Abstract
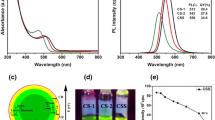
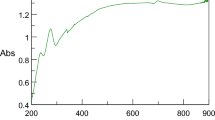
Chalcopyrite quantum dots (QDs) have emerged as a safe alternative to cadmium-based QDs for bio-applications. However, the research on AgInS2 chalcopyrite QDs has not been widely explored in terms of their toxicity. Herein, we report a synthesis of biocompatible AgInS2/ZnS QDs via a greener approach. The emission intensity of the as-synthesized AgInS2 core QDs was enhanced 2-fold after the ZnS shell growth. X-ray diffraction revealed the tetragonal crystal structure of QDs, and high-resolution transmission electron microscope images show that the QDs are spherical in shape and crystalline in nature. Cell viability assays conducted on different cell lines, such as HeLa, A549, and BHK-21 cells, indicated that AgInS2/ZnS QDs are least toxic at a QD concentration range of 100 µg/mL. The fluorescent microscope analysis of A549 cells incubated with AgInS2/ZnS QDs shows that the QDs were accumulated in the cell membranes. The as-synthesized AgInS2/ZnS QDs are less toxic and eco-friendly, and can be used for biolabeling.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
A. Aboulaich, M. Michalska, R. Schneider, A. Potdevin, J. Deschamps, R. Deloncle, G. Chadeyron, and R. Mahiou: Ce-doped YAG nanophosphor and red emitting CuInS2/ZnS core/shell quantum dots for warm white light-emitting diode with high color rendering index. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 6, 252–258 (2013).
G.H. Carey, A.L. Abdelhady, Z. Ning, S.M. Thon, O.M. Bakr, and E.H. Sargent: Colloidal quantum dot solar cells. Chem. Rev. 115, 12732–12763 (2015).
L. Jing, S.V. Kershaw, Y. Li, X. Huang, Y. Li, A.L. Rogach, and M. Gao: Aqueous based semiconductor nanocrystals. Chem. Rev. 116, 10623–10730 (2016).
M. Gazouli, A. Lyberopoulou, P. Pericleous, S. Rizos, G. Aravantinos, N. Nikiteas, N.P. Anagnou, and E.P. Efstathopoulos: Development of a quantum-dot-labelled magnetic immunoassay method for circulating colorectal cancer cell detection. World J. Gastroenterol. 18, 4419 (2012).
E. Liandris, M. Gazouli, M. Andreadou, L.A. Sechi, V. Rosu, and J. Ikonomopoulos: Detection of pathogenic mycobacteria based on functionalized quantum dots coupled with immunomagnetic separation. PLoS One 6, e20026 (2011).
Z. Ranjbar-Navazi, Y. Omidi, M. Eskandani, and S. Davaran: Cadmium-free quantum dot-based theranostics. TrAC. Trends Anal. Chem. 118, 386–400 (2019).
E. Petryayeva, W.R. Algar, and I.L. Medintz: Quantum dots in bioanalysis: A review of applications across various platforms for fluorescence spectroscopy and imaging. Appl. Spectrosc. 67, 215–252 (2013).
Y. Chen, S. Li, L. Huang, and D. Pan: Low-cost and gram-scale synthesis of water-soluble Cu–In–S/ZnS core/shell quantum dots in an electric pressure cooker. Nanoscale 6, 1295–1298 (2014).
L. Li, T.J. Daou, I. Texier, T.T. Kim Chi, N.Q. Liem, and P. Reiss: Highly luminescent CuInS2/ZnS core/shell nanocrystals: Cadmium-free quantum dots for in vivo imaging. Chem. Mater. 21, 2422–2429 (2009).
Z. Lin, X. Fei, Q. Ma, X. Gao, and X. Su: CuInS2 quantum dots@ silica near-infrared fluorescent nanoprobe for cell imaging. New J. Chem. 38, 90–96 (2014).
D. Deng, L. Qu, and Y. Gu: Near-infrared broadly emissive AgInSe2/ZnS quantum dots for biomedical optical imaging. J. Mater. Chem. C 2, 7077–7085 (2014).
M.Z. Fahmi and J.Y. Chang: Forming double layer-encapsulated quantum dots for bio-imaging and cell targeting. Nanoscale 5, 1517–1528 (2013).
D. Che, X. Zhu, H. Wang, Y. Duan, Q. Zhang, and Y. Li: Aqueous synthesis of high bright and tunable near-infrared AgInSe2–ZnSe quantum dots for bioimaging. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 463, 1–7 (2016).
