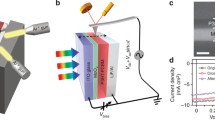
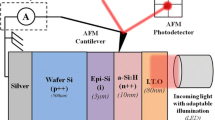
Abstract
In situ and operando measurement techniques combined with nanoscale resolution have proven invaluable in multiple fields of study. We argue that evaluating device performance as well as material behavior by correlative X-ray microscopy with <100 nm resolution can radically change the approach for optimizing absorbers, interfaces and full devices in solar cell research. In this article, we thoroughly discuss the measurement technique of X-ray beam induced current and point out fundamental differences between measurements of wafer-based silicon and thin-film solar cells. Based on reports of the last years, we showcase the potential that X-ray microscopy measurements have in combination with in situ and operando approaches throughout the solar cell lifecycle: from the growth of individual layers to the performance under operating conditions and degradation mechanisms. Enabled by new developments in synchrotron beamlines, the combination of high spatial resolution with high brilliance and a safe working distance allows for the insertion of measurement equipment that can pave the way for a new class of experiments. Applied to photovoltaics research, we highlight today’s opportunities and challenges in the field of nanoscale X-ray microscopy, and give an outlook on future developments.
















Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
Although multiple exciton generation (MEG) by single photons has been demonstrated e.g., in Ref. 161 for quantum-dot solar cells, solar cells with internal quantum efficiencies above 1 are of no practical relevance so far beyond fundamental research.
Although experimentally not confirmed, there may be cases, where layers adjacent to the absorber layer could contribute to the X-ray beam induced photocurrent as discussed in Ref. 65.
One can think of a device and measurement architecture, where more electrons leave the back surface than the front surface, e.g., with a front that is transparent for X-rays but absorbs heavily electrons, and a back that absorbs X-rays efficiently. However, we have in practice never encountered such a case, in which the grounding scheme would need to be inverted.
“Front” and “back” side of a device denotes here the side exposed to or turned away from the incident X-rays. Obviously, this does not have to be the side of a solar cell that is exposed to the sun. As demonstrated in Fig. 2, for standard operation, the sun light enters this type of perovskite solar cell through the glass, but its high absorption of X-rays forced us to shine the X-rays through the other side.
In most cases, the fraction of photons transmitted through the solar cell is not directly measurable by a down-stream detector, as most of them will be absorbed in the cell substrate.
We used the attenuation coefficients included in the Penelope package for Beer–Lambert’s law and Monte–Carlo simulations, which justifies a direct comparison. Note that different databases for element-specific X-ray coefficients are available. A relatively recent database is presented in Ref. 162, and online80,163 as well as offline sources68,86 are available.
All absorption length values reported in this section were calculated using the functions “material.f” and “tables.f”, both being part of the Monte-Carlo simulation software package Penelope.68 For broader discussion of absorption length of different solar cell absorber layers, we refer to our publication in prep.69
Note that the discrete layers do not need to correspond to physically distinct layers. In most cases, we use max. 1 nm thick layers for the calculation of the correction, which allows to take into account depth-dependent composition gradients as they are standard in many solar cell architectures. Whereas such depth-dependent composition variations are not accessible in plan view XRF measurements, they can be determined by other means (secondary ion mass spectroscopy, glow-discharge optical emission spectroscopy, cross-section XRF, etc.), and be taken into account for the calculation of the correction.
Although I0 represents the intensity of the incoming photon beam as in Beer–Lambert’s law, I does not represent the intensity of the outgoing photon beam in Eq. (9)—in contrast to Eq. (10). Instead, I represents the outgoing photon beam intensity if there was no angular scattering or reemission of photons (fluorescence probability 100%).
For the quantification of raw XRF counts into area concentrations by fitting of the reference and sample spectra, we typically use the MAPS software package developed at APS.79
Poly{[N,N-9-bis(2-octyldodecyl)naphthalene-1,4,5,8-bis(dicarboximide)-2,6-diyl]-alt-5,59-(2,29-bithiophene)}.
References
A. Louwen, W.G.J.H.M. van Sark, A.P.C. Faaij, and R.E.I. Schropp: Re-assessment of net energy production and greenhouse gas emissions avoidance after 40 years of photovoltaics development. Nat. Commun. 7, 13728 (2016).
C. Breyer and A. Gerlach: Global overview on grid-parity. Prog. Photovolt. Res. Appl. 21, 121 (2013).
G. Masson and M. Brunisholz: 2015 Snapshot of Global Photovoltaic Markets. Report IEA PVPS T1–T292016 1 (IEEE, 2016).
M.A. Green: Rare materials for photovoltaics: Recent tellurium price fluctuations and availability from copper refining. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 119, 256 (2013).
J. Jean, P.R. Brown, R.L. Jaffe, T. Buonassisi, and V. Bulovic: Pathways for solar photovoltaics. Energy Environ. Sci. 8(4), 1200 (2015).
W. Shockley and H.J. Queisser: Detailed balance limit of efficiency of p–n junction solar cells. J. Appl. Phys. 32(3), 510 (1961).
Z. (Jason) Yu, M. Leilaeioun, and Z. Holman: Selecting tandem partners for silicon solar cells. Nat. Energy 1, 16137 (2016).
M.C. Beard, J.M. Luther, and A.J. Nozik: The promise and challenge of nanostructured solar cells. Nat. Nanotechnol. 9(12), 951 (2014).
X. Sheng, C.A. Bower, S. Bonafede, J.W. Wilson, B. Fisher, M. Meitl, H. Yuen, S. Wang, L. Shen, A.R. Banks, C.J. Corcoran, R.G. Nuzzo, S. Burroughs, and J.A. Rogers: Printing-based assembly of quadruple-junction four-terminal microscale solar cells and their use in high-efficiency modules. Nat. Mater. 13(6), 593 (2014).
M.I. Bertoni, D.P. Fenning, M. Rinio, V. Rose, M. Holt, J. Maser, and T. Buonassisi: Nanoprobe X-ray fluorescence characterization of defects in large-area solar cells. Energy Environ. Sci. 4(10), 4252 (2011).
T. Buonassisi, A.A. Istratov, M.A. Marcus, B. Lai, Z. Cai, S.M. Heald, and E.R. Weber: Engineering metal-impurity nanodefects for low-cost solar cells. Nat. Mater. 4(9), 676 (2005).
A.E. Morishige, M.A. Jensen, J. Hofstetter, P.X.T. Yen, C. Wang, B. Lai, D.P. Fenning, and T. Buonassisi: Synchrotron-based investigation of transition-metal getterability in n-type multicrystalline silicon. Appl. Phys. Lett. 108, 202104 (2016).
