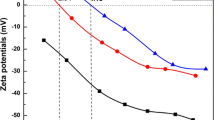
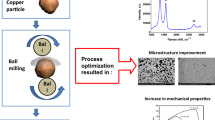
Abstract
As an emerging carbon material with advantages of thinnest, ultrahigh strength, superior thermal conductivity and electrical conductivity, graphene (Gr) is called the “black gold” and will have a profound applying potential in the field of materials science and engineering. Many researches concerning preparation of the Cu-Gr composite via various approaches have been reported. However, only few works are related to the electrochemical deposition method. As a simple, low cost, large scale production method, electrodeposition method has been widely used in industry for manufacturing foils involving copper-clad laminate (CCL), printed circuit board (PCB) and the negative current collector of lithium ion battery, where the copper foil not only serve as the carrier of the cathode active material but also play a role in collecting and conducting electrons. In the present article, we review the research progress on preparations and mechanical properties of the Cu-Gr composite foils by electrochemical method, and introduce our recent work in this area. The advancement of the process and the perspective industrial productions are also discussed.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
K. S. Novoselov, A. K. Geim, S. V. Morozov, D. Jiang, Y. Zhang, S. V. Dubonos, I. V. Grigorieva and A.A. Firsov. Science 306, 666 (2004).
F. Chen, J. Ying, Y. Wang, S. Du, Z. Liu and Q. Huang. Carbon 96, 836 (2016).
J. Hwang, T. Yoon, S.H. Jin, J. Lee, T.S. Kim, S.H. Hong and S. Jeon. Adv. Mater. 25, 6724 (2013).
C.L. Pavithra, B.V. Sarada, K.V. Rajulapati, T.N. Rao and G. Sundararajan. Sci. Rep. 4, 4049 (2014).
G. Huang, H. Wang, P. Cheng, H. Wang, B. Sun, S. Sun, C. Zhang, M. Chen and G. Ding. Microelectron. Eng. 157, 7 (2016).
H. S. Maharana, P. K. Rai and A. Basu1. J. Mater. Sci. 52, 1089 (2017).
Z. Protich, K. S. V. Santhanam, A. Jaikumar, S. G. Kandlikar and P. Wong. J. Electrochem. Soc. 163, E166(2016).
Y.J. Mai, M.P. Zhou, H.J. Ling, F.X. Chen, W.Q. Lian, X.H. Jie. Appl. Surf. Sci. 433, 232(2018).
K. Jagannadham. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 44, 552 (2013).
K. Jagannadham. Metall. Mater. Trans. B 43B, 316(2012).
K. Jagannadham. J. Vac. Sci. Technol. B, 30, 03D109(2012).
G. Xie, M. Forslund and J. Pan. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 6, 7444 (2014).9.
G. Song, Z. Wang, Y. Gong, Y. Yang, Q. Fu and C. Pan. RSC Adv. 7, 1735 (2017).
G. Song, Y. Yang, Q. Fu, C.Pan. J. Electrochem. Soc. 164, D652 (2017).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Song, G., Fu, Q. & Pan, C. Copper-Graphene Composite Foils via Electro-Deposition: A Mini Review. MRS Advances 3, 37–44 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1557/adv.2018.28
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1557/adv.2018.28