Abstract
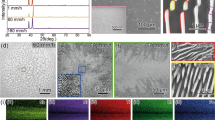
High-entropy composites (HECs) were subjected to severe straining by high-pressure torsion (HPT) to evaluate their influence on the evolution of microstructure and deformation behavior. Severe straining leads to a homogeneously strained microstructure and inhomogeneous micro-shear bands in these HECs. Nb addition in HECs varies the microstructure from single phase to eutectic, and the Vickers microhardness in HPT HECs increases to 7.45 GPa. Nb addition up to x = 0.80 in as-cast HECs improves the strength of these materials at the expense of its plasticity. Nevertheless, severe straining provides a better combination of strength and ductility without sacrificing its plasticity. Such improvement in properties is attributed to the evolved microstructural features, formation of “transformation-shear bands (T-SBs)” and “deformation-shear bands (D-SBs)” at severe straining. This assures the homogeneous deformation by shear banding and suggests that shear banding is the dominant deformation mechanism when the lamellar spacing becomes saturated upon severe straining.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
G. He, J. Eckert, W. Löser, and L. Schultz: Novel Ti based nanostructure–dendrite composites with enhanced plasticity. Nat. Mater. 2, 33 (2003).
J. Eckert, J. Das, S. Pauly, and C. Duhamel: Mechanical properties of bulk metallic glasses and composites. J. Mater. Res. 22, 285 (2007).
L.C. Zhang, J. Das, H.B. Lu, C. Duhamel, M. Calin, and J. Eckert: High strength Ti–Fe–Sn ultrafine composites with large plasticity. Scr. Mater. 57, 101 (2007).
T. Maity, B. Roy, and J. Das: Mechanism of lamellae deformation and phase rearrangement in ultrafine lamellar β-Ti/FeTi eutectic composites. Acta Mater. 97, 170 (2015).
L.C. Zhang, H.B. Lu, C. Mickel, and J. Eckert: Ductile ultrafine-grained Ti-based alloys with high yield strength. Appl. Phys. Lett. 91, 051906 (2007).
J. Das, K.B. Kim, F. Baier, W. Löser, and J. Eckert: High-strength Ti-base ultrafine eutectic with enhanced ductility. Appl. Phys. Lett. 87, 161907 (2005).
T. Maity and J. Das: High strength Ni–Zr–(Al) nano/-eutectic composites with large plasticity. Intermetallics 63, 51 (2015).
T. Maity, A. Singh, A. Dutta, and J. Das: Microstructure mechanism on the evolution of plasticity in nanolamellar γ-Ni/Ni5Zr eutectic composites. Mater. Sci. Eng., A 666, 72 (2016).
S.W. Lee, J.T. Kim, S.H. Hong, H.J. Park, J.Y. Park, N.S. Lee, Y. Seo, J.Y. Suh, J. Eckert, D.H. Kim, J.M. Park, and K.B. Kim: Micro-to-nano-scale deformation mechanisms of a bimodal ultrafine eutectic composites. Sci. Rep. 4, 6500 (2014).
T. Maity, A. Dutta, P.P. Jana, K.G. Prashanth, J. Eckert, and J. Das: Influence of Nb on the microstructure and fracture toughness of (Zr0.76Fe0.24)100−xNbx nanoeutectic composites. Materials 11, 113 (2018).
J.T. Kim, S.H. Hong, H.J. Park, G.H. Park, J.Y. Suh, J.M. Park, and K.B. Kim: Influence of microstructural evolution on mechanical behavior of Fe–Nb–B ultrafine composites with a correlation to elastic modulus and hardness. J. Alloys Compd. 647, 886 (2015).
J.T. Kim, S.H. Hong, H.J. Park, Y.S. Kim, J.Y. Suh, J.K. Lee, J.M. Park, T. Maity, J. Eckert, and K.B. Kim: Deformation mechanisms to ameliorate the mechanical properties of novel TRIP/TWIP Co–Cr–Mo–(Cu) ultrafine eutectic alloys. Sci. Rep. 7, 39959 (2017).
