Abstract
Purpose
The peritoneal cancer index (PCI) is used to refer gastrointestinal malignancy patients to either palliative or curative management of their peritoneal carcinomatosis. The aim of this retrospective study was to evaluate the prognostic value of the PCI in patients with primary advanced epithelial ovarian cancer (EOC) after complete cytoreductive surgery.
Methods
PCI quantitatively assesses cancer distribution on the peritoneum by calculating tumor sizes in each of 13 abdominopelvic regions. Correlation between PCI score and clinical factors were analyzed using Kendall's tau b. Univariate and multivariate survival analyses were performed with the Kaplan–Meier method and Cox regression model, respectively.
Results
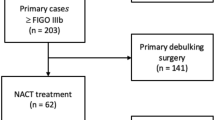
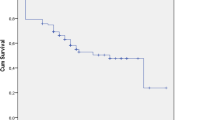
We retrospectively enrolled 80 consecutive patients with primary EOC treated in our gynecology department. All patients underwent complete cytoreductive surgery. Patients whose history included interval tumor debulking and completion cytoreductive surgery were excluded. Most tumors were of a serous histological subtype (96.3 %). Median age at diagnosis was 58.0 years. Their median PCI score was 12.0 (range 3–32). We found statistical correlations between PCI and ascites (p = 0.001), surgery duration (p < 0.001), T status of TNM staging (p = 0.036), and preoperative CA 125 (p = 0.025). In the univariate analysis, higher PCI scores were related to poor overall (OS) and progression-free (PFS) survival rates (p = 0.036 and p < 0.001, respectively). Multivariate analysis showed that the association remained significant only for PFS (p = 0.005), not for OS (p = 0.162).
Conclusions
PCI did not portend OS in patients with primary ovarian cancer. Further prospective and multicenter studies are needed to validate these results.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jemal A, Bray F, Center MM, Ferlay J, Ward E, Forman D. Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin. 2011;61(2):69–90.
Holschneider CH, Berek JS. Ovarian cancer: epidemiology, biology, and prognostic factors. Semin Surg Oncol. 2000;19(1):3–10.
Heintz AP, Odicino F, Maisonneuve P, et al. Carcinoma of the ovary. FIGO 26th Annual Report on the Results of Treatment in Gynecological Cancer. Int J Gynaecol Obstet. 2006;95(Suppl 1):S161–92.
Engel J, Eckel R, Schubert-Fritschle G, et al. Moderate progress for ovarian cancer in the last 20 years: prolongation of survival, but no improvement in the cure rate. Eur J Cancer. 2002;38(18):2435–45.
Meyers MA. Distribution of intra-abdominal malignant seeding: dependency on dynamics of flow of ascitic fluid. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1973;119(1):198–206.
Gilly FN, Carry PY, Sayag AC, et al. Regional chemotherapy (with mitomycin C) and intra-operative hyperthermia for digestive cancers with peritoneal carcinomatosis. Hepatogastroenterology. 1994;41(2):124–9.
Kajitani T. The general rules for the gastric cancer study in surgery and pathology. Part I. Clinical classification. Jpn J Surg. 1981;11(2):127–39.
Sugarbaker PH, Jablonski KA. Prognostic features of 51 colorectal and 130 appendiceal cancer patients with peritoneal carcinomatosis treated by cytoreductive surgery and intraperitoneal chemotherapy. Ann Surg. 1995;221(2):124–32.
Verwaal VJ, van Tinteren H, van Ruth S, Zoetmulder FA. Predicting the survival of patients with peritoneal carcinomatosis of colorectal origin treated by aggressive cytoreduction and hyperthermic intraperitoneal chemotherapy. Br J Surg. 2004;91(6):739–46.
Eisenkop SM, Spirtos NM, Friedman RL, Lin WC, Pisani AL, Perticucci S. Relative influences of tumor volume before surgery and the cytoreductive outcome on survival for patients with advanced ovarian cancer: a prospective study. Gynecol Oncol. 2003;90(2):390–6.
Sehouli J, Konsgen D, Mustea A, et al. [“IMO”–intraoperative mapping of ovarian cancer]. Zentralbl Gynakol. 2003;125(3–4):129–35.
Sehouli J, Senyuva F, Fotopoulou C, et al. Intra-abdominal tumor dissemination pattern and surgical outcome in 214 patients with primary ovarian cancer. J Surg Oncol. 2009;99(7):424–7.
