Abstract
Background
Poorly managed mechanical low back pain (MLBP) and its sequelae, such as severe pain, physical inactivity, and disability, negatively impact patients’ quality of life (QoL). The study aimed to determine the pain intensity (PI), physical activity (PA), QoL, and disability, the association between selected sociodemographic variables and PI, PA, QoL, and disability, and the relationship between PI, PA, QoL, and disability among Nigerians with chronic MLBP.
Methods
This cross-sectional study employed a consecutive sampling technique. Outcome measures included the Numeric Pain Scale, International Physical Activity Questionnaire-Short Form, WHO Quality-of-Life Brief, and Oswestry Disability Index for PI, PA, QoL, and disability, respectively. Descriptive statistics were used to summarize participants’ sociodemographic variables. Chi-square, Spearman’s correlation, and structural equation modeling (SEM) were used for inferential analyses.
Results
Two hundred and fifty chronic MLBP patients comprising 154 females and 96 males, completed the study. The mean PA, PI, QoL, and disability levels were 1118.03MET ± 615.30, 5.97 ± 2.69, 73.45% ± 14.21, and 21.7% ± 18.94, respectively. There was a significant correlation between PA and QoL (rho = 0.36, p = 0.001), PA and disability (rho = −0.42, p = 0.010), QoL and disability (rho = −0.21, p = 0.008), QoL and PI (rho = −6.72, p = 0.025), PI and disability (rho = 0.90, p = 0.022). Aside from age and PA (χ2 = 8.52, p = 0.045), there was no significant association between the sociodemographic variables and PI, PA, QoL, or disability. SEM showed a strong positive association between PI and disability (β = 0.80, p < 0.001).
Conclusion
Individuals with chronic MLBP had a low PA, moderate QoL, and significant disability. Incorporating PA, QoL, and disability assessments may enhance the evaluation and management of MLBP.
Similar content being viewed by others
Introduction
Pain is a physiological response to tissue damage. It causes significant neuromuscular, emotional, and psychosocial distress [1, 2]. Lower back pain (LBP) is a common musculoskeletal disorder experienced by humans [3, 4]. Mechanical low back pain (MLBP) refers to back pain that arises intrinsically from the spinal column, intervertebral discs, or surrounding soft tissues. It includes pain from vertebral compression fractures, lumbosacral muscle strain, disc herniation, lumbar spondylosis, spondylolisthesis, spondylolysis, and acute or chronic traumatic injury [5, 6].
Low back pain was the leading cause of years lived with disability (YLDs) worldwide and is associated with a high disease burden [7]. There was a substantial increase in global prevalence from 1990 (386.0 million) to 2019 (568.4 million) [7]. In Nigeria, the 12-month prevalence of LBP was 44%, while the point prevalence was 39%, with the greatest burden accounted for by people living in rural areas [8, 9]. The prevalence of LBP increases with age, and many older Nigerians are rural dwellers [9]. Relative to urban settlements, rurality imposes a huge disadvantage in access to health care, leading to higher disease burdens such as MLBP, disability, and poor quality of life (QoL) [9, 10].
Mechanical low back pain is associated with physical, emotional, and psychosocial distress and has negative socioeconomic consequences for the patients and their community [11]. It reduces an individual’s daily functioning capacity, and severe cases may lead to temporal or permanent disability, increasing the health care burden, absenteeism from work, and depletion of the community workforce [12]. Therefore, a comprehensive management plan for MLBP should involve an assessment of PI, PA, QoL, disability, psychological, sociocultural, and economic factors [13, 14]. These parameters have been incorporated into the MLBP management guidelines in some countries [15, 16]. There is a need to replicate such a study in sub-Saharan Africa to inform evidence for adopting these practices [10]. Africans have distinct sociocultural factors that impact their pain threshold, quality of life, and access to care [17]. With a population estimate of about 200 million people, Nigeria is the most populous country in sub-Saharan Africa and the most populous Black nation in the world [18]. Although few studies have assessed the correlation between some of these constructs, the present study further explored the direct and the PA- and QoL-mediated effects of chronic MLBP on disability using a multivariate structural equation model.