J.T. Kim, S.H. Hong, H.J. Park, Y.S. Kim, G.H. Park, J. Park, N. Lee, Y. Seo, J.M. Park, and K.B. Kim: Improving the plasticity and strength of Fe–Nb–B ultrafine eutectic composite. Mater. Des. 76, 190 (2015).
C. Yang, L.M. Kang, X.X. Li, W.W. Zhang, D.T. Zhang, Z.Q. Fu, Y.Y. Li, L.C. Zhang, and E.J. Lavernia: Bimodal titanium alloys with ultrafine lamellar eutectic structure fabricated by semi-solid sintering. Acta Mater. 132, 491 (2017).
L.H. Liu, C. Yang, F. Wang, S.G. Qu, X.Q. Li, W.W. Zhang, Y.Y. Li, and L.C. Zhang: Ultrafine grained Ti-based composites with ultrahigh strength and ductility achieved by equiaxing microstructure. Mater. Des. 79, 1 (2015).
Y. Lu, Y. Dong, S. Guo, H. Kang, T. Wang, B. Wen, Z. Wang, J. Jie, Z. Cao, H. Ruan, and T. Li: A promising new class of high-temperature alloys: Eutectic high-entropy alloys. Sci. Rep. 4, 6200 (2014).
M.C. Gao, J.W. Yeh, P.K. Liaw, and Y. Zhang: High-Entropy Alloys: Fundamentals and Applications, 1st ed. (Springer International Publishing, Cham, Switzerland, 2016).
F. He, Z. Wang, P. Cheng, J. Li, Y. Dang, J. Wang, and C.T. Liu: Designing eutectic high entropy alloys of CoCrFeNiNbx. J. Alloys Compd. 656, 284 (2016).
Y. Dong, L. Jiang, H. Jiang, Y. Lu, T. Wang, and T. Li: Effect of annealing treatment on microstructure and hardness of bulk AlCrFeNiMo0.2 eutectic high entropy alloy. Mater. Des. 82, 91 (2015).
M.H. Tsai, A.C. Fan, and H.A. Wang: Effect of atomic size difference on the type of major intermetallic phase in arc-melted CoCrFeNix high-entropy alloys. J. Alloys Compd. 695, 1479 (2017).
F. He, Z. Wang, M. Zhu, J. Li, Y. Dang, and J. Wang: The phase stability of Ni2CrFeMox multi-principal-component alloys with medium configurational entropy. Mater. Des. 85, 1 (2015).
F. He, Z. Wang, X. Shang, C. Leng, J. Li, and J. Wang: Stability of lamellar structures in Co–Cr–Fe–Ni–Nbx eutectic high entropy alloys at elevated temperatures. Mater. Des. 104, 259 (2016).
T. Maity, K.G. Prashanth, O. Balci, Z. Wang, Y.D. Jia, and J. Eckert: Plastic defamation mechanisms in severely strained eutectic high entropy composites explained via strain rate sensitivity and activation volume. Composites, Part B 150, 7 (2018).
T. Maity, K.G. Prashanth, O. Balci, J.T. Kim, T. Schöberl, Z. Wang, and J. Eckert: Influence of severe straining and strain rate on the evolution of dislocation structure during micro-/nanoindentation in high entropy lamellar eutectics. Int. J. Plast. 109, 121 (2018).
T.S. Reddy, I.S. Wani, T. Bhattacharjee, S.R. Reddy, R. Saha, and P.P. Bhattacharjee: Severe plastic deformation driven nanostructure and phase evolution in a Al0.5CoCrFeNi dual phase high entropy alloy. Intermetallics 91, 150 (2017).
Y. Lu, X. Gao, L. Jiang, Z. Chen, T. Wang, J. Jie, H. Kang, Y. Zhang, S. Guo, H. Ruan, Y. Zhao, Z. Cao, and T. Li: Directly cast bulk eutectic and near eutectic high entropy alloys with balanced strength and ductility in a wide temperature range. Acta Mater. 124, 143 (2017).
