanical properties were investigated. As compared with the WNbMoTa and WNbMoTaV derivative alloys, the present WNbMoTaVZrx RHEAs demonstrated significantly improved strength and hardness, especially the specific yield strength. The increase of the strength was attributed to the solid solution strengthening effect, resulting from the severe lattice distortion associated with lager-atomic-sized Zr element. With the increase of Zr content, the microstructure changed from grain morphology to dendritic structures. The formation of the second phase with the increase of Zr content was also observed, and its effects on the strengthening, plastic deformation and fracture behaviors were discussed. The deformation-evolution investigations have shown that under applied loadings, microcracks initiated at interdendritic regions with relatively soft second phase. The phase thermostability analysis suggests that the phase structure of typical WNbMoTaVZrx RHEAs could be stable at elevated temperature.
Graphical abstract










Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets generated during and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Code availability
No applicable.
References
J.W. Yeh, S.K. Chen, S.J. Lin, J.Y. Gan, T.S. Chin, T.T. Shun, C.H. Tsau, S.Y. Chang, Nanostructured high-entropy alloys with multiple principal elements: novel alloy design concepts and outcomes. Adv. Eng. Mater. 6(5), 299–303 (2004)
J.W. Yeh, Physical metallurgy of high-entropy alloys. JOM 67(10), 2254–2261 (2015)
Y. Zhang, T.T. Zuo, Z. Tang, M.C. Gao, K.A. Dahmen, P.K. Liaw, Z.P. Lu, Microstructures and properties of high-entropy alloys. Prog. Mater. Sci. 61, 1–93 (2014)
S. Ranganathan, Alloyed pleasures: Multimetallic cocktails. Curr. Sci. 85(10), 1404–1406 (2003)
C. Xiang, H.M. Fu, Z.M. Zhang, E.H. Han, H.F. Zhang, J.Q. Wang, G.D. Hu, Effect of Cr content on microstructure and properties of Mo0.5VNbTiCrx high-entropy alloys. J. Alloys Compd. 818, 153352 (2020)
Z.D. Han, N. Chen, S.F. Zhao, L.W. Fan, G.N. Yang, Y. Shao, K.F. Yao, Effect of Ti additions on mechanical properties of NbMoTaW and VNbMoTaW refractory high entropy alloys. Intermetallics 84, 153–157 (2017)
É. Fazakas, V. Zadorozhnyy, L.K. Varga, A. Inoue, D.V. Louzguine-Luzgin, F. Tian, L. Vitos, Experimental and theoretical study of Ti20Zr20Hf20Nb20X20 (X=V or Cr) refractory high-entropy alloys. Int. J. Refract. Met. H 47, 131–138 (2014)
M. Wang, Z. Ma, Z. Xu, X. Cheng, Microstructures and mechanical properties of HfNbTaTiZrW and HfNbTaTiZrMoW refractory high-entropy alloys. J. Alloys Compd. 803, 778–785 (2019)
C.C. Juan, M.H. Tsai, C.W. Tsai, C.M. Lin, W.R. Wang, C.C. Yang, S.K. Chen, S.J. Lin, J.W. Yeh, Enhanced mechanical properties of HfMoTaTiZr and HfMoNbTaTiZr refractory high-entropy alloys. Intermetallics 62, 76–83 (2015)
T.E. Whitfield, H.J. Stone, C.N. Jones, N.G. Jones, Microstructural degradation of the AlMo0.5NbTa0.5TiZr refractory metal high-entropy superalloy at elevated temperatures. Entropy 23(1), 80 (2021)
O.N. Senkov, G.B. Wilks, J.M. Scott, D.B. Miracle, Mechanical properties of Nb25Mo25Ta25W25 and V20Nb20Mo20Ta20W20 refractory high entropy alloys. Intermetallics 19(5), 698–706 (2011)
Y. Liu, Y. Zhang, H. Zhang, N. Wang, X. Chen, H. Zhang, Y. Li, Microstructure and mechanical properties of refractory HfMo0.5NbTiV0.5Six high-entropy composites. J. Alloys Compd. 694, 869–876 (2017)
B. Gorr, F. Müller, M. Azim, H.-J. Christ, T. Müller, H. Chen, A. Kauffmann, M. Heilmaier, High-temperature oxidation behavior of refractory high-entropy alloys: effect of alloy composition. Oxid. Met. 88(3–4), 339–349 (2017)