The overall aim of the study was to determine the levels and correlates of PI, physical activity (PA), QoL, and disability, among people with chronic MLBP in public-funded hospitals in Anambra State, Nigeria. The study hypotheses were that there would be no significant (i) correlation between PI, PA, QoL, and disability, (ii) association between PI, PA, QoL, and disability and the participants’ sociodemographic characteristics, and (iii) direct effect of MLBP on disability while accounting for QoL and PA as mediator variables.
Methods
Study design
This study was a cross-sectional survey, a type of observational study that obtains and analyses data from a population at a specific point in time [19]. A consecutive non-probability sampling technique was used to recruit participants from public-funded hospitals in Anambra State, Nigeria, between May and July 2021. The institutional Human Research Ethics Committees of the Faculty of Health Sciences and Technology, Nnamdi Azikiwe University, Anambra, Nigeria, approved the study protocol (reference number: NAU/FHST/2021/MRH60). The approved protocol, participants’ privacy, and confidentiality of data were strictly adhered to. Participants were informed of their right to withdraw at any point in the study. Each eligible participant signed an individual informed consent form before participating in the study. All methods were carried out in accordance with the guidelines of the World Medical Association Declaration of Helsinki: ethical principles for medical research involving human subjects [20]. The study was reported following the Strengthening the Reporting of Observational Studies in Epidemiology (STROBE) guidelines for reporting cross-sectional studies [21].
Participants and setting
Participants were recruited from persons with chronic MLBP attending physiotherapy clinics in public-funded hospitals in Anambra State, Nigeria. Following the submission of a copy of the approved study protocol, written permission was granted by the physiotherapist heading each clinic to assess the patients who met the inclusion criteria. In Nigerian hospitals, physiotherapy is accessed after initial diagnosis and referral from a primary physician or surgeon [1, 22,23,24]. Therefore, the participants enrolled in this study were diagnosed by consultant orthopedic doctors and referred to physiotherapy clinics for physical therapy.
Eligibility criteria
Participant inclusion criteria were being (i) diagnosed with MLBP of at least three months duration, (b) attending follow-up physiotherapy appointments in any of the public-funded hospitals in Anambra State, Nigeria, (c) fluent in the English language, and (d) willing to grant an informed consent and participate in the study procedures.
Participants were excluded if they were below 18 years of age, non-ambulant, diagnosed with non-MLBP, neurological or musculoskeletal disorders affecting their ambulation, or acute traumatic back injury. Patients with systemic diseases such as sickle cell disease, complex regional pain syndrome, cancer, chronic kidney disease, cardiovascular diseases, uncontrolled diabetes, patients on corticosteroids, or who had prior spinal surgery or epidural injection within one month before the study were also excluded.
Sample size estimation
The sample size (n = 226) was calculated using a simple size formula for prevalence studies, n = (Z2P [1 – P])/d2; where n is the sample size, Z-score = 1.96 (95% level of confidence), d (precision/ effect size) = 0.05 and P (proportion) = 0.82 because the orthopedic-clinic-based prevalence of MLBP in the region was 82% [25]. In anticipation of a 10% incomplete survey response, we recruited 250 participants.
Research instruments and procedures for data collection
Participants’ sociodemographic variables of age, gender, marital status, education level, employment, and location were obtained using a bio-data form. The Numeric Pain Scale (NPS) was used to obtain participants’ PI on a scale of 0 (no pain) to 10 (worst imaginable pain). The NPS is a convenient, valid, reliable, and responsive measure of pain intensity among people with MLBP [26]. The interclass correlation reliability, r = 0.99 [26]. Afterwards, the participants were administered three questionnaires: International Physical Activity Questionnaire Short Form (IPAQ-SF), World Health Organization Quality of Life-Brief (WHOQoL-Brief), and Oswestry disability index (ODI), respectively.
