Abstract
Background
Pediatric neck masses are a common complaint in children. The most common etiologies include congenital lesions, lymphadenopathy, vascular malformations, inflammatory, and malignant lesions. Spontaneous sternocleidomastoid hematoma is exceptional in infant.
Case presentation
We describe a case of spontaneous cervical hematoma diagnosed in a 4-month-old child. Past history did not reveal a neck trauma, a history of difficult labor, a bleeding disorder or a pertinent family history. The diagnosis was suspected based on the imaging features and confirmed after surgical removal.
Conclusions
Sternocleidomastoid swelling is commonly encountered in infancy.
Ultrasound still remains the initial modality of choice. The management modalities are controversial.
Similar content being viewed by others
Background
Palpable neck masses are a common clinical concern in pediatric pathology. The diagnosis includes a wide range of etiologies, such as inflammatory, congenital, traumatic, and tumoral lesions [1, 2].
Spontaneous hematoma in infant are uncommon and they occur abruptly without any preceding trauma or iatrogenic damage [1].
Although they are benign, they can be life-threatening due to the risk of upper airway obstruction and vessel compression. Presenting symptoms are usually non-specific, making it difficult to get a definite diagnosis.
The management of spontaneous cervical hematoma is controversial, although it is agreed that the evaluation of upper airway obstruction and its permeability is mandatory.
We report herein a case of spontaneous hematoma of the sternocleidomastoid muscle in a 4-month-old girl who initially presented with anterior cervical swelling.
Case presentation
A 4-month-old girl was transferred to our institution complaining of a 1-month history of an anterior cervical swelling. She had no dyspnea or hoarseness. Past history did not reveal a neck trauma, a history of difficult labor, a bleeding disorder or a pertinent family history. It was a normal 3600-g female, born by caesarean section. The child was under breastfeeding, and his mother was not receiving an anticoagulant therapy.
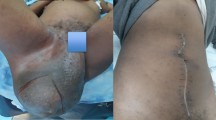
On physical examination, a firm, but not fluctuant, tender swelling of 4 cm was palpated over the left sternocleidomastoid muscle without ecchymosis (Fig. 1). No thrill or bruits could be found over the swelling. There was no limitation of the mobility of the head and the neck. The infant was afebrile.
All blood tests in particular regard to clotting were normal, excluding an unrevealed coagulopathy. Ultrasound (US) (Fig. 2) revealed a well-defined anechoic multilocular swelling measuring about 44 × 30 mm in its maximum dimensions, situated in the belly of the left sternocleidomastoid muscle. Color Doppler imaging did not reveal any vascularity within the lesion. These findings were compatible with an organized hematoma of the sternocleidomastoid muscle or a cystic lymphangioma. Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) (Fig. 3) showed the characteristic signal intensity of late subacute hemorrhage. Hemorrhage within a macrocystic lymphatic malformation is on top of the differential possibilities. It revealed a 37 × 33 × 31 mm well demarcated round tumor depending on the left sternocleidomastoid muscle with heterogenous high signal intensity on T2-weighted imaging. The mass was displacing the airway and the left thyroid lobe laterally. For these reasons, the patient underwent surgery using an anterior approach.
The neck was incised vertically to the left of the midline and the mass was exposed. The per-operative aspect of the mass was compatible with organizing hematoma of the left sternocleidomastoid muscle. The mass adhered to the internal jugular vein but it was easily dissected from the surrounding tissue. The hematoma was removed (Fig. 4). Histopathology confirmed the diagnosis of a hematoma. Histopathological examination of the hematoma including the vascular structure revealed no evidence of tumors, abnormal blood vessels, or vascular malformations.
The postoperative course was unremarkable. No recurrence was observed at the last follow-up.
Discussion
Neck masses are a common presenting complaint within the pediatric population with a broad and varied etiologies. The etiology of neck masses varies from benign/neoplastic lesions which may be diagnosed at birth to acquired/congenital lesions which may manifest in late childhood [2, 3]. The vast majority of neck masses in children are benign lesions. The most common etiologies include inflammatory lesions, lymphadenopathy, and congenital lesions [4, 5].
Benign lymphadenopathies are frequently encountered in pediatric medicine and present as superficial swelling usually associated with an acute upper respiratory infection or with chronic infection of the tonsils and adenoids [1, 4, 5].
Congenital neck masses are to be considered. They are divided into central and lateral masses. Thyroglossal duct cysts, the most common congenital neck masses, are well-circumscribed midline lesions, and they characteristically elevate with tongue protrusion or swallowing. Dermoid and epidermoid cysts are midline lesions and are extremely mobile and superficial to underlying structures. Lateral congenital neck masses are commonly well-circumscribed, painless, and mobile. They are dominated par second branchial cleft cyst [1, 4, 5].
Congenital vascular malformations are frequently encountered in the head and neck and are classified into two distinct subtypes: infantile hemangiomas and vascular malformations.
Lipomas are within the most frequent benign neck neoplasms. They are painless, soft, and mobile on examination. Other benign tumors that can be encountered include pilomatrixoma and neurofibroma.
Although rare, malignant lesions such as lymphoma, rhabdomyosarcoma, thyroid carcinoma, and metastatic nasopharyngeal carcinoma can occur in children. Malignancy is suspected upon hard, firm, or rubbery consistency; fixed mass; supraclavicular mass; lymph node larger than 2 cm in diameter; persistent enlargement for more than 2 weeks and is confirmed by anatomopathological examination [1, 4, 5].
Sternocleidomastoid swelling is commonly encountered in infancy as Fibromatosis Colli following a hematoma due to difficult labor [2, 6].
Herein we report a case of spontaneous unilateral hematoma of the left sternocleidomastoid muscle giving rise to a rapidly progressive neck swelling in a 4-month-old child.
