Abstract
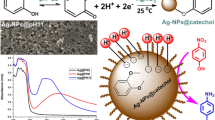
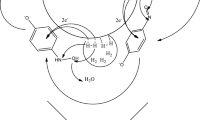
A simple and efficient method for in situ preparation of highly stable polyimide (PI)-supported silver nanoparticles (AgNPs) was proposed. This process achieves excellent dispersion and high stability of AgNPs in the PI matrix. The formation of AgNPs in PI and the morphology evolution of PI/Ag nanocomposites were characterized by x-ray diffraction, transmission electron microscopy, Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FT-IR), and x-ray photoelectron spectra studies. The catalytic properties of these PI-supported AgNPs were investigated by monitoring the reduction of 4-nitrophenol by excess NaBH4 in water. The catalytic reaction was observed to have a pseudo first-order rate constant of 0.567 min−1 (9.45 × 10−3 s−1), which is comparable to other heterogeneous silver catalysts reported in the literature. Notably, the PI-supported AgNPs retained their relatively high catalytic activity over seven recycles with almost no leaching of catalytic species in the reaction solution. Moreover, the catalytic activity of the catalyst is still quite appreciable even after a six-month shelf-storage under room temperature.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Y. Zhu, C.N. Lee, R.A. Kemp, N.S. Hosmane, and J.A. Maguire: Latest developments in the catalytic application of nanoscaled neutral group 8–10 metals. Chem. — Asian J. 3, 650 (2008).
J.M. Campelo, D. Luna, R. Luque, J.M. Marinas, and A.A. Romero: Sustainable preparation of supported metal nanoparticles and their applications in catalysis. ChemSusChem 2, 18 (2009).
N.J. Halas, S. Lal, W-S. Chang, S. Link, and P. Nordlander: Plasmons in strongly coupled metallic nanostructures. Chem. Rev. 111, 3913 (2011).
P.K. Jain, X. Huang, I.H. El-Sayed, and M.A. El-Sayed: Noble metals on the nanoscale: optical and photothermal properties and some applications in imaging, sensing, biology, and medicine. Acc. Chem. Res. 41, 1578 (2008).
J.A. Polo and A. Lakhtakia: Surface electromagnetic waves: A review. Laser Photonics Rev. 5, 234 (2011).
C. Marambio-Jones and E.M. Hoek: A review of the antibacterial effects of silver nanomaterials and potential implications for human health and the environment. J. Nanopart. Res. 12, 1531 (2010).
M. Zhu, C. Wang, D. Meng, and G. Diao: In situ synthesis of silver nanostructures on magnetic Fe3O4@C core–shell nanocomposites and their application in catalytic reduction reactions. J. Mater. Chem. A 1, 2118 (2013).
S. Jana, S.K. Ghosh, S. Nath, S. Pande, S. Praharaj, S. Panigrahi, S. Basu, T. Endo, and T. Pal: Synthesis of silver nanoshell-coated cationic polystyrene beads: A solid phase catalyst for the reduction of 4-nitrophenol. Appl. Catal., A 313, 41 (2006).
P. Christopher and S. Linic: Shape- and size-specific chemistry of Ag nanostructures in catalytic ethylene epoxidation. ChemCatChem 2, 78 (2010).
D-H. Zhang, H-B. Li, G-D. Li, and J-S. Chen: Magnetically recyclable Ag-ferrite catalysts: General synthesis and support effects in the epoxidation of styrene. Dalton Trans. 47, 10527 (2009).
P. Zhang, C. Shao, Z. Zhang, M. Zhang, J. Mu, Z. Guo, and Y. Liu: In situ assembly of well-dispersed Ag nanoparticles (AgNPs) on electrospun carbon nanofibers (CNFs) for catalytic reduction of 4-nitrophenol. Nanoscale 3, 3357 (2011).
A. Murugadoss and A. Chattopadhyay: A’green’chitosan–silver nanoparticle composite as a heterogeneous as well as micro-heterogeneous catalyst. Nanotechnology 19, 015603 (2008).
A.M. Signori, K.d.O. Santos, R. Eising, B.L. Albuquerque, F.C. Giacomelli, and J.B. Domingos: Formation of catalytic silver nanoparticles supported on branched polyethyleneimine derivatives. Langmuir 26, 17772 (2010).
C. Wang, H. Yin, R. Chan, S. Peng, S. Dai, and S. Sun: One-pot synthesis of oleylamine coated AuAg alloy NPs and their catalysis for CO oxidation. Chem. Mater. 21, 433 (2009).
