Abstract
This paper presents a review of four existing growth models for near-neutral pH stress corrosion cracking (NNpHSCC) defects on buried oil and gas pipelines: Chen et al.’s model, two models developed at the Southwest Research Institute (SwRI) and Xing et al.’s model. All four models consider corrosion fatigue enhanced by hydrogen embrittlement as the main growth mechanism for NNpHSCC. The predictive accuracy of these growth models is investigated based on 39 crack growth rates obtained from full-scale tests conducted at the CanmetMATERIALS of Natural Resources Canada of pipe specimens that are in contact with NNpH soils and subjected to cyclic internal pressures. The comparison of the observed and predicted crack growth rates indicates that the hydrogen-enhanced decohesion (HEDE) component of Xing et al.’s model leads to on average reasonably accurate predictions with the corresponding mean and coefficient of variation (COV) of the observed-to-predicted ratios being 1.06 and 61.2%, respectively. The predictive accuracy of the other three models are markedly poorer. The analysis results suggest that further research is needed to improve existing growth models or develop new growth models to facilitate the pipeline integrity management practice with respect to NNpHSCC.
Similar content being viewed by others
Introduction
Steel oil and gas pipelines are part of critical infrastructure systems in a modern society. There are about 4,000,000 and 840,000 km of transmission, gathering, feeder, and distribution pipelines in the US and Canada [1, 2], respectively, most of which are buried underground. The structural integrity of pipelines is threatened by various failure mechanisms such as the third-party interference, corrosion, stress corrosion cracking and ground movement. Failures of pipelines can have severe safety, environmental and economic consequences. The present study focuses on one of the leading causes of failure for buried pipelines [3,4,5,6,7,8,9], namely the near-neutral pH stress corrosion cracking (NNpHSCC). NNpHSCC defects on pipelines grow over time and compromise the pipeline’s pressure containment capacity, i.e. burst capacity. If unmitigated, such defects may lead to significant failure incidents such as the rupture and subsequent fire on a 914 mm-diameter natural gas pipeline near Prince George, BC, Canada on October 9, 2018, and the rupture of a 609 mm-diameter natural gas pipeline near Unityville, PA, USA on June 9, 2015. To evaluate the growth rate of NNpHSCC defects with a reasonable accuracy is critically important for the pipeline integrity management program as it allows integrity engineers to predict the deterioration of the burst capacity of the pipeline with confidence and carry out effective, timely mitigation actions, if necessary. The objective of this study is to review the current understanding of the mechanism of NNpHSCC on pipelines and several existing models in the literature to predict the growth of NNpHSCC defects, and to examine the accuracy of these growth models based on experimental data obtained from full-scale pipe specimens.
The rest of the paper is structured as follows. Section "NNpHSCC on pipelines" presents a review of the literature related to the mechanism of NNpHSCC on pipelines. Section "Growth models for NNpHSCC defects on pipelines" describes several NNpHSCC growth models proposed in the literature. Section "Accuracy of NNpHSCC crack growth models" describes a test program on the growth of NNpHSCC defects in full-scale pipe specimens conducted by researchers at Natural Resources Canada. A comparison between the SCC growth rates observed in the test program and corresponding growth rates predicted by the growth models reviewed is also presented in this section. Conclusions are presented in the last section.
NNpHSCC on pipelines
Stress corrosion cracking (SCC) is defined as one type of environmentally assisted cracking (EAC), which occurs under the synergistic effects of corrosion reactions and mechanical stress [10]. SCC requires three essential factors present simultaneously to initiate and propagate: the tensile stress (mechanical factor), susceptible material (metallurgical factor), and corrosive environment (electrochemical factor) [11]. Two types of SCC have been identified on pipelines based on the electrolyte in contact with the metal surface: the high pH SCC and near-neutral pH SCC. The high pH SCC was first documented in Louisiana, US in the mid 1960s [12], whereas NNpHSCC was first reported on Canadian pipelines in the mid 1980s [13, 14]. NNpHSCC is so named because the local electrolyte has a pH value between 5.5 and 7.5 [11]. The tensile stress essential to the occurrence of NNpHSCC is mainly caused by the high internal operating pressure of the pipeline [15]. Cracks caused by NNpHSCC move across the grains of the pipe steel and are therefore transgranular. In contrast, cracks caused by high pH SCC move along the grain boundaries and are therefore intergranular [3].