The IPAQ-SF is a reliable, valid, and standardized self-completed questionnaire designed to measure the amount of energy spent on tasks (metabolic equivalent of task [MET]) or duration (minutes) and frequency (days) of physical activity in the last seven days based on the seven domains: job-related activity, active transportation, housework and maintenance, family care, recreation, sport, and leisure-time, and sitting time [27]. The IPAQ-SF was recommended for population prevalence studies, where time is limited because it is easier and more feasible to complete than the long form [27]. The IPAQ-SF was scored by rating PA level as multiples of metabolic equivalent (METs) expressed as MET-min per week, such that walking MET-minutes/week = 3.3*walking minutes*walking days, moderate MET-minutes/week = 4.0*moderate-intensity activity minutes*moderate days, and vigorous MET-minutes/week = 8.0*vigorous-intensity activity minutes*vigorous days. Total PA MET-minutes/week = sum of walking + moderate + vigorous MET-minutes/week scores. Sub-scores can be calculated for walking, moderate-intensity, and vigorous-intensity activities. The total physical activity test–retest reliability of a Hausa (Nigerian) language version of IPAQ-SF was (r) = 0.61, and concurrent validity with the English version was (r) = 0.92 [28].
The WHOQoL-Brief was used to assess the participants’ QoL. It is a standardized, reliable, and valid self-administered questionnaire comprising 26 questions on individuals’ perceptions of their physical and physiological health, social relationships, and environmental well-being over the previous two weeks [29]. The responses are based on a 5-point Likert scale (1 = “disagree” or “not at all” and 5 = “completely agree” or “extremely”). Domain scores were scaled positively such that higher aggregate scores signify a better QoL. Participants’ aggregate scores were converted to percentages, expected range (26–130) = 20 to 100%. The test-retest reliability of WHOQoL-Brief was (r) = 0.95 [29].
The ODI, a self-completed standardized, valid, and reliable questionnaire, was used to assess disability among the participants. It is a 10-item questionnaire which gives a subjective percentage score of the level of function (disability) in activities of daily living in patients experiencing low back pain. The domains include pain intensity, personal care, lifting, walking, sitting, standing, sleeping, traveling, sex, and social life. Each of the 10 items is scored 0 to 5, giving a total score range of 0 to 50, converted to a percentage (0 to 100%) as described by Fairbank and Pynsent [30]. The ODI is an internally consistent (α = 0.85) unidimensional scale with overall excellent construct validity and the ability to discriminate the severity of functional disability [31].
A staff physiotherapist trained as a research assistant in each of the selected hospitals assisted with questionnaire administration and data collection. The questionnaires were retrieved immediately from participants on completion and stored in a sealed brown envelope. At the end of the study, one of the authors retrieved all the completed questionnaires in person. Data were extracted with an encrypted electronic spreadsheet stored in a password-protected flash drive and locked in a drawer at the primary investigator’s office till the time of data analysis. All the hard copies of the questionnaire were destroyed immediately.
Variables
The primary outcomes: PI, PA, disability, and QoL, were assessed with appropriate instruments and recoded as continuous variables. The primary outcomes were categorized for PI (≤ 3 = mild, 4–6 = moderate, and ≥ 7 = severe pain) [32], PA (< 600 = low, 600–1500 = moderate, and > 1500 high MET) [27], disability (≤ 20% = mild, 21–40% = moderate, and ≥ 41 = severe disability) [33], and QoL (< 55 = poor, 55–85 = moderate, and > 85 = good QoL, using 70 ± 15 as the normative value [34]. The sociodemographic variable: age (years), was recorded as a continuous variable. Marital status (single = 1, married = 2, divorced/separated = 3, widowed = 4) was a nominal variable. Education level (informal = 1, primary = 2, secondary = 3, tertiary = 4) was considered an ordinal variable. Gender (female = 0, male = 1), employment (no = 0, yes = 1), and location (rural = 0, urban = 1) were dichotomous nominal variables.
Sampling and bias
The probability of sampling bias in the present study is low. The participants were consecutively drawn from eligible participants from all the selected hospitals synchronously. All persons who met the inclusion criteria had a chance to participate in the study. Consecutive sampling is a non-probability sampling technique in which every subject meeting the inclusion criteria is selected until the required sample size is achieved. It is better than convenience sampling in controlling sampling bias [35]. Moreover, the adequate sample size was carefully calculated and met.
