Abstract
Purpose
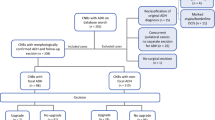
The aim of this study was to determine the upgrade rate of image-guided core needle biopsy (CNB)-proven benign breast intraductal papillomas (IDPs) without atypia to high-risk benign lesions or malignancy after surgical excision.
Methods
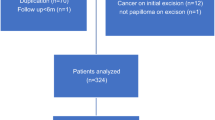
A retrospective database search at a single institution identified 102 adult female patients with benign breast IDPs without atypia diagnosed on imaging-guided CNBs who subsequently had surgical excisions between 2011 and 2016. Patient characteristics, imaging features, biopsy techniques, and the pathology reports from imaging-guided CNBs and subsequent surgical excisions were reviewed. The upgrade rate to malignancies or high-risk benign lesions was determined at the patient level.
Results
The upgrade rate to malignancy was 2.9% (3/102), including two cases of ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS) and one case of microinvasive (< 1 mm) ductal carcinoma arising from DCIS. The upgrade rate to high-risk benign lesions was 7.8% (8/102), with seven cases of atypical ductal hyperplasia and one case of atypical lobular hyperplasia. A personal history of breast cancer and a larger mean lesion size were significantly associated with an upgrade to malignancy (p < 0.05).
Conclusions
The management of benign breast IDPs without atypia detected on imaging-guided CNBs is controversial. Our results suggest risk stratification is important in approaching these patients. Although surgical excision should be considered for all benign breast IDPs without atypia, observation with serial imaging may be appropriate in selected low-risk patients. This approach will save many women from surgeries and decrease the cost of medical care.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Sohn V, Keylock J, Arthurs Z, et al. Breast papillomas in the era of percutaneous needle biopsy. Ann Surg Oncol. 2007;14:2979–2984.
Valdes EK, Feldman SM, Boolbol SK. Papillary lesions: a review of the literature. Ann Surg Oncol. 2007;14:1009–1013.
Ueng SH, Mezzetti T, Tavassoli FA. Papillary neoplasms of the breast: a review. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2009;133:893–907.
Liberman L. Clinical management issues in percutaneous core breast biopsy. Radiol Clin North Am. 2000;38:791–807.
Tavassoli F. Intraductal papillary neoplasms. In: Tavassoli FA, Young RH, Stratton MR (eds). WHO classification of tumours pathology and genetics of tumours of the breast and female genital organs. Lyon: IARC; 2003. pp. 76–80.
Tavassoli FA. Papillary lesions. In: Tavassoli FA (ed). Pathology of the breast. Norwalk: Appleton & Lange; 1992. pp. 193–227.
Mercado CL, Hamele-Bena D, Oken SM, Singer CI, Cangiarella J. Papillary lesions of the breast at percutaneous core-needle biopsy. Radiology. 2006;238:801–808.
Liberman L, Bracero N, Vuolo MA, et al. Percutaneous large core biopsy of papillary breast lesions. Am J Roentgenol. 1999;172:331–337.
Rosen EL, Bentley RC, Baker JA, Soo MS. Imaging-guided core needle biopsy of papillary lesions of the breast. Am J Roentgenol. 2002;179:1185–1192.
Page DL, Salhany KE, Jensen RA, Dupont WD. Subsequent breast carcinoma risk after biopsy with atypia in a breast papilloma. Cancer. 1996;78:258–266.
Ivan D, Selinko V, Sahin AA, Sneige N, Middleton LP. Accuracy of core needle biopsy diagnosis in assessing papillary breast lesions: histologic predictors of malignancy. Mod Pathol. 2004;17:165–171.
Jacobs TW, Connolly JL, Schnitt SJ. Nonmalignant lesions in breast core needle biopsies: to excise or not to excise? Am J Surg Pathol. 2002;26:1095–1110.
Ahmadiyeh N, Stoleru MA, Raza S, Lester SC, Golshan M. Management of intraductal papillomas of the breast: an analysis of 129 cases and their outcome. Ann Surg Oncol. 2009;16:2264–2269.
Agoff SN, Lawton TJ. Papillary lesions of the breast with and without atypical ductal hyperplasia: can we accurately predict benign behavior from core needle biopsy? Am J Clin Pathol. 2004;122:440–443.
Renshaw AA, Derhagopian RP, Tizol-Blanco DM, Gould EW. Papillomas and atypical papillomas in breast core needle biopsy specimens: risk of carcinoma in subsequent excision. Am J Clin Pathol. 2004;122:217–221.