S. Bernardis, B.K. Newman, M. Di Sabatino, S.C. Fakra, M.I. Bertoni, D.P. Fenning, R.B. Larsen, and T. Buonassisi: Synchrotron-based microprobe investigation of impurities in raw quartz-bearing and carbon-bearing feedstock materials for photovoltaic applications. Prog. Photovolt. Res. Appl. 20(2), 217 (2012).
M.I. Bertoni, S. Hudelson, B.K. Newman, D.P. Fenning, H.F.W. Dekkers, E. Cornagliotti, A. Zuschlag, G. Micard, G. Hahn, G. Coletti, B. Lai, and T. Buonassisi: Influence of defect type on hydrogen passivation efficacy in multicrystalline silicon solar cells. Prog. Photovolt. Res. Appl. 19(2), 187 (2011).
T. Buonassisi, M. Heuer, O.F. Vyvenko, A.A. Istratov, E.R. Weber, Z. Cai, B. Lai, T.F. Ciszek, and R. Schindler: Applications of synchrotron radiation X-ray techniques on the analysis of the behavior of transition metals in solar cells and single-crystalline silicon with extended defects. Phys. B 340–342, 1137 (2003).
T. Buonassisi, A.A. Istratov, M.D. Pickett, M.A. Marcus, G. Hahn, S. Riepe, J. Isenberg, W. Warta, G. Willeke, T.F. Ciszek, and E.R. Weber: Quantifying the effect of metal-rich precipitates on minority carrier diffusion length in multicrystalline silicon using synchrotron-based spectrally resolved X-ray beam-induced current. Appl. Phys. Lett. 87, 044101 (2005).
O.F. Vyvenko, T. Buonassisi, A.A. Istratov, and E.R. Weber: X-ray beam induced current/microprobe X-ray fluorescence: Synchrotron radiation based X-ray microprobe techniques for analysis of the recombination activity and chemical nature of metal impurities in silicon. J. Phys.: Condens. Matter 16(6), S141 (2004).
S. Bernardini, S. Johnston, B. West, B. Lai, T. Naerland, M. Stuckelberger, and M.I. Bertoni: Nano-XRF analysis of metal impurities distribution at PL active grain boundaries during mc-silicon solar cell processing. IEEE J. Photovolt. 7(1), 244 (2017).
S. Siebentritt: What limits the efficiency of chalcopyrite solar cells? Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 95(6), 1471 (2011).
U. Rau and J.H. Werner: Radiative efficiency limits of solar cells with lateral band-gap fluctuations. Appl. Phys. Lett. 84(19), 3735 (2004).
L. Gütay, C. Lienau, and G.H. Bauer: Subgrain size inhomogeneities in the luminescence spectra of thin film chalcopyrites. Appl. Phys. Lett. 97(5), 52110 (2010).
L. Gütay and G.H. Bauer: Non-uniformities of opto-electronic properties in Cu(In,Ga)Se2 thin films and their influence on cell performance with confocal photoluminescence. In 2009 34th IEEE Photovoltaic Specialists Conference (IEEE, Philadelphia, 2009); p. 874.
J.S. Yun, A. Ho-Baillie, S. Huang, S.H. Woo, Y. Heo, J. Seidel, F. Huang, Y.B. Cheng, and M.A. Green: Benefit of grain boundaries in organic–inorganic halide planar perovskite solar cells. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 6(5), 875 (2015).
D.W. de Quilettes, S.M. Vorpahl, S.D. Stranks, H. Nagaoka, G.E. Eperon, M.E. Ziffer, H.J. Snaith, and D.S. Ginger: Impact of microstructure on local carrier lifetime in perovskite solar cells. Science 348(6235), 683 (2015).
Y. Luo, S. Gamliel, S. Nijem, S. Aharon, M. Holt, B. Stripe, V. Rose, M.I. Bertoni, L. Etgar, and D.P. Fenning: Heterogeneous chlorine incorporation in organic–inorganic perovskite solar cells. Chem. Mater. 28(18), 6536 (2016).
M.A. Green, K. Emery, Y. Hishikawa, W. Warta, E.D. Dunlop, D.H. Levi, and A.W.Y. Ho-Baillie: Solar cell efficiency tables (version 49). Prog. Photovolt. Res. Appl. 25(1), 3 (2017).
E.J. Crumlin, Z. Liu, H. Bluhm, W. Yang, J. Guo, and Z. Hussain: X-ray spectroscopy of energy materials under in situ/operando conditions. J. Electron Spectrosc. Relat. Phenom. 200, 264 (2015).
D. Abou-Ras: Correlative microscopy analyses of thin-film solar cells at multiple scales. Mater. Sci. Semicond. Process. (2016), in press.
M. Senoner and W.E.S. Unger: SIMS imaging of the nanoworld: Applications in science and technology. J. Anal. At. Spectrom. 27(7), 1050 (2012).
A. Merkle, L. Lechner, A. Steinbach, J. Gelb, M. Kienle, M. Phaneuf, and N. Chawla: Automated correlative tomography using XRM and FIB-SEM to span length scales and modalities in 3D materials. Microsc. Anal. 28, S10 (2014).
T.L. Burnett, S.A. McDonald, A. Gholinia, R. Geurts, M. Janus, T. Slater, S.J. Haigh, C. Ornek, F. Almuaili, D.L. Engelberg, G.E. Thompson, and P.J. Withers: Correlative tomography. Sci. Rep. 4, 4711 (2014).
A. Sakdinawat and D. Attwood: Nanoscale X-ray imaging. Nat. Photonics 4(12), 840 (2010).
H. Hieslmair, A.A. Istratov, R. Sachdeva, and E.R. Weber: New synchrotron-radiation based technique to study localized defects in silicon: “EBIC” with X-ray excitation. In 10th Work. Cryst. Silicon Sol. Cell Mater. Process. (NREL, Copper Mountain, 2000); pp. 162–165.
O.F. Vyvenko, T. Buonassisi, A.A. Istratov, H. Hieslmair, A.C. Thompson, R. Schindler, and E.R. Weber: X-ray beam induced current—A synchrotron radiation based technique for the in situ analysis of recombination properties and chemical nature of metal clusters in silicon. J. Appl. Phys. 91(6), 3614 (2002).
T. Buonassisi, A.A. Istratov, M.D. Pickett, M.A. Marcus, G. Hahn, S. Riepe, J. Isenberg, W. Warta, G. Willeke, T.F. Ciszek, and E.R. Weber: Synchrotron-based spectrally-resolved X-ray beam induced current: a technique to quantify the effect of metal-rich precipitates on minority carrier diffusion length in multicrystalline silicon. In 15th Work. Cryst. Silicon Sol. Cells Modul. Mater. Process. (NREL, Vail, 2005); pp. 141–144.
