Abstract
Background
Hepatitis C virus (HCV) infection is a high prevalent disease. Sofosbuvir/ledipasvir (SOF/LDV) can successfully treat HCV and it was until recently that SOF/LDV was approved by the FDA in haemodialysis patients, but not in patients with liver cirrhosis. This study reports patients on haemodialysis and compensated liver cirrhosis who used this regiment. This is a retrospective study on patients who were on haemodialysis and used SOF/LDV for HCV treatment in one secondary health care facility (a hospital). Treatment consisted of 400g SOF and of 90g LDV once daily. Patients were assessed for HCV RNA at the end of treatment after 12 weeks and after 24 weeks for patients. New symptoms were also assessed.
Results
Our sample contained 16 males and 5 females with a mean age of 40.9 years. Nineteen patients had no cirrhosis of the liver, and the other two had clinical and radiological cirrhosis and had Child–Turcotte–Pugh (CTP) type B. Full follow-up was for only 20 patients and they all had HCV resolved as one patient had died from a stroke. Other factors were assessed such as HCV genotypes, but treatment had the same results with no difference in symptoms development (p>0.05). Twelve patients had HCV genotype 1, eight patients had HCV genotype 4, and one patient had HCV genotype 5.
Conclusion
Despite the small sample size, SOF/LDV combination is suggested to be effective in patients on haemodialysis and who had compensated cirrhosis and CTP type B without the need of dose adjustment or increase duration of treatment, and there were no major complications overall.
Similar content being viewed by others
Background
Hepatitis C virus (HCV) infection has a prevalence of 3% worldwide, it is more frequent in long-term haemodialysis patients and it reached 7.5% in developed countries. Nevertheless, it was demonstrated that having a positive anti-HCV serologic was associated with a higher incidence of chronic kidney disease (CKD) in the population [1, 2]. Furthermore, there was an increase of extrahepatic manifestation in CKD patients with chronic HCV such as an increased risk of 51% of proteinuria [2]. Moreover, haemodialysis itself is a major risk for HCV despite blood testing which is one of major causes of chronic liver disease in such patients [3], and it substantially increases mortality [4].
Antiviral therapy has a positive outcome on patients on haemodialysis as it increased survival [5]. Sofosbuvir/ledipasvir (SOF/LDV) combination is considered one of the treatment combinations for HCV as they have 100% eradication rate in acutely affected HCV genotype 1. Sofosbuvir is also approved for genotypes 1 through 6 [6]. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has recently approved for regiments containing sofosbuvir/ledipasvir (SOF/LDV) for HCV treatment in renal disease with estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) <30 and haemodialysis [7, 8]. However, not much data about using this regime in decompensating liver disease is available. And therefore it is still not recommended [9]. SOF/LDV treatment can go for 12 weeks, and the recommended doses were at 400 mg for sofosbuvir, and 90 mg for ledipasvir daily [6].
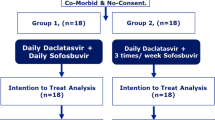
Prevalence for HCV varies across the world with developing countries having the highest rates [10]. Syria has been suffering from war since 2011, and its medical sector and economy have taken a huge hit as only 1.5 hospital beds with only 1.22 physicians were dedicated for each 1000 of population [11]. SOF/LDV combination is commonly used in Syria despite the global restrictions and high prices on drugs. These restrictions made it hard to obtain other alternatives in Syria for patients such as in cases with CKD and cirrhosis. This study contains 21 patients who used SOF/LDV regiment at Damascus Hospital although they had end-stage renal disease (ESRD) and were on haemodialysis with two patients having cirrhosis.
Methods
This study included 21 patients who presented at Damascus Hospital in the period between February 2018 and August 2019. All patients used SOF/LDV for HCV and were on haemodialysis from ESKD.
Patient and ethical consent
This study was ethically and scientifically approved by Damascus Hospital ethical committee, and gastroenterology department number 113297ب. Patient written consent was taken before administration of drugs. Risks and benefits were explained, and patients agreed on taking the drugs. Patients’ oral consent was later taken for collecting and publishing their data for research purposes.
