Abstract
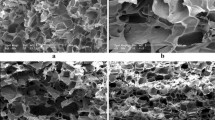
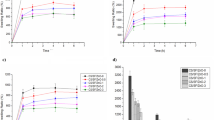
Mucilage/ polymer hybrids are promising materials for biomedical applications and tissue engineering. Plantago psyllium mucilage/ chitosan composite scaffold was prepared by the freeze-drying method. The different ratio (v/v) of mucilage (2.5%, 5%) and chitosan (5%) was used to obtain the perfect scaffold with optimum properties. The scanning electron microscope images exhibited composite scaffolds have relatively large cylindrical porosity in which small spherical pores are enclosed and the porosity is reduced and come close to spherical shape by increasing the concentration of Plantago psyllium mucilage from 2.5% to 5%. The in vitro degradation studies showed the decreasing weight loss % with the addition of chitosan. Antibacterial activity of the obtained scaffolds against Escherichia coli and Staphylococcus aureus bacteria indicated acceptable activity against both of them.
Graphical abstract









Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Data sharing is not applicable to this article as no datasets were generated or analyzed during the current study.
References
M. Rodríguez-Vázquez, B. Vega-Ruiz, R. Ramos-Zúñiga, D.A. Saldaña-Koppel, L.F. Quiñones-Olvera, Chitosan and its potential use as a scaffold for tissue engineering in regenerative medicine. Biomed. Res. Int. (2015). https://doi.org/10.1155/2015/821279
F. Croisier, C. Jérôme, Chitosan-based biomaterials for tissue engineering. Eur. Polym. J. 49, 780–792 (2013)
A. Mohandas, S. Deepthi, R. Biswas, R. Jayakumar, Chitosan based metallic nanocomposite scaffolds as antimicrobial wound dressings. Bioact. Mater. 3(2018), 267–277 (2018)
R. Zeeshan, Z. Mutahir et al., Hydroxypropylmethyl cellulose (HPMC) crosslinked chitosan (CH) based scaffolds containing bioactive glass (BG) and zinc oxide (ZnO) for alveolar bone repair. Carbohydr. Polym 193, 9–18 (2018)
T. Vieira, J.C. Silva, A.B. do Rego, J.P. Borges, C. Henriques, Electrospun biodegradable chitosan based-poly (urethane urea) scaffolds for soft tissue engineering. Mate. Sci. Eng. C (2019) doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msec.2019.109819
M. Shakir, R. Jolly et al., Resol based chitosan/nano-hydroxyapatite nanoensemble for effective bone tissue engineering. Carbohydr. Polym. 179, 317–327 (2018)
H.T. Lu, T.W. Lu, C.H. Chen, F.L. Mi, Development of genipin-crosslinked and fucoidan-adsorbed nano-hydroxyapatite/hydroxypropyl chitosan composite scaffolds for bone tissue engineering. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 128, 973–984 (2019)
K. Saekhor, W. Udomsinprasert, S. Honsawek, W. Tachaboonyakiat, Preparation of an injectable modified chitosan-based hydrogel approaching for bone tissue engineering. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 123, 167–173 (2019)
S. Shafiee, H. Abbastabar Ahangar, A. Saffar, Taguchi method optimization for synthesis of Fe3O4 @chitosan/Tragacanth Gum nanocomposite as a drug delivery system. Carbohdr. Polym. 7: 114982. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2019.114982. (2019)
G. Archana, K. Sabina et al., Preparation and characterization of mucilage polysaccharide for biomedical applications. Carbohydr. Polym. 98, 89–94 (2013)
N.C. Ngwuluka, N.A. Ochekpe, O.I. Aruoma, Naturapolyceutics: The Science of Utilizing Natural Polymers for Drug Delivery. Polymers 6, 1312–1332 (2014)
T. Bal, S. Swain, Microwave assisted synthesis of polyacrylamide grafted polymeric blend of fenugreek seed mucilage-Polyvinyl alcohol (FSM-PVA-g-PAM) and its characterizations as tissue engineered scaffold and as a drug delivery device. DARU J. Pharm. Sci. (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40199-019-00237-8