R.B. Merrifield: Solid phase peptide synthesis. I. The synthesis of a tetrapeptide. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 85, 2149 (1963).
D.E. Bergbreiter, J. Tian, and C. Hongfa: Using soluble polymer supports to facilitate homogeneous catalysis. Chem. Rev. 109, 530 (2009).
J. Lu and P.H. Toy: Organic polymer supports for synthesis and for reagent and catalyst immobilization. Chem. Rev. 109, 815 (2009).
B. Clapham, T.S. Reger, and K.D. Janda: Polymer-supported catalysis in synthetic organic chemistry. Tetrahedron 57, 4637 (2001).
L. Wu, Y. Zhang, and Y-G. Ji: Homogeneous recyclable catalysts based on metal nanoparticles for organic synthesis. Curr. Org. Chem. 17, 1288 (2013).
Y. Wang, Z. Xiao, and L. Wu: Metal-nanoparticles supported on solid as heterogeneous catalysts. Curr. Org. Chem. 17, 1325 (2013).
P.G.N. Mertens, P. Vandezande, X. Ye, H. Poelman, D.E. De Vos, and I.F.J. Vankelecom: Membrane-occluded gold-palladium nanoclusters as heterogeneous catalysts for the selective oxidation of alcohols to carbonyl compounds. Adv. Synth. Catal. 350, 1241 (2008).
B.M. Dioos, I.F. Vankelecom, and P.A. Jacobs: Aspects of immobilisation of catalysts on polymeric supports. Adv. Synth. Catal. 348, 1413 (2006).
D-J. Liaw, K-L. Wang, Y-C. Huang, K-R. Lee, J-Y. Lai, and C-S. Ha: Advanced polyimide materials: Syntheses, physical properties and applications. Prog. Polym. Sci. 37, 907 (2012).
A. Quaranta, S. Carturan, M. Bonafini, G. Maggioni, M. Tonezzer, G. Mattei, C. de Julian Fernandez, G. Della Mea, and P. Mazzoldi: Optical sensing to organic vapors of fluorinated polyimide nanocomposites containing silver nanoclusters. Sens. Actuators, B 118, 418 (2006).
K. Vanherck, I. Vankelecom, and T. Verbiest: Improving fluxes of polyimide membranes containing gold nanoparticles by photothermal heating. J. Membr. Sci. 373, 5 (2011).
S.R. Halper and R.M. Villahermosa: Cobalt-containing polyimides for moisture sensing and absorption. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 1, 1041 (2009).
S. Park, K. Kim, D.M. Kim, W. Kwon, J. Choi, and M. Ree: High temperature polyimide containing anthracene moiety and its structure, and interface, and nonvolatile memory behavior. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 3, 765 (2011).
C. Samyn, T. Verbiest, and A. Persoons: Second-order non-linear optical polymers. Macromol. Rapid Commun. 21(1), 1–15 (2000).
Y. Matsumura, Y. Enomoto, T. Tsuruoka, K. Akamatsu, and H. Nawafune: Fabrication of copper damascene patterns on polyimide using direct metallization on trench templates generated by imprint lithography. Langmuir 26, 12448 (2010).
J-H. Ahn, J-C. Kim, S-K. Ihm, C-G. Oh, and D.C. Sherrington: Epoxidation of olefins by molybdenum (VI) catalysts supported on functional polyimide particulates. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 44, 8560 (2005).
R. Jin, Z. Bian, J. Li, M. Ding, and L. Gao: ZIF-8 crystal coatings on a polyimide substrate and their catalytic behaviours for the Knoevenagel reaction. Dalton Trans. 42, 3936 (2013).
J-H. Ahn and D.C. Sherrington: Wacker oxidation of Oct-1-ene using a palladium (II) complex supported on cyano-functionalized polyimide beads. Macromolecules 29, 4164 (1996).
J. Huang, X. Qian, J. Yin, Z. Zhu, and H. Xu: Preparation of soluble polyimide–silver nanocomposites by a convenient ultraviolet irradiation technique. Mater. Chem. Phys. 69, 172 (2001).
Q. Zhang, D. Wu, S. Qi, Z. Wu, X. Yang, and R. Jin: Preparation of ultra-fine polyimide fibers containing silver nanoparticles via in situ technique. Mater. Lett. 61, 4027 (2007).