A hematoma is defined as a local accumulation of blood in a tissue, space, or organ. Cervical hematomas are generally associated with trauma, iatrogenic events, surgery, and tumors [7,8,9,10,11].
Some authors described prolonged coughing, sneezing, and vomiting as possible intrinsic factors [12].
Two mechanisms of injury lead to muscular hematomas: direct (after contusion or direct impact) and indirect (after rupture of fibers of the muscle or a tear) [8, 9].
Spontaneous hematoma in the neck, without any comorbidity, are rather rare in infants [12, 13]. Schroder and Mair [13] reported a case of spontaneous hematoma of the left submandibular region in a 6-year-old girl. Whereas an obvious vascular anomaly was present in their case, we failed to reveal the etiology and so did Zhuang and Al [12].
Symptoms may include cervical swelling, and as there is the potential for communication between spaces within the neck, obstruction of the airway could develop if the collection spread.
Ultrasound is generally recommended in the first instance, for evaluation of neck masses, especially in children [3, 6]. It is an accurate, safe, non-ionizing cost-effective, non-invasive preoperative analysis [6].
Ultrasound still remains the initial modality of choice, although MRI better demonstrates the extent of muscle involvement [6].
The management of the hematoma itself is controversial [7, 10,11,12]. No standardized treatment and follow-up are established for patients with acute spontaneous neck hematomas. Some authors suggest surgical drainage when the hematoma progresses to other deep neck spaces or involves the upper airway [7, 11]. Most authors prefer to wait for natural absorption [10, 12]. The hematoma will usually resolve in 2 to 4 weeks [10, 12].
Conclusion
Although the etiology of the spontaneous hematoma of the sternocleidomastoid muscle in the current patient has not been determined, we report this case to increase awareness about this exceptional entity in infant.
Availability of data and materials
Not applicable
Abbreviations
- US:
-
Ultrasound
- MRI:
-
Magnetic resonance imaging
- T1WI:
-
T1-weighted image
- T2WI:
-
T2-weighted image
References
Lucumay EM, Gilyoma JM, Rambau PF, Chalya PL. Paediatric neck masses at a University teaching hospital in northwestern Tanzania: a prospective analysis of 148 cases. BMC Res Notes. 2014;7:772.
Skelton E, Howlett D. Fibromatosis colli: the sternocleidomastoid pseudotumour of infancy. J Paediatr Child Health. 2014 Oct;50(10):833–5. https://doi.org/10.1111/jpc.12506.
Brown RE, Harave S. Diagnostic imaging of benign and malignant neck masses in children-a pictorial review. Quant Imaging Med Surg. 2016 Oct;6(5):591–604. https://doi.org/10.21037/qims.2016.10.10.
Jackson DL. Evaluation and Management of Pediatric Neck Masses. Physician Assist Clin. 2018 Apr;3(2):245–69. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cpha.2017.12.003.
Meier JD, Grimmer JF. Evaluation and management of neck masses in children. Am Fam Physician. 2014 Mar 1;89(5):353–8.
Bansal AG, Oudsema R, Masseaux JA, Rosenberg HK. US of pediatric superficial masses of the head and neck. Radiogr Rev Publ Radiol Soc N Am Inc. 2018 Aug;38(4):1239–63.
Dohan A, Darnige L, Sapoval M, Pellerin O. Spontaneous soft tissue hematomas. Diagn Interv Imaging. 2015 Aug;96(7–8):789–96. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.diii.2015.03.014.
Saotome K, Koguchi Y, Tamai K, Sakai H, Ohno W, Yamato M. Enlarging intramuscular hematoma and fibrinolytic parameters. J Orthop Sci Off J Jpn Orthop Assoc. 2003;8(2):132–6.
Verma PSFVK, Fotydar S, Katyal VK. Hematoma of sternocleidomastoid aspirin can be a cause. J Assoc Physicians India. 2019 Apr;67(4):75.
DiFrancesco RC, Escamilla JS, Sennes LU, Voegles RL, Tsuji DH. Spontaneous cervical hematoma: a report of two cases. Ear Nose Throat J. 1999;78(3):168, 171, 175–75. https://doi.org/10.1177/014556139907800310.
Nguyen Son C, Belhous K, Curtis W, Angoulvant F, Chéron G. Cervical trauma in children: be aware of the risk of infection. Arch Pediatr Organe Off Soc Francaise Pediatr. 2019 Jul;26(5):298–300.
Zhuang S, Ye J, Li J. Acute spontaneous neck haematoma in children: a rare entity. BMC Pediatr. 2015 Apr 11;15(1):38. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12887-015-0356-1.
Schrøder KE, Mair IW. Spontaneous haematoma in the head and neck. J Laryngol Otol. 1978;92(3):215–21. https://doi.org/10.1017/S002221510008525X.
Acknowledgements
Not applicable
Funding
Not applicable
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
MG: conception of the work, data collection analysis and interpretation, drafting the article, and final approval of the version to be published. LC: data collection, drafting the article. JH: data collection, drafting the article, bibliography selecting. HBM: data collection, drafting the article. MB: critical revision of the article. WK: critical revision of the article. AM: data collection. M A: critical revision of the article. All the authors have read and agreed the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
The study has a retrospective nature and was conducted ethically. All authors approve their participation. All the authors have read and agreed the final manuscript.
Consent for publication
A written informed consent to publish these information was obtained from the parent of the child.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
About this article
Cite this article
Ghammam, M., Chouchane, L., Houas, J. et al. A case report of a spontaneous sternocleidomastoid hematoma: a challenging diagnosis in infantile neck swellings. Ann Pediatr Surg 17, 36 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1186/s43159-021-00102-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s43159-021-00102-x