Abstract
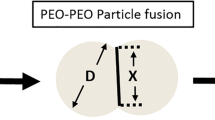
The abuse of prescription opioid drugs is a well-documented and very serious problem. One of the typical first steps an abuser will take is to manipulate a tablet into to a fine powder. To deter this behavior, formulators use crush-resistant technologies like polyethylene oxide (PEO). When heat-treated, PEO creates a hard, flexible tablet that cannot be easily ground down into a fine powder. We investigated the effects of PEO molecular weight (MW), annealing temperature, and annealing time on tablet compression deformation behavior and fracture resistance. These tests were designed to represent an abuser’s attempt to smash and grind a tablet, respectively. Annealing temperatures above the melting point of PEO showed the most improvement in mechanical properties compared with that in unannealed tablets. The minimum annealing time was dependent on the polymer MW and annealing temperature. Tablets were manipulated using a coffee grinder, and the particle size of the resulting powders was measured. The particle size correlated well with fracture toughness, demonstrating that increasing fracture toughness increases the manipulation resistance of a PEO tablet.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Compton WM, Volkow ND. Major increases in opioid analgesic abuse in the United States: concerns and strategies. Drug Alcohol Depend. 2006;81(2):103–7.
Wright C, Schnoll S, Bernstein D. Risk evaluation and mitigation strategies for drugs with abuse liability. Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences. 2008;1141(1):284–303.
Ostling PS, Davidson KS, Anyama BO, Helander EM, Wyche MQ, Kaye AD. America’s opioid epidemic: a comprehensive review and look into the rising crisis. Curr Pain Headache Rep. 2018;22(5):32.
Maincent J, Zhang F. Recent advances in abuse-deterrent technologies for the delivery of opioids. Int J Pharm. 2016;510:57–72.
Omidian A, Mastropietro D, Omidian H. Routes of opioid abuse and its novel deterrent formulations. J Dev Drugs. 2015;4(5):141–7.
Schaeffer T. Abuse-deterrent formulations, an evolving technology against the abuse and misuse of opioid analgesics. J Med Toxicol. 2012;8(4):400–7.
Tygesen PH, Oevergaard JM, Lindhardt K, Lyhne-Iversen LI, Olsen MR, Haahr A-M, et al., Inventors; Egalet A/S, assignee. Pharmaceutical compositions resistant to abuse. US patent 8603526. 2010.
Webster L, Marie BS, McCarberg B, Passik SD, Panchal SJ, Voth E. Review article Current status and evolving role of abuse-deterrent opioids in managing patients with chronic pain. J Opioid Manag 2011;7(3):235–245.
Muley S, inventor; Purdue Pharma L.P., assignee. Pharmaceutical dosage forms comprising poly(epsilon-caprolactone) and polyethylene oxide 2013 June 13.
Bartholomaus J, Kugelmann H, Arkenau-Marlc E, inventors; Grunenthal GmbH, assignee. Abuse-proofed dosage form. The United States of America patent US 8,309,060 B2. 2012 November 13.
Bartholomaeus JH, Arkenau-Maric E, Galia E. Opioid extended-release tablets with improved tamper-resistant properties. Expert Opin Drug Deliv. 2012;9(8):879–91.
Wright C, Oshlack B, Breder C, inventors; Purdue Pharma L.P., assignee. Pharmaceutical formulation containing gelling agent. United States 2012 December 25.
Rahman Z, Yang Y, Korang-Yeboah M, Siddiqui A, Xu X, Ashraf M, et al. Assessing impact of formulation and process variables on in-vitro performance of directly compressed abuse deterrent formulations. Int J Pharm. 2016;502(1–2):138–50.
Rahman Z, Zidan AS, Korang-Yeboah M, Yang Y, Siddiqui A, Shakleya D, et al. Effects of excipients and curing process on the abuse deterrent properties of directly compressed tablets. Int J Pharm. 2017;517(1–2):303–11.
Casettari L, Bonacucina G, Cespi M, Perinelli DR, Micheli M, Cacciatore I, et al. Effect of manufacturing temperature and molecular weights on compression, mechanical and dissolution properties of PEO matrix tablets. J Drug Deliv Sci Technol. 2016;32:236–40.