G.K. Jani, D.P. Shah, V.D. Prajapati, V.C. Jain, Gums and mucilages: versatile excipients for pharmaceutical formulations. Asian J. Pharm. Sci. 4, 309–323 (2009)
M. Saeedi, K. Morteza-Semnani, F. Ansoroudi, S. Fallah, G. Amin, Evaluation of binding properties of Plantago psyllium seed mucilage. Acta Pharm. 60, 339–348 (2010)
T. Ponrasu, P. Vishal, R. Kannan, L. Suguna, V. Muthuvijayan, Isabgol–silk fibroin 3D composite scaffolds as an effective dermal substitute for cutaneous wound healing in rats. RSC Adv. 6, 73617–73626 (2016)
S. Mirzaei, V. Javanbakht, Dye removal from aqueous solution by a novel dual cross-linked biocomposite obtained from mucilage of Plantago Psyllium and eggshell membrane. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 134, 1187–1204 (2019)
I. Zia, S. Mirza, R. Jolly, A. Rehman, R. Ullah, M. Shakir, Trigonella foenum graecum seed polysaccharide coupled nano hydroxyapatite-chitosan: A ternary nanocomposite for bone tissue engineering. Inter. J. Biol. Macromol. 124, 88–101 (2019)
A.R. Allafchian, S.A.H. Jalali, S.E. Mousavi, Biocompatible biodegradable polycaprolactone/basil seed mucilage scaffold for cell culture. IET Nanobiotechnol. 12(2018), 1108–1113 (2018)
H. Majmudar, V. Mourya, S. Devdhe, R. Chandak, Pharmaceutical Applications of Ispaghula Husk: Mucilage. Int. J. Pharm. Sci. Rev. Res. 18(2013), 49–55 (2013)
Q. Guo, S.W. Cui, Q. Wang, J.C. Young, Fractionation and physicochemical characterization of psyllium gum. Carbohydr. Polym. 73(2008), 35–43 (2008)
A.I. Canas, J.P. Delgado, C. Gartner, Biocompatible scaffolds composed of chemically crosslinked chitosan and gelatin for tissue engineering. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 43814(2016), 2–10 (2016)
D. Kumar, R. Chandra, R. Dubey, Synthesis and characterisation of cross-linked polymers of acrylic acid and psyllium mucilage (Psy-cl-AA). J. Technol. Adv. Sci. Res. 2, 185–189 (2016)
H.N. Öztop, D. Saraydin, S. Cetinus, pH-sensitive chitosan films for baker’s yeast immobilization. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 101(2002), 239–249 (2002)
B. Leukers, H. Gülkan, S.H. Irsen, S. Milz, C. Tille, M. Schieker, H. Seitz, Hydroxyapatite scaffolds fir bone tissue engineering made by 3D printing". J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 16, 1121–1124 (2005)
A. Kara, S. Tamburaci, F. Tihminlioglu, H. Havitcioglu, Bioactive fish scale incorporated chitosan biocomposite scaffolds for bone tissue engineering. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 130, 266–279 (2019)
M.R. Salton, Studies of the bacterial cell wall: IV. The composition of the cell walls of some gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 10, 512–523 (1953)
Z. Emami-Karvani, P. Chehrazi, Antibacterial activity of ZnO nanoparticle on gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria. Afr. J. Microbiol. Res. 5, 1368–1373 (2011)
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to express their personal thanks to Islamic Azad University, Najafabad, Iran.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
There is no conflict of interest to declare in this study.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Beheshti, F., Ahangar, H.A. & Poorazizi, E. Fabrication and characterization of Plantago psyllium mucilage/ chitosan composite scaffold: Physico-mechanical and antibacterial properties. Journal of Materials Research 37, 1440–1450 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1557/s43578-022-00544-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1557/s43578-022-00544-y