The underlying mechanisms of NNpHSCC on pipelines have not been conclusively established. Many researchers [16,17,18] suggest that NNpHSCC is driven by the synergistic effect of hydrogen embrittlement (HE), anodic dissolution (AD), and cyclic stress. Parkins et al. [19] first suggested that both the dissolution and hydrogen ingress into the steel are responsible for the crack growth in NNpH environments. Gu et al. [20] proposed a hydrogen-facilitated anodic dissolution mechanism for NNpHSCC. Lu et al. [21] reported that the synergistic effect due to the interaction of dissolved hydrogen and local stress field on the active dissolution is negligible and suggested that NNpHSCC is unlikely to be controlled by the hydrogen-facilitated anodic dissolution mechanism based on their thermodynamic analysis and experimental observations. Lu et al. [22] further suggested that the crack propagation in pipeline steels in contact with NNpH groundwater is dominated by the dissolved hydrogen concentration and less influenced by AD. Cheng and his co-investigators also suggested that hydrogen plays a critical role in NNpHSCC of pipeline steels through the HE mechanism [23,24,25]. A recent experiment [17] demonstrated that about one-tenth of the measured NNpHSCC growth rate is due to AD, which implies that HE plays a dominant role in the NNpHSCC growth. HE occurs when hydrogen atoms enter the lattice of the metal and reduce its ductility and toughness. The atomistic mechanism for HE has been under investigation for the past several decades [26]. The following three theories of HE are widely referenced in the literature: 1) hydrogen-enhanced decohesion (HEDE), which postulates that hydrogen atoms trapped near a crack reduces the free surface energy, thus facilitating cleavage-like failure [27, 28]; 2) hydrogen-enhanced localized plasticity (HELP), which suggests that solute hydrogen enhances dislocation movements [29], and 3) adsorption-induced dislocation emission (AIDE), which hypothesizes that the adsorption of hydrogen facilitates the dislocation nucleation [30, 31].
Many researchers have claimed that cyclic stress is essential to the growth of NNpHSCC cracks [32,33,34,35,36]. Full-scale experiments showed that the absence of cyclic components in the loading spectra led to non-growth of NNpHSCC cracks in pipe specimens and that controlling pressure fluctuations in pipelines resulted in reduced crack growth [32]. A similar phenomenon was also observed in small-scale tests: no crack growth was detected in the specimen subjected to a monotonic loading even at the highest stress intensity factor used in the study [33]. It is therefore suggested in [34,35,36] that the growth of NNpHSCC cracks can be better characterized by corrosion fatigue (CF) than SCC. CF is one type of EAC that occurs under the synergistic effects of corrosion and cyclic stress [11, 37]. Note that internal pressures in pipelines are generally fluctuating, resulting in cyclic stresses in the pipeline. Although small-scale tests reported in [38,39,40,41] have shown that cracks can initiate and propagate in specimens in an NNpH environment under quasi-static and static loading conditions, extensive full-scale tests [42, 43] have demonstrated that cyclic stress facilitates the propagation of NNpH cracks far more than static stress. The present study considers CF enhanced by HE as the main mechanism for the growth of NNpH cracks. However, the terminology NNpHSCC is still adopted in the following discussions to be consistent with the literature and avoid confusion.
Growth models for NNpHSCC defects on pipelines
Growth models developed at SwRI
Chen and Sutherby [34] investigated the crack growth behaviour of the X65 pipe steel in NNpH environments by using compact tension (C(T)) specimens subjected to cyclic loads. They observed that the combined parameter, KmaxΔK2f-0.1, results in the best fit to the experimentally-obtained da/dN values corresponding to different stress ratios and loading frequencies. In the above, a denotes the crack depth (i.e. in the through pipe wall thickness direction); N denotes the number of stress cycles; da/dN is the crack depth growth rate per stress cycle; Kmax and ΔK are respectively the maximum stress intensity factor and stress intensity factor range in a load cycle, and f is the loading frequency. Lu [16] suggested that the term KmaxΔK2 can be considered the mechanical parameter controlling the initiation of microcracks in the fracture process zone (FPZ) ahead of the crack tip and that the term f-0.1 represents the enhanced crack growth by the corrosive environment, whose effects decrease as f increases.
Based on Chen and Sutherby’s combined parameter, researchers at the Southwest Research Institute (SwRI) [44, 45] proposed the following crack growth model for NNpHSCC (referred to as the SwRI model):
where B0 is a fitting coefficient; C0 is the atomic hydrogen concentration in the lattice of bulk steel, and CcrLat is the critical hydrogen concentration in the lattice of FPZ to cause the initiation of microcracks. The two main sources for the hydrogen consumed in the HE process are the hydrogen evolution reaction in the crack and hydrogen dissolved in the bulk steel [16, 46]. An experimental study carried out by Chen et al. [47] suggests that the latter is the primary source; therefore, C0 in Eq. (1) is replaced by CB, the hydrogen concentration in the bulk material, which can be determined from hydrogen permeation measurements [48]. The value of CB is generally in the order of 10− 2 to 101 mol/m3 depending on the pipe steel grade (representing the effect of the microstructure of steel), solution pH and steel potential [48]. Song et al. [44] developed the following empirical equation to estimate CB as a function of the solution pH and steel potential (ignoring the influence of the steel grade):
where φ is the potential measured versus the copper/copper-sulfate reference electrode (CSE). Based on fitting to the experimental data, Song et al. [44] estimated the value of CcrLat and B0 in Eq. (1) to be 3.3 × 104 mol/m3 and 1.9 × 10− 13 MPa− 6 m− 2 s-1/5, respectively. These parameters are obtained by linearly fitting three data points, each representing one type of NNpH solution and having one C0 value.