Tocce E, Balwinski K, Lapham M, Bishop M, Watson T, Grasman N. Mechanical properties of polyethylene oxide for use in abuse deterrent formulations. AAPS Annual Meeting and Exposition; San Diego, CA2017.
Bailey FE, Koleske JV. Poly(ethylene oxide). New York, NY: Academic Press, Inc.; 1976. 173 p.
Back DM, Schmitt R. Ethylene oxide polymers. Kirk-Othmer encyclopedia of chemical technology. 10: John Wiley & Sons, Inc.; 2004. p. 673–696.
Broek D. The practical use of fracture mechanics: Kluwer Academic Publishers; 1988.
Moore J, Flanner HH. Mathematical comparison of dissolution profiles. Pharm Technol. 1996(June:64–74.
Fracture behaviour of polymers. Kinloch AJ, Young RJ, editors. London and New York: Applied Science Publishers; 1983. 114 p.
Polymer Blends: Formulatin and Performance, Two-Volume Set. Paul D, Crockrell E, editors: Wiley-Interscience; 2000.
Goodier JN. Concentration of stress around spherical and cylindrical inclusions and flaws. J Appl Mech. 1933;55:39–44.
Eshelby JD, Peierls RE. The determination of the elastic field of an ellipsoidal inclusion, and related problems. Proceedings of the Royal Society of London Series A Mathematical and Physical Sciences. 1957;241(1226):376–96.
Sue H-J, Yee AF. Deformation behaviour of a polycarbonate plate with a circular hole: finite elements model and experimental observations. Polymer. 1988;29(9):1619–24.
Sue H-J. University of Michigan, Ann Arbor; 1988.
Jans E, Marie J, Kiekens F, Rene I, Voorspoels J, Firmin M, et al., inventors; Grunenthal GMBH, assignee. Pharmaceutical Dosage Form 2009.
Jarosz PJ, Parrott EL. Factors influencing axial and radial tensile strengths of tablets. J Pharm Sci. 1982;71(6):607–14.
Rajulu SL, Klute GK. A comparison of hand grasp breakaway strengths and bare-handed grip strengths of the astronauts, SML III test subjects, and the subjects from the general population. NASA: NASA, 1993 January. Report No.: Contract No.: NASA Technical Paper 3286.
Man-Systems Integration Standards - Section 4 Human Performance Capabilities. In: NASA, editor. https://msis.jsc.nasa.gov/sections/section04.htm: National Aeronautics and Space Administration.
Maddineni S, Battu SK, Morott J, Majumdar S, Repka MA. Formulation optimization of hot melt extruded abuse deterrent pellet dosage form utilizing design of experiments. J Pharm Pharmacol. 2014;66(2):309–22.
Zhang F, Meng F, Lubach J, Koleng J, Watson NA. Properties and mechanisms of drug release from matrix tablets containing poly(ethylene oxide) and poly(acrylic acid) as release retardants. Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2016;105:97–105.
L’Hote-Gaston J, Karas C, Schmitt R, editors. Effect of polymer concentration, polymer molecular weight, drug solubility, and filler solubility on drug release from polyethylene oxide hydrophilic extended release matrices. AAPS; 2010; New Orleans, LA.
L’Hote-Gaston J, Schmitt R, Levina M, Wen G, Rajabi-Siahboomi A, editors. The use of polyethylene oxide mixtures to study formulation robustness in hydrophilic extended release matrix tablets. AAPS Annual Meeting and Exposition; 2009 November 8–12; Los Angeles, CA.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Guest Editors: Heather Boyce, Steve R. Byrn, and Stephen W. Hoag
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic Supplementary Material
ESM 1
(DOCX 103 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tocce, E., Bishop, M., Balwinski, K. et al. Mechanical Characterization of Thermally Annealed Tablets Containing Polyethylene Oxide for Abuse Deterrence. AAPS PharmSciTech 21, 2 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1208/s12249-019-1528-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1208/s12249-019-1528-3