Abstract
Background
Breast cancer is the world’s most prevalent cancer, and many breast cancer patients undergo mastectomy as the choice of treatment, often with post-mastectomy breast reconstruction. Acellular dermal matrix (ADM) use has become a method to improve outcomes of reconstruction for these patients. We aimed to compare postoperative complications and patient-reported outcomes, which are still poorly characterized, between groups utilizing acellular dermal matrix during reconstruction and those without.
Materials and Methods
We searched electronic databases from inception to 16 June 2022 for randomized controlled trials and prospective cohort studies comparing the outcomes of patients who have and have not received acellular dermal matrix in implant-based breast reconstruction. The results were quantitatively combined and analyzed using random-effects models.
Results
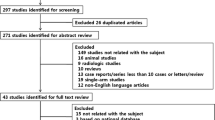
A total of nine studies were included, representing 3161 breasts. There was no significant difference in postoperative outcomes, such as seroma formation (p = 0.51), hematomas (p = 0.20), infections (p = 0.21), wound dehiscence (p = 0.09), reoperations (p = 0.70), implant loss (p = 0.27), or skin necrosis (p = 0.21). Only two of the studies included evaluated patient-reported outcomes between the use and non-use of ADM in implant-based breast reconstruction using BREAST-Q questionnaire, as well as self-reported pain. There was no reported significant difference in BREAST-Q or pain scores.
Conclusions
This meta-analysis shows comparable short- and long-term outcomes between ADM and non-ADM breast reconstruction, suggesting that the use of ADM may not be necessary in all cases given their additional cost. However, there is a paucity of data for patient-reported outcomes, and further research is required to determine whether ADM use affects patient-reported outcomes.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ferlay J, Colombet M, Soerjomataram I, Mathers C, Parkin DM, Piñeros M, et al. Estimating the global cancer incidence and mortality in 2018: GLOBOCAN sources and methods. Int J Cancer. 2019;144(8):1941–53.
Saldanha IJ, Broyles JM, Adam GP, Cao W, Bhuma MR, Mehta S, et al. Implant-based breast reconstruction after mastectomy for breast cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Plast Reconstr Surg Glob Open. 2022;10(3).
Zhao R, Jin M, Gao J, Zhang L, Tao L, Bao X. A cross-sectional study of breast cancer surgery and the cost based on data from 77 Chinese 3A hospitals in 2015. Front Oncol. 2022;12:857359.
Jonczyk MM, Jean J, Graham R, Chatterjee A. Surgical trends in breast cancer: a rise in novel operative treatment options over a 12 year analysis. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2019;173(2):267–74.
Panchal H, Matros E. Current trends in postmastectomy breast reconstruction. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2017;140(5S Advances in Breast Reconstruction):7s–13s.
Wilkins EG, Cederna PS, Lowery JC, Davis JA, Kim HM, Roth RS, et al. Prospective analysis of psychosocial outcomes in breast reconstruction: one-year postoperative results from the Michigan Breast Reconstruction Outcome Study. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2000;106(5):1014–25.
Breuing KH, Warren SM. Immediate bilateral breast reconstruction with implants and inferolateral AlloDerm slings. Ann Plast Surg. 2005;55(3):232–9.
JoAnna Nguyen T, Carey JN, Wong AK. Use of human acellular dermal matrix in implant-based breast reconstruction: evaluating the evidence. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg. 2011;64(12):1553–61.
DeLong MR, Tandon VJ, Farajzadeh M, Berlin NL, MacEachern MP, Rudkin GH, et al. Systematic review of the impact of acellular dermal matrix on aesthetics and patient satisfaction in tissue expander-to-implant breast reconstructions. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2019;144(6):967e-e974.
Negenborn VL, Smit JM, Dikmans REG, Winters HAH, Twisk JWR, Ruhé PQ, et al. Short-term cost-effectiveness of one-stage implant-based breast reconstruction with an acellular dermal matrix versus two-stage expander-implant reconstruction from a multicentre randomized clinical trial. Br J Surg. 2019;106(5):586–95.
