Abstract
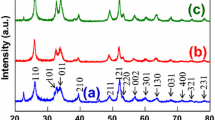
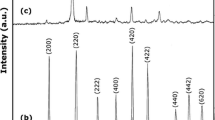
The development of ceramic nanomaterials with unique structure is necessary for discovery of novel property. We developed a novel niobium oxide nanoparticles with a spiky morphology. The spiky structure was composed of two kinds of component: niobium oxide hydrate sphere core and niobium pentoxide nanorods. These spiky niobium oxide nanoparticles are easily synthesized by hydrothermal treatment of niobium oxalate solution at 200 °C for 2 h, and their particle size could be tuned from 80 to 300 nm with 5–10 nm of nanorod on the surface by adjusting niobium concentration in the niobium oxalate solution. The band gap energy of the spiky nanoparticles was around 3.4 eV, and the spiky niobium oxide nanoparticles showed a light absorption in a wide wave length range from 380 to 700 nm. The niobium oxide nanoparticles are applicable as both solid acid catalyst and photocatalyst because of their spiky and two-layer structure.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
B. Kumara and S.W. Kim: Energy harvesting based on semiconducting piezoelectric ZnO nanostructures. Nano Energy 1, 342–355 (2012).
K. Mimura and K. Kato: Enhanced dielectric properties of BaTiO3 nanocube assembled film in metal–insulator–metal capacitor structure. Appl. Phys. Express 7, 061501 (2014).
K.M.L. Taylor-Pashow, J.D. Rocca, R.C. Huxford, and W. Lin: Hybrid nanomaterials for biomedical applications. Chem. Commun. 46, 5832–5849 (2010).
J. Lv, T. Kako, Z. Li, Z. Zou, and J. Ye: Synthesis and photocatalytic activities of NaNbO3 rods modified by In2O3 nanoparticles. J. Phys. Chem. C 114, 6157–6162 (2010).
S. Uchida, Y. Inoue, Y. Fujishiro, and T. Sato: Hydrothermal synthesis of K4Nb6O17. J. Mater. Sci. 33, 5125 (1998).
C.H. Lu, S.Y. Lo, and H.C. Lin: Hydrothermal synthesis of nonlinear optical potassium niobate ceramic powder. Mater. Lett. 34, 172–176 (1998).
J.F. Liu, X.L. Li, and Y.D. Li: Novel synthesis of polymorphous nanocrystalline KNbO3 by a low temperature solution method. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2, 617 (2002).
S. Lee, T. Park, G. Choi, K. Koo, and W. Kim: Effects of KOH/BaTi and Ba/Ti ratios on synthesis of BaTiO3 powder by coprecipitation/hydrothermal reaction. Mater. Chem. Phys. 82, 742 (2003).
A. Sehgal, Y. Lalatonne, J-F. Berret, and M. Morvan: Precipitation-redispersion of cerium oxide nanoparticles with poly(acrylic acid): Toward stable dispersions. Langmuir 21, 9359–9364 (2005).
C. Burda, X.B. Chen, R. Narayaman, and M.A. El-Sayed: Chemistry and properties of nanocrystals of different shapes. Chem. Rev. 105, 1025–1102 (2005).
L. Zhang and Y.J. Zhu: Microwave-assisted solvothermal synthesis of AlOOH hierarchically nanostructured microspheres and their transformation to γ-Al2O3 with similar morphologies. J. Phys. Chem. C 112, 16764 (2008).
Z.L. Wang and J.H. Song: Piezoelectric nanogenerators based on zinc oxide nanowire arrays. Science 312, 242 (2006).
V. Polshettiwar, B. Baruwati, and R.S. Varma: Self-assembly of metal oxides into three-dimensional nanostructures: Synthesis and application in catalysis. ACS Nano 3(3), 728–736 (2009).
X. Xie, Y. Li, Z-Q. Liu, M. Haruta, and W. Shen: Low-temperature oxidation of CO catalysed by Co3O4 nanorods. Nature 458, 746–749 (2011).
Y.D. Wang, L.F. Yang, Z.L. Zhou, Y.F. Li, and X.H. Wu: Effects of calcination temperature on latice constants and gas sensing properties of Nb2O5. Mater. Lett. 49, 277 (2001).
P. Carniti, A. Gervasini, and M. Marzo: Dispersed NbOx catalytic phases in silica matrixes: Influence of niobium concentration and preparative route. J. Phys. Chem. C 112, 14064 (2008).
S.H. Mujawar, A.I. Inamdar, S.B. Patil, and P.S. Patil: Electrochromic properties of spray-deposited niobium oxide thin films. Solid State Ionics 177, 3333 (2006).
R. Jose, V. Thavasi, and S. Ramakrishna: Metal oxides for dyesensitized solar cells. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 92, 289 (2009).
K.S. Ahn, M.S. Kang, J.K. Lee, B.C. Shin, and J.W. Lee: Enhanced electron diffusion length of mesoporous TiO2 film by using Nb2O5 energy barrier for dye-sensitized solar cells. Appl. Phys. Lett. 89, 013103 (2006).
A.C. Mackey, R.L. Karlinsey, T.G. Chu, M. MacPherson, and D.L. Alge: Development of niobium oxide coatings on sand-blasted titanium alloy dental implants. Mater. Sci. Appl. 3, 301–305 (2012).
