Abstract
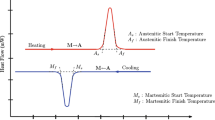
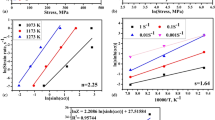
The present study was conducted to predict the hot deformation behavior of the as-forged Nitinol 60 shape memory alloy by using the Arrhenius type, multiple-linear, and artificial neural network (ANN) models. The acquired flow stress data from isothermal hot compression tests in a temperature range of 650–850 °C under strain rate range of 0.01–1 s−1 were used to calculate the material constants for establishing the corresponding constitutive equations. Furthermore, a comparative study has been made on the capability of the aforementioned models to predict the high-temperature deformation behavior by comparing the prediction relative errors, average absolute relative error, and correlation coefficient. The results show that multiple-linear model predicts the flow behavior more accurately than the Arrhenius type model. The ANN model is much more efficient and has a better prediction power for the as-forged Nitinol 60 alloy than both the Arrhenius type and multiple-linear models.













Similar content being viewed by others
References
Q.F. Zeng and G.N. Dong: Superlubricity behaviors of Nitinol 60 alloy under oil lubrication. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 24, 354 (2014).
D.J. Clingman, F.T. Calkins, J.P. Smith, and The Boeing Company: Thermo mechanical properties of Ni 60% weight Ti 40% weight. Smart Struct. Mater. 5053, 219 (2003).
R.R. Adharapurapu and K.S. Vecchio: Superelasticity in a new bioimplant material: Ni-rich 55NiTi alloy. Exp. Mech. 47, 365 (2007).
K. Dehghani and A.A. Khamei: Hot deformation behavior of 60Nitinol (Ni 60wt%–Ti 40wt%) alloy: Experimental and computational studies. Mater. Sci. Eng., A 527, 684 (2010).
A.A. Khamei and K. Dehghani: A study on the mechanical behavior and microstructural evolution of Ni 60wt%–Ti4 0wt% (60Nitinol) intermetallic compound during hot deformation. Mater. Chem. Phys. 123, 269 (2010).
A.A. Khamei and K. Dehghani: Microstructural evolution during the hot deformation of Ti–55Ni (at. pct) intermetallic alloy. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 41A, 2595 (2010).
A. Shamsolhodaei, A. Zarei-Hanzaki, M. Ghambari, and S. Moemeni: The high temperature flow behavior modeling of NiTi shape memory alloy employing phenomenological and physical based constitutive models: A comparative study. Intermetallics 53, 140 (2014).
S.M. Fatemi-Varzaneh, A. Zarei-Hanzaki, and M. Haghshenash: A study on the effect of thermo-mechanical parameters on the deformation behavior of Mg–3Al–1Zn. Mater. Sci. Eng., A 497, 438 (2008).
D. Samantaray, S. Mandal, and A.K. Bhaduri: Constitutive analysis to predict high-temperature flow stress in modified 9Cr-1Mo (P91) steel. Mater. Des. 31, 981 (2010).
H.J. McQueen and N.D. Ryan: Constitutive analysis in hot working. Mater. Sci. Eng., A 322, 43 (2002).
X.G. Fan and H. Yang: Internal-state-variable based self-consistent constitutive modeling for hot working of two-phase titanium alloys coupling microstructure evolution. Int. J. Plast. 27, 1833 (2011).
F.A. Slooff, J. Zhou, J. Duszczyk, and L. Katgerman: Constitutive analysis of wrought magnesium alloy Mg-Al4-Zn1. Scr. Mater. 57, 759 (2007).
H.R. Rezaei Ashtiani, M.H. Parsa, and H. Bisadi: Constitutive equations for elevated temperature flow behavior of commercial purity aluminum. Mater. Sci. Eng., A 545, 61 (2012).
Z.P. Zeng, S. Jonsson, and Y.S. Zhang: Constitutive equations for pure titanium at elevated temperatures. Mater. Sci. Eng., A 505, 116 (2009).
S. Mandal, V. Rakesh, P.V. Sivaprasad, S. Venugopal, and K.V. Kasiviswanathan: Constitutive equations to predict high temperature flow stress in a Ti-modified austenitic stainless steel. Mater. Sci. Eng., A 500, 114 (2009).
X.N. Peng, H.Z. Guo, Z.F. Shi, C. Qin, and Z.L. Zhao: Constitutive equations for high temperature flow stress of TC4-DT alloy incorporating strain, strain rate and temperature. Mater. Des. 50, 198 (2013).
Z.P. Guan, M.W. Ren, P. Zhao, P.K. Ma, and Q.L. Wang: Constitutive equations with varying parameters for superplastic flow behavior of Al-Zn-Mg-Zr alloy. Mater. Des. 54, 906 (2014).
G.Z. Quan, K.W. Liu, J. Zhou, and B. Chen: Dynamic softening behaviors of 7075 aluminum alloy. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 19, s537 (2009).
J.W. Zhao, H. Ding, W.J. Zhao, M.L. Huang, D.B. Wei, and Z.Y. Jiang: Modelling of the hot deformation behaviour of a titanium alloy using constitutive equations and artificial neural network. Comput. Mater. Sci. 92, 47 (2014).
Y. Han, G.J. Qiao, J.P. Sun, and D.N. Zou: A comparative study on constitutive relationship of as-cast 904L austenitic stainless steel during hot deformation based on Arrhenius-type and artificial neural network models. Comput. Mater. Sci. 67, 93 (2013).
O. Sabokpa, A. Zarei-Hanzaki, H.R. Abedi, and N. Haghdadi: Artificial neural network modeling to predict the high temperature flow behavior of an AZ81 magnesium alloy. Mater. Des. 39, 390 (2012).
R. Kapoora, D. Palb, and J.K. Chakravarttya: Use of artificial neural networks to predict the deformation behavior of Zr-2.5 Nb-0.5 Cu. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 169, 199 (2005).
K. Otsuka and X. Ren: Physical metallurgy of Ti-Ni-based shape memory alloys. Prog. Mater. Sci. 50, 511 (2005).
C.M. Sellars and W.J. McTegart: On the mechanism of hot deformation. Acta Met. 14, 1136 (1966).
A.A. Khamei and K. Dehghani: Modeling the hot-deformation behavior of Ni60wt%-Ti40wt% intermetallic alloy. J. Alloys Compd. 490, 377 (2010).
X. Xiao, G.Q. Liu, B.F. Hu, X. Zheng, L.N. Wang, S.J. Chen, and A. Ullah: A comparative study on Arrhenius-type constitutive equations and artificial neural network model to predict high-temperature deformation behavior in 12Cr3WV steel. Comput. Mater. Sci. 62, 227 (2012).
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
We would like to thank our anonymous reviewers for extremely helpful comments. We acknowledge the support from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 51164030) and Natural Science Foundation of Jiangxi Province (Grant No. 20122 BAB216018).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shu, X., Lu, S., Wang, K. et al. A comparative study on constitutive equations and artificial neural network model to predict high-temperature deformation behavior in Nitinol 60 shape memory alloy. Journal of Materials Research 30, 1988–1998 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1557/jmr.2015.144
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1557/jmr.2015.144