Abstract
Purpose
An increasing proportion of breast cancer patients undergo contralateral prophylactic mastectomy (CPM) to reduce their risk of contralateral breast cancer (CBC). Our goal was to evaluate CBC risk perception changes over time among breast cancer patients.
Methods
We conducted a prospective, longitudinal study of women with newly diagnosed unilateral breast cancer. Patients completed a survey before and approximately 2 years after treatment. Survey questions used open-ended responses or 5-point Likert scale scoring (e.g., 5 = very likely, 1 = not at all likely).
Results
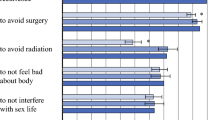
A total of 74 women completed the presurgical treatment survey, and 43 completed the postsurgical treatment survey. Baseline characteristics were not significantly different between responders and nonresponders of the follow-up survey. The mean estimated 10-year risk of CBC was 35.7 % on the presurgical treatment survey and 13.8 % on the postsurgical treatment survey (p < 0.001). The perceived risks of developing cancer in the same breast and elsewhere in the body significantly decreased between surveys. Both CPM and non-CPM (breast-conserving surgery or unilateral mastectomy) patients’ perceived risk of CBC significantly decreased from pre- to postsurgical treatment surveys. Compared with non-CPM patients, CPM patients had a significantly lower perceived 10-year risk of CBC (5.8 vs. 17.3 %, p = 0.046) on postsurgical treatment surveys.
Conclusions
The perceived risk of CBC significantly attenuated over time for both CPM and non-CPM patients. These data emphasize the importance of early physician counseling and improvement in patient education to provide women with accurate risk information before they make surgical treatment decisions.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Early Breast Cancer Trialists’ Collaborative G, Davies C, Godwin J, et al. Relevance of breast cancer hormone receptors and other factors to the efficacy of adjuvant tamoxifen: patient-level meta-analysis of randomised trials. Lancet. 2011;378:771–84.
Nichols HB, Berrington de Gonzalez A, Lacey JV, Jr., Rosenberg PS, Anderson WF. Declining incidence of contralateral breast cancer in the United States from 1975 to 2006. J Clin Oncol. 2011;29:1564–9.
King TA, Sakr R, Patil S, et al. Clinical management factors contribute to the decision for contralateral prophylactic mastectomy. J Clin Oncol. 2011;29:2158–64.
McLaughlin CC, Lillquist PP, Edge SB. Surveillance of prophylactic mastectomy: trends in use from 1995 through 2005. Cancer. 2009;115:5404–12.
Sorbero ME, Dick AW, Beckjord EB, Ahrendt G. Diagnostic breast magnetic resonance imaging and contralateral prophylactic mastectomy. Ann Surg Oncol. 2009;16:1597–605.
Tuttle TM, Habermann EB, Grund EH, Morris TJ, Virnig BA. Increasing use of contralateral prophylactic mastectomy for breast cancer patients: a trend toward more aggressive surgical treatment. J Clin Oncol. 2007;25:5203–9.
Tuttle TM, Jarosek S, Habermann EB, et al. Increasing rates of contralateral prophylactic mastectomy among patients with ductal carcinoma in situ. J Clin Oncol. 2009;27:1362–7.
Yao K, Stewart AK, Winchester DJ, Winchester DP. Trends in contralateral prophylactic mastectomy for unilateral cancer: a report from the National Cancer Data Base, 1998-2007. Ann Surg Oncol. 2010;17:2554–62.
Abbott A, Rueth N, Pappas-Varco S, Kuntz K, Kerr E, Tuttle T. Perceptions of contralateral breast cancer: an overestimation of risk. Ann Surg Oncol. 2011;18:3129–36.
Rakovitch E, Franssen E, Kim J, et al. A comparison of risk perception and psychological morbidity in women with ductal carcinoma in situ and early invasive breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2003;77:285–93.
Yi M, Hunt KK, Arun BK, et al. Factors affecting the decision of breast cancer patients to undergo contralateral prophylactic mastectomy. Cancer Prev Res. 2010;3(8):1026–34.
Rosenberg SM, Tracy MS, Meyer ME, et al. Perceptions, knowledge, and satisfaction with contralateral prophylactic mastectomy among young women with breast cancer: a cross-sectional survey. Ann Intern Med. 2013;159:373–81.
Liu Y, Perez M, Schootman M, et al. A longitudinal study of factors associated with perceived risk of recurrence in women with ductal carcinoma in situ and early-stage invasive breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2010;124:835–44.
Partridge A, Adloff K, Blood E, et al. Risk perceptions and psychosocial outcomes of women with ductal carcinoma in situ: longitudinal results from a cohort study. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2008;100:243–51.
Alexander NE, Ross J, Sumner W, Nease RF, Jr., Littenberg B. The effect of an educational intervention on the perceived risk of breast cancer. J Gen Intern Med. 1996;11:92–7.
Quillin JM, McClish DK, Jones RM, et al. Duration of an intervention’s impact on perceived breast cancer risk. Health Educ Behav. 2008;35:855–65.
Goldflam K, Hunt KK, Gershenwald JE, et al. Contralateral prophylactic mastectomy. Predictors of significant histologic findings. Cancer. 2004;101:1977–86.
Frost MH, Slezak JM, Tran NV, et al. Satisfaction after contralateral prophylactic mastectomy: the significance of mastectomy type, reconstructive complications, and body appearance. J Clin Oncol. 2005;23:7849–56.
Altschuler A, Nekhlyudov L, Rolnick SJ, et al. Positive, negative, and disparate: women’s differing long-term psychosocial experiences of bilateral or contralateral prophylactic mastectomy. Breast J. 2008;14:25–32.
Montgomery LL, Tran KN, Heelan MC, et al. Issues of regret in women with contralateral prophylactic mastectomies. Ann Surg Oncol. 1999;6:546–52.
Herrinton LJ, Barlow WE, Yu O, et al. Efficacy of prophylactic mastectomy in women with unilateral breast cancer: a cancer research network project. J Clin Oncol. 2005;23:4275–86.
McDonnell SK, Schaid DJ, Myers JL, et al. Efficacy of contralateral prophylactic mastectomy in women with a personal and family history of breast cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2001;19:3938–43.
Peralta EA, Ellenhorn JD, Wagman LD, Dagis A, Andersen JS, Chu DZ. Contralateral prophylactic mastectomy improves the outcome of selected patients undergoing mastectomy for breast cancer. Am J Surg. 2000;180:439–45.
van Sprundel TC, Schmidt MK, Rookus MA, et al. Risk reduction of contralateral breast cancer and survival after contralateral prophylactic mastectomy in BRCA1 or BRCA2 mutation carriers. Br J Cancer. 2005;93:287–92.
Disclosure
None.
Funding
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Portschy, P.R., Abbott, A.M., Burke, E.E. et al. Perceptions of Contralateral Breast Cancer Risk: A Prospective, Longitudinal Study. Ann Surg Oncol 22, 3846–3852 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1245/s10434-015-4442-2
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1245/s10434-015-4442-2