Abstract
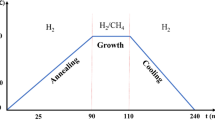
Chemical vapor deposition is the most proficient method for growing graphene on copper foils due to its scalability, repeatability, and uniformity, etc. Herein, we systematically study the effect of oxygen (O2) exposure on graphene growth. We introduced O2 before and during the growth, and then studied its effects on the morphology, crystallinity, and nucleation density of graphene. We observe that introducing O2 during growth significantly improves the graphene crystallinity while pre-dosing O2 before growth reduces the graphene nucleation density. These studies suggest that intermittent O2 exposure play a significant role in graphene growth, enabling scalable production of high-quality graphene.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
P.R. Wallace: The band theory of graphite. Phys. Rev. 71, 622 (1947).
K.S. Novoselov, A.K. Geim, S.V. Morozov, D. Jiang, Y. Zhang, S.V. Dubonos, I.V. Grigorieva, and A.A. Firsov: Electric field effect in atomically thin carbon films. Science 306, 666 (2004).
K. Ziegler: Robust transport properties in graphene. Phys. Rev. Lett. 97, 266802 (2006).
S.D. Sarma, S. Adam, E.H. Hwang, and E. Rossi: Electronic transport in two-dimensional graphene. Rev. Mod. Phys. 83, 407 (2011).
R.S. Shishir and D.K. Ferry: Intrinsic mobility in graphene. J. Phys., Condens. Matter. 21, 232204 (2009).
L. Banszerus, M. Schmitz, S. Engels, J. Dauber, M. Oellers, F. Haupt, K. Watanabe, T. Taniguchi, B. Beschoten, and C. Stampfer: Ultrahigh-mobility graphene devices from chemical vapor deposition on reusable copper. Sci. Adv. 1, e1500222 (2015).
A. Zandiatashbar, G.-H. Lee, S.J. An, S. Lee, N. Mathew, M. Terrones, T. Hayashi, C.R. Picu, J. Hone, and N. Koratkar: Effect of defects on the intrinsic strength and stiffness of graphene. Nat. Commun. 5, 3186 (2014).
X. Li, L. Colombo, and R.S. Ruoff: Synthesis of graphene films on copper foils by chemical vapor deposition. Adv. Mater. 28, 6247 (2016).
K.V. Emtsev, A. Bostwick, K. Horn, J. Jobst, G.L. Kellogg, L. Ley, J.L. McChesney, T. Ohta, S.A. Reshanov, J. Röhrl, E. Rotenberg, A.K. Schmid, D. Waldmann, H.B. Weber, and T. Seyller: Towards wafer-size graphene layers by atmospheric pressure graphitization of silicon carbide. Nat. Mater. 8, 203 (2009).
D. Li, M.B. Müller, S. Gilje, R.B. Kaner, and G.G. Wallace: Processable aqueous dispersions of graphene nanosheets. Nat. Nanotechnol. 3, 101 (2008).
C.Y. Su, A.Y. Lu, Y. Xu, F.R. Chen, A.N. Khlobystov, and L.J. Li: High-quality thin graphene films from fast electrochemical exfoliation. ACS Nano 5, 2332 (2011).
G.H. Han, F. Gunes, J.J. Bae, E.S. Kim, S.J. Chae, H.J. Shin, J.Y. Choi, D. Pribat, and Y.H. Lee: Influence of copper morphology in forming nucleation seeds for graphene growth. Nano Lett. 11, 4144 (2011).
I. Vlassiouk, S. Smirnov, M. Regmi, S.P. Surwade, N. Srivastava, R. Feenstra, G. Eres, C. Parish, N. Lavrik, P. Datskos, S. Dai, and P. Fulvio: Graphene nucleation density on copper: fundamental role of background pressure. J. Phys. Chem. C 117, 18919 (2013).
P. Zhao, Y. Cheng, D. Zhao, K. Yin, X. Zhang, M. Song, S. Yin, Y. Song, P. Wang, M. Wang, Y. Xia, and H. Wang: The role of hydrogen in oxygen-assisted chemical vapor deposition growth of millimeter-sized graphene single crystals. Nanoscale 8, 7646 (2016).