Data analysis
Data were analyzed using the Statistical Package for Social Sciences (SPSS) version 26. Descriptive statistics such as frequency, percentage, mean, and standard deviation were used to summarize the participants’ sociodemographic characteristics. We examined the association between sociodemographic variables and the primary outcomes using Chi-square (χ2), and the correlation among the primary outcomes using Spearman’s correlation coefficient (rho); because PA data was skew. Finally, we completed a structural equation modeling (SEM) using IBM Analysis of Moment Structure (AMOS) software [36] to explore the direct effect and PA- and QoL-mediated effects of chronic MLBP intensity on disability. The paths’ standardized regression coefficients, 95% CI, and p values were generated using the maximum likelihood estimation approach. The model’s fitness indices threshold were the chi-square (p > 0.05), the root-mean-square error of approximation (RMSEA < 0.06), the goodness of fit index (GFI > 0.90), and the Tucker-Lewis index (TLI ≥ 0.90) [36]. The alpha level was set at 0.05.
Results
Participants’ sociodemographic characteristics
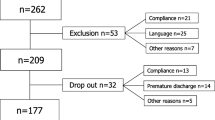
A total of 250 individuals with MLBP completed the study and were included in the analysis. Table 1 shows the participants’ sociodemographic characteristics. The majority of the participants 154 (61.6%) were women, and 127 (50.8%) were aged 50 years and above. Participants were mainly married 146 (58.3%), had secondary education 133 (83.2%), unemployed or retired 173 (69.2%), and resided in the urban area 164 (65.6%).
Univariate analyses: pain intensity, physical activity, disability, and quality of life
The average (mean ± SD) participants’ PI (5.97 ± 2.69), PA (1118.03 MET ± 615.30), disability (21.78% ± 18.94), and QoL (73.45 ± 14.21) were all moderate. Table 2 shows the frequency distribution of participants’ PI, PA, QoL, and disability across the categorical levels. Remarkably, a greater number of the participants had low levels of PA.
Bivariate analyses
The chi-square test showed a significant association between PA and participant’s age (χ2 = 8.52; p = 0.045) and between educational level and QoL (χ2 = 0.75; p = 0.022). There was no significant difference between other sociodemographic variables and the primary outcomes (Table 3). On the other hand, Spearman’s correlation coefficient (Table 4) showed a significant negative correlation between PA and disability (rho = −0.45; p = 0.010), but a significantly positive correlation with QoL (rho = 0.36; p = 0.001). Similarly, PI had a strong inverse correlation with QoL (rho = −6.72; p = 0.025) and a positive correlation with disability (rho = 0.90, p = 0.022). Although there were negative correlations between PA and PI and between QoL and disability, these correlations were of low strength and not statistically significant (Table 4).
Multivariate analyses
Figure 1 shows the standardized regression coefficient for the direct effect of PI on disability and the mediation (indirect) effects of QoL and PA on the path. The SEM met the recommended threshold for fitness indices, χ2 (1) = 0.420, p = 0.517, RMSEA = 0.000, CFI = 1.000, TLI = 1.000, GFI = 0.994, and AGFI = 0.941 (Table 5). The direct effect of chronic MLBP intensity (PI) and disability was significant (β = 0.80, p < 0.001). However, the direct effects of PI on PA (β = −0.16, p = 0.327), QoL (β = −0.14, p = 0.396), and PA (β = −0.09, p = 0.310) and QoL (β = −0.19, p = 0.022) on disability, were not significant. The total mediation (indirect) effect of PA and QoL (β = 0.041, p = 0.322) was insignificant. The SEM results aligned with Table 4, which showed that disability had the strongest correlation with PI.
Discussion
This study aimed to determine the association between sociodemographic factors, pain intensity, physical activity, quality of life, and disability among individuals with chronic MLBP. Although these parameters have been incorporated into the MLBP management guidelines in some countries [14, 15], more sub-Saharan African studies are needed to inform evidence for adopting these practices in the region [10]. The disease burden of MLBP is not limited to biophysical disorders and distress. Instead, psychosocial implications of MLBP can lead to increased sedentary behavior, disability, and poor QoL [13, 14]. Therefore, a comprehensive management plan for MLBP should involve an assessment of PI, PA, disability, QoL, and sociodemographic factors [9, 13]. The current study went beyond the simplistic analysis of these factors with bivariate models to construct a multivariate structural equation model for a holistic analysis of the constructs.