X. Hu, T. Chen, Y. Xu, M. Wang, W. Jiang, and W. Jiang: Hydrothermal synthesis of bright and stable AgInS2 quantum dots with tunable visible emission. J. Lumin. 200, 189–195 (2018).
X. Kang, L. Huang, Y. Yang, and D. Pan: Scaling up the aqueous synthesis of visible light emitting multinary AgInS2/ZnS core/shell quantum dots. J. Phys. Chem. C 119, 7933–7940 (2015).
F. Bray, J. Ferlay, I. Soerjomataram, R.L. Siegel, L.A. Torre, and A. Jemal: Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. Ca-Cancer J. Clin. 68, 394–424 (2018).
B.M. May, S. Parani, and O.S. Oluwafemi: Detection of ascorbic acid using green synthesized AgInS2 quantum dots. Mater. Lett. 236, 432–435 (2019).
L. Zi, Y. Huang, Z. Yan, and S. Liao: Thioglycolic acid-capped CuInS2/ZnS quantum dots as fluorescent probe for cobalt ion detection. J. Lumin. 148, 359–363 (2014).
W.W. Xiong, G.H. Yang, X.C. Wu, and J.J. Zhu: Microwave-assisted synthesis of highly luminescent AgInS2/ZnS nanocrystals for dynamic intracellular Cu(II) detection. J. Mater. Chem. B 1, 4160–4165 (2013).
H. Shang, Q. Di, M. Ji, B. Bai, J. Liu, W. Chen, M. Xu, H. Rong, J. Liu, and J. Zhang: From indium-doped Ag2S to AgInS2 nanocrystals: Low-temperature in situ conversion of colloidal Ag2S nanoparticles and their NIR fluorescence. Chem. - Eur. J. 24, 13676–13680 (2018).
S. Peng, S. Zhang, S.G. Mhaisalkar, and S. Ramakrishna: Synthesis of AgInS2 nanocrystal ink and its photoelectrical application. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 14, 8523–8529 (2012).
M. Mousavi-Kamazani and M. Salavati-Niasari: A simple microwave approach for synthesis and characterization of Ag2S–AgInS2 nanocomposites. Composites, Part B 56, 490–496 (2014).
L. Tan, S. Liu, X. Li, I.S. Chronakis, and Y. Shen: A new strategy for synthesizing AgInS2 quantum dots emitting brightly in near-infrared window for in vivo imaging. Colloids Surf., B 125, 222–229 (2015).
L. Wang, X. Kang, and D. Pan: Gram-scale synthesis of hydrophilic PEI-coated AgInS2 quantum dots and its application in hydrogen peroxide/glucose detection and cell imaging. Inorg. Chem. 56, 6122–6130 (2017).
H. Shinchi, M. Wakao, N. Nagata, M. Sakamoto, E. Mochizuki, T. Uematsu, S. Kuwabata, and Y. Suda: Cadmium-free sugar-chain-immobilized fluorescent nanoparticles containing low-toxicity ZnS-AgInS2 cores for probing lectin and cells. Bioconjugate Chem. 25, 286–295 (2014).
J.Y. Chang, G.Q. Wang, C.Y. Cheng, W.X. Lin, and J.C. Hsu: Strategies for photoluminescence enhancement of AgInS2 quantum dots and their application as bioimaging probes. J. Mater. Chem. 22, 10609–10618 (2012).
J. Song, C. Ma, W. Zhang, X. Li, W. Zhang, R. Wu, X. Cheng, A. Ali, M. Yang, L. Zhu, and R. Xia: Bandgap and structure engineering via cation exchange: From binary Ag2S to ternary AgInS2, quaternary AgZnInS alloy and AgZnInS/ZnS core/shell fluorescent nanocrystals for bioimaging. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 8, 24826–24836 (2016).
G. Chen, F. Tian, Y. Zhang, Y. Zhang, C. Li, and Q. Wang: Tracking of transplanted human mesenchymal stem cells in living mice using near-infrared Ag2S quantum dots. Adv. Funct. Mater. 24, 2481–2488 (2014).
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank UJ-Global Excellence Stature; National Research Foundation (NRF) under Scarce Skills and Innovation scholarship; Competitive Program for Rated Researchers (CPRR), Grant No. 106060; and the University of Johannesburg (URC) and Faculty of Science (FRC) for financial support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Oluwafemi, O.S., May, B.M.M., Parani, S. et al. Cell viability assessments of green synthesized water-soluble AgInS2/ZnS core/shell quantum dots against different cancer cell lines. Journal of Materials Research 34, 4037–4044 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1557/jmr.2019.362
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1557/jmr.2019.362