Lu [16] suggested mechanistic meanings of the SwRI model by proposing four basic hypotheses underpinning the model.
-
1.
The crack propagation is dominated by CF enhanced by HE, and anodic dissolution effects are negligible.
-
2.
The cracked body is at the steady state and under the small-scale yield condition.
-
3.
The crack grows discontinuously through the mechanism of microcracks forming and developing in FPZ and eventually merging into the main crack.
-
4.
The crack growth rate is approximately proportional to the size of FPZ.
Based on the above hypotheses, Lu [16] suggested that the interval in a loading cycle provides the time necessary for hydrogen to diffuse into FPZ; therefore, da/dN is a function of the loading frequency f as reflected in Eq. (1). The crack growth rate increases as f decreases because longer time is available in a given load cycle for the hydrogen transport (diffusion). If f is below a lower threshold, all the microcracks in FPZ can connect with the main crack in one load cycle effect. In this case, the effect of f on the crack growth rate becomes saturated, and the growth rate is independent of f. If f is above an upper threshold, hydrogen atoms have insufficient time to diffuse to FPZ and participate in the crack growth process. In this case, da/dN is dominated by the fatigue mechanism and independent of f.
A slightly modified SwRI model was further proposed by Lu [16] as follows:
where ΔKeq = K1/3 maxΔK2/3, B′ 0 = 8.8 × 10− 14 MPa− 6 m−2 s-0.25, and (ΔKeq/f1/24)th is the threshold value for the combined parameter (ΔKeq/f1/24) below which the crack growth is considered negligible. Note that Lu [16] did not indicate the specific value of (ΔKeq/f1/24)th or how it can be estimated. A comparison of Eqs. (1) and (4) reveals that the modified SwRI model differs slightly from the SwRI model in terms of the exponent on f on the right-hand side of the two equations: it is − 0.2 in Eq. (1) and − 0.25 in Eq. (4). Note that the latter value is obtained by fitting to the experimental data obtained in simulated groundwater with near-neutral pH [46, 49].
The development of the SwRI and modified SwRI models involves expressing the maximum hydrostatic stress in FPZ in terms of the stress intensity factor based on linear elastic fracture mechanics solutions for the crack-tip stress field. This, however, is problematic given that such solutions are inapplicable to the stress field within FPZ, which are associated with large strains and considerable plastic deformations.
Xing et al.’s model
Xing et al. [50] proposed a growth model for NNpHSCC by considering both AIDE and HEDE, that is,
The crack growth rate due to HEDE only, (da/dN)HEDE, considers the effects of hydrogen potential, diffusivity, hydrostatic stress near the crack tip and critical loading frequency [51,52,53], and is given by:
where fcrit represents the minimum loading frequency under which the crack growth rate reaches the maximum value and is independent of f; ν is Poisson’s ratio; Ω (m3) is the partial volume of hydrogen atom; kB is the Boltzmann constant (= 1.3806 × 10− 23 m2 kg s− 2 K− 1); T (K) is the temperature; c0 is the atomic ratio of H/Fe away from the crack tip, which can vary from zero up to 5 × 10− 4 [50]; R = Kmin/Kmax is the stress ratio; γ is a material constant to be obtained from data fitting; D is the hydrogen diffusivity rate (m2/s); rp is the size of the plastic zone ahead of the crack tip (Fig. 1), and Req is the outer radius of the annulus region that supplies as well as depletes hydrogen atoms to the plastic zone during cyclic loading.
The schematic of the hydrogen enhanced crack growth model [50]
Xing et al. [50] further suggested that da/dN can be related to (da/dN)HEDE through an empirical relationship: log(da/dN)/log(da/dN)HEDE = n, where n is a fitted constant for a given steel. It follows from Eq. (6) that da/dN is given by
Based on fitting to the experimental data of the X65 and X52 steels [34, 54, 55], Xing et al. [28] recommended that γ be taken as 0.1 and n be taken as 0.92 and 0.88 for the X65 and X52 steels, respectively. It follows that the combined parameter in Xing et al.’s model is [(1 + R)/(1-R)]ΔK2(f/fcrit)-0.1, which is somewhat similar to the combined parameter, KmaxΔK2f-0.1, proposed by Chen and Sutherby [34]. Xing et al. [56] suggested that the value of the combined parameter [(1 + R)/(1-R)]ΔK2(f/fcrit)-0.1 can be used to divide the crack growth process into three phases. A crack is in the dormant, initiation and fast growth phases if the corresponding value of [(1 + R)/(1-R)]ΔK2(f/fcrit)-0.1 is less than 500 MPa2 m, between 500 and 1000 MPa2 m, and greater than 1000 MPa2 m, respectively.