The goal of any healthcare system is to optimize care, including reduction of pain and disability and improvement of physical functioning and QoL. In the present study, a greater number of the participants recorded a low level of physical activity, moderate levels of pain intensity, disability, and QoL. This outcome was in line with Majedi et al. [37], who reported that most LBP patients with moderate pain intensity also had a moderate disability. The results also concurred with Johansson et al. [38], where most participants recorded moderate pain intensity and low physical functioning. However, the present study’s participants had moderate QoL, while those in Johansson et al. [38] had good QoL. Although the average QoL in our study was 73.45%, we used more stringent criteria to categorize the levels of QoL based on the literature [34]. Unlike other instruments that have established cut-off points for their outcomes: NPS [32], IPAQ-SF [27], and ODI [32], there is a paucity of data on the benchmark for WHOQoL-Brief among people with MLBP. Moreover, we used WHOQoL-Brief on the general population with MLBP, while Johansson et al. [38] used the Health-related Quality of Life Questionnaire on older adults. There is a need for future studies to establish categorical benchmarks for WHOQoL-Brief among people with MLBP. For instance, a WHOQoL score of 50% should be interpretable as fair, good, very good, or excellent QoL.
The bivariate analysis showed a significant positive correlation between physical activity and QoL. Research has shown that sedentary adults tend to report poorer QoL than their more physically active counterparts [39]. Moderate-to-severe low back pain can be debilitating, causing the patient to be less physically active, especially among older adults [3]. Similarly, Rétsági et al. [40] reported a positive relationship between physical activity level and QoL among adults. Physically active individuals are more capable of engaging in activities of daily living which lead to subjective satisfaction about one’s life and wellbeing. Furthermore, there was a moderate inverse correlation between QoL, pain intensity, and disability. Kovacs et al. [41] opined that low back pain influences disability and QoL. Although disabling pain affected both the physical and psychological domains of QoL, the physical domain of quality of life is the most strongly related factor to disability levels compared to other domains [42].
The present study also found correlations between pain intensity, physical activity, and disability, such that an increase in pain intensity correlated with a decrease in physical activity. In contrast, a reduction in physical activity correlated with increased disability. It appears that pain intensity has both a direct impact on disability and a mediating influence between physical inactivity and disability. These observations were confirmed by the multivariate SEM (Fig. 1), that increased pain intensity reduced physical activities and quality of life, in addition to the direct effect of pain leading to increased disability. Our study supported the finding of Houde et al. [43] that there was a significant positive correlation between pain intensity and disability in patients with low back pain. Chung et al. [44] also correlated low back pain intensity and physical disability among 55 patients with chronic low back pain and reported a linear correlation between the two variables. Another study found an association between pain intensity and disability in 195 hospital-attending patients with common low back pain [41]. On the other hand, Lin et al. [45] concluded from a systematic review of 18 studies that there was an association between physical activity and low back pain-related disability. Due to the observed negative correlation between physical activity, and disability among people with low back pain, Ryan et al. [46] suggested that physical activity can be used as an outcome measure of functional ability in people with chronic low back pain.
Clinical implications
The clinical implication of this study is that incorporating disability, physical activity, and quality of life assessment in the management and follow-up of people with MLBP may enhance the traditional biophysical approach mainly based on structural evaluation. Attention has been paid in the last decade to the biopsychosocial factors that may lead to the development and sustenance of LBP. Pain intensity, health-related QoL, and the degree of pain interference with an individual’s daily activities (disability) belong to a set of primary-based outcomes in LBP [14]. However, research findings in this area are inconsistent because of the difficulty in standardizing the outcome measures and controlling for confounding factors [47]. Clinicians should expect psychosocial limitations such as poor QoL, activity restriction, and disability among clients with MLBP and be proactive in providing comprehensive care.
