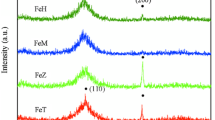
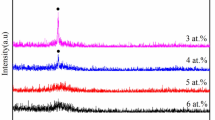
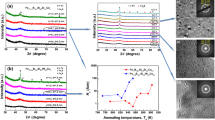
Abstract
Thermocalc simulations identified compositions with good glass-forming ability (GFA) by locating minima in liquidus temperature, and solidification range in (Fe70 Ni30)x(B-Si-Nb)100-x alloys with x = 82% and x = 85%, increased compared to previously developed x = 80% alloys. 3 compositions in the x = 82% system and 1 in the x = 85% system were successfully cast as amorphous magnetic ribbon. Magnetic properties of as-cast alloys showed improvements in Curie temperature and saturation induction, especially for the 85% alloy. Crystallization behavior in the 85% alloy was determined to occur as a 2-step process. Annealing studies showed (Fe70Ni30)82Nb2Si0B16 and (Fe70Ni30)82Nb3Si0B15 alloys to exhibit low coercivity and high Bs with annealing. TEM results show significant crystallization in as-cast ribbon. The (Fe70Ni30)85Nb0.5Si0B14.5 alloy as-cast has small, uniformly distributed grains, allowing a useful nanocrystalline alloy to be produced as cast. Finally, the parameter ΔTxg, the temperature range in which the material can be thermomechanically processed, was in the range of 12–23 °C.
Graphic abstract









Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Available upon request.
References
P. Waide, C.U. Brunner, 2011. Energy-efficiency policy opportunities for electric motor-driven systems https://doi.org/10.1787/5kgg52gb9gjd-en
A.M. Leary, P.R. Ohodnicki, M.E. Mchenry, Soft magnetic materials in high-frequency, high-power conversion applications. JOM. 64, 772–781 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11837-012-0350-0
N. Aronhime, V. DeGeorge, V. Keylin, P. Ohodnicki, M.E. McHenry, The effects of strain-annealing on tuning permeability and lowering losses in Fe-Ni-based metal amorphous nanocomposites. JOM. 69, 2164–2170 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11837-017-2480-x
M.E. McHenry, D.E. Laughlin, Magnetic Properties of Metals and Alloys, in: Phys. Metall. Fifth Ed., Elsevier B.V., 2014: pp. 1881–2008. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-444-53770-6.00019-8.
I. Škorvánek, R. Gerling, The influence of neutron irradiation on the soft magnetic and mechanical properties of amorphous and nanocrystalline Fe73.5Cu1Nb3Si13.5B9 alloys. J. Appl. Phys. 72, 3417–3422 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.351414
M.A. Willard, F. Johnson, J.H. Claassen, R.M. Stroud, M.E. McHenry, V.G. Harris, Soft magnetic nanocrystalline alloys for high temperature applications. Mater. Trans. 43, 2000–2005 (2002). https://doi.org/10.2320/matertrans.43.2000
A.M. Leary, V. Keylin, P.R. Ohodnicki, M.E. McHenry, Stress induced anisotropy in CoFeMn soft magnetic nanocomposites. J. Appl. Phys. 117, 1–5 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.4919230
T.M. Heil, K.J. Wahl, A.C. Lewis, J.D. Mattison, M.A. Willard, Nanocrystalline soft magnetic ribbons with high relative strain at fracture. Appl. Phys. Lett. (2007). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.2742598
M. Kurniawan, V. Keylin, M.E. McHenry, Effect of alloy substituents on soft magnetic properties and economics of Fe-based and Co-based alloys. J. Mater. Res. 30, 2231–2237 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1557/jmr.2015.197
M. Kurniawan, V. Keylin, M.E. McHenry, Alloy substituents for cost reduction in soft magnetic materials. J. Mater. Res. 30, 1072–1077 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1557/jmr.2015.56
N. Aronhime, E. Zoghlin, V. Keylin, X. Jin, P. Ohodnicki, M.E. McHenry, Magnetic properties and crystallization kinetics of (Fe100−xNix)80Nb4Si2B14 metal amorphous nanocomposites. Scr. Mater. 142, 133–137 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2017.08.043
J.M. Silveyra, A. Leary, V. DeGeorge, S. Simizu, M.E. McHenry, High speed electric motors based on high performance novel soft magnets. J. Appl. Phys. 115, 17A319 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.4864247