A.A. Istratov, T. Buonassisi, E.R. Weber, M.A. Marcus, and T.F. Ciszek: Dependence of precipitation behavior of Cu and Ni in CZ multicrystalline silicon on cooling conditions. In 14th Work. Cryst. Silicon Sol. Cells Modul. (NREL, Winter Park, 2004); pp. 1–5.
T. Buonassisi, A.A. Istratov, M.A. Marcus, S. Peters, C. Ballif, M. Heuer, T.F. Ciszek, Z. Cai, B. Lai, R. Schindler, and E.R. Weber: Synchrotron-based investigations into metallic impurity distribution and defect engineering in multicrystalline silicon via thermal treatments. In 2005 30th IEEE Photovoltaic Specialists Conference (IEEE, Lake Buena Vista, 2005); pp. 1027–1030.
M. Rinio, C. Ballif, T. Buonassisi, and D. Borchert: Defects in the deteriorated border layer of block-cast multicrystalline silicon ingots. In 19th Eur. Photovolt. Sol. Energy Conf. Exhib. (WIP, Paris, 2004); pp. 762–765.
T. Buonassisi, O.F. Vyvenko, A.A. Istratov, E.R. Weber, G. Hahn, D. Sontag, J.P. Rakotoniaina, O. Breitenstein, J. Isenberg, and R. Schindler: Observation of transition metals at shunt locations in multicrystalline silicon solar cells. J. Appl. Phys. 95(3), 1556 (2004).
M. Trushin, W. Seifert, O. Vyvenko, J. Bauer, G. Martinez-Criado, M. Salome, and M. Kittler: XBIC/μ-XRF/μ-XAS analysis of metals precipitation in block-cast solar silicon. Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res., Sect. B 268(3–4), 254 (2010).
M. Trushin, O. Vyvenko, W. Seifert, M. Kittler, I. Zizak, A. Erko, M. Seibt, and C. Rudolf: Combined XBIC/μ-XRF/μ-XAS/DLTS investigation of chemical character and electrical properties of Cu and Ni precipitates in silicon. Phys. Status Solidi C 6(8), 1868 (2009).
T.A. Lafford, J. Villanova, N. Plassat, S. Dubois, and D. Camel: Synchrotron X-ray imaging applied to solar photovoltaic silicon. J. Phys.: Conf. Ser. 425(19), 192019 (2013).
T. Buonassisi, O.F. Vyvenko, A.A. Istratov, E.R. Weber, G. Hahn, D. Sontag, J-P. Rakotoniaina, O. Breitenstein, J. Isenberg, and R. Schindler: Assessing the role of transition metals in shunting mechanisms using synchrotron-based techniques. In 3rd IEEE World Conf. Photovolt. Energy Convers. (WCPEC-3 Organizing Committee, Osaka, 2003); pp. 1120–1123.
W. Seifert, O.F. Vyvenko, T. Arguirov, A. Erko, M. Kittler, C. Rudolf, M. Salome, M. Trushin, and I. Zizak: Synchrotron microscopy and spectroscopy for analysis of crystal defects in silicon. Phys. Status Solidi 6(3), 765 (2009).
W. Seifert, O. Vyvenko, T. Arguirov, M. Kittler, M. Salome, M. Seibt, and M. Trushin: Synchrotron-based investigation of iron precipitation in multicrystalline silicon. Superlattices Microstruct. 45(4–5), 168 (2009).
J. Villanova, J. Segura-Ruiz, T. Lafford, and G. Martinez-Criado: Synchrotron microanalysis techniques applied to potential photovoltaic materials. J. Synchrotron Radiat. 19(4), 521 (2012).
O.F. Vyvenko, T. Buonassisi, A.A. Istratov, E.R. Weber, M. Kittler, and W. Seifert: Application of synchrotron-radiation-based X-ray microprobe techniques for the analysis of recombination activity of metals precipitated at Si/SiGe misfit dislocations. J. Phys.: Condens. Matter 14, 13079 (2002).
R.R. Fahrtdinov, O.V. Feklisova, M.V. Grigoriev, D.V. Irzhak, D.V. Roshchupkin, and E.B. Yakimov: XBIC investigation of the grain boundaries in multicrystalline Si on the laboratory X-ray source. Solid State Phenom. 178–179, 226 (2011).
M.V. Grigoriev, R.R. Fakhrtdinov, D.V. Irzhak, D.V. Roshchupkin, and E.B. Yakimov: XBIC using a laboratory X-ray source. Bull. Russ. Acad. Sci.: Phys. 77(1), 21 (2013).
R.R. Fakhrtdinov, M.V. Grigoriev, and V.N. Pavlov: Optimization of the scanning process in the X-ray-beam-induced current method. J. Surf. Invest. 7(4), 685 (2013).
M.V. Grigoriev, D.V. Roshchupkin, R.R. Fakhrtdinov, and E.B. Yakimov: Studying stacking faults in SiC by the XBIC method using a laboratory X-ray source. J. Surf. Invest. 8(1), 155 (2014).
V.I. Orlov, O.V. Feklisova, and E.B. Yakimov: A comparison of EBIC, LBIC and XBIC methods as tools for multicrystalline Si characterization. Solid State Phenom. 205–206, 142 (2014).
Y.L. Shabel’nikova and E.B. Yakimov: Rate of generation of nonequilibrium charge carriers by a focused X-ray beam. J. Surf. Invest: X-Ray, Synchrotron Neutron Tech. 7(5), 859 (2013).
Y. Shabelnikova and E. Yakimov: Diffusion length and grain boundary recombination activity determination by means of induced current methods. Superlattices Microstruct. 99, 108 (2016).
Y.L. Shabel’nikova and E.B. Yakimov: Comparison between the EBIC and XBIC contrasts of dislocations and grain boundaries. J. Surf. Invest.: X-Ray, Synchrotron Neutron Tech. 6(6), 894 (2012).
Y.L. Shabel’nikova, E.B. Yakimov, M.V. Grigor’ev, R.R. Fahrtdinov, V.A. Bushuev, and A. Bushuev: Calculating the extended defect contrast for the X-ray-beam-induced current method. Tech. Phys. Lett. 38(10), 913 (2012).
R.P. Winarski, M.V. Holt, V. Rose, P. Fuesz, D. Carbaugh, C. Benson, D. Shu, D. Kline, G. Brian Stephenson, I. McNulty, and J. Maser: A hard X-ray nanoprobe beamline for nanoscale microscopy. J. Synchrotron Radiat. 19(6), 1056 (2012).