Bianchi S, Bendinelli B, Saladino V, et al. Non-malignant breast papillary lesions–b3 diagnosed on ultrasound-guided 14-gauge needle core biopsy: analysis of 114 cases from a single institution and review of the literature. Pathol Oncol Res. 2015;21(3):535–546.
Chang JM, Han W, Moon WK, et al. Papillary lesions initially diagnosed at ultrasound-guided vacuum-assisted breast biopsy: rate of malignancy based on subsequent surgical excision. Ann Surg Oncol. 2011;18(9):2506–2514.
Glenn ME, Throckmorton AD, Thomison JB 3rd, Bienkowski RS. Papillomas of the breast 15 mm or smaller: 4-year experience in a community-based dedicated breast imaging clinic. Ann Surg Oncol. 2015;22(4):1133–1139.
Hawley JR, Lawther H, Erdal BS, Yildiz VO, Carkaci S. Outcomes of benign breast papillomas diagnosed at image-guided vacuum-assisted core needle biopsy. Clin Imaging. 2015;39(4):576–581.
Kibil W, Hodorowicz-Zaniewska D, Popiela TJ, Kulig J. Vacuum-assisted core biopsy in diagnosis and treatment of intraductal papillomas. Clin Breast Cancer. 2013;13(2):129–132.
Kim MJ, Kim EK, Kwak JY, et al. Nonmalignant papillary lesions of the breast at US-guided directional vacuum-assisted removal: a preliminary report. Eur Radiol. 2008;18(9):1774–1783.
Kim SY, Kim EK, Lee HS, et al. Asymptomatic benign papilloma without atypia diagnosed at ultrasonography-guided 14-gauge core needle biopsy: which subgroup can be managed by observation? Ann Surg Oncol. 2016;23(6):1860–1866.
Ko D, Kang E, Park SY, et al. The management strategy of benign solitary intraductal papilloma on breast core biopsy. Clin Breast Cancer. 2017;17(5):367–372.
Ahn SK, Han W, Moon HG, et al. Management of benign papilloma without atypia diagnosed at ultrasound-guided core needle biopsy: scoring system for predicting malignancy. Eur J Surg Oncol. 2018;44(1):53–58.
Maxwell AJ. Ultrasound-guided vacuum-assisted excision of breast papillomas: review of 6-years experience. Clin Radiol. 2009;64(8):801–806.
Moon HJ, Jung I, Kim MJ, Kim EK. Breast papilloma without atypia and risk of breast carcinoma. Breast J. 2014;20(5):525–533.
Pareja F, Corben AD, Brennan SB, et al. Breast intraductal papillomas without atypia in radiologic-pathologic concordant core-needle biopsies: rate of upgrade to carcinoma at excision. Cancer. 2016;122(18):2819–2827.
Seely JM, Verma R, Kielar A, et al. Benign papillomas of the breast diagnosed on large-gauge vacuum biopsy compared with 14 gauge core needle biopsy: do they require surgical excision? Breast J. 2017;23(2):146–153.
Shiino S, Tsuda H, Yoshida M, et al. Intraductal papillomas on core biopsy can be upgraded to malignancy on subsequent excisional biopsy regardless of the presence of atypical features. Pathol Int. 2015;65(6):293–300.
Swapp RE, Glazebrook KN, Jones KN, et al. Management of benign intraductal solitary papilloma diagnosed on core needle biopsy. Ann Surg Oncol. 2013;20(6):1900–1905.
Wyss P, Varga Z, Rössle M, Rageth CJ. Papillary lesions of the breast: outcomes of 156 patients managed without excisional biopsy. Breast J. 2014;20(4):394–401.
Yamaguchi R, Tanaka M, Tse GM, et al. Management of breast papillary lesions diagnosed in ultrasound-guided vacuum-assisted and core needle biopsies. Histopathology. 2015;66(4):565–576.
Yang Y, Fan Z, Liu Y, He Y, Ouyang T. Is surgical excision necessary in breast papillomas 10 mm or smaller at core biopsy. Oncol Res Treat. 2018;41(1-2):29–34.
Youk JH, Kim MJ, Son EJ, Kwak JY, Kim EK. US-guided vacuum-assisted percutaneous excision for management of benign papilloma without atypia diagnosed at US-guided 14-gauge core needle biopsy. Ann Surg Oncol. 2012;19(3):922–928.
Fu CY, Chen TW, Hong ZJ, et al. Papillary breast lesions diagnosed by core biopsy require complete excision. Eur J Surg Oncol. 2012;38:1029–1035.