Inclusion/exclusion criteria
Our sample included patients who had HCV diagnosed by polymerase chain reaction (PCR), had ESRD (GFR <15 mL/min), and were on haemodialysis when initiating HCV treatment. PCR is the best diagnostic method in haemodialysis patients [12]. We did not enrol patients who had other severe uncontrolled comorbidities that were not directly related to HCV, cirrhosis, or renal failure, such as uncontrolled diabetes with persistent high HbA1c and severe uncontrolled hypertension. We enrolled patients who used SOF/LDV for the treatment of HCV. No patient received other treatment for HCV before initiating SOF/LDV (naïve).
Child–Turcotte–Pugh (CTP) was used to determine the severity of cirrhosis. CTP is based on multiple factors, encephalopathy, ascites, bilirubin, albumin, and prothrombin time. CTP was used as it is an easy method to use in the daily practice with a high prognostic accuracy in 6-month period [13]. Cirrhosis was diagnosed based on radiological, and clinical features, not by using invasive procedures.
Dosing
Standard doses for SOF/LDV were indicated as it was found that no adjustment is needed for ESRD patients who are on haemodialysis. Doses were 90 mg for ledipasvir, and 400 mg for sofosbuvir for once daily for 12 week [7, 8].
Progress
Only reported symptoms that newly developed or exacerbated after treatment initiation were reported. Assessment for new symptoms and routine blood tests (full blood count, urea, electrolytes, creatinine, and liver function tests) were conducted at the beginning, middle (6-week period), and at the end of treatment period which was after 12 weeks to determine if any changes in labs were transient or not and to check for new symptoms. These tests and examination were conducted 1 day before haemodialysis.
HCV PCR testing was conducted at the beginning, after 12 weeks (end treatment response or ETR), and after ETR by 12 weeks to assess sustained virological response (SVR12) as no longer follow-ups were possible (SVR24). Any patient who had haemoglobin below 11 was considered as anaemic.
Statistical analysis
Data was processed using IBM SPSS software version 25 for Windows (SPSS Inc, IL, USA). Chi-square, Fisher’s exact, independent T, and one-way ANNOVA tests were performed to determine the statistical significance between the groups of cases and controls. Values of less than 0.05 for the two-tailed P values were considered statistically significant. However, multivariate tests were avoided due to large amounts of variables and small sample size.
Results
Our sample included 16 males (76.2%) and five females (23.8%) with a mean age of 40.90 ± 11.05 years. Two male patients were single (12.5%), one was engaged (6.25%), and 13 were married (81.25%). In contrast, one female patient was single (20%), and four were married (80%). While ten male patients lived in the suburbs (62.5%), and six male patients lived in an urban area (37.5%), all female patients lived in suburbs. Three males and one female patient had a history of smoking with an average of 22.5 pack/year history. None of the patients drank alcohol regularly. One patient had a haemorrhagic stroke in week 5 of treatment and died. The remaining 20 patients continued treatment until the end, and one of them had successful renal transplant after SVR12.
There were no significant differences in routine blood between before and after the treatment for all types in our research.
All patients who were followed up until SVR12 had 0 copies of HCV RNA when using PCR when finishing 12 weeks of treatment. No patient declared medication ceasing due to adverse effect or deteriorating of the symptoms. No major changes were found in liver and renal function during the study period. No major complications or deaths were declared except for one patient who had the stroke.
HCV genotypes
Ten patients (47.6%) had HCV genotype 1a, two (9.5%) genotype 1b, eight (38.1%) genotype 4, and one (4.8%) genotype 5. All females had no cirrhosis whereas two males (17.6%) had clinical and radiological findings of cirrhosis with CTP B (Fig. 1). HCV genotype 1b was associated with having a headache (p=0.047). Having a headache was also associated with female gender (p=0.026). However, having a headache overall was only in one patient. No statistically significant differences were found when comparing HCV genotype with any of the other symptoms, or smoking (p<0.05). HCV genotypes were also not associated with gender, and CTP scores (p<0.05).