I.S. Wani, T. Bhattacharjee, S. Sheikh, P. Lu, S. Chatterjee, P.P. Bhattacharjee, S. Guo, and N. Tsuji: Ultrafine-grained AlCoCrFeNi2.1 eutectic high-entropy alloy. Mater. Res. Lett. 4, 174 (2016).
L. Rogal, J. Morgiel, Z. Swiatek, and F. Czerwinski: Microstructure and mechanical properties of the new Nb25Sc25Ti25Zr25 eutectic high entropy alloy. Mater. Sci. Eng., A 651, 590–597 (2016).
H. Jiang, H. Zhang, T. Huang, Y. Lu, T. Wang, and T. Li: Microstructures and mechanical properties of Co2MoxNi2VWx eutectic high entropy alloys. Mater. Des. 109, 539 (2016).
L. Jiang, Y. Lu, W. Wu, Z. Cao, and T. Li: Microstructure and mechanical properties of a CoFeNi2V0.5Nb0.75 eutectic high entropy alloy in as-cast and heat-treated conditions. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 32, 245 (2016).
Y. Tan, J. Li, J. Wang, and H. Kou: Seaweed eutectic-dendritic solidification pattern in a CoCrFeNiMnPd eutectic high-entropy alloy. Intermetallics 85, 74 (2017).
Z.Y. Ding, Q.F. He, Q. Wang, and Y. Yang: Superb strength and high plasticity in laves phase rich eutectic medium-entropy-alloy nanocomposites. Int. J. Plast. 106, 57 (2018).
S. Sasmal, M.R. Rahul, R.S. Kottada, and G. Phanikumar: Hot deformation behavior and processing map of Co–Cu–Fe–Ni–Ti eutectic high entropy alloy. Mater. Sci. Eng., A 664, 227 (2016).
T.M. Pollock and S. Tin: Nickel based super-alloys for advanced turbine engines: Chemistry, microstructure, and properties. J. Propul. Power 22, 361 (2006).
S.R. Dey, L. Hollang, B. Beausir, E. Hieckmann, and W. Skrotzki: Formation of micro shear bands during cyclic deformation of sub-microcrystalline nickel. Scr. Mater. 68, 631 (2013).
M. Böhme and M.F.X. Wagner: On the correlation of shear band formation and texture evolution in α-brass during accumulative roll bonding. Scr. Mater. 154, 172 (2018).
J.P. Ligda, B.E. Schuster, and Q. Wei: Transition in the deformation mode of nanocrystalline tantalum processed by high pressure torsion. Scr. Mater. 67, 253 (2012).
Q. Wie, D. Jia, K.T. Ramesh, and E. Ma: Evolution and microstructure of shear bands in nanostructured Fe. Appl. Phys. Lett. 81, 1240 (2002).
T. Hebesberger, H.P. Stüwe, A. Vorhauer, F. Wetscher, and R. Pippan: Structure of copper deformed by high pressure torsion. Acta Mater. 53, 393 (2005).
M. Hafok and R. Pippan: Post-shear deformation of high pressure torsion-deformed nickel under hydrostatic pressure. Scr. Mater. 56, 757 (2007).
F. Wetscher, A. Vorhauer, and R. Pippan: Strain hardening during high pressure torsion deformation. Mater. Sci. Eng., A 410–411, 213 (2005).
M.G. Zelin, N.A. Krasilnikov, R.Z. Valiev, M.W. Grabski, H.S. Yang, and A.K. Mukherjee: On the microstructural aspects of the nonhomogeneity of superplastic deformation at the level of grain groups. Acta Metall. 42, 119 (1994).
S.D. Wu, Z.G. Wang, C.B. Jiang, and G.Y. Li: Scanning electron microscopy-electron channeling contrast investigation of recrystallization during cyclic deformation of ultrafine grained copper processed by equal channel angular pressing. Philos. Mag. Lett. 82, 559 (2002).
