Abstract
Background
This study aimed to compare the cost and resource use between our first-year experience using breast-conserving surgery (BCS) with radioactive seed localization (RSL) and the previous-year standard practice of BCS with wire-guided localization (WGL) for patients with nonpalpable breast cancer at a large Canadian tertiary center.
Methods
For this retrospective cohort study, data for BCS cases with RSL was collected from 1 April 2015 to 31 March 2016 and for BCS cases with WGL from 1 April 2014 to 31 March 2015.
Results
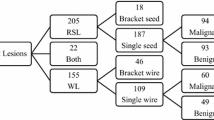
The study compared 153 WGL patients with 194 RSL patients. The two groups had no significant demographic differences. The average cost per patient for RSL, including opportunity costs, was $250.90 versus $1130.41 for WGL. Dedicated allocated radiology appointments to RSL increased (9 per day), and fewer radiologists were required for these procedures per day. Patients were transported to the operating room more quickly for RSL procedures (120 vs. 254 min; p < 0.001). Fewer vasovagal reactions occurred after insertion of RSL versus WGL (p = 0.05). No significant differences were observed in terms of surgical time, specimen volume, positive margins, or margin reexcision rates. No significant differences in postoperative complication rates were observed.
Conclusions
In this study, RSL had lower costs than WGL, allowed for more efficient use of radiology scheduling and resources, and had shorter wait times for patients on their day of surgery. In addition, RSL led to fewer vasovagal reactions at insertion. Therefore, RSL should be used instead of WGL given the reduced cost, decreased need of human resources, improved efficiency, and potential benefits to the patient experience.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Pouw B, De Wit-Van der Veen LJ, Stokkel MPM, Loo CE, Vrancken Peeters MTFD, Valdes Olmos RA. Heading toward radioactive seed localization in non-palpable breast cancer surgery? A meta-analysis. J Surg Oncol. 2015;111:185–91.
Barentsz MW, van den Bosch MAAJ, Veldhuis WB, van Diest PJ, Pijnappel RM, Witkamp AJ, Verkooijen HM. Radioactive seed localization for non-palpable breast cancer. Br J Surg. 2013;100:582–8.
Fleming FJ, Hill AD, McDermott EW, O’Doherty A, O’Higgins NJ, Quinn CM. Intraoperative margin assessment and reexcision rate in breast-conserving surgery. Eur J Surg Oncol. 2004;8:711–5.
Jakub JW, Gray RJ, Degnim AC, Boughey JC, Gardner M, Cox CE. Current status of radioactive seed for localization of non-palpable breast lesions. Am J Surg. 2010;199:522–8.
Murphy JO, Moo TA, King TA, et al. Radioactive seed localization compared to wire localization in breast-conserving surgery: initial 6-month experience. Ann Surg Oncol. 2013;20:4121–7.
Diego EJ, Soran A, McGuire KP, et al. Localizing high-risk lesions for excisional breast biopsy: a comparison between radioactive seed localization and wire localization. Ann Surg Oncol. 2014;21:3268–72.
Bloomquist EV, Ajkay N, Patil S, et al. A randomized prospective comparison of patient-assessed satisfaction and clinical outcomes with radioactive seed localization vs wire localization. Breast J. 2016;22:151–7.
Gray RJ, Salud C, Nguyen K, et al. Randomized prospective evaluation of a novel technique for biopsy o lumpectomy of non-palpable breast lesions: radioactive seed versus wire localization. Ann Surg Oncol. 2001;8:711–5.
Lovrics PJ, Goldsmith CH, Hodgson N, et al. A multi-centered, randomized, controlled trial comparing radio-guided seed localization to standard wire localization for non-palpable, invasive, and in situ breast carcinomas. Ann Surg Oncol. 2011;18:3407–14.
Loving VA, Edwards DB, Roche KT, et al. Monte Carlo simulation to analyze the cost-benefit of radioactive seed localization versus wire localization for breast-conserving surgery in fee-for-service healthcare systems compared with accountable care organizations. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2014;202:1383–8.
Sharek D, Zuley ML, Zhang JY, Sora A, Ahrendt GM, Ganott MA. Radioactive seed localization versus wire localization for lumpectomies: a comparison of outcomes. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2015;204:872–7.
Acknowledgment
The authors acknowledge Sasha Van Katwyk, a health economist at the Ottawa Hospital Research Institute, for his contributions to the cost comparison calculations.
DISCLOSURE
There are no conflicts of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, Y., Seely, J., Cordeiro, E. et al. Radioactive Seed Localization Versus Wire-Guided Localization for Nonpalpable Breast Cancer: A Cost and Operating Room Efficiency Analysis. Ann Surg Oncol 24, 3567–3573 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1245/s10434-017-6084-z
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1245/s10434-017-6084-z