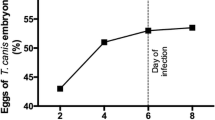
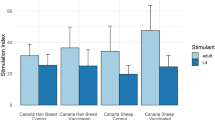
Abstract
The study was focused on the dynamics of humoral response to Toxocara canis excretory-secretory antigens (TES antigens) in mice experimentally infected by T. canis L3 larvae in different ways. In particular, we compared the effect of infection with two doses of 1000 larvae vs. repeated infections with a low number of larvae (daily infection with 10 larvae and weekly infection with 100 larvae in the course of 22 weeks). In ELISA, all infections, including both schemes with lower larval doses, elicited significant antibody response. Elevated levels of total IgE and TES-antigen-specific IgM were detected on day 12 after the first infection, followed by IgG and IgG1, and later by IgG3, IgG2a and IgG2b; specific IgE response was not detected. It seems that the high levels of IgM and IgG1 represent the best markers of infection. In addition, gradual increase of IgG2a and IgG2b could help in determination of the infection course. As a byproduct of our work, a new method of infection by repeated drinking of larvae was introduced; it minimizes the pain and discomfort for the experimental mice.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Antolová D., Reiterová K., Stanko M., Zalesny G., Fričová J., Dvorožňáková E. 2013. Small mammals: paratenic hosts for species of Toxocara in eastern Slovakia. Journal of Helminthology, 87, 52–58. DOI: 10.1017/S0022149X11000848
Boldiš V., Ondriska F., Špitálská E., Reiterová K. 2015. Immunodiagnostic approaches for the detection of human toxocariasis. Experimental Parasitology, 159, 252–258. DOI: 10.1016/j.exppara.2015.10.006
Bowman D.D., Mika-Grieve M., Grieve R.B. 1987. Circulating excretory-secretory antigen levels and specific antibody response in mice infected with Toxocara canis. The American Journal of Tropical Medicine and Hygiene, 36, 75–82
Chan P.W., Anuar A.K., Fong M.Y., Debruyne J.A., Ibrahim J. 2001. Toxocara seroprevalence and childhood asthma among Malaysian children. Pediatrics International, 43, 350–353. DOI: 10.1046/j.1442-200X-2001-01421.x
Cox D.M., Holland C.V. 2001. Influence of mouse strain, infective dose and larval burden in the brain on activity in Toxocarainfected mice. Journal of Helminthology, 75, 23–32
De Savigny D.H. 1975. In vitro maintenance of Toxocara canis larvae and a simple method for the production of Toxocara ES antigen for use in serodiagnostic tests for visceral larva migrans. Journal of Parasitology, 61, 781–782
De Savigny D.H., Voller A., Woodruff A.W. 1979. Toxocariasis: serological diagnosis by enzyme immunoassay. Journal of Clinical Pathology, 32, 781–782
Dlugosz E., Wisniewski M. 2016. Toxocara canis glycans influence antigen recognitionby mouse IgG1 and IgM antibodies. Acta Parasitologica, 61, 191–194. DOI: 10.1515/ap-2016-0026
Fan C-K., Lin Y.H., Hung C.C., Su K.E. 2004. Larval migratory behavior of long-term-maintained Toxocara canis embryonated eggs in mice. Taiwan Veterinary Journal, 30, 99–105
Fan C-K., Liao C-W., Cheng Y-C. 2013. Factor affecting disease manifestation of toxocariasis in humans: Genetics and environment. Veterinary Parasitology, 193, 342–352. DOI: 10.1016/j.vetpar.2012.12.030
Fan C-K., Holland C.V., Loxton K., Barghouth U. 2015. Cerebral toxocariasis: silent progression to neurodegenerative disorders? Clinical Microbiology Reviews, 28(3), 663–686. DOI: 10.1128/CMR.00106-14
Fillaux J., Mangaval F.J. 2013. Laboratory diagnosis of human toxocariasis. Veterinary Parasitology, 193, 327–336. DOI: 10.1016/j.vetpar.2012.12.028
Fenoy S., Rodero M., Pons E., Aguila C., Cuellar C. 2008. Followup of antibody avidity in BALB/c mice infected with Toxocara canis. Parasitology, 135, 725–733. DOI: 10.1017/S0031182008004368