Q. Fang, Y. Chen, J. Li, Y. Liu, Y. Liu, Microstructure and mechanical properties of FeCoCrNiNbX high-entropy alloy coatings. Physica B 550, 112–116 (2018)
Y.J. Hsu, W.C. Chiang, J.K. Wu, Corrosion behavior tion. Mater. Chem. Phys. 92(1), 112–117 (2005)
Y. Chen, T. Duval, U. Hung, J. Yeh, H. Shih, Microstructure and electrochemical properties of high entropy alloys-a comparison with type-304 stainless steel. Corros. Sci. 47(9), 2257–2279 (2005)
O.N. Senkov, G.B. Wilks, D.B. Miracle, C.P. Chuang, P.K. Liaw, Refractory high-entropy alloys. Intermetallics 18(9), 1758–1765 (2010)
Y.C. Wu, Corrosion behavior of FeCoNiCrCux high-entropy alloys in 3.5% sodium chloride solution. Acta Metall. Sin. 55(2), 171–180 (2018)
Z.D. Han, H.W. Luan, X. Liu, N. Chen, X.Y. Li, Y. Shao, K.F. Yao, Microstructures and mechanical properties of TixNbMoTaW refractory high-entropy alloys. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 712, 380–385 (2018)
Y. Tong, L. Bai, X. Liang, Y. Chen, Z. Zhang, J. Liu, Y. Li, Y. Hu, Influence of alloying elements on mechanical and electronic properties of NbMoTaWX (X= Cr, Zr, V, Hf and Re) refractory high entropy alloys. Intermetallics 126, 106928 (2020)
J. Zhang, Y. Hu, Q. Wei, Y. Xiao, P. Chen, G. Luo, Q. Shen, Microstructure and mechanical properties of RexNbMoTaW high-entropy alloys prepared by arc melting using metal powders. J. Alloys Compd. 827, 154301 (2020)
J. Chen, P. Niu, Y. Liu, Y. Lu, X. Wang, Y. Peng, J. Liu, Effect of Zr content on microstructure and mechanical properties of AlCoCrFeNi high entropy alloy. Mater. Des. 94, 39–44 (2016)
S.S.M. Pauzi, W. Darham, R. Ramli, M. Harun, M.K. Talari, Effect of Zr addition on microstructure and properties of FeCrNiMnCoZrx and Al0.5FeCrNiMnCoZrx high entropy alloys. Trans. Indian. Inst. Met. 66(4), 305–308 (2013)
Y. Zhang, Y.J. Zhou, J.P. Lin, G.L. Chen, P.K. Liaw, Solid-solution phase formation rules for multi-component alloys. Adv. Eng. Mater. 10(6), 534–538 (2008)
A. Takeuchi, A. Inoue, Classification of bulk metallic glasses by atomic size difference, heat of mixing and period of constituent elements and its application to characterization of the main alloying element. Mater. Trans. 46(12), 2817–2829 (2005)
S. Guo, C. Ng, J. Lu, C.T. Liu, Effect of valence electron concentration on stability of fcc or bcc phase in high entropy alloys. J. Appl. Phys. 109(10), 103505 (2011)
X. Yang, Y. Zhang, Prediction of high-entropy stabilized solid-solution in multi-component alloys. Mater. Chem. Phys. 132(2–3), 233–238 (2012)
C.J. Tong, Y.L. Chen, J.W. Yeh, S.J. Lin, S.K. Chen, T.T. Shun, C.H. Tsau, S.Y. Chang, Microstructure characterization of AlxCoCrCuFeNi high-entropy alloy system with multiprincipal elements. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 36(4), 881–893 (2005)
K.Y. Tsai, M.H. Tsai, J.W. Yeh, Sluggish diffusion in Co–Cr–Fe–Mn–Ni high-entropy alloys. Acta Mater. 61(13), 4887–4897 (2013)
Z.Q. Xu, Z.L. Ma, M. Wang, Y.W. Chen, Y.D. Tan, X.W. Cheng, Design of novel low-density refractory high entropy alloys for high-temperature applications. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 755, 318–322 (2019)
Y. Guo, H. Wang, Q. Liu, Microstructure evolution and strengthening mechanism of laser-cladding MoFeCrTiWAlNb refractory high-entropy alloy coatings. J. Alloys Compd. 834, 155147 (2020)