Fagotti A, Ferrandina G, Fanfani F, et al. A laparoscopy-based score to predict surgical outcome in patients with advanced ovarian carcinoma: a pilot study. Ann Surg Oncol. 2006;13(8):1156–61.
Zivanovic O, Sima CS, Iasonos A, et al. The effect of primary cytoreduction on outcomes of patients with FIGO stage IIIC ovarian cancer stratified by the initial tumor burden in the upper abdomen cephalad to the greater omentum. Gynecol Oncol. 2010;116(3):351–7.
Aletti GD, Eisenhauer EL, Santillan A, et al. Identification of patient groups at highest risk from traditional approach to ovarian cancer treatment. Gynecol Oncol. 2011;120(1):23–8.
Verleye L, Ottevanger PB, van der Graaf W, et al. EORTC-GCG process quality indicators for ovarian cancer surgery. Eur J Cancer. 2009;45(4):517–26.
Bristow RE, Tomacruz RS, Armstrong DK, Trimble EL, Montz FJ. Survival effect of maximal cytoreductive surgery for advanced ovarian carcinoma during the platinum era: a meta-analysis. J Clin Oncol. 2002;20(5):1248–59.
Panici PB, Maggioni A, Hacker N, et al. Systematic aortic and pelvic lymphadenectomy versus resection of bulky nodes only in optimally debulked advanced ovarian cancer: a randomized clinical trial. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2005;97(8):560–6.
Sehouli J, Savvatis K, Braicu EI, Schmidt SC, Lichtenegger W, Fotopoulou C. Primary versus interval debulking surgery in advanced ovarian cancer: results from a systematic single-center analysis. Int J Gynecol Cancer. 2010;20(8):1331–40.
Cornelis S, Van Calster B, Amant F, Leunen K, van der Zee AG, Vergote I. Role of neoadjuvant chemotherapy in the management of stage IIIC-IV ovarian cancer: survey results from the members of the European Society of Gynecological Oncology. Int J Gynecol Cancer. 2012;22(3):407–16.
Grabowski JP, Harter P, Hils R, et al. Outcome of immediate re-operation or interval debulking after chemotherapy at a gynecologic oncology center after initially incomplete cytoreduction of advanced ovarian cancer. Gynecol Oncol. 2012;126(1):54–7.
Gagliardi AR, Fung MF, Langer B, Stern H, Brown AD. Development of ovarian cancer surgery quality indicators using a modified Delphi approach. Gynecol Oncol. 2005;97(2):446–56.
Jacquet P, Sugarbaker PH. Clinical research methodologies in diagnosis and staging of patients with peritoneal carcinomatosis. Cancer Treat Res. 1996;82:359–74.
Sugarbaker PH. Successful management of microscopic residual disease in large bowel cancer. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 1999;43(Suppl):S15–25.
Elias D, Souadka A, Fayard F, et al. Variation in the peritoneal cancer index scores between surgeons and according to when they are determined (before or after cytoreductive surgery). Eur J Surg Oncol. 2012;38(6):503–8.
Eisenhauer EA, Therasse P, Bogaerts J, et al. New response evaluation criteria in solid tumours: revised RECIST guideline (version 1.1). Eur J Cancer. 2009;45(2):228–47.
Morgan RJ Jr., Alvarez RD, Armstrong DK, et al. Ovarian cancer: clinical practice guidelines in oncology. J Natl Compr Cancer Netw 2008;6(8):766–94.
Portilla AG, Sugarbaker PH, Chang D. Second-look surgery after cytoreduction and intraperitoneal chemotherapy for peritoneal carcinomatosis from colorectal cancer: analysis of prognostic features. World J Surg. 1999;23(1):23–9.
Elias D, Blot F, El Otmany A, et al. Curative treatment of peritoneal carcinomatosis arising from colorectal cancer by complete resection and intraperitoneal chemotherapy. Cancer. 2001;92(1):71–6.
Glehen O, Gilly FN, Boutitie F, et al. Toward curative treatment of peritoneal carcinomatosis from nonovarian origin by cytoreductive surgery combined with perioperative intraperitoneal chemotherapy: a multi-institutional study of 1,290 patients. Cancer. 2010;116(24):5608–18.
Harmon RL, Sugarbaker PH. Prognostic indicators in peritoneal carcinomatosis from gastrointestinal cancer. Int Semin Surg Oncol. 2005;2(1):3.