Fonseca G.R, Santos S.V., Chieffi P.P., Paula F.M., Gryschek R.C.B., Lescano S.A.Z. 2017. Experimental toxocariasis in BALB/c mice: relationship between parasite inoculum and the IgG immune response. Memórias do Instituto Oswaldo Cruz, Rio de Janeiro, 112, 382–386. DOI: 10.1590/0074-02760160341
Forstl M., Buchta V., Psohlavec J., Čermák P., Čermáková Z., Urban J., Chrzová M. 2004. Diagnostics of larval toxocariasis. Klinická mikrobiologie a infekční lékařství, 10, 181–185
Galvin T.J. 1964. Experimental Toxocara canis infection in chicken and pigeons. Journal of Parasitology, 50, 124–127
Gawor J., Borecka A., Marczynska M., Dobosz S., Zarnowska-Prymek H. 2015. Risk of human toxocarosis in Poland due to Toxocara infection of dogs and cats. Acta Parasitologica, 60, 99–104. DOI: 10.1515/ap-2015-0012
Hamilton C.M., Stafford P., Pinelli E., Holland C.V. 2006. A murine model for cerebral toxocariasis: characterization of host susceptibility and behavior. Parasitology, 132, 791–801. DOI: 10.1017/S0031182006009887
Hamilton C.M., Brandes S., Holland C., Pinelli E. 2008. Cytokine expression in the brain of Toxocara canis-infected mice. Parasite Immunology, 30, 181–185. DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-3024.2007.01002.x
Havasiová-Reiterová K., Tomašovičová O., Dubinský P. 1995. Effect of various doses of infective Toxocara canis and Toxocara cati eggs on the humoral response and distribution of larvae in mice. Parasitology Research, 81, 13–17
Holland C.V., Hamilton C.M. 2013. Review: The significance of cerebral toxocariasis: a model system for exploring the link between brain involvement, behavior and the immune response. Journal of Experimental Biology, 216, 78–83. DOI: 10.1242/jeb.074120
Hubner J., Uhlíková M., Leissová M. 2001. Diagnosis of the early phase of larval toxocariasis using IgG avidity. Epidemiologie, Mikrobiologie, Imunologie, 50, 67–70
Janecek E., Beineke A., Schnieder T., Strube C. 2014. Neurotoxocarosis: marked preference of Toxocara canis for the cerebrum and T. cati for the cerebellum in the paratenic model host mouse. Parasites & Vectors, 7, 194. DOI: 10.1186/1756-3305-7-194
Jin Y., Shen C., Huh S., Sohn W.M., Choi M.H., Hong S.T. 2013. Serodiagnosis of toxocariasis by ELISA using crude antigen of Toxocara canis larvae. Korean Journal of Parasitology, 51, 433–439. DOI: 10.3347/kjp.2013.51.4.433
Kolbeková P., Kolářová L., Větvička D., Syrůček M. 2011a. Imaging of Toxocara canis larvae labelled by CFSE in BALB/c mice. Parasitology Research, 108, 1007–1014. DOI: 10.1007/s00436-010-2145-y
Kolbeková P., Větvička D., Svoboda J., Skírnissson K., Leissová M., Syrůček M., Marečková H., Kolářová L. 2011b. Toxocara canis larvae reinfectiong BALB/c mice exhibit accelerated speed of migration to the CNS. Parasitology Research, 109, 1267–1278. DOI: 10.1007/s00436-011-2371-y
Lloyd S. 1993. Toxocara canis: the dog. In: (Eds J.W. Lewis, R.M. Maizels) Toxocara and Toxocarariasis: Clinical, epidemiological and molecular perspectives. London, Institute of Biology and the British Society for Parasitology, 11–22
Mangaval J.F., Galindo V., Glickmann L.T., Clanet M. 1997. Human Toxocara infection of the central nervous system and neurological disorders: a case-control study. Parasitology, 115, 537–543
Ngugi A.K., Bottomley C., Kleinschmidt I., Wagner R.G., Kakooza-Mwesige A., Ae-Ngibise K., Owusu-Agyei S., Masanja H., Kamuyu G., Odhiambo R., Chengo E., Sander J.W., Newton C.R., SEEDS Group. 2013. Prevalence of active convulsive epilepsy in sub-Saharan Africa and associated risk factors: cross-sectional and case-control studies. The Lancet Neurology, 12, 253–263. DOI: 10.1016/S1474-4422(13)70003-6