J.M. Silveyra, P. Xu, V. Keylin, V. DeGeorge, A. Leary, M.E. McHenry, Amorphous and nanocomposite materials for energy-efficient electric motors. J. Electron. Mater. 45, 219–225 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11664-015-3968-1
A. Urata, H. Matsumoto, S. Sato, A. Makino, High Bs nanocrystalline alloys with high amorphous-forming ability. J. Appl. Phys. 105, 2007–2010 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.3072373
C. Wang, A. He, A. Wang, J. Pang, X. Liang, Q. Li, C. Chang, K. Qiu, X. Wang, Effect of P on glass forming ability, magnetic properties and oxidation behavior of FeSiBP amorphous alloys. Intermetallics 84, 142–147 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.intermet.2016.12.024
A. Wang, C. Zhao, A. He, H. Men, C. Chang, X. Wang, Composition design of high Bs Fe-based amorphous alloys with good amorphous-forming ability. J. Alloys Compd. 656, 729–734 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2015.09.216
T. Liu, A. Wang, C. Zhao, S. Yue, X. Wang, C.T. Liu, Compositional design and crystallization mechanism of high Bs nanocrystalline alloys. Mater. Res. Bull. 112, 323–330 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.materresbull.2019.01.007
J. Xu, Y.Z. Yang, W. Li, Z.W. Xie, X.C. Chen, Effect of the substitution of C for Si on microstructure, magnetic properties and bending ductility in high Fe content FeSiBCuPC alloy ribbons. J. Alloys Compd. 727, 610–615 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2017.08.181
J. Xu, Y.Z. Yang, W. Li, X.C. Chen, Z.W. Xie, Effect of P addition on glass forming ability and soft magnetic properties of melt-spun FeSiBCuC alloy ribbons. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 417, 291–293 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2016.05.103
E. Dastanpour, M.H. Enayati, A. Masood, V. Ström, On the glass forming ability (GFA), crystallization behavior and soft magnetic properties of nanomet-substituted alloys. J. Non. Cryst. Solids. 529, 119774 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jnoncrysol.2019.119774
X.Y. Yan, Y.A. Chang, Y. Yang, F.Y. Xie, S.L. Chen, F. Zhang, S. Daniel, M.H. He, A thermodynamic approach for predicting the tendency of multicomponent metallic alloys for glass formation. Intermetallics 9, 535–538 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0966-9795(01)00036-X
D. Ma, H. Cao, L. Ding, Y.A. Chang, K.C. Hsieh, Y. Pan, Bulkier glass formability enhanced by minor alloying additions. Appl. Phys. Lett. 87, 1–3 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.2115074
H. Cao, D. Ma, K.C. Hsieh, L. Ding, W.G. Stratton, P.M. Voyles, Y. Pan, M. Cai, J.T. Dickinson, Y.A. Chang, Computational thermodynamics to identify Zr-Ti-Ni-Cu-Al alloys with high glass-forming ability. Acta Mater. 54, 2975–2982 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2006.02.051
F. Zhang, C. Zhang, D. Lv, J. Zhu, W. Cao, S. Chen, R. Schmid-Fetzer, Prediction of glass forming ability through high throughput calculation. J. Phase Equilib. Diffus. 39, 562–570 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11669-018-0643-2
Y. Krimer, N. Aronhime, P. Ohodnicki, M.E. McHenry, Prediction of good glass forming ability in amorphous soft magnetic alloys by thermocalc simulation with experimental validation. J. Alloys Compd. 814, 152294 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2019.152294
Z.P. Lu, C.T. Liu, A new glass-forming ability criterion for bulk metallic glasses. Acta Mater. 50, 3501–3512 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1016/S1359-6454(02)00166-0
C.A. Schuh, T.C. Hufnagel, U. Ramamurty, Mechanical behavior of amorphous alloys. Acta Mater. 55, 4067–4109 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2007.01.052
J. Lu, G. Ravichandran, W.L. Johnson, Deformation behavior of the Zr41.2Ti13.8Cu12.5Ni10Be22.5 bulk metallic glass over a wide range of strain-rates and temperatures. Acta Mater. 51, 3429–3443 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1016/S1359-6454(03)00164-2
N.J. DeCristofaro, P.J. Stamatis, G.E. Fish, Bulk amorphous metal magnetic components for electric motors, US6462456 B1, 2002. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.(73).