Limitations
The study has some limitations. Participants were sampled by a non-probability (consecutive) method—affecting the generalizability of our findings. However, the participants’ demographic characteristics in the present study were similar to two previous studies conducted among people with LBP in the same region of the country [9, 25]. Self-reported instruments were used for data collection, which may lead to recall and social desirability biases. For instance, participants may overestimate their pain intensity or physical activity levels.
Conclusion
There was a correlation between pain intensity, physical activity, and disability, such that an increased pain intensity reduced physical activities and quality of life, in addition to the direct effect of pain leading to increased disability. Therefore, incorporating physical activity, disability, and QoL assessment in the management and follow-up of people with chronic mechanical low back pain may enhance the traditional biophysical approach that has to do with structural evaluation.
Availability of data and materials
The dataset generated and analyzed during the current study will be made public by 2026 but is available from the corresponding author at a reasonable request. This is in adherence to our institution’s 5-year data retention policy.
Abbreviations
- AGFI:
-
Adjusted Goodness of Fit Index
- CFI:
-
Comparative Fit Index
- GFI:
-
Goodness of Fit Index
- LBP:
-
Lower back pain
- MLBP:
-
Mechanical lower back pain
- PA:
-
Physical activity
- PI:
-
Pain intensity
- QoL:
-
Quality of life
- RMSEA:
-
Root-mean-square error of approximation
- SD:
-
Standard deviation
- SEM:
-
Structural equation model
- TLI:
-
Tucker-Lewis’s Index
- YLD:
-
Years lived with disability
References
Jensen MP, Moore MR, Bockow TB, Ehde DM, Engel JM. Psychosocial factors and adjustment to chronic pain in persons with physical disabilities: a systematic review. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2011;92(1):146–60.
Raja SN, Carr DB, Cohen M, Finnerup NB, Flor H, Gibson S, et al. The revised International Association for the Study of Pain definition of pain: concepts, challenges, and compromises. Pain. 2020;161(9):1976–82.
Pitchai P, Chauhan SK, Sreeraj SR. Impact of kinesiophobia on quality of life in subjects with low back pain: a cross-sectional study. Int J Physiother Res. 2017;5(4):2232–9.
Ezema CI, Onyeso OK, Nna EO, Awosoga OA, Odole AC, Kalu ME, et al. Transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation effects on pain-intensity and endogenous opioids levels among chronic low-back pain patients: a randomised controlled trial. J Back Musculoskelet Rehabil. 2022;35(5):1053–64.
Patrick N, Emanski E, Knaub MA. Acute and chronic low back pain. Med Clin North Am. 2014;98(4):777–89.
Will JS, Bury DC, Miller JA. Mechanical low back pain. Am Fam Physician. 2018;98(7):421–8.
Chen S, Chen M, Wu X, Lin S, Tao C, Cao H, et al. Global, regional and national burden of low back pain 1990–2019: a systematic analysis of the global burden of disease study 2019. J Orthop Transl. 2022;32:49–58.
Omokhodion FO. Low back pain in an urban population in southwest Nigeria. Trop Doct. 2004;34(1):17–20.
Igwesi-Chidobe CN, Coker B, Onwasigwe CN, Sorinola IO, Godfrey EL. Biopsychosocial factors associated with chronic low back pain disability in rural Nigeria: a population-based cross-sectional study. BMJ Glob Health. 2017;2(3):e000284.
Igwesi-Chidobe CN, Ezeonu F, Onwasigwe C, Kitchen S, Sorinola IO, Godfrey E. Predictors of self-reported disability in community dwelling adults with non-specific chronic low back pain in rural Nigeria. Physiotherapy. 2015;101:e637–8.
Wong AYL, Karppinen J, Samartzis D. Low back pain in older adults: risk factors, management options and future directions. Scoliosis Spinal Disord. 2017;12:14.
Serranheira F, Sousa-Uva M, Heranz F, Kovacs F, Sousa-Uva A. Low back pain (LBP), work and absenteeism. Work. 2020;65(2):463–9.
Agnus Tom A, Rajkumar E, John R, Joshua GA. Determinants of quality of life in individuals with chronic low back pain: a systematic review. Health Psychol Behav Med. 2022;10(1):124–44.
