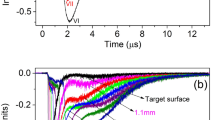
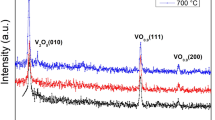
Abstract
Pulsed laser deposition (PLD) is a technique which utilizes a high energy pulsed laser ablation of targets to deposit thin films on substrates in a vacuum chamber. The high-intensity laser pulses create a plasma plume from the target material which is projected towards the substrate whereupon it condenses to deposit a thin film. Here we investigate the properties of vanadium oxide thin films prepared utilizing two variations of the pulsed laser deposition (PLD) technique: femtosecond PLD and nanosecond PLD. Femtosecond PLD (f-PLD) has a significantly higher peak intensity and shorter duration laser pulse compared to that of the excimer-based nanosecond PLD (n-PLD). Experiments have been conducted on the growth of thin films prepared from V2O5 targets on glass substrates using f-PLD and n-PLD. Characterization using SEM, XRD and Raman spectroscopy shows that the f-PLD films have significantly rougher texture prior to annealing and exhibit with an amorphous nano-crystalline character whereas the thin films grown using n-PLD are much smoother and highly predominantly amorphous. The surface morphology, structural, vibrational, and chemical- and electronic-state elemental properties of the vanadium oxide thin films, both prior to and after annealing to 450 °C, will be discussed.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
S. Beke, Thin Solid Films 519, 1761–1771 (2011).
C. Wu, F. Feng, Y. Xie, Chem. Soc. Rev. 42, 5157–5183 (2013).
S. Amoruso, G. Ausanio, R. Bruzzese, M. Vitiello, X. Wang, Phys. Rev. B 71, 033406 (2005).
M. Okoshi, K. Higashikawa, M. Hanabusa, Appl. Surf. Sci. 154–155, 424–427 (2000).
M. Sanz, R. de Nalda, J.F. Marco, J.G. Izquierdo, L. Ban˜ ares, M. Castillejo, J. Phys. Chem. C 114, 4864–4868 (2010).
Ramana, C. V., Hussain, O. M., Pinto, R. & Julien, C. M., Appl. Surf. Sci. 207, 135–138 (2003).
Ramana, C. V., Smith, R. J., Hussain, O. M., Massot, M. & Julien, C. M. Surface and Interface Analysis 37, 406–411 (2005).
G. Rampelberg, B. De Schutter, W. Devulder, K. Martens, I. Radub, C. Detavernier, J. Mater. Chem. C, 3, 11357–11365 (2015).
R.T. Rajendrakumar, B. Karunagaran, D. Mangalaraj, Sa.K. Narayandass, P. Manoravi, M. Joseph, Mater. Sci. Semicond. Proces. 6, 375–377 (2003).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Deng, Y., Pelton, A. & Mayanovic, R.A. Comparison of Vanadium Oxide Thin Films Prepared Using Femtosecond and Nanosecond Pulsed Laser Deposition. MRS Advances 1, 2737–2742 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1557/adv.2016.311
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1557/adv.2016.311