T. Fukao, A. Chiba, M. Matsui, Test results on a super-highspeed amorphous-iron reluctance motor. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 25, 119–125 (1989). https://doi.org/10.1109/28.18881
N. Nishiyama, K. Tanimoto, A. Makino, Outstanding efficiency in energy conversion for electric motors constructed by nanocrystalline soft magnetic alloy “nANOMET®” cores. AIP Adv. 6, 5 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.4944341
T. Gheiratmand, H.R.M. Hosseini, Finemet nanocrystalline soft magnetic alloy: investigation of glass forming ability, crystallization mechanism, production techniques, magnetic softness and the effect of replacing the main constituents by other elements. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 408, 177–192 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2016.02.057
N. Aronhime, P. Ohodnicki, M.E. McHenry, Virtual bound states elements and their effects on magnetic and electrical properties of Fe-Ni based metal amorphous nanocomposites. Scr. Mater. 169, 9–13 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2019.05.003
P. Ohodnicki, E.J. Kautz, A. Devaraj, Y. Yu, N. Aronhime, Y. Krimer, M.E. Mchenry, A. Leary, Nanostructure and compositional segregation of soft magnetic FeNi-based nanocomposites with multiple nanocrystalline phases. J Mater Res (2020). https://doi.org/10.1557/jmr.2020.242
Z. Li, R. Parsons, B. Zang, H. Kishimoto, T. Shoji, A. Kato, J. Karel, K. Suzuki, Dramatic grain refinement and magnetic softening induced by Ni addition in Fe[sbnd]B based nanocrystalline soft magnetic alloys. Scr. Mater. 181, 82–85 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2020.02.020
P.R. Ohodnicki, S.Y. Park, H.K. McWilliams, K. Ramos, D.E. Laughlin, M.E. McHenry, Phase evolution during crystallization of nanocomposite alloys with Co: Fe ratios in the two-phase region of the binary Fe-Co phase diagram. J. Appl. Phys. 101, 1–3 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.2711283
J. Long, P.R. Ohodnicki, D.E. Laughlin, M.E. McHenry, T. Ohkubo, K. Hono, Structural studies of secondary crystallization products of the Fe23 B6 -type in a nanocrystalline FeCoB-based alloy. J. Appl. Phys. 101, 2007–2009 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.2714250
P.R. Ohodnicki, N.C. Cates, D.E. Laughlin, M.E. McHenry, M. Widom, Ab initio theoretical study of magnetization and phase stability of the (Fe Co, Ni)23B6 and (Fe Co, Ni)23Zr6 structures of Cr23C6 and Mn23Th6 prototypes. Phys. Rev. B 78, 1–13 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevB.78.144414
T. Pradell, D. Crespo, N. Clavaguera, M.T. Clavaguera-Mora, Diffusion controlled grain growth in primary crystallization: Avrami exponents revisited. J. Phys. Condens. Matter. 10, 3833–3844 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1088/0953-8984/10/17/014
R. Parsons, B. Zang, K. Onodera, H. Kishimoto, A. Kato, K. Suzuki, Soft magnetic properties of rapidly-annealed nanocrystalline Fe-Nb-B-(Cu) alloys. J. Alloys Compd. 723, 408–417 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2017.06.208
K. Suzuki, R. Parsons, B. Zang, K. Onodera, H. Kishimoto, A. Kato, Copper-free nanocrystalline soft magnetic materials with high saturation magnetization comparable to that of Si steel. Appl. Phys. Lett. 110, 6–10 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.4973772
K. Suzuki, R. Parsons, B. Zang, K. Onodera, H. Kishimoto, T. Shoji, A. Kato, Nano-crystallization of amorphous alloys by ultra-rapid annealing: an effective approach to magnetic softening. J. Alloys Compd. 735, 613–618 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2017.11.110
S.J. Kernion, M.S. Lucas, J. Horwath, Z. Turgut, E. Michel, V. Keylin, J.F. Huth, A.M. Leary, S. Shen, M.E. McHenry, Reduced losses in rolled Fe73.5Si15.5Nb3B7Cu1 nanocrystalline ribbon. J. Appl. Phys. 113, 15–18 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.4794131
Y. Takahara, H. Matsuda, Change in Magnetic Properties with Annealing of a Cold Rolled Amorphous Fe79B16Si5 Alloy. Mater. Trans. JIM. 35, 435–438 (1994)
Acknowledgments
This material is based upon work supported by the U.S. Department of Energy’s Office of Energy Efficiency and Renewable Energy (EERE) under the Vehicle Technologies Program Office Award Number DE-EE0008870. This work was also supported by the DOE/EERE—Office of Advanced Manufacturing Program under Award DE-EE0007867. This work was additionally supported by Carpenter Technologies Corporation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
On behalf of all authors, the corresponding author states that there is no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Krimer, Y., Barberis, A. & McHenry, M.E. Development of high Bs Fe–Ni-based metal amorphous nanocomposite by optimization of glass-forming ability. Journal of Materials Research 36, 1666–1677 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1557/s43578-021-00183-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1557/s43578-021-00183-9