B. West, S. Husein, M. Stuckelberger, B. Lai, J. Maser, B. Stripe, V. Rose, H. Guthrey, M. Al-jassim, and M. Bertoni: Correlation between grain composition and charge carrier collection in Cu(In,Ga)Se2 solar cells. In 2015 42nd IEEE Photovoltaic Specialists Conference (IEEE, New Orleans, 2015); p. 1.
B. West, M. Stuckelberger, H. Guthrey, L. Chen, B. Lai, J. Maser, J.J. Dynes, W. Shafarman, M. Al-Jassim, and M.I. Bertoni: Synchrotron X-ray characterization of alkali elements at grain boundaries in Cu(In,Ga)Se2 solar cells. In 2016 43rd IEEE Photovoltaic Specialists Conference (IEEE, Portland, 2016); p. 31–34.
B. West, M. Stuckelberger, A. Jeffries, S. Gangam, B. Lai, B. Stripe, J. Maser, V. Rose, S. Vogt, and M. Bertoni: X-ray fluorescence at nanoscale resolution for multicomponent layered structures: A solar cell case study. J. Synchrotron Radiat. 24, 288 (2017).
B.M. West, M. Stuckelberger, H. Guthrey, L. Chen, B. Lai, J. Maser, V. Rose, W. Shafarman, M. Al-Jassim, and M.I. Bertoni: Grain engineering: How nanoscale inhomogeneities can control charge collection in solar cells. Nano Energy 32, 488 (2017).
M. Stuckelberger, B. West, S. Husein, H. Guthrey, J. Maser, M. Al-Jassim, B. Stripe, V. Rose, and M.I. Bertoni: Latest developments in the X-ray based characterization of thin-film solar cells. In 2015 42nd IEEE Photovoltaic Specialists Conference (IEEE, New Orleans, 2015); p. 1–6.
B. Watts, D. Queen, A.L.D. Kilcoyne, T. Tyliszczak, F. Hellman, and H. Ade: Soft X-ray beam induced current technique. In 9th International Conference on X-ray Microscopy (IOP, Zurich, 2009); p. 12023.
M. Stuckelberger, T. Nietzold, G.N. Hall, B. West, J. Werner, C. Ballif, V. Rose, D.P. Fenning, and M.I. Bertoni: Elemental distribution and charge collection at the nanoscale on perovskite solar cells. 2016 43rd IEEE Photovoltaic Specialists Conference (IEEE, Portland, 2016); p. 1191.
M. Stuckelberger, T. Nietzold, G.N. Hall, B. West, J. Werner, B. Niesen, C. Ballif, V. Rose, D.P. Fenning, and M.I. Bertoni: Charge collection in hybrid perovskite solar cells: Relation to the nanoscale elemental distribution. IEEE J. Photovolt. 7(2), 590 (2017).
J. Hofstetter, D.P. Fenning, M.I. Bertoni, J.F. Lelievre, C. Del Canizo, and T. Buonassisi: Impurity-to-efficiency simulator: Predictive simulation of silicon solar cell performance based on iron content and distribution. Prog. Photovolt. Res. Appl. 19(4), 487 (2011).
P.T. Pinard, H. Demers, F. Salvat, and R. Gauvin: PyPenelope. Available at: http://pypenelope.sourceforge.net/ (accessed October 4, 2016).
F. Salvat, J.M. Fernandez-Varea, E. Acosta, and J. Sempau: PENELOPE, a code system for Monte Carlo simulation of electron and photon transport. Available at: http://www.oecd-nea.org/tools/abstract/detail/nea-1525 (accessed October 4, 2016).
M.E. Stuckelberger, B. West, and M.I. Bertoni: X-ray beam induced current: Measuring electrical properties of solar cells at multiple length scales. Manuscr. Prep. (2017).
R. Chakraborty, J. Serdy, B. West, M. Stuckelberger, B. Lai, J. Maser, M.I. Bertoni, M.L. Culpepper, and T. Buonassisi: Development of an in situ temperature stage for synchrotron X-ray spectromicroscopy. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 86(11), 113705 (2015).
K. Emery: Photovoltaic calibrations at the National Renewable Energy Laboratory and uncertainty analysis following the ISO 17025 guidelines. Technical Report, NREL, 2016.
F. Pianezzi, A. Chirilă, P. Plösch, S. Seyrling, B. Buecheler, L. Kranz, C. Fella, and A.N. Tiwari: Solar cells utilizing small molecular weight organic semiconductors. Prog. Photovolt. Res. Appl. 20, 253 (2012).
A. Gottwald, U. Kroth, M. Krumrey, M. Richter, F. Scholze, and G. Ulm: The PTB high-accuracy spectral responsivity scale in the VUV and X-ray range. Metrologia 43(2), S125 (2006).
C.A. Klein: Bandgap dependence and related features of radiation ionization energies in semiconductors. J. Appl. Phys. 39(4), 2029 (1968).
W. Yun, B. Lai, Z. Cai, J. Maser, D. Legnini, E. Gluskin, Z. Chen, A.A. Krasnoperova, Y. Vladimirsky, F. Cerrina, E. Di Fabrizio, and M. Gentili: Nanometer focusing of hard X-rays by phase zone plates. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 70(5), 2238 (1999).
S. Chen, J. Deng, Y. Yuan, C. Flachenecker, R. Mak, B. Hornberger, Q. Jin, D. Shu, B. Lai, J. Maser, C. Roehrig, T. Paunesku, S.C. Gleber, D.J. Vine, L. Finney, J. Vonosinski, M. Bolbat, I. Spink, Z. Chen, J. Steele, D. Trapp, J. Irwin, M. Feser, E. Snyder, K. Brister, C. Jacobsen, G. Woloschak, and S. Vogt: The bionanoprobe: Hard X-ray fluorescence nanoprobe with cryogenic capabilities. J. Synchrotron Radiat. 21(1), 66 (2014).
B. West, M. Stuckelberger, L. Chen, R. Lovelett, B. Lai, J. Maser, and M.I. Bertoni: Growth of Cu(In,Ga)(S,Se)2 films: Unravelling the mysteries by in situ X-ray imaging. In 2016 43rd IEEE Photovoltaic Specialists Conference (IEEE, Portland, 2016); p. 1.
B. West, H. Guthrey, L. Chen, A. Jeffries, S. Bernardini, B. Lai, J. Maser, W. Shafarman, M. Al-Jasim, and M. Bertoni: Electrical and compositional characterization of gallium grading in Cu(In,Ga)Se2 solar cells. In 2014 41st IEEE Photovoltaic Specialists Conference (IEEE, Denver, 2014); p. 1726.
S. Vogt: MAPS: A set of software tools for analysis and visualization of 3D X-ray fluorescence data sets. J. Phys. IV 104, 635 (2003).
National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST). Available at: https://www.nist.gov/ (accessed February 20, 2017).