A. Llordés, G. Garcia, J. Gazquez, and D.J. Milliron: Tunable near-infrared and visible-light transmittance in nanocrystal-in-glass composites. Nature 500, 323–326 (2013).
Y. Guo, K. Kakimoto, and H. Ohsato: Phase transitional behavior and piezoelectric properties of (Na0.5K0.5)NbO3–LiNbO3(Na0.5K0.5)NbO3–LiNbO3 ceramics. Appl. Phys. Lett. 85, 4121 (2004).
Y. Saito, H. Takao, T. Tani, T. Nonoyama, K. Takatori, T. Homma, T. Nagaya, and M. Nakamura: Lead-free piezoceramics. Nature 432, 84–87 (2004).
T.R. Shrout and S.J. Zhang: Lead-free piezoelectric ceramics: Alternatives for PZT?J. Electroceram. 19, 113–126 (2007).
G. Vats and R. Vaish: Selection of optimal sintering temperature of K0.5Na0.5NbO3 ceramics for electromechanical applications. J. Asian Ceram. Soc. 2, 5–10 (2014).
D. Mohanty, G. Chaubey, A. Yourdkhani, S. Adireddy, G. Caruntu, and J. Wiley: Synthesis and piezoelectric response of cubic and spherical LiNbO3 nanocrystals. RSC Adv. 2, 1913–1916 (2012).
K. Saito and A. Kudo: Niobium-complex-based syntheses of sodium niobate nanowires possessing superior photocatalytic properties. Inorg. Chem. 49, 2017–2019 (2010).
H. Zhu, Z. Zheng, X. Gao, Y. Huang, Z. Yan, J. Zou, H. Yin, Q. Zou, S.H. Kable, J. Zhao, Y. Xi, W.N. Martens, and R.L. Frost: Structural evolution in a hydrothermal reaction between Nb2O5 and NaOH solution: From Nb2O5 grains to microporous Na2Nb2O6/3H2O fibers and NaNbO3 cubes. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 128, 2373–2384 (2006).
K. Nakajima, Y. Baba, R. Noma, M. Kitano, J.N. Kondo, S. Hayashi, and M. Hara: Nb2O5n H2O as a heterogeneous catalyst with water-tolerant Lewis acid sites. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 133, 4224–4227 (2011).
A.G.S. Prado, L.B. Bolzon, C.P. Pedroso, A.O. Moura, and L.L. Costa: Nb2O5 as efficient and recyclable photocatalyst for indigo carmine degradation. Appl. Catal., B 82, 219–224 (2008).
J. Wu, J. Li, X. Lü, L. Zhang, J. Yao, F. Zhang, F. Huang, and F. Xu: A one-pot method to grow pyrochlore H4Nb2O7-octahedron-based photocatalyst. J. Mater. Chem. 20, 1942–1946 (2010).
H. Luo, M. Wei, and K. Wei: Synthesis of Nb2O5 nanorods by a soft chemical process. J. Nanomater. 2009, 1–4 (2009).
W. Fan, Q. Zhang, W. Deng, and Y. Wang: Niobic acid nanosheets synthesized by a simple hydrothermal method as efficient brønsted acid catalysts. Chem. Mater. 25, 3277–3287 (2013).
M.Y. Rafique, L. Pan, W.S. Khan, M.Z. Iqbal, H. Qiu, M.H. Farooq, M. Ellahi, and Z. Guo: Controlled synthesis, phase formation, growth mechanism, and magnetic properties of 3-D CoNi alloy microstructures composed of nanorods. CrystEngComm 15, 5314–5325 (2013).
J. Yin, X. Zhao, L. Xiang, X. Xia, and Z. Zhang: Enhanced electrorheology of suspensions containing sea-urchin-like hierarchical Cr-doped titania particles. Soft Matter 5, 4687–4697 (2009).
Y. Ye, J. Chen, Q. Ding, D. Lin, R. Dong, L. Yang, and J. Liu: Sea-urchin-like Fe3O4@C@Ag particles: An efficient SERS substrate for detection of organic pollutants. Nanoscale 5, 5887–5895 (2013).
E.R. Camargo and M. Kakihana: Low temperature synthesis of lithium niobate powders based on water-soluble niobium malato complexes. Solid State Ionics 151, 413–418 (2002).
T. Murayama, J. Chen, J. Hirata, K. Matsumoto, and W. Ueda: Hydrothermal synthesis of octahedra-based layered niobium oxide and its catalytic activity as a solid acid. Catal. Sci. Technol. 4, 4250–4257 (2014).
T. Fuchigami and K. Kakimoto: Synthesis of niobium pentoxide nanoparticles in single flow supercritical water. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 55, 10TB06 (2016).
Y. Zhao, C. Eley, J. Hu, J.S. Foord, L. Ye, and H. He: Shapedependent acidity and photocatalytic activity of Nb2O5 nanocrystals with active TT (001) surface. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 51, 3846–3849 (2012).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fuchigami, T., Kakimoto, Ki. Spiky niobium oxide nanoparticles through hydrothermal synthesis. Journal of Materials Research 32, 3326–3332 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1557/jmr.2017.200
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1557/jmr.2017.200