Tentes AA, Tripsiannis G, Markakidis SK, et al. Peritoneal cancer index: a prognostic indicator of survival in advanced ovarian cancer. Eur J Surg Oncol. 2003;29(1):69–73.
Makar AP, Baekelandt M, Trope CG, Kristensen GB. The prognostic significance of residual disease, FIGO substage, tumor histology, and grade in patients with FIGO stage III ovarian cancer. Gynecol Oncol. 1995;56(2):175–80.
Eisenkop SM, Friedman RL, Wang HJ. Complete cytoreductive surgery is feasible and maximizes survival in patients with advanced epithelial ovarian cancer: a prospective study. Gynecol Oncol. 1998;69(2):103–8.
Griffiths CT. Surgical resection of tumor bulk in the primary treatment of ovarian carcinoma. Natl Cancer Inst Monogr. 1975;42:101–4.
Hacker NF, Berek JS, Lagasse LD, Nieberg RK, Elashoff RM. Primary cytoreductive surgery for epithelial ovarian cancer. Obstet Gynecol. 1983;61(4):413–20.
Allen DG, Heintz AP, Touw FW. A meta-analysis of residual disease and survival in stage III and IV carcinoma of the ovary. Eur J Gynaecol Oncol. 1995;16(5):349–56.
Le T, Krepart GV, Lotocki RJ, Heywood MS. Does debulking surgery improve survival in biologically aggressive ovarian carcinoma? Gynecol Oncol. 1997;67(2):208–14.
Wimberger P, Lehmann N, Kimmig R, et al. Prognostic factors for complete debulking in advanced ovarian cancer and its impact on survival: an exploratory analysis of a prospectively randomized phase III study of the Arbeitsgemeinschaft Gynaekologische Onkologie Ovarian Cancer Study Group (AGO-OVAR). Gynecol Oncol. 2007;106(1):69–74.
Konigsrainer I, Zieker D, Glatzle J, et al. Experience after 100 patients treated with cytoreductive surgery and hyperthermic intraperitoneal chemotherapy. World J Gastroenterol 2012;18(17):2061–6.
Sugarbaker PH. Management of peritoneal-surface malignancy: the surgeon’s role. Langenbecks Arch Surg. 1999;384(6):576–87.
Swellengrebel HA, Zoetmulder FA, Smeenk RM, Antonini N, Verwaal VJ. Quantitative intra-operative assessment of peritoneal carcinomatosis: a comparison of three prognostic tools. Eur J Surg Oncol. 2009;35(10):1078–84.
Koh JL, Yan TD, Glenn D, Morris DL. Evaluation of preoperative computed tomography in estimating peritoneal cancer index in colorectal peritoneal carcinomatosis. Ann Surg Oncol. 2009;16(2):327–33.
De Bree E, Koops W, Kroger R, van Ruth S, Witkamp AJ, Zoetmulder FA. Peritoneal carcinomatosis from colorectal or appendiceal origin: correlation of preoperative CT with intraoperative findings and evaluation of interobserver agreement. J Surg Oncol. 2004;86(2):64–73.
Dromain C, Leboulleux S, Auperin A, et al. Staging of peritoneal carcinomatosis: enhanced CT vs. PET/CT. Abdom Imaging. 2008;33(1):87–93.
Esquivel J, Chua TC, Stojadinovic A, et al. Accuracy and clinical relevance of computed tomography scan interpretation of peritoneal cancer index in colorectal cancer peritoneal carcinomatosis: a multi-institutional study. J Surg Oncol. 2010;102(6):565–70.
Pfannenberg C, Konigsrainer I, Aschoff P, et al. (18)F-FDG-PET/CT to select patients with peritoneal carcinomatosis for cytoreductive surgery and hyperthermic intraperitoneal chemotherapy. Ann Surg Oncol. 2009;16(5):1295–303.
Acknowledgment
This project was supported by a research grant form Berliner Krebsgesellschaft e. V.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gasimli, K., Braicu, E.I., Richter, R. et al. Prognostic and Predictive Value of the Peritoneal Cancer Index in Primary Advanced Epithelial Ovarian Cancer Patients After Complete Cytoreductive Surgery: Study of Tumor Bank Ovarian Cancer. Ann Surg Oncol 22, 2729–2737 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1245/s10434-014-4329-7
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1245/s10434-014-4329-7