AXO Dresden. Available at: http://www.axo-dresden.de/(accessed February 20, 2017).
T. Nietzold, B. West, M. Stuckelberger, B. Lai, S. Vogt, and M.I. Bertoni: Quantifying X-ray fluorescence data using MAPS. J. Visual Experiments (2017), in preparation.
M. Mantler: X-ray fluorescence analysis of multiple-layer films. Anal. Chem. Acta 188, 25 (1986).
D.K.G. de Boer: Calculation of X-ray fluorescence intensities from bulk and multilayer samples. X-Ray Spectrom. 19(3), 145 (1990).
B. Ravel and M. Newville: ATHENA, ARTEMIS, HEPHAESTUS: Data analysis for X-ray absorption spectroscopy using IFEFFIT. J. Synchrotron Radiat. 12(4), 537 (2005).
B. Ravel: Demeter Software Package. Available at: https://bruceravel.github.io/demeter/(accessed February 25, 2017).
M. Tsukahara, S. Mitrovic, V. Gajdosik, G. Margaritondo, L. Pournin, M. Ramaioli, D. Sage, Y. Hwu, M. Unser, and T.M. Liebling: Coupled tomography and distinct-element-method approach to exploring the granular media microstructure in a jamming hourglass. Phys. Rev. E 77(6), 61306 (2008).
J.W. Meyer: Determination of iron, calcium, and silicon in calcium silicates by X-ray fluorescence. Anal. Chem. 33(6), 692 (1961).
S.A. McHugo, A.C. Thompson, C. Flink, E.R. Weber, G. Lamble, B. Gunion, A. MacDowell, R. Celestre, H.A. Padmore, and Z. Hussain: Synchrotron-based impurity mapping. J. Cryst. Growth 210(1–3), 395 (2000).
S.A. McHugo, A.C. Thompson, A. Mohammed, G. Lamble, I. Périchaud, S. Martinuzzi, M. Werner, M. Rinio, W. Koch, H-U. Hoefs, and C. Haessler: Nanometer-scale metal precipitates in multicrystalline silicon solar cells. J. Appl. Phys. 89(8), 4282 (2001).
A.A. Istratov, H. Hieslmair, and E.R. Weber: Iron contamination in silicon technology. Appl. Phys. A 70, 489 (2000).
T. Buonassisi, A.A. Istratov, M. Heuer, M.A. Marcus, R. Jonczyk, J. Isenberg, B. Lai, Z. Cai, S. Heald, W. Warta, R. Schindler, G. Willeke, and E.R. Weber: Synchrotron-based investigations of the nature and impact of iron contamination in multicrystalline silicon solar cells. J. Appl. Phys. 97(7), 74901 (2005).
T. Buonassisi, M.A. Marcus, A. Istratov, M. Heuer, T.F. Ciszek, B. Lai, Z. Cai, and E.R. Weber: Analysis of copper-rich precipitates in silicon: Chemical state, gettering, and impact on multicrystalline silicon solar cell material. J. Appl. Phys. 97(6), 63503 (2005).
T. Buonassisi, A.A. Istratov, M.D. Pickett, M.A. Marcus, T.F. Ciszek, and E.R. Weber: Metal precipitation at grain boundaries in silicon: Dependence on grain boundary character and dislocation decoration. Appl. Phys. Lett. 89(4), 042102 (2006).
T. Buonassisi, A.A. Istratov, M.A. Marcus, M. Heuer, M.D. Pickett, B. Lai, Z. Cai, S.M. Heald, and E.R. Weber: Local measurements of diffusion length and chemical character of metal clusters in multicrystalline silicon. Solid State Phenom. 108–109, 577 (2005).
A.A. Istratov, T. Buonassisi, R.J. McDonald, A.R. Smith, R. Schindler, J.A. Rand, J.P. Kalejs, and E.R. Weber: Metal content of multicrystalline silicon for solar cells and its impact on minority carrier diffusion length. J. Appl. Phys. 94(10), 6552 (2003).
T. Buonassisi, A.A. Istratov, M.D. Pickett, J.P. Rakotoniaina, O. Breitenstein, M.A. Marcus, S.M. Heald, and E.R. Weber: Transition metals in photovoltaic-grade ingot-cast multicrystalline silicon: Assessing the role of impurities in silicon nitride crucible lining material. J. Cryst. Growth 287(2), 402 (2006).
T. Buonassisi, A.A. Istratov, S. Peters, C. Ballif, J. Isenberg, S. Riepe, W. Warta, R. Schindler, G. Willeke, Z. Cai, B. Lai, and E.R. Weber: Impact of metal silicide precipitate dissolution during rapid thermal processing of multicrystalline silicon solar cells. Appl. Phys. Lett. 87, 121918 (2005).
T. Buonassisi, A.A. Istratov, M.D. Pickett, M. Heuer, J.P. Kalejs, G. Hahn, M.A. Marcus, B. Lai, Z. Cai, S.M. Heald, T.F. Ciszek, R.F. Clark, D.W. Cunningham, A.M. Gabor, R. Jonczyk, S. Narayanan, E. Sauar, and E.R. Weber: Chemical natures and distributions of metal impurities in multicrystalline silicon materials. Prog. Photovolt. Res. Appl. 14(6), 512 (2006).
T. Buonassisi, M. Heuer, A.A. Istratov, M.D. Pickett, M.A. Marcus, B. Lai, Z. Cai, S.M. Heald, and E.R. Weber: Transition metal co-precipitation mechanisms in silicon. Acta Mater. 55(18), 6119 (2007).
S. Hudelson, B.K. Newman, S. Bernardis, D.P. Fenning, M.I. Bertoni, M.A. Marcus, S.C. Fakra, B. Lai, and T. Buonassisi: Retrograde melting and internal liquid gettering in silicon. Adv. Mater. 22(35), 3948 (2010).
D.P. Fenning, B.K. Newman, M.I. Bertoni, S. Hudelson, S. Bernardis, M.A. Marcus, S.C. Fakra, and T. Buonassisi: Local melting in silicon driven by retrograde solubility. Acta Mater. 61(12), 4320 (2013).
D.P. Fenning, J. Hofstetter, M.I. Bertoni, S. Hudelson, M. Rinio, J.F. Lelievre, B. Lai, C. Del Canizo, and T. Buonassisi: Iron distribution in silicon after solar cell processing: Synchrotron analysis and predictive modeling. Appl. Phys. Lett. 98, 162103 (2011).
D.P. Fenning, J. Hofstetter, A.E. Morishige, D.M. Powell, A. Zuschlag, G. Hahn, and T. Buonassisi: Darwin at high temperature: Advancing solar cell material design using defect kinetics simulations and evolutionary optimization. Adv. Energy Mater. 4(13), 1 (2014).
