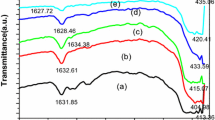
Abstract
Antimony doped tin oxide (ATO) is an ideal material for thermal insulation. To obtain the stable performance of ATO nanodispersions and measure the transparent and thermal insulation properties of the ATO coatings, we investigated how a dispersant and sand milling affect the stability of ATO dispersion, which has come to the results that adding an appropriate dispersant and sand milling for 2.0 h were beneficial to the ATO dispersion. We characterized the morphology, nanostructure, particle size distribution, zeta potential, and optical properties of the ATO dispersions by a transmission electron microscope (TEM), a laser particle size analyzer, and a spectrometer. The results show that the average particle size of the dispersions is about 50 nm and their absolute values of all zeta potentials are more than 40 mV. We coated the thermal insulation water-based coatings on quartz glasses by spin coating method, the effect of thermal insulation is evident with the increase of the ATO content, and there exists approximately 10 °C difference between the ATO sample and blank sample with the condition for maintaining high transmittance of visual light.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
K-M. Zhang and Z-G. Wen: Review and challenges of policies of environmental protection and sustainable development in China. J. Environ. Manage. 88, 1249 (2008).
Q. Wang and Y. Chen: Energy saving and emission reduction revolutionizing China’s environmental protection. Renewable Sustainable Energy Rev. 14, 535 (2010).
C. Filippín, S.F. Larsen, A. Beascochea, and G. Lesino: Response of conventional and energy-saving buildings to design and human dependent factors. Sol. Energy 78, 455 (2005).
T.C. Lowe, A. Bishop, C. Burns, A. Hartford, D. Parkin, and J. Trewhella: Nanoscale science and technology at Los Alamos National Laboratory. J. Nanopart. Res. 2, 249 (2000).
K. Ariga, H. Ito, J.P. Hillab, and H. Tsukube: Molecular recognition: From solution science to nano/materials technology. Chem. Soc. Rev. 41, 5800 (2012).
M. Tang, Y.Q. Guo, J. Yuan, Q. Wei, S.J. Sun, W. Zhou, and Y. Zhang: Review of some recent progress on materials science researches in China. Sci. China: Chem. 55, 2497 (2012).
X.J. Duan and C.M. Lieber: Nanoscience and the nano-bioelectronics frontier. Nano Res. 8, 1 (2015).
G.H. Shih, C.G. Allen, and B.G. Potter, Jr.: RF-sputtered Ge–ITO nanocomposite thin films for photovoltaic applications. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 94, 797 (2010).
H. Hosono: Recent progress in transparent oxide semiconductors: Materials and device application. Thin Solid Films 515, 6000 (2007).
V. Senthilkumar, P. Vickraman, and R. Ravikumar: Synthesis of fluorine doped tin oxide nanoparticles by sol–gel technique and their characterization. J. Sol-Gel Sci. Technol. 53, 316 (2010).
K. Ravichandran, P. Ravikumar, and B. Sakthivel: Fabrication of protective over layer for enhanced thermal stability of zinc oxide based TCO films. Appl. Surf. Sci. 287, 323 (2013).
S. Sharma, A.M. Volosin, D. Schmitt, and D-K. Seo: Preparation and electrochemical properties of nanoporous transparent antimony-doped tin oxide (ATO) coatings. J. Mater. Chem. A 1, 699 (2013).
X. Hou, K-L. Choy, and J-P. Liu: Electrical and optical performance of transparent conducting oxide films deposited by electrostatic spray assisted vapour deposition. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 11, 8114 (2011).
G. Song, J. Ryu, S. Ko, B.M. Bang, S. Choi, M. Shin, S-Y. Lee, and S. Park: Revisiting surface modification of graphite: Dual-layer coating for high-performance lithium battery anode materials. Chem.–Asian J. 11, 1711 (2016).
H. Sun, X. Liu, B.S. Liu, and Z.D. Yin: Preparation and properties of antimony doped tin oxide nanopowders and their conductivity. Mater. Res. Bull. 83, 354 (2016).
S-W. Seo, S.H. Won, H. Chae, and S.M. Cho: Low-temperature growth of highly conductive and transparent aluminum-doped ZnO film by ultrasonic-mist deposition. Korean J. Chem. Eng. 29, 525 (2012).
D. Zhang, Y. Tang, F. Jiang, Z. Han, and J. Chen: Electrodeposition of silver nanoparticle arrays on transparent conductive oxides. Appl. Surf. Sci. 369, 178 (2016).
T. Minami: Transparent conducting oxide semiconductors for transparent electrodes. Semicond. Sci. Technol. 20, S35 (2005).
M. Zhou, H. Zhu, Y. Jiao, Y. Rao, S. Hark, Y. Liu, L. Peng, and Q. Li: Optical and electrical properties of Ga-doped ZnO nanowire arrays on conducting substrates. J. Phys. Chem. C 113, 8945 (2009).