Scholich SL, Hallner D, Wittenberg RH, Hasenbring MI, Rusu AC. The relationship between pain, disability, quality of life and cognitive-behavioural factors in chronic back pain. Disabil Rehabil. 2012;34(23):1993–2000.
Alzahrani H, Mackey M, Stamatakis E, Zadro JR, Shirley D. Author correction: The association between physical activity and low back pain: a systematic review and meta-analysis of observational studies. Sci Rep. 2020;10(1):5987.
Pillastrini P, Gardenghi I, Bonetti F, Capra F, Guccione A, Mugnai R, et al. An updated overview of clinical guidelines for chronic low back pain management in primary care. Joint Bone Spine. 2012;79(2):176–85.
Campbell CM, Edwards RR. Ethnic differences in pain and pain management. Pain Manag. 2012;2(3):219–30.
Amoo EO, Adekeye O, Olawole-Isaac A, Fasina F, Adekola PO, Samuel GW, et al. Nigeria and Italy divergences in coronavirus experience: impact of population density. Sci World J. 2020;2020:8923036.
Wang X, Cheng Z. Cross-sectional studies: strengths, weaknesses, and recommendations. Chest. 2020;158(1s):S65-s71.
World Medical Association. World medical association declaration of Helsinki: ethical principles for medical research involving human subjects. JAMA. 2013;310(20):2191–4.
von Elm E, Altman DG, Egger M, Pocock SJ, Gøtzsche PC, Vandenbroucke JP. The Strengthening the Reporting of Observational Studies in Epidemiology (STROBE) statement: guidelines for reporting observational studies. Int J Surg. 2014;12(12):1495–9.
Ayanniyi O, Lasisi OT, Adegoke BOA, Oni-Orisan MO. Management of low back pain:-attitudes and treatment preferences of physiotherapists in Nigeria. Afr J Biomed Res. 2007;10(1):41–9.
Onyeso OK, Umunnah JO, Ezema CI, Balogun JA, Uchenwoke CI, Nwankwo MJ, et al. An evaluation of the nature and level of musculoskeletal imaging training in physiotherapy educational programmes in Nigeria. BMC Med Educ. 2020;20(1):252.
Onyeso OKK, Umunnah JO, Ezema CI, Anyachukwu CC, Nwankwo MJ, Odole AC, et al. Profile of practitioners, and factors influencing home care physiotherapy model of practice in Nigeria. Home Health Care Serv Q. 2020;39(3):168–83.
Omoke NI, Amaraegbulam PI. Low back pain as seen in orthopedic clinics of a Nigerian teaching hospital. Niger J Clin Pract. 2016;19(2):212–7.
Yao M, Xu BP, Li ZJ, Zhu S, Tian ZR, Li DH, et al. A comparison between the low back pain scales for patients with lumbar disc herniation: Validity, reliability, and responsiveness. Health Qual Life Outcomes. 2020;18(1):175.
Craig CL, Marshall AL, Sjöström M, Bauman AE, Booth ML, Ainsworth BE, et al. International Physical Activity Questionnaire: 12-country reliability and validity. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2003;35(8):1381–95.
Oyeyemi AL, Oyeyemi AY, Adegoke BO, Oyetoke FO, Aliyu HN, Aliyu SU, et al. The short international physical activity questionnaire: cross-cultural adaptation, validation and reliability of the Hausa language version in Nigeria. BMC Med Res Methodol. 2011;11(1):156.
Ohaeri JU, Awadalla AW. The reliability and validity of the short version of the who quality of life instrument in an Arab general population. Ann Saudi Med. 2009;29(2):98–104.
Fairbank JC, Pynsent PB. The Oswestry disability index. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2000;25(22):2940–52, discussion 52.
Saltychev M, Mattie R, McCormick Z, Bärlund E, Laimi K. Psychometric properties of the Oswestry disability index. Int J Rehabil Res. 2017;40(3):202–8.
Boonstra AM, Stewart RE, Köke AJ, Oosterwijk RF, Swaan JL, Schreurs KM, et al. Cut-off points for mild, moderate, and severe pain on the numeric rating scale for pain in patients with chronic musculoskeletal pain: variability and influence of sex and catastrophizing. Front Psychol. 2016;7:1466.