A. Haarahiltunen, H. Savin, M. Yli-Koski, H. Talvitie, M.I. Asghar, and J. Sinkkonen: As-grown iron precipitates and gettering in multicrystalline silicon. Mater. Sci. Eng., B 159–160, 248 (2009).
D.P. Fenning, J. Hofstetter, M.I. Bertoni, G. Coletti, B. Lai, C. Del Canizo, and T. Buonassisi: Precipitated iron: A limit on gettering efficacy in multicrystalline silicon. J. Appl. Phys. 113, 044521 (2013).
D.P. Fenning, A.S. Zuschlag, M.I. Bertoni, B. Lai, G. Hahn, and T. Buonassisi: Improved iron gettering of contaminated multicrystalline silicon by high-temperature phosphorus diffusion. J. Appl. Phys. 113, 214504 (2013).
J. Hofstetter, D.P. Fenning, D.M. Powell, A.E. Morishige, H. Wagner, and T. Buonassisi: Sorting metrics for customized phosphorus diffusion gettering. IEEE J. Photovolt. 4(6), 1421 (2014).
M.A. Jensen, J. Hofstetter, A.E. Morishige, G. Coletti, B. Lai, D.P. Fenning, and T. Buonassisi: Synchrotron-based analysis of chromium distributions in multicrystalline silicon for solar cells. Appl. Phys. Lett. 106(20), 202104 (2015).
W.K. Kim, E.A. Payzant, S. Yoon, and T.J. Anderson: In situ investigation on selenization kinetics of Cu–In precursor using time-resolved, high temperature X-ray diffraction. J. Cryst. Growth 294(2), 231 (2006).
R. Mainz and R. Klenk: In situ analysis of elemental depth distributions in thin films by combined evaluation of synchrotron X-ray fluorescence and diffraction. J. Appl. Phys. 109, 123515 (2011).
D.M. Berg, F. Cheng, and W.N. Shafarman: H2S reaction of Se-capped metallic precursors to form Cu(In,Ga)(S,Se)2 absorber layers. 2014 41st IEEE Photovoltaic Specialists Conference (IEEE, Denver, 2014); p. 323.
L. Chen, J. Lee, and W.N. Shafarman: The comparison of (Ag,Cu)(In,Ga)Se2 and Cu(In,Ga)Se2 thin films deposited by three-stage coevaporation. IEEE J. Photovolt. 4(1), 447 (2014).
A.E. Morishige, H.S. Laine, M.A. Jensen, P.X.T. Yen, E.E. Looney, S. Vogt, B. Lai, H. Savin, and T. Buonassisi: Accelerating synchrotron-based characterization of solar materials: Development of flyscan capability. 2016 43rd IEEE Photovoltaic Specialists Conference (IEEE, Portland, 2016); p. 2006.
M. Jørgensen, K. Norrman, S.A. Gevorgyan, T. Tromholt, B. Andreasen, and F.C. Krebs: Stability of polymer solar cells. Adv. Mater. 24(5), 580 (2012).
D.M. Tanenbaum, M. Hermenau, E. Voroshazi, M.T. Lloyd, Y. Galagan, B. Zimmermann, M. Hosel, H.F. Dam, M. Jørgensen, S.A. Gevorgyan, S. Kudret, W. Maes, L. Lutsen, D. Vanderzande, U. Wurfel, R. Andriessen, R. Rosch, H. Hoppe, G. Teran-Escobar, M. Lira-Cantu, A. Rivaton, G.Y. Uzunoglu, D. Germack, B. Andreasen, M.V. Madsen, K. Norrman, and F.C. Krebs: The ISOS-3 inter-laboratory collaboration focused on the stability of a variety of organic photovoltaic devices. RSC Adv. 2, 882 (2012).
B.A. Collins, J.R. Tumbleston, and H. Ade: Miscibility, crystallinity, and phase development in P3HT/PCBM solar cells: Toward an enlightened understanding of device morphology and stability. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2(24), 3135 (2011).
B.A. Collins, J.E. Cochran, H. Yan, E. Gann, C. Hub, R. Fink, C. Wang, T. Schuettfort, C.R. McNeill, M.L. Chabinyc, and H. Ade: Polarized X-ray scattering reveals non-crystalline orientational ordering in organic films. Nat. Mater. 11(6), 536 (2012).
M.P. Nikiforov, B. Lai, W. Chen, S. Chen, R.D. Schaller, J. Strzalka, J. Maser, and S.B. Darling: Detection and role of trace impurities in high-performance organic solar cells. Energy Environ. Sci. 6(5), 1513 (2013).
T. Agostinelli, S. Lilliu, J.G. Labram, M. Campoy-Quiles, M. Hampton, E. Pires, J. Rawle, O. Bikondoa, D.D.C. Bradley, T.D. Anthopoulos, J. Nelson, and J.E. MacDonald: Real-time investigation of crystallization and phase-segregation dynamics in P3HT:PCBM solar cells during thermal annealing. Adv. Funct. Mater. 21(9), 1701 (2011).
S. Lilliu, T. Agostinelli, E. Pires, M. Hampton, J. Nelson, and J.E. MacDonald: Dynamics of crystallization and disorder during annealing of P3HT/PCBM bulk heterojunctions. Macromolecules 44(8), 2725 (2011).
Z.M. Beiley, E.T. Hoke, R. Noriega, J. Dacuña, G.F. Burkhard, J.A. Bartelt, A. Salleo, M.F. Toney, and M.D. McGehee: Morphology-dependent trap formation in high performance polymer bulk heterojunction solar cells. Adv. Energy Mater. 1(5), 954 (2011).
J.A. Bartelt, Z.M. Beiley, E.T. Hoke, W.R. Mateker, J.D. Douglas, B.A. Collins, J.R. Tumbleston, K.R. Graham, A. Amassian, H. Ade, J.M.J. Fréchet, M.F. Toney, and M.D. McGhee: The importance of fullerene percolation in the mixed regions of polymer–fullerene bulk heterojunction solar cells. Adv. Energy Mater. 3(3), 364 (2013).
J. Rivnay, R. Steyrleuthner, L.H. Jimison, A. Casadei, Z. Chen, M.F. Toney, A. Facchetti, D. Neher, and A. Salleo: Drastic control of texture in a high performance n-type polymeric semiconductor and implications for charge transport. Macromolecules 44(13), 5246 (2011).
S. Qian, S. Misra, J. Lu, Z. Yu, L. Yu, J. Xu, J. Wang, L. Xu, Y. Shi, K. Chen, and P.R.i. Cabarrocas: Full potential of radial junction Si thin film solar cells with advanced junction materials and design. Appl. Phys. Lett. 107(4), 43902 (2015).