A. AlKahlout: A wet chemical preparation of transparent conducting thin films of Ga-doped ZnO nanoparticles. J. Sol-Gel Sci. Technol. 67, 331 (2013).
S. Cimitan, S. Albonetti, L. Forni, F. Peri, and D. Lazzari: Solvothermal synthesis and properties control of doped ZnO nanoparticles. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 329, 73 (2009).
B-R. Koo and H-J. Ahn: Structural, electrical, and optical properties of Sb-doped SnO2 transparent conductive oxides fabricated using an electrospray technique. Ceram. Int. 40, 4375 (2014).
D-W. Kim, D-S. Kim, Y-G. Kim, Y-C. Kim, and S-G. Oh: Preparation of hard agglomerates free and weakly agglomerated antimony doped tin oxide (ATO) nanoparticles by coprecipitation reaction in methanol reaction medium. Mater. Chem. Phys. 97, 452 (2006).
H.F. Lu, R.Y. Hong, L.S. Wang, H.D. Xie, and S.Q. Zhao: Preparation of ATO nanorods and electrical resistivity analysis. Mater. Lett. 68, 237 (2012).
L.S. Wang, H.F. Lu, R.Y. Hong, and W.G. Feng: Synthesis and electrical resistivity analysis of ATO-coated talc. Powder Technol. 224, 124 (2012).
H. Liu, Q. Li, L. Wang, Y. Mao, and C. Wu: Effect of SnO2 and Sb doped SnO2 on the structure and electrical conductivity of epichlorohydrin rubber. Polym. Compos. 37, 2411 (2016).
Y. Li, J. Wang, B. Feng, K. Duan, and J. Weng: Synthesis and characterization of antimony-doped tin oxide (ATO) nanoparticles with high conductivity using a facile ammonia-diffusion co-precipitation method. J. Alloys Compd. 634, 37 (2015).
X. Wang, Y. Hu, L. Song, W. Xing, H. Lu, P. Lv, and G. Jie: Effect of antimony doped tin oxide on behaviors of waterborne polyurethane acrylate nanocomposite coatings. Surf. Coat. Technol. 205, 1864 (2010).
N. Li, Q. Meng, and N. Zhang: Dispersion stabilization of antimony-doped tin oxide (ATO) nanoparticles used for energy-efficient glass coating. Particuology 17, 49 (2014).
E. Redel, C. Huai, Ö. Dag, S. Petrov, P.G. O’Brien, M.G. Helander, J. Mlynarski, and G.A. Ozin: From bare metal powders to colloidally stable TCO dispersions and transparent nanoporous conducting metal oxide thin films. Small 8, 3806 (2012).
K. Peters, P. Zeller, G. Stefanic, V. Skoromets, H. Nemec, P. Kuzel, and D. Fattakhova-Rohlfing: Water-dispersible small monodisperse electrically conducting antimony doped tin oxide nanoparticles. Chem. Mater. 27, 1090 (2015).
Y-S. Cho, H-M. Kim, J-J. Hong, G-R. Yi, S.H. Jang, and S-M. Yang: Dispersion stabilization of conductive transparent oxide nanoparticles. Colloids Surf., A 336, 88 (2009).
J. Liu, Q. Xu, F. Shi, S. Liu, J. Luo, L. Bao, and X. Feng: Dispersion of Cs0.33WO3 particles for preparing its coatings with higher near infrared shielding properties. Appl. Surf. Sci. 309, 175 (2014).
C. Biswas, K.K. Kim, H-Z. Geng, H.K. Park, S.C. Lim, S.J. Chae, S.M. Kim, and Y.H. Lee: Strategy for high concentration nanodispersion of single-walled carbon nanotubes with diameter selectivity. J. Phys. Chem. C 113, 10044 (2009).
S. Sung and D.S. Kim: UV-curing and mechanical properties of polyester acrylate nanocomposites films with silane-modified antimony doped tin oxide nanoparticles. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 129, 1340 (2013).
S.X. Luo, Z. Song, and J.L. Li: Research on the dispersion uniformity and stability of nano-ATO. J. Funct. Mater. 44, 1603 (2013).
Q. Tan, G. Yu, Y. Liao, B.N. Hu, and X.Y. Zhang: Preparation of stable aqueous suspensions of antimony-doped tin oxide nanoparticles used for transparent and thermal insulation fluorocarbon coating. Colloid Polym. Sci. 292, 3233 (2014).
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
The authors declare no competing financial interest. We gratefully acknowledge support from the Nanning Science and Technology Project (Grant No. 20155347) and the Guangxi Nonferrous Metals and Featured Materials Processing Laboratory Foundation (Grant No. GXKFJ12-20).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sun, H., Liu, B., Liu, X. et al. Dispersion of antimony doped tin oxide nanopowders for preparing transparent thermal insulation water-based coatings. Journal of Materials Research 32, 2414–2422 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1557/jmr.2017.211
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1557/jmr.2017.211