Smith JM, Broyles JM, Guo Y, Tuffaha SH, Mathes D, Sacks JM. Human acellular dermis increases surgical site infection and overall complication profile when compared with submuscular breast reconstruction: an updated meta-analysis incorporating new products(✰). J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg. 2018;71(11):1547–56.
Lee KT, Mun GH. Updated evidence of acellular dermal matrix use for implant-based breast reconstruction: a meta-analysis. Ann Surg Oncol. 2016;23(2):600–10. https://doi.org/10.1245/s10434-015-4873-9.
Zhao X, Wu X, Dong J, Liu Y, Zheng L, Zhang L. A meta-analysis of postoperative complications of tissue expander/implant breast reconstruction using acellular dermal matrix. Aesthet Plast Surg. 2015;39(6):892–901.
Liu J, Hou J, Li Z, Wang B, Sun J. Efficacy of acellular dermal matrix in capsular contracture of implant-based breast reconstruction: a single-arm meta-analysis. Aesthet Plast Surg. 2020;44(3):735–42.
Heidemann LN, Gunnarsson GL, Salzberg CA, Sørensen JA, Thomsen JB. Complications following nipple-sparing mastectomy and immediate acellular dermal matrix implant-based breast reconstruction: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Plast Reconstr Surg Glob Open. 2018;6(1):e1625.
Hallberg H, Rafnsdottir S, Selvaggi G, Strandell A, Samuelsson O, Stadig I, et al. Benefits and risks with acellular dermal matrix (ADM) and mesh support in immediate breast reconstruction: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Plast Surg Hand Surg. 2018;52(3):130–47.
Saldanha IJ, Broyles JM, Adam GP, Cao W, Bhuma MR, Mehta S, et al. Autologous reconstruction after mastectomy for breast cancer. Plast Reconstr Surg Glob Open. 2022;10(3):e4181.
McCarthy CM, Lee CN, Halvorson EG, Riedel E, Pusic AL, Mehrara BJ, et al. The use of acellular dermal matrices in two-stage expander/implant reconstruction: a multicenter, blinded, randomized controlled trial. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2012;130(5 Suppl 2):57s–66s.
Dikmans RE, Negenborn VL, Bouman MB, Winters HA, Twisk JW, Ruhé PQ, et al. Two-stage implant-based breast reconstruction compared with immediate one-stage implant-based breast reconstruction augmented with an acellular dermal matrix: an open-label, phase 4, multicentre, randomised, controlled trial. Lancet Oncol. 2017;18(2):251–8.
Lohmander F, Lagergren J, Roy PG, Johansson H, Brandberg Y, Eriksen C, et al. Implant based breast reconstruction with acellular dermal matrix: safety data from an open-label, multicenter, randomized, controlled trial in the setting of breast cancer treatment. Ann Surg. 2019;269(5):836–41.
Ganesh Kumar N, Berlin NL, Kim HM, Hamill JB, Kozlow JH, Wilkins EG. Development of an evidence-based approach to the use of acellular dermal matrix in immediate expander-implant-based breast reconstruction. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg. 2021;74(1):30–40.
Weichman KE, Wilson SC, Saadeh PB, Hazen A, Levine JP, Choi M, et al. Sterile “ready-to-use” AlloDerm decreases postoperative infectious complications in patients undergoing immediate implant-based breast reconstruction with acellular dermal matrix. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2013;132(4):725–36.
Hillberg NS, Ferdinandus PI, Dikmans REG, Winkens B, Hommes J, van der Hulst R. Is single-stage implant-based breast reconstruction (SSBR) with an acellular matrix safe?: Strattice™ or Meso Biomatrix® in SSBR. Eur J Plast Surg. 2018;41(4):429–38.