J-H. Im, J. Luo, M. Franckevicius, N. Pellet, P. Gao, T. Moehl, S.M. Zakeeruddin, M.K. Nazeeruddin, M. Grätzel, and N-G. Park: Nanowire perovskite solar cell. Nano Lett. 15(3), 2120 (2015).
J. Wallentin, N. Anttu, D. Asoli, M. Huffman, I. Aberg, M.H. Magnusson, G. Siefer, P. Fuss-Kailuweit, F. Dimroth, B. Witzigmann, H.Q. Xu, L. Samuelson, K. Deppert, M.T. Borgström, W.U. Huynh, J.J. Dittmer, A.P. Alivisatos, B. O’Regan, M. Grätzel, A. Polman, H.A. Atwater, T. Mårtensson, C. Colombo, M. Heiβ, M. Grätzel, A. Fontcuberta i Morral, J.F. Wang, M.S. Gudiksen, X. Duan, Y. Cui, C.M. Lieber, M.T. Borgström, E.C. Garnett, M.L. Brongersma, Y. Cui, M.D. McGehee, H. Goto, J. Kupec, R.L. Stoop, B. Witzigmann, L. Hu, G. Chen, N. Anttu, H.Q. Xu, M.D. Kelzenberg, E. Garnett, P.D. Yang, M.A. Green, K. Emery, Y. Hishikawa, W. Warta, E.D. Dunlop, M.T. Borgström, T. Mårtensson, N. Anttu, H.Q. Xu, P.M. Wu, N. Anttu, H.Q. Xu, L. Samuelson, M.E. Pistol, S. Münch, H.J. Joyce, A. Mishra, M.H.M. van Weert, A. Yella, A.H. Ip, E. Popov, M. Nevière, B. Gralak, G. Tayeb, J.G.E. Jellison, and F.A. Modine: InP nanowire array solar cells achieving 13.8% efficiency by exceeding the ray optics limit. Science 339(6123), 1057 (2013).
P. Parkinson, Y.H. Lee, L. Fu, S. Breuer, H.H. Tan, and C. Jagadish: Three-dimensional in situ photocurrent mapping for nanowire photovoltaics. Nano Lett. 13(4), 1405 (2013).
P. Krogstrup, H.I. Jørgensen, M. Heiss, O. Demichel, J.V. Holm, M. Aagesen, J. Nygard, and A. Fontcuberta i Morral: Single-nanowire solar cells beyond the Shockley–Queisser limit. Nat. Photonics 7, 306 (2013).
J. Segura-Ruiz, G. Martínez-Criado, C. Denker, J. Malindretos, and A. Rizzi: Phase separation in single InxGa1− xN nanowires revealed through a hard X-ray synchrotron nanoprobe. Nano Lett. 14, 1300 (2014).
J. Segura-Ruiz, G. Martínez-Criado, M.H. Chu, C. Denker, J. Malindretos, and A. Rizzi: Synchrotron nanoimaging of single In-rich InGaN nanowires. J. Appl. Phys. 113, 136511 (2013).
G. Martínez-Criado, J. Segura-Ruiz, B. Alén, J. Eymery, A. Rogalev, R. Tucoulou, and A. Homs: Exploring single semiconductor nanowires with a multimodal hard X-ray nanoprobe. Adv. Mater. 26(46), 7873 (2014).
G. Martínez-Criado, A. Homs, B. Alén, J.A. Sans, J. Segura-Ruiz, A. Molina-Sanchez, J. Susini, J. Yoo, and G.C. Yi: Probing quantum confinement within single core-multishell nanowires. Nano Lett. 12(11), 5829 (2012).
M.H. Chu, G. Martínez-Criado, J. Segura-Ruiz, S. Geburt, and C. Ronning: Local lattice distortions in single Co-implanted ZnO nanowires. Appl. Phys. Lett. 103, 141911 (2013).
M.H. Chu, G. Martínez-Criado, J. Segura-Ruiz, S. Geburt, and C. Ronning: Structural order in single Co-implanted ZnO nanowires. Phys. Status Solidi 211(2), 483 (2014).
R.A. Rosenberg, G.K. Shenoy, F. Heigl, S-T. Lee, P-S.G. Kim, X-T. Zhou, and T.K. Sham: Determination of the local structure of luminescent sites in ZnS nanowires using x-ray excited optical luminescence. Appl. Phys. Lett. 87, 253105 (2005).
E.L. Unger, A.R. Bowring, C.J. Tassone, V.L. Pool, A. Gold-Parker, R. Cheacharoen, K.H. Stone, E.T. Hoke, M.F. Toney, and M.D. McGehee: Chloride in lead chloride-derived organo-metal halides for perovskite-absorber solar cells. Chem. Mater. 26(24), 7158 (2014).
J. Werner, G. Dubuis, A. Walter, P. Löper, S-J. Moon, S. Nicolay, M. Morales-Masis, S. De Wolf, B. Niesen, and C. Ballif: Sputtered rear electrode with broadband transparency for perovskite solar cells. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 141, 407 (2015).
M. Stuckelberger, T. Nietzold, G. Hall, B. West, X. Meng, J. Werner, B. Niesen, B. Lai, J. Maser, V. Rose, C. Ballif, and M.I. Bertoni: Low degradation of metal-halide perovskite layers under x-ray irradiation enables synchrotron-based characterization methods. Presented at the MRS Spring Meet. (MRS, Phoenix, 2016).
S.Y. Leblebici, L. Leppert, Y. Li, S.E. Reyes-Lillo, S. Wickenburg, E. Wong, J. Lee, M. Melli, D. Ziegler, D.K. Angell, D.F. Ogletree, P.D. Ashby, F.M. Toma, J.B. Neaton, I.D. Sharp, and A. Weber-Bargioni: Facet-dependent photovoltaic efficiency variations in single grains of hybrid halide perovskite. Nat. Energy 1(8), 16093 (2016).
E. Nazaretski, W. Xu, N. Bouet, J. Zhou, H. Yan, X. Huang, and Y.S. Chu: Development and characterization of monolithic multilayer Laue lens nanofocusing optics. Appl. Phys. Lett. 108, 261102 (2016).
Y. Chu, H. Yan, E. Nazaretski, S. Kalbfleisch, X. Huang, K. Lauer, and N. Bouet: NSLS HXN News: Hard X-ray nanoprobe facility at the national synchroton light source II. SPIE Newsroom, August 31, 2015.
J. Maser, B. Lai, T. Buonassisi, Z. Cai, S. Chen, L. Finney, S-C. Gleber, C. Jacobsen, C. Preissner, C. Roehrig, V. Rose, D. Shu, D. Vine, and S. Vogt: A next-generation hard X-ray nanoprobe beamline for in situ studies of energy materials and devices. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 45(1), 85 (2014).