A. Vorhauer and R. Pippan: On the homogeneity of deformation by high pressure torsion. Scr. Mater. 51, 921 (2004).
K.S. Kormut, P. Ghosh, A. Bachmaier, A. Hohenwarter, and R. Pippan: Effect of processing temperature on the microstructural characteristics of Cu–Ag nanocomposites: From super saturation to complete phase decomposition. Acta Mater. 154, 33 (2018).
J.T. Kim, S.H. Hong, J.M. Park, J. Eckert, and K.B. Kim: Microstructure and mechanical properties of hierarchical multi-phase composites based on Al–Ni-type intermetallic compounds in the Al–Ni–Cu–Si alloys system. J. Alloys Compd. 749, 205 (2018).
Y.Z. Tian, S.D. Wu, Z.F. Zhang, R.B. Figueiredo, N. Gao, and T.G. Langdon: Microstructural evolution and mechanical properties of a two phase Cu–Ag alloy processed by high-pressure torsion to ultrahigh strains. Acta Mater. 59, 2783 (2011).
D. Chicot: Hardness length-scale factor to model nano- and micro-indentation size effects. Mater. Sci. Eng., A 499, 454 (2009).
M. Tanaka, H. Saito, M. Yasumaru, and K. Hagishida: Nature of delamination cracks in perlitic steels. Scr. Mater. 112, 32 (2016).
Y.B. Xu, W.L. Zhong, Y.J. Chen, L.T. Shen, Q. Liu, Y.L. Bai, and M.A. Meyers: Shear localization and recrystallization in dynamic deformation of 8090 Al–Li alloy. Mater. Sci. Eng., A 299, 287 (2001).
G.J. Fan, G.Y. Wang, H. Choo, P.K. Liaw, Y.S. Park, B.Q. Han, and E.J. Lavernia: Deformation behaviour of an ultrafine-grained Al–Mg alloy at different strain rates. Scr. Mater. 52, 929 (2005).
T.W. Wright and H. Ockendon: A scaling law for the effect of inertia on the formation of adiabatic shear bands. Int. J. Plast. 12, 927 (1996).
A.M. Mayer, V.F. Nesterenko, J.C. Lasalvia, and Q. Xue: Shear localization in dynamic deformation of materials: Microstructural evolution and self-organization. Mater. Sci. Eng., A 317, 204 (2001).
M. Kapp, O. Renk, T. Leitner, P. Ghosh, B. Yang, and R. Pippan: Cyclic induced grain growth within shear bands investigated in UFG Ni by cyclic high pressure torsion. J. Mater. Res. 32, 4317 (2017).
R. Pippan, S. Scheriau, A. Taylor, M. Hafok, A. Hohenwarter, and A. Bachmaier: Saturation of fragmentation during severe plastic deformation. Annu. Rev. Mater. Res. 40, 319 (2010).
F.X. Li, P.D. Hao, J.H. Yi, Z. Chen, K.G. Prashanth, T. Maity, and J. Eckert: Microstructure and strength of nano-/ultrafine-grain carbon nanotube-reinforced titanium composites processed by high pressure torsion. Mater. Sci. Eng., A 722, 122 (2018).
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank Prof. R. Pippan, T. Hohenwarter, P. Kutlesa, and S. Modritsch for their help with high-pressure torsion experiments and metallographic sample preparation, respectively. Financial support was provided through the European Research Council under the ERC Advanced Grant INTELHYB (grant ERC-2013-ADG-340025) and Estonian Research Council under the structural funds MOBERC15.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This author was an editor of this journal during the review and decision stage. For the JMR policy on review and publication of manuscripts authored by editors, please refer to http://www.mrs.org/editor-manuscripts/.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Maity, T., Prashanth, K.G., Janda, A. et al. Mechanism of high-pressure torsion-induced shear banding and lamellar thickness saturation in Co–Cr–Fe–Ni–Nb high-entropy composites. Journal of Materials Research 34, 2672–2682 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1557/jmr.2019.149
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1557/jmr.2019.149