Vianin M. Psychometric properties and clinical usefulness of the Oswestry Disability Index. J Chiropr Med. 2008;7(4):161–3.
Hawthorne G, Herrman H, Murphy B. Interpreting the WHOQOL-brèf: preliminary population norms and effect sizes. Soc Indic Res. 2006;77(1):37–59.
Polit D, Beck C. Essentials of nursing research: appraising evidence for nursing practice. Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins; 2020.
Thakkar JJ. Applications of structural equation modelling with AMOS 21, IBM SPSS. In: Thakkar JJ, editor. Structural equation modelling: application for research and practice (with AMOS and R). Singapore: Springer Singapore; 2020. p. 35–89.
Majedi H, Amini MH, Yousefshahi F, Khazaeipour Z, Majedi M, Rahimi M, et al. Predicting factors of pain duration in patients with chronic pain: a large population-based study. Anesth Pain Med. 2020;10(1):e95776.
Johansson MM, Barbero M, Peolsson A, Falla D, Cescon C, Folli A, et al. Pain characteristics and quality of life in older people at high risk of future hospitalization. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2021;18(3):958.
Rebar AL, Duncan MJ, Short C, Vandelanotte C. Differences in health-related quality of life between three clusters of physical activity, sitting time, depression, anxiety, and stress. BMC Public Health. 2014;14:1088.
Rétsági E, Prémusz V, Makai A, Melczer C, Betlehem J, Lampek K, et al. Association with subjective measured physical activity (GPAQ) and quality of life (WHOQOL-brief) of ageing adults in Hungary, a cross-sectional study. BMC Public Health. 2020;20(Suppl 1):1061.
Kovacs FM, Abraira V, Zamora J, Teresa Gil del Real M, Llobera J, Fernández C, et al. Correlation between pain, disability, and quality of life in patients with common low back pain. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2004;29(2):206–10.
Stefane T, Santos AMD, Marinovic A, Hortense P. Chronic low back pain: pain intensity, disability and quality of life. Acta Paul Enferm. 2013;26(1):14–20.
Houde F, Cabana F, Léonard G. Does age affect the relationship between pain and disability? A descriptive study in individuals suffering from chronic low back pain. J Geriatr Phys Ther. 2016;39(3):140–5.
Chung EJ, Hur YG, Lee BH. A study of the relationship among fear-avoidance beliefs, pain and disability index in patients with low back pain. J Exerc Rehabil. 2013;9(6):532–5.
Lin CC, McAuley JH, Macedo L, Barnett DC, Smeets RJ, Verbunt JA. Relationship between physical activity and disability in low back pain: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Pain. 2011;152(3):607–13.
Ryan CG, Grant PM, Gray H, Newton M, Granat MH. Measuring postural physical activity in people with chronic low back pain. J Back Musculoskelet Rehabil. 2008;21:43–50.
Pincus T, Burton AK, Vogel S, Field AP. A systematic review of psychological factors as predictors of chronicity/disability in prospective cohorts of low back pain. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2002;27(5):E109-20.
Acknowledgements
The authors thank the patients, staff, and management of the public hospitals in Anambra State, Nigeria, where this study was conducted.
Funding
There was no external funding for this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
ECE and CVO contributed to the conception of this study. All authors made substantial contributions to the design and acquisition of data. OKO performed the statistical analysis. ECE and OKO were responsible for drafting the article and its critical revision. All authors approved the final manuscript for publication.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
The study protocol was approved by the Human Research Ethics Committees of the Faculty of Health Sciences and Technology, Nnamdi Azikiwe University, Anambra, Nigeria (NAU/FHST/2021/MRH60). The study’s objectives were clearly explained to each participant, who then signed an informed consent form. The approved protocol, participants’ privacy, and confidentiality of data were strictly adhered to.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
About this article
Cite this article
Ekediegwu, E.C., Onwukike, C.V. & Onyeso, O.K. Pain intensity, physical activity, quality of life, and disability in patients with mechanical low back pain: a cross-sectional study. Bull Fac Phys Ther 29, 1 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1186/s43161-023-00167-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s43161-023-00167-2