Y. Hao, M.S. Bharathi, L. Wang, Y. Liu, H. Chen, S. Nie, X. Wang, H. Chou, C. Tan, B. Fallahazad, H. Ramanarayan, C.W. Magnuson, E. Tutuc, B.I. Yakobson, K.F. McCarty, Y.W. Zhang, P. Kim, J. Hone, L. Colombo, and R.S. Ruoff: The role of surface oxygen in the growth of large single-crystal graphene on copper. Science 342, 720 (2013).
S.M. Kim, A. Hsu, Y.H. Lee, M. Dresselhaus, T. Palacios, K.K. Kim, and J. Kong: The effect of copper pre-cleaning on graphene synthesis. Nanotechnology 24, 365602 (2013).
Y. Wang, Y. Zheng, X. Xu, E. Dubuisson, Q. Bao, J. Lu, and K.P. Loh: Electrochemical delamination of CVD-grown graphene film: toward the recyclable use of copper catalyst. ACS Nano 5, 9927 (2011).
A.C. Ferrari: Raman spectroscopy of graphene and graphite: disorder, electron–phonon coupling, doping and nonadiabatic effects. Solid State Commun. 143, 47 (2007).
Y.Y. Wang, Z.H. Ni, T. Yu, Z.X. Shen, H.M. Wang, Y.H. Wu, W. Chen, and A.T.S. Wee: Raman studies of monolayer graphene: the substrate effect. J. Phys. Chem. C 112, 10637 (2008).
L.M. Malard, M.A.A. Pimenta, G. Dresselhaus, and M.S. Dresselhaus: Raman spectroscopy in graphene. Phys. Rep. 473, 51 (2009).
Z. Mutlu, S. Shahrezaei, S. Temiz, M. Ozkan, and C.S. Ozkan: Facile synthesis and characterization of two dimensional layered tin disulfide nanowalls. J. Electron. Mater. 45, 2115 (2016).
K. Kim, S. Coh, L.Z. Tan, W. Regan, J.M. Yuk, E. Chatterjee, M.F. Crommie, M.L. Cohen, S.G. Louie, and A. Zettl: Raman spectroscopy study of rotated double-layer graphene: misorientation-angle dependence of electronic structure. Phys. Rev. Lett. 108, 246103 (2012).
Z. Mutlu, R.J. Wu, D. Wickramaratne, S. Shahrezaei, C. Liu, S. Temiz, A. Patalano, M. Ozkan, R.K. Lake, K.A. Mkhoyan, and C.S. Ozkan: Phase engineering of 2D tin sulfides. Small 12, 2998 (2016).
Z. Mutlu, I. Ruiz, R. Wu, R. Ionescu, S. Shahrezaei, S. Temiz, M. Ozkan, A.K. Mkhoyan, and C. S. Ozkan: Chemical vapor deposition of partially oxidized graphene. RSC Adv. 7, 32209 (2017).
I. Childres, L.A. Jauregui, W. Park, H. Cao, and Y.P. Chen: Raman spectroscopy of graphene and related materials. In New Developments in Photon and Materials Research, edited by J.I. Jang (Nova Science, 2013), pp. 1–20.
Z. Ni, Y. Wang, T. Yu, and Z. Shen: Raman spectroscopy and imaging of graphene. Nano Res. 1, 273 (2008).
D. Ferrah, O. Renault, C. Petit-Etienne, H. Okuno, C. Berne, V. Bouchiat, and G. Cunge: XPS investigations of graphene surface cleaning using H2- and Cl2-based inductively coupled plasma. Surf. Interface Anal. 48, 451 (2016).
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the STARnet center C-SPIN (Center for Spintronic Materials, Interfaces and Novel Architectures), through the Semiconductor Research Corporation sponsored by the MARCO (Microelectronics Advanced Research Corporation) and the DARPA (Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency). X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) was performed at the Analytical Chemistry Instrumentation Facility (ACIF) of the University of California, Riverside, which receives support from the NSF (National Science Foundation) through the MRI (Major Research Instrumentation) program (DMR-0958796).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Supporting Information
Supplementary material
Supplementary material
The supplementary material for this article can be found at https://doi.org/10.1557/mrc.2017.111.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Temiz, S., Mutlu, Z., Shahrezaei, S. et al. Effect of intermittent oxygen exposure on chemical vapor deposition of graphene. MRS Communications 7, 826–831 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1557/mrc.2017.111
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1557/mrc.2017.111