Noordin R., Smith H.V., Mohamad S., Maizels R.M., Fong M.Y. 2005. Comparison of IgG-ELISA and IgG4-ELISA for Toxocara serodiagnosis. Acta Tropica, 93, 57–62. DOI: 10.1016/j.actatropica.2004.09.009
Pilarczyk B., Doligalska M.J., Donskow-Schmelter K., Balicka-Ramisz A., Ramisz A. 2008. Selenium supplementation enhances the protective response to Toxocara canis larvae in mice. Parasite Immunology, 30, 394–402. DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-3024.2008.01039.x
Pinelli E., Withagen C., Fonville M., Verlaan A., Dormans J., van Loveren H., Nicoll G., Maizels R.M., van der Giessen J. 2005. Persistent airway hyper-responsiveness and inflammation in Toxocara canis-infected BALB/c mice. Clinical and Experimental Allergy, 35, 826–832. DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2222.2005.02250.x
Pinelli E., Brandes S., Dormans J., Fonville M., Hamilton C.M., van der Giessen J. Toxocara canis: (2007): Effect of inoculum size on pulmonary pathology and cytokine expression in BALB/c mice. Experimental Parasitology, 115, 76–82. DOI: 10.1016/j.exppara.2006.06.002
Quattrocchi G., Nicoletti A., Marin B., Bruno E., Druet-Cabanac M., Preux P.M. 2012. Toxocariasis and epilepsy: systematic review and metaanalysis. PLoS Neglected Tropical Diseases, 6, e1775. DOI: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0001775.
Ranasuriya G., Mian A., Boujaoude Z., Tsigrelis C. 2014. Pulmonary toxocariasis: a case report and literature review. Infection, 42: 575–578. DOI: 10.1007/s15010-014-0587-3
Reiterová K., Antolová D., Zalesny G., Stanko M., Špilovská S., Mošanský L. 2013. Small rodents — permanent reservoirs of toxocarosis in different habitats of Slovakia. Helminthologia, 50, 20–26. DOI 10.2478/s11687-013-0103-9
Roldan WH., Elefant GR., Ferreira AW. 2017. Immunoglobulin M antibodies are not specific for serodiagnosis of human toxocariasis. Parasite Immunology, 39, e12447. DOI: 10.1111/pim.12447
Schoenardie E.R., Scaini C.J., de Costa de Avila L.F., Sperotto R.L., Borsuk S., Felicetti C.D.F., Pepe M., Berne M.E.A. 2014. Determination of avidity in BALB/c mice experimentally infected with Toxocara canis. Brazilian Journal of Veterinary Parasitology, 23(4), 403–406. DOI: 10.1590/S1984-29612014060
Smith H.V. 1993. Antibody reactivity in toxocariasis. In: (Eds. J.W. Lewis, R.M. Maizels) Toxocara and Toxocarariasis: Clinical, epidemiological and molecular perspectives. London, Institute of Biology and the British Society for Parasitology, 91–109
Smith H.V., Holland C.W., Taylor M., Mangaval J.F., Schantz P., Maizels R.M. 2009. How common is human toxocariasis? Towards standardizing our knowledge. Trends in Parasitology, 25, 182–188. DOI: 10.1016/j.pt.2009.01.006
Watthanakulpanich D., Smith H.V., Hobbs G., Whalley A., Billington D. 2008. Application of Toxocara canis excretory-secretory antigens and IgG subclass antibodies (IgG1-4) in serodiagnostic assay of human toxocariasis. Acta Tropica, 106, 90–95. DOI: 10.1016/j.actatropica.2008.01.008
Yamasaki H., Araki K., Lim P.K., Zasmy N., Mak J.W., Taib R., Aoki T. 2000. Development of a highly specific recombinant Toxocara canis second-stage larva excretory-secretory antigen for Immunodiagnosis of human toxocariasis. Journal of Clinical Microbiology, 38, 1409–1413
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Novák, J., Panská, L., Macháček, T. et al. Humoral response of mice infected with Toxocara canis following different infection schemes. Acta Parasit. 62, 823–835 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1515/ap-2017-0099
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1515/ap-2017-0099