Sbitany H, Wang F, Peled AW, Alvarado M, Ewing CA, Esserman LJ, et al. Tissue expander reconstruction after total skin-sparing mastectomy: defining the effects of coverage technique on nipple/areola preservation. Ann Plast Surg. 2016;77(1):17–24.
Israeli Ben-Noon H, Farber N, Weissman O, Tessone A, Stavrou D, Shabtai M, et al. The effect of acellular dermal matrix on drain secretions after immediate prosthetic breast reconstruction. J Plast Surg Hand Surg. 2013;47(4):308–12.
Peled AW, Foster RD, Garwood ER, Moore DH, Ewing CA, Alvarado M, et al. The effects of acellular dermal matrix in expander-implant breast reconstruction after total skin-sparing mastectomy: results of a prospective practice improvement study. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2012;129(6):901e-e908.
Sbitany H, Serletti JM. Acellular dermis–assisted prosthetic breast reconstruction: a systematic and critical review of efficacy and associated morbidity. Plast Reconst Surg. 2011;128(6):1162–9.
Caputo GG, Franchini Z, Maritan M, Dalla Pozza E, Vigato E, Tedeschi U, et al. Daily serum collection after acellular dermal matrix-assisted breast reconstruction. Arch Plast Surg. 2015;42(3):321–6.
Nahabedian MY. AlloDerm performance in the setting of prosthetic breast surgery, infection, and irradiation. Plast Reconst Surg. 2009;124(6).
Citron I, Dower R, Ho-Asjoe M. Protocol for the prevention and management of complications related to ADM implant-based breast reconstructions. GMS Interdiscip Plast Reconstr Surg DGPW. 2016;5:Doc06.
Wagner RD, Braun TL, Zhu H, Winocour S. A systematic review of complications in prepectoral breast reconstruction. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg. 2019;72(7):1051–9.
Petrie K, Cox CT, Becker BC, MacKay BJ. Clinical applications of acellular dermal matrices: a review. Scars Burn Heal. 2022;8:20595131211038310.
Myckatyn TM, Cavallo JA, Sharma K, Gangopadhyay N, Dudas JR, Roma AA, et al. The impact of chemotherapy and radiation therapy on the remodeling of acellular dermal matrices in staged, prosthetic breast reconstruction. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2015;135(1):43e–57e.
Lardi AM, Ho-Asjoe M, Mohanna PN, Farhadi J. Immediate breast reconstruction with acellular dermal matrix: factors affecting outcome. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg. 2014;67(8):1098–105.
Jung SM, Jeon B-J, Woo J, Ryu JM, Lee SK, Chae B-J, et al. Does chemotherapy or radiotherapy affect the postoperative complication in breast cancer patients who underwent immediate breast reconstruction with tissue expander? BMC Cancer. 2021;21(1):88.
Israeli R, Feingold RS. Acellular dermal matrix in breast reconstruction in the setting of radiotherapy. Aesthet Surg J. 2011;31(7 Suppl):51s–64s.
Wagner DS, Mirhaidari SJ. Capsulectomy, implant exchange, and placement of acellular dermal matrix is effective in treating capsular contracture in breast augmentation patients. Aesthet Surg J. 2019;41(3):304–12.
Costeira B, Oom R, Costa CS, Moniz JV, Abecasis N, Santos CR. Learning curve for implant-based immediate breast reconstruction using ADM (acellular dermal matrix): the experience from an oncologic center. Eur J Surg Oncol. 2023;49(2):e72.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Disclosure
No funding or conflicts to declare.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Ng, T.P., Loo, B.Y.K., Yong, N. et al. Review: Implant-Based Breast Reconstruction After Mastectomy for Breast Cancer: A Meta-analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials and Prospective Studies Comparing Use of Acellular Dermal Matrix (ADM) Versus Without ADM. Ann Surg Oncol 31, 3366–3376 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1245/s10434-024-14943-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1245/s10434-024-14943-4