Boin DP, Baez JJ, Guajardo MP, et al. Breast papillary lesions: an analysis of 70 cases. Ecancermedicalscience. 2014;8:461.
Wang H, Tsang P, D’Cruz C, Clarke K. Follow-up of breast papillary lesion on core needle biopsy: experience in African–American population. Diagn Pathol. 2014;9:86.
Rozentsvayg E, Carver K, Borkar S, et al. Surgical excision of benign papillomas diagnosed with core biopsy: a community hospital approach. Radiol Res Pract. 2011;2011:679864.
Shouhed D, Amersi FF, Spurrier R, et al. Intraductal papillary lesions of the breast: clinical and pathological correlation. Am Surg. 2012;78(10):1161–1165.
Al Hassan T, Delli Fraine P, El-Khoury M, et al. Accuracy of percutaneous core needle biopsy in diagnosing papillary breast lesions and potential impact of sonographic features on their management. J Clin Ultrasound. 2013;41:1–9.
Gilani S, Tashjian R, Kowalski P. Histological evaluation of papillary lesions of the breast from needle biopsy to the excised specimen: a single-institutional experience. Pathologica. 2013;105(2):51–55.
Shamonki J, Chung A, Huynh KT, et al. Management of papillary lesions of the breast: can larger core needle biopsy samples identify patients who may avoid surgical excision? Ann Surg Oncol. 2013;20:4137–4144.
Holley SO, Appleton CM, Farria DM, et al. Pathologic outcomes of nonmalignant papillary breast lesions diagnosed at imaging-guided core needle biopsy. Radiology. 2012;265(2):379–384.
Maxwell AJ, Mataka G, Pearson JM. Benign papilloma diagnosed on image-guided 14 G core biopsy of the breast: effect of lesion type on likelihood of malignancy at excision. Clin Radiol. 2013;68:383–387.
Bennett LE, Ghate SV, Bentley R, Baker JA. Is surgical excision of core biopsy proven benign papillomas of the breast necessary? Acad Radiol. 2010;17:553–557.
Wiratkapun C, Keeratitragoon T, Lertsithichai P, Chanplakorn N. Upgrading rate of papillary breast lesions diagnosed by core needle biopsy. Diagn Interv Radiol. 2013;19:371–376.
D’Orsi CJ, Sickles EA, Mendelson EB. ACR BI-RADS Atlas, Breast Imaging Reporting and Data System. 5th ed. Reston, VA: American College of Radiology; 2013.
Chen YA, Mack JA, Karamcandani DM, et al. Excision recommended in high-risk patients: revisiting the diagnosis of papilloma on core biopsy in the context of patient risk. Breast J. 2019;25:232–236.
Chen P, Zhou D, Wang C, et al. Treatment and outcome of 341 papillary breast lesions. World J Surg. 2019; 43(10):2477–2482.
Choi HY, Kim SM, Jang M. et al. Benign breast papilloma without atypia: outcomes of surgical excision versus US-guided directional vacuum-assisted removal or US follow-up. Radiology. 2019; 293(1):72–80.
Foley NM, Racz JM, Al-Hilli Z, et al. An international review of the malignancy rate of excised papillomatous breast lesions. Ann Surg Oncol. 2015;22:S385–S390.
Han SH, Kim M, Chung YR, et al. Benign intraductal papilloma without atypia on core needle biopsy has a low rate of upgrading to malignancy after excision. J Breast Cancer. 2018;21(1):80–86.
Kuehner G, Darbinian J, Habel L, et al. Benign papillary breast mass lesions: favorable outcomes with surgical excision or imaging surveillance. Ann Surg Oncol. 2019;26:1695–1703.
MacColl C, Salehi A, Parpia S, et al. Benign breast papillary lesions diagnosed on core biopsy: upgrade rate and risk factors associated with malignancy on surgical excision. Virchows Arch. 2019;475(6):701–707.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Disclosures
Tanya Moseley, Bella Desai, Gary J. Whitman, Emily K. Robinson, Tamara Saunders, Anneliese Gonzalez, and Hongying He have no disclosures of any commercial interest relevant to the subject matter of this study.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Moseley, T., Desai, B., Whitman, G.J. et al. Benign Breast Intraductal Papillomas Without Atypia at Core Needle Biopsies: Is Surgical Excision Necessary?. Ann Surg Oncol 28, 1347–1355 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1245/s10434-020-09061-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1245/s10434-020-09061-w