CTP score and symptoms
At the end of follow-up, newly developed symptoms were recorded for 17 patients containing the two patients with CTP B. The other 3 patients’ follow-ups were not valid, and the final fourth patient had a stroke at week 5.
Out of the 17 patients, four (23.5%) developed lethargy or “an increased in tiredness”, one (5.9%) developed sustained headache, seven (41.2%) declared an increase of nausea, five (29.4%) declared an increased frequency of passing stools, four (23.5%) an increased dizziness, one (5.9%) an increased shortness of breath, five (29.4%) an increased insomnia, eight (47.1%) an increased arthralgia, and six (35.3%) an increased mood swings or more negative mood (Table 1).
Developing new symptoms were not statistically significantly associated with gender, or smoking (p<0.05). Developing arthralgia was insignificantly associated with smoking (p=0.072). However, CTP scores were associated with developing dizziness (p=0.007) as all patients with CTP B (2 patients) had dizziness. Moreover, CTP B was associated with a shortness of breath (p=0.005) and nausea (p=0.072) as only one patient had shortness of breath, and he had CTP type B. There were no patients who developed any new pulmonary, or dermatology symptoms, or coughing.
CBC and symptoms
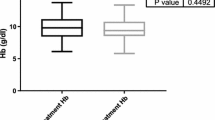
Mean haemoglobin level and platelet count for patients who achieved SVR12 were respectively 9.04 g/dl and 201,712 × 109 per litter when medications were initiated, and 9.95 g/dl and 205,750 × 109 per litter after 12 weeks. Moreover, 16 patients had an anaemia (Hb<11 g/dl) when initiating drugs with levels ranging from 6.3 to 12.40 g/dl. No statistically significant difference was found when comparing HCV RNA copies when diagnosed, age, haemoglobin level, and platelet counts at the beginning or the end, with developing lethargy, nausea, diarrhoea, dizziness, shortness of breath, insomnia, arthralgia, and mood disturbances (p<0.05). There were no statistically significant differences when comparing age, haemoglobin level at the beginning or the end, HCV RNA copies when diagnosed with developing headache (p<0.05). However, it was found that having lower platelets when diagnosed or after 12 weeks of treatment was correlated with having a headache (p=0.040 and p=0.086 respectively).
Other variables
No statistically significant differences were found when comparing HCV RNA copies with smoking cigarettes, amount smoked, haemoglobin levels, and platelet counts (p<0.05).
Discussion
Our study
All patients had no evidence of HCV on PCR when followed up despite having ESRD and regardless of having CTP type B at SVR12. No significant side effects were developed regardless of having the clinical and radiological cirrhosis and CTP type B or not. No dose adjustment was required in the two patients of CTP B, and SOF/LDV was effective in patients with HCV genotypes of 1a, 1b, 4, and 5.
Interestingly, a slight improvement in anaemia and low platelets was noticed after HCV treatment for some patients. No associations were found between any of the variables of HCV genotypes, symptoms developed, HCV RNA copies when diagnosed, HCV genotypes, gender, cigarette smoking, amount smoked, and having CTP B.
Other studies
A decline of eGFR and anaemia were observed in a large study of SOF/LDV in ESRD [8]. However, using the alternative older drugs such as ribavirin, interferon (IFN) alfa, or pegylated IFN was associated with more severe anaemia [14]. Many adverse effects were noticed for LDV/SOF treatment, but they were mild to moderate in 93% of patients [15]. Fatigue, headache, insomnia, and nausea were the most common adverse effects [15], and anaemia has occurred in some patients [16]. Sofosbuvir is the first peg-interferon-free combination regimen with high SVR rates. It has fewer side effects and requires shorter treatment compared to old drugs [10, 17]. We speculated that anaemia was alleviated as the chronic infection (HCV) was resolved and thus slightly improving the anaemia, or it was just coincidental.