J. Li, Y. Fang, G. He, and H. Li: Preparation and characterization of poly (amic acid)-stabilized silver nanoparticles. J. Cent. South Univ. 20, 1475 (2013).
P. Herves, M. Pérez-Lorenzo, L.M. Liz-Marzán, J. Dzubiella, Y. Lu, and M. Ballauff: Catalysis by metallic nanoparticles in aqueous solution: Model reactions. Chem. Soc. Rev. 41, 5577 (2012).
R.E. Southward and D.M. Stoakley: Reflective and electrically conductive surface silvered polyimide films and coatings prepared via unusual single-stage self-metallization techniques. Prog. Org. Coat. 41, 99 (2001).
R.E. Southward and D.W. Thompson: Metal-polyimide nanocomposite films: Single-stage synthesis of silvered polyimide films prepared from silver (I) complexes and BPDA/4, 4’-ODA. Chem. Mater. 16, 1277 (2004).
S. Qi, X. Shen, Z. Lin, G. Tian, D. Wu, and R. Jin: Synthesis of silver nanocubes with controlled size using water-soluble poly (amic acid) salt as the intermediate via a novel ion-exchange self-assembly technique. Nanoscale 5, 12132 (2013).
N. Du, C. Wong, M. Feurstein, O.A. Sadik, C. Umbach, and B. Sammakia: Flexible poly (amic acid) conducting polymers: Effect of chemical composition on structural, electrochemical, and mechanical properties. Langmuir 26, 14194 (2010).
X. Fang, Z. Wang, Z. Yang, L. Gao, Q. Li, and M. Ding: Novel polyimides derived from 2, 3, 3′, 4′-benzophenonetetracarboxylic dianhydride. Polymer 44, 2641 (2003).
R.E. Southward, D.S. Thompson, D.W. Thompson, M.L. Caplan, and A.K. St.Clair: Synthesis of reflective polyimide films via in situ silver (I) reduction. Chem. Mater. 7, 2171 (1995).
S. Tang, S. Vongehr, and X. Meng: Carbon spheres with controllable silver nanoparticle doping. J. Phys. Chem. C 114, 977 (2009).
X. Du, J. He, J. Zhu, L. Sun, and S. An: Ag-deposited silica-coated Fe3O4 magnetic nanoparticles catalyzed reduction of p-nitrophenol. Appl. Surf. Sci. 258, 2717 (2012).
M. Wang, D. Tian, P. Tian, and L. Yuan: Synthesis of micron-SiO2@ nano-Ag particles and their catalytic performance in 4-nitrophenol reduction. Appl. Surf. Sci. 283, 389 (2013).
S. Deshmukh, R. Dhokale, H. Yadav, S. Achary, and S. Delekar: Titania–supported silver nanoparticles: An efficient and reusable catalyst for reduction of 4-nitrophenol. Appl. Surf. Sci. 273, 676 (2013).
X. Huang, Y. Xiao, W. Zhang, and M. Lang: In-situ formation of silver nanoparticles stabilized by amphiphilic star-shaped copolymer and their catalytic application. Appl. Surf. Sci. 258, 2655 (2012).
M. Chang, T. Kim, H-W. Park, M. Kang, E. Reichmanis, and H. Yoon: Imparting chemical stability in nanoparticulate silver via a conjugated polymer casing approach. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 4, 4357 (2012).
N. Pradhan, A. Pal, and T. Pal: Silver nanoparticle catalyzed reduction of aromatic nitro compounds. Colloids Surf., A 196, 247 (2002).
B.J. Hornstein and R.G. Finke: Transition-metal nanocluster catalysts: Scaled-up synthesis, characterization, storage conditions, stability, and catalytic activity before and after storage of polyoxoanion-and tetrabutylammonium-stabilized Ir (0) nanoclusters. Chem. Mater. 15, 899 (2003).
C-W. Yen, M-L. Lin, A. Wang, S-A. Chen, J-M. Chen, and C-Y. Mou: CO oxidation catalyzed by Au–Ag bimetallic nanoparticles supported in mesoporous silica. J. Phys. Chem. C 113, 17831 (2009).
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
This work was supported by the Faculty Research Fund of Central South University (2013JSJJ002) and the Hunan Provincial Innovation Foundation for Graduate Students (CX2014B049).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, J., Wang, Y., Wang, M. et al. A highly robust and reusable polyimide-supported nanosilver catalyst for the reduction of 4-nitrophenol. Journal of Materials Research 30, 2713–2721 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1557/jmr.2015.258
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1557/jmr.2015.258