Xing et al. [50] did not recommend specific values of parameters Ω and c0 in Eq. (6). Bockris et al. [57] suggested the partial volume of hydrogen, VH, equals to 2.60 cm3/mol and 1.84 cm3/mol in α-Fe and AISI 4340 steel, respectively, at 27 °C under tensile stress, which is equivalent to 4.317 × 10− 30 m3 and 3.055 × 10− 30 m3 for the value of Ω, respectively. Lee and Gangloff [58] suggested VH to equal 2.0 cm3/mol (Ω = 3.321 × 10− 30 m3) for ultra-high-strength steel. Yu et al. [59] suggested Ω to be 2.0 × 10− 30 m3, whereas Song and Curtin [52, 53] suggested Ω to equal 3.818 × 10− 30 m3. Song and Curtin [52] further suggested values of c0 for pipe steels of different grades: c0 equals 0.16 × 10− 6 and 0.12 × 10− 6 for the X52 and X42 steels, respectively. Xing [60] suggested c0 to equal 2.0 × 10− 6 regardless of the steel grade. Song and Curtin [52] suggested D to equal 2.7 × 10− 11 m2/s for both X52 and X42 steels. Xing et al. [50] argued that the diffusivity of hydrogen in steels under tension can be much higher than that in steels under zero stress, and recommended D to equal 1.7 × 10− 9 m2/s regardless of the steel grade. Yu et al. [59] further suggested that D could range from 1.5 × 10− 9 m2/s and 2.0 × 10− 9 m2/s with varying stress and strain.
Chen et al.’s model
A modification of Xing et al.’s model was proposed by Chen and his co-investigators [61, 62] as follows:
where n’ = 2, and fcrit is suggested to be 10− 3 Hz. It is however unclear how the value of n’ is estimated. All the other parameters in Eq. (9) have been defined previously. Chen et al.’s model differs from Xing et al.’s model in that the former employs the combined parameter proposed by Chen and Sutherby [34], i.e. KmaxΔK2f-0.1. A few observations of Chen et al.’s model are noteworthy. First, the applicability of the model for f ≤ fcrit is not explicitly indicated by Chen et al., although it can be assumed that da/dN is independent of f for f ≤ fcrit with da/dN values for f ≤ fcrit equal to that for f = fcrit. Second, care must be taken to ensure the consistency in the units of both sides of Eq. (9) due to the fact that the combined parameter in Eq. (9) involves the frequency directly, as opposed to a normalized frequency, i.e. f/fcrit, employed in Xing et al.’s model. A dimensional analysis shows that the constant \(\sqrt{2.476}\) on the right side of Eq. (9) must have a unit of m-0.3 s-0.23 kg0.1 to be compatible with the unit of m/cycle of da/dN. This unit consistency requirement hinders the practical application of Chen et al.’s model.
Accuracy of NNpHSCC crack growth models
Crack growth data from tests of full-scale pipe specimens
Between 1993 and 1996, researchers at the CanmetMATERIALS (formerly Canmet Materials Technology Lab, or MTL) of Natural Resources Canada conducted full-scale NNpHSCC growth tests on three X52 pipes [32, 63]. The growth data collected from two of the three specimens (pipes #1 and #2) are employed in this study to validate the growth models described in Section 3; the other specimen is not considered because of limitations in the data recorded during the test. The outside diameters (d), wall thicknesses (t) of pipes #1 and #2 are 610 mm and 6.4 mm, respectively. The yield and tensile strengths (σy and σu) determined from tensile coupon tests for the specimens are 421 and 538 MPa, respectively.
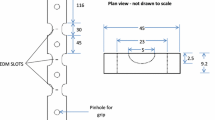
Sixteen cracks equally distributed over four circumferential positions (i.e. 3, 6, 9 and 12 o’clock positions) were introduced on each of the two specimens. At a given clock position, four cracks are oriented along the longitudinal axis of the specimen with an end-to-end separation distance (s) of about 100 mm (Fig. 2). The specimens were internally pressurized by hydraulic oil. The pressure level and rate of loading were controlled by a feedback system consisting of a pressure gauge, servovalves, servovalve controllers and interfacing hardware. Two end plates were welded on each specimen to contain the internal pressure. The local NNpH environments for the cracks were realized by using a soil box enclosing the pipe external surface (Fig. 2). The soil box was filled with a clay-type soil collected from a failure site of a pipeline caused by NNpH SCC. The average pH of the soil environment around the pipe surface was