In decompensated liver failure, more adverse effects were found, mainly in CTP B and C. However, many studies found that most of these effects were from ribavirin [9]. Other studies also found that SVR was lower in high CTP scores with higher relapse. These studies used the same fixed dose of SOF/LDV despite the cirrhosis. However, these drugs are still not recommended in hepatic decompensation until more studies are conducted [9]. SOF/LDV is indicated in patients with HCV who did not benefit from peginterferon alfa plus ribavirin and who is treatment naïve without cirrhosis or with compensated cirrhosis [17]. In our study, regular doses were used for SOF/LDV for 12 weeks with no major side effects.
Limitations
No data was available on eGFR or ECG changes after giving the medications; data only contained full-blood count, electrolytes, liver function creatinine, and urea levels which were not substantially changed throughout the study and we could not include more tests or take more frequent test which means that there was a possibility to miss point changes in values. Some patients’ follow-ups for symptoms were missing, and new symptoms could not be accurately determined if they were from medications, or other causes. No weekly visits were scheduled which could have left a gab in new or transient symptoms detection as visits and blood testing were only scheduled on the first day, 6 weeks, and 12 weeks after initiating the medication. Drugs were not administered before the haemodialysis so we could not observe the direct effect of haemodialysis on the drug. Moreover, the effect of other medications, and medical conditions, and the aetiology of ESRD and HCV were not studied. Our sample study was small, particularly for patients with cirrhosis with CTP B as they were only two patients and for patients with particular HCV genotypes. Finally, longer follow-ups were not feasible due to limited resources of the hospital and most patients not being compliant for longer follow-ups.
Conclusions
The results suggest that sofosbuvir/ledipasvir can be used in renal failure patients on haemodialysis to treat HCV genotypes 1a, 1b, 4 and 5, and when having clinical and radiological cirrhosis with CTP B. No dose adjustment or an increase of duration was required. Also, no additional severe symptoms were developed in patients with CTP B in comparison to the other patients. Treatment was administered after the haemodialysis. Further studies on larger study groups should be conducted to confirm these findings. Our sample size was small and contained only two patients with cirrhosis which was diagnosed on radiological and clinical basis.
Availability of data and materials
Data will be made available upon reasonable request.
Abbreviations
- CTP:
-
Child–Turcotte–Pugh
- CKD:
-
Chronic kidney disease
- ESRD:
-
End-stage renal disease
- ETR:
-
End treatment response
- eGFR:
-
Estimated glomerular filtration rate
- Hb:
-
Haemoglobin
- HCV:
-
Hepatitis C virus
- IFN:
-
Interferon
- PCR:
-
Polymerase chain reaction
- RNA:
-
Ribonucleic acid
- SOF/LDV:
-
Sofosbuvir/ledipasvir
- SVR:
-
Sustained virological response
References
Goodkin DA, Bieber B, Jadoul M, Martin P, Kanda E, Pisoni RL (2017) Mortality, hospitalization, and quality of life among patients with hepatitis C infection on hemodialysis. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol 12(2):287–297
Fabrizi F, Verdesca S, Messa P, Martin P (2015) Hepatitis C virus infection increases the risk of developing chronic kidney disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Digest Dis Sci 60(12):3801–3813
Marinaki S (2015) Hepatitis C in hemodialysis patients. World J Hepatol 7(3):548. https://doi.org/10.4254/wjh.v7.i3.548. ISSN: 1948-5182
Kalantar-Zadeh K, Kilpatrick RD, McAllister CJ, Miller LG, Daar ES, Gjertson DW et al (2007) Hepatitis C virus and death risk in hemodialysis patients. J Am Soc Nephrol. 18(5):1584–1593
Söderholm J, Millbourn C, Büsch K (2018) et a. Higher risk of renal disease in chronic hepatitis C patients: Antiviral therapy survival benefit in patients on hemodialysis. J Hepatol. 68(5):904–911
Zeuzem S (2017) Treatment options in hepatitis C: the current state of the art. Deutsches Aerzteblatt Online. https://doi.org/10.3238/arztebl.2017.0011. ISSN: 1866-0452
AASLD-IDSA. HCV guidance: recommendations for testing, managing, and treating hepatitis C; patients with renal impairment [updated December 10, 2019; cited 2020 February 14]. Available from: https://www.hcvguidelines.org/unique-populations/renal-impairment.