M.L. Cummings, T.Y. Chien, C. Preissner, V. Madhavan, D. Diesing, M. Bode, J.W. Freeland, and V. Rose: Combining scanning tunneling microscopy and synchrotron radiation for high-resolution imaging and spectroscopy with chemical, electronic, and magnetic contrast. Ultramicroscopy 112, 22 (2012).
N. Shirato, M. Cummings, H. Kersell, Y. Li, B. Stripe, D. Rosenmann, S.W. Hla, and V. Rose: Elemental fingerprinting of materials with sensitivity at the atomic limit. Nano Lett. 14(11), 6499 (2014).
W. Yang, X. Huang, R. Harder, J.N. Clark, I.K. Robinson, and H. Mao: Coherent diffraction imaging of nanoscale strain evolution in a single crystal under high pressure. Nat. Commun. 4, 1680 (2013).
M. Dierolf, A. Menzel, P. Thibault, P. Schneider, C.M. Kewish, R. Wepf, O. Bunk, and F. Pfeiffer: Ptychographic X-ray computed tomography at the nanoscale. Nature 467(7314), 436 (2010).
A. Ulvestad, A. Singer, J.N. Clark, H.M. Cho, J.W. Kim, R. Harder, J. Maser, Y.S. Meng, and O.G. Shpyrko: Topological defect dynamics in operando battery nanoparticles. Science 348(6241), 1344 (2015).
A. Ulvestad, M.J. Welland, W. Cha, Y. Liu, J.W. Kim, R. Harder, E. Maxey, J.N. Clark, M.J. Highland, H. You, P. Zapol, S.O. Hruszkewycz, and G.B. Stephenson: Three-dimensional imaging of dislocation dynamics during the hydriding phase transformation. Nat. Mater. 4842, 1 (2017).
Y. Liu, P.P. Lopes, W. Cha, R. Harder, J. Maser, E. Maxey, M.J. Highland, N.M. Markovic, S.O. Hruszkewycz, G.B. Stephenson, H. You, and A. Ulvestad: Stability limits and defect dynamics in Ag nanoparticles probed by Bragg coherent diffractive imaging. Nano Lett. 17(3), 1595 (2017).
D. Einfeld: Multi-bend achromat lattices for storage ring light sources. Synchrotron Radiat. News 27(6), 4 (2014).
R.C. Alig, S. Bloom, and C.W. Struck: Scattering by ionization and phonon emission in semiconductors. Phys. Rev. B: Condens. Matter Mater. Phys. 22(12), 5565 (1980).
A. Walsh and K.T. Butler: Prediction of electron energies in metal oxides. Acc. Chem. Res. 47(2), 364 (2014).
S.O. Kasap and J.A. Rowlands: Direct-conversion flat-panel X-ray image sensors for digital radiography. Proc. IEEE 90(4), 591 (2002).
J. Emara, T. Schnier, N. Pourdavoud, T. Riedl, K. Meerholz, and S. Olthof: Impact of film stoichiometry on the ionization energy and electronic structure of CH3NH3PbI3 perovskites. Adv. Mater. 28(3), 553 (2016).
J. Grant, W. Cunningham, A. Blue, V. O’Shea, J. Vaitkus, E. Baubas, and M. Rahman: Wide bandgap semiconductor detectors for harsh radiation environments. Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res., Sect. A 546, 213 (2005).
A. Owens and A. Peacock: Compound semiconductor radiation detectors. Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res., Sect. A 531, 18 (2004).
S. Awadalla: Solid-state Radiation Detectors: Technology and Applications (CRC Press, Boca Raton, 2015).
L.I. Berger: Handbook of Chemistry and Physics (CRC Press, Boca Raton, 2015).
S.J. Pearton, C.R. Abernathy, M.E. Overberg, G.T. Thaler, D.P. Norton, N. Theodoropoulou, A.F. Hebard, Y.D. Park, F. Ren, J. Kim, and L.A. Boatner: Wide band gap ferromagnetic semiconductors and oxides. J. Appl. Phys. 93(1), 1 (2003).
O.E. Semonin, J.M. Luther, S. Choi, H-Y. Chen, J. Gao, A.J. Nozik, and M.C. Beard: Peak external photocurrent quantum efficiency exceeding 100% via MEG in a quantum dot solar cell. Science 334, 1530 (2011).
W.T. Elam, B.D. Ravel, and J.R. Sieber: A new atomic database for X-ray spectroscopic calculations. Radiat. Phys. Chem. 63(2), 121 (2002).
B.L. Henke: X-ray interactions with matter. Available at: http://henke.lbl.gov/optical_constants/ (accessed February 25, 2017).
V.A. Solé, E. Papillon, M. Cotte, P. Walter, and J. Susini: A multiplatform code for the analysis of energy-dispersive X-ray fluorescence spectra. Spectrochim. Acta, Part B 62(1), 63 (2007).
PyMCA. Available at: http://pymca.sourceforge.net/index.html (accessed February 26, 2017).
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
We greatly acknowledge Jérémie Werner, Bjoern Niesen, Christophe Ballif (all EPFL, Switzerland), Harvey Guthrey, Mowafak Al-Jassim (all NREL, USA), Lei Chen, William Shafarman (all U. of Delaware, USA) for providing solar cells; Rupak Chakraborty, Jim Serdy, Tonio Buonassisi (all MIT, USA) for their contributions building the heating stage, David Fenning (UC San Diego, USA) for fruitful discussions, Chris Roehrig and Martin Holt (both ANL, USA) for practical help with XBIC measurements, Yanqi Luo (UC San Diego, USA) for measurement of the PbI2 reference, and Genevieve Hall, Sebastian Husein, Srikanth Gangam, and April Jeffries (all ASU, USA) for their contribution to measurements and discussions.
We acknowledge funding from the U.S. Department of Energy under contract DEEE0005848. Use of the Center for Nanoscale Materials and the Advanced Photon Source, both Office of Science user facilities, was supported by the U.S. Department of Energy, Office of Science, Office of Basic Energy Sciences, under Contract No. DE-AC02-06CH11357. This material is based upon work supported in part by the National Science Foundation (NSF) and the Department of Energy (DOE) under NSF CA No. EEC-1041895. Any opinions, findings and conclusions or recommendations expressed in this material are those of the author(s) and do not necessarily reflect those of NSF or DOE.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Stuckelberger, M., West, B., Nietzold, T. et al. Engineering solar cells based on correlative X-ray microscopy. Journal of Materials Research 32, 1825–1854 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1557/jmr.2017.108
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1557/jmr.2017.108