Abstract
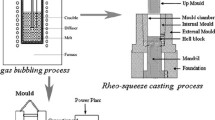
In this study, semi-solid slurry of AZ91–2 wt% Ca (AZ91–2Ca) alloy was prepared by gas bubbling and shaped by rheo-squeeze casting process. The results indicate that fine semi-solid slurry of AZ91–2Ca alloy could be obtained by gas bubbling within 30 s, with primary α-Mg particles having an average diameter less than 50 μm and average shape factor higher than 0.7. With the decrease of pouring temperature from 599 to 590 °C, both tensile strength and elongation of rheo-squeeze casting AZ91–2Ca alloy first increased and then decreased. The rheo-squeeze casting AZ91–2Ca alloy sample prepared at pouring temperature of 596 °C exhibited the peak tensile strength and elongation. Compared with conventional squeeze casting, the improvement in mechanical properties of rheo-squeeze casting AZ91–2Ca alloy was mainly attributed to the grain refinement strengthening, including the refinement and spheroidization of primary α-Mg particles and the refinement in the residual melt.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
M.C. Flemings: Behavior of metal alloys in the semisolid state. Metall. Trans. B 22 (3), 269 (1991).
D.H. Kirkwood: Semisolid metal processing. Int. Mater. Rev. 39 (5), 173 (1994).
Z. Fan: Semisolid metal processing. Int. Mater. Rev. 47 (2), 49 (2002).
Z. Xiao, J. Luo, S. Wu, D. Li, Y. Mao, and X. Song: Study on a semi-solid rheo-diecasting process with AZ91D alloy slurry. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 13 (1), 60 (2004).
S. Lü, S. Wu, W. Dai, C. Lin, and P. An: The indirect ultrasonic vibration process for rheo-squeeze casting of A356 aluminum alloy. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 212 (6), 1281 (2012).
S. Lü, S. Wu, L. Wan, and P. An: Microstructure and tensile properties of wrought Al alloy 5052 produced by rheo-squeeze casting. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 44 (6), 2735 (2013).
S. Wu, G. Zhong, P. An, L. Wan, and H. Nakae: Microstructural characteristics of Al–20Si–2Cu–0.4 Mg–1Ni alloy formed by rheo-squeeze casting after ultrasonic vibration treatment. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 22 (12), 2863 (2012).
W. Dai, S. Wu, S. Lü, and C. Lin: Effects of rheo-squeeze casting parameters on microstructure and mechanical properties of AlCuMnTi alloy. Mater. Sci. Eng., A 538, 320 (2012).
C. Yim and K. Shin: Changes in microstructure and hardness of rheocast AZ91HP magnesium alloy with stirring conditions. Mater. Sci. Eng., A 395, 226 (2005).
X.L. Zhang, T.J. Li, S.S. Xie, H.T. Teng, and J.Z. Jin: Microstructure analysis of rheoformed AZ91 alloy produced by rotating magnetic fields. J. Alloys Compd. 461 (1), 106 (2008).
S. Wu, S. Lü, P. An, and H. Nakae: Microstructure and property of rheocasting aluminum-alloy made with indirect ultrasonic vibration process. Mater. Lett. 73, 150 (2012).
J. Wannasin, R. Martinez, and M. Flemings: Grain refinement of an aluminum alloy by introducing gas bubbles during solidification. Scr. Mater. 55 (2), 115 (2006).
W. Qudong, C. Wenzhou, Z. Xiaoqin, L. Yizhen, D. Wenjiang, Z. Yanping, and X. Xiaoping: Effects of Ca addition on the microstructure and mechanical properties of AZ91magnesium alloy. J. Mater. Sci. 36 (12), 3035 (2001).
G. Wu, Y. Fan, H. Gao, C. Zhai, and Y.P. Zhu: The effect of Ca and rare earth elements on the microstructure, mechanical properties and corrosion behavior of AZ91D. Mater. Sci. Eng., A 408, 255 (2005).
R. Canyook, S. Petsut, S. Wisutmethangoon, and M. Flemings, J. Wannasin: Evolution of microstructure in semi-solid slurries of rheocast aluminum alloy. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 20 (9), 1649 (2010).
R. Canyook, J. Wannasin, S. Wisuthmethangkul, and M. Flemings: Characterization of the microstructure evolution of a semi-solid metal slurry during the early stages. Acta Mater. 60 (8), 3501 (2012).
Z. Fan and G. Liu: Solidification behaviour of AZ91D alloy under intensive forced convection in the RDC process. Acta Mater. 53 (16), 4345 (2005).
Z. Fan, G. Liu, and M. Hitchcock: Solidification behaviour under intensive forced convection. Mater. Sci. Eng., A 413, 229 (2005).
S. Liang, R. Chen, J. Blandin, M. Suery, and E. Han: Thermal analysis and solidification pathways of Mg–Al–Ca system alloys. Mater. Sci. Eng., A 480, 365 (2008).
H.M. Guo, A.S. Zhang, B. Hu, Y. Ding, and X.B. Liu: Refining microstructure of AZ91 magnesium alloy by introducing limited angular oscillation during initial stage of solidification. Mater. Sci. Eng., A 532, 221 (2012).
S. Kleiner, E. Ogris, O. Beffort, and P.J. Uggowitzer: Semi-solid metal processing of aluminum alloy A356 and magnesium alloy AZ91: Comparison based on metallurgical consideration. Adv. Eng. Mater. 5 (9), 653 (2003).
S. Nafisi and R. Ghomashchi: Effects of modification during conventional and semi-solid metal processing of A356 Al-Si alloy. Mater. Sci. Eng., A 415, 273 (2006).
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
This work was financially supported by Science Research Fund for the Doctoral Program of Higher Education of China (Nos. 20120073120011 and 20130073110052), National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 51275295), and Shanghai Yang-Fan Program (No. 14YF1402000).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, Y., Wu, G., Liu, W. et al. Preparation and rheo-squeeze casting of semi-solid AZ91–2 wt% Ca magnesium alloy by gas bubbling process. Journal of Materials Research 30, 825–832 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1557/jmr.2015.36
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1557/jmr.2015.36