Butt AA, Ren Y, Puenpatom A, Arduino JM, Kumar R, Abou-Samra AB (2018) Effectiveness, treatment completion and safety of sofosbuvir/ledipasvir and paritaprevir/ritonavir/ombitasvir + dasabuvir in patients with chronic kidney disease: an ERCHIVES study. Alimentary Pharmacol Ther 48(1):35–43
AASLD-IDSA. HCV guidance: recommendations for testing, managing, and treating hepatitis C; patients with decompensated cirrhosis [updated November 6, 2019; cited 2020 March 9]. Available from: https://www.hcvguidelines.org/unique-populations/decompensated-cirrhosis.
Mohamed AA, Hepatitis C (2015) Virus: a global view. World J Hepatol. 7(26):2676. https://doi.org/10.4254/wjh.v7.i26.2676. ISSN: 1948-5182
Agency. CgCI. Middle East :: Syria [updated FEBRUARY 20, 2020. Available from: https://www.cia.gov/library/publications/resources/the-world-factbook/geos/sy.html.
Firdaus R, Saha K, Biswas A, Sadhukhan PC (2015) Current molecular methods for the detection of hepatitis C virus in high risk group population: a systematic review. World J Virol. 4(1):25–32
Wu S-L, Zheng Y-X, Tian Z-W, Chen M-S, Tan H-Z (2018) Scoring systems for prediction of mortality in decompensated liver cirrhosis: a meta-analysis of test accuracy. World Journal of Clinical Cases. 6(15):995–1006
Sulkowski MS (2003) Anemia in the treatment of hepatitis C virus infection. Clinical Infectious Diseases. 37(s4):S315–SS22
Afdhal N, Zeuzem S, Kwo P, Chojkier M, Gitlin N, Puoti M et al (2014) Ledipasvir and sofosbuvir for untreated HCV genotype 1 infection. New England Journal of Medicine. 370(20):1889–1898
Ferreira VL, Assis Jarek NA, Tonin FS, Borba HHL, Wiens A, Muzzillo DA et al (2017) Ledipasvir/sofosbuvir with or without ribavirin for the treatment of chronic hepatitis C genotype 1: a pairwise meta-analysis. Journal of Gastroenterology and Hepatology. 32(4):749–755
Ledipasvir/sofosbuvir (Harvoni): for the treatment of cronic hepatitis C virus (CHC) G1 infection in adults [Internet]. Ottawa (ON): Canadian Agency for Drugs and Technologies in Health; 2015. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK362646/
Acknowledgements
This study has a preprint on https://doi.org/10.21203/rs.3.rs-21371/v2 and on https://www.researchsquare.com/article/rs-21371/v1.
Funding
We received no funding.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors adhere to the ICMJE definition of authorship and they have complete access to the study data that support the publication. EB: conceptualisation, supervision, validation, revewing and editing the draft, project administration, and resources. KC: supervision, validation, project administration, and resources. NH: data curation, investigation, revewing and editing the draft, supervision, visualization, resources, and software. RA: investigation, methodology, project administration, resources, and visualization. MWA: reviewing the draft and software. All authors read and approved the final manuscript. AK: visualization, writing original draft, revewing and editing, software, data curation, methodology, and formal analysis.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
This study was ethically and scientifically approved by Damascus Hospital ethical committee, and gastroenterology department number 113297ب. Patient’s written consent was taken before administration of drugs as this drug regime was not approved at the time of treatment for haemodialysis patients. Risks and benefits were explained and patients agreed on taken the drugs
Consent for publication
N/A
Competing interests
No competing interests to declare.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
About this article
Cite this article
Boushi, E., Cheha, K., Hedar, N. et al. Sofosbuvir/ledipasvir safety and efficacy for HCV patients with haemodialysis and liver cirrhosis: a small retrospective study. Egypt Liver Journal 11, 82 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1186/s43066-021-00150-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s43066-021-00150-3