D. Patel, M.D. Richardson, B. Jim, S. Akhmadaliev, R. Goodall, A.S. Gandy, Radiation damage tolerance of a novel metastable refractory high entropy alloy V2.5Cr1.2WMoCo0.04. J. Nucl. Mater. 531, 152005 (2020)
Z. Sun, X. Li, Z. Wang, Microstructure and mechanical properties of low activation Fe–Ti–Cr–V–W multi-principal element alloys. J. Nucl. Mater. 533, 152078 (2020)
W. Zhang, P.K. Liaw, Y. Zhang, A Novel low-activation VCrFeTaxWx (x = 0.1, 0.2, 0.3, 0.4, and 1) high-entropy alloys with excellent heat-softening resistance. Entropy 20(12), 951 (2018)
S.P. Wang, J. Xu, TiZrNbTaMo high-entropy alloy designed for orthopedic implants: as-cast microstructure and mechanical properties. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 73, 80–89 (2017)
H. Zhang, L. Zhang, X. Liu, Q. Chen, Y. Xu, Effect of Zr addition on the microstructure and mechanical properties of CoCrFeNiMn high-entropy alloy synthesized by spark plasma sintering. Entropy 20(11), 810 (2018)
S. Gao, T. Kong, M. Zhang, X. Chen, Y. Sui, Y. Ren, J. Qi, F. Wei, Y. He, Q. Meng, Z. Sun, Effects of titanium addition on microstructure and mechanical properties of CrFeNiTi x (x = 0.2 0.6) compositionally complex alloys. J. Mater. Res. 34, 819–828 (2019)
D.J.M. King, S.T.Y. Cheung, S.A. Humphry-Baker, C. Parkin, A. Couet, M.B. Cortie, G.R. Lumpkin, S.C. Middleburgh, A.J. Knowles, High temperature, low neutron cross-section high-entropy alloys in the Nb-Ti-V-Zr system. Acta Mater. 166, 435–446 (2019)
L. Wang, L. Wang, Y. Tang, L. Luo, L. Luo, Y. Su, J. Guo, H. Fu, Microstructure and mechanical properties of CoCrFeNiW high entropy alloys reinforced by μ phase particles. J. Alloys Compd. 843, 155997 (2020)
O.N. Senkov, J. Gild, T.M. Butler, Microstructure, mechanical properties and oxidation behavior of NbTaTi and NbTaZr refractory alloys. J. Alloys Compd. 862, 158003 (2021)
S.H. Chen, J.Y. Wang, L. Xia, Y.C. Wu, Deformation behavior of bulk metallic glasses and high entropy alloys under complex stress fields: a review. Entropy 21(1), 54 (2019)
M. Pole, M. Sadeghilaridjani, J. Shittu, A. Ayyagari, S. Mukherjee, High temperature wear behavior of refractory high entropy alloys based on 4-5-6 elemental palette. J. Alloys Compd. 843, 156004 (2020)
Z. Niu, J. Xu, T. Wang, N. Wang, Z. Han, Y. Wang, Microstructure, mechanical properties and corrosion resistance of CoCrFeNiW (x = 0, 0.2, 0.5) high entropy alloys. Intermetallics 112, 106550 (2019)
T.M. Pollock, S. Tin, Nickel-based superalloys for advanced turbine engines: chemistry, microstructure and properties. J. Propul. Power 22(2), 361–374 (2006)
J. Chen, X. Zhou, W. Wang, B. Liu, Y. Lv, W. Yang, D. Xu, Y. Liu, A review on fundamental of high entropy alloys with promising high-temperature properties. J. Alloys Compd. 760, 15–30 (2018)
S.H. Chen, K.C. Chan, F.F. Wu, L. Xia, Pronounced energy absorption capacity of cellular bulk metallic glasses. Appl. Phys. Lett. 104, 111907 (2014)
Funding
The work was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 51801049) and the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities of China (No. PA2019GDZC0096).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
No applicable.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no interest conflicts to declare in this article.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, C., Chen, S.H., Wu, Z.W. et al. Development of high-strength WNbMoTaVZrx refractory high entropy alloys. Journal of Materials Research 37, 1664–1678 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1557/s43578-022-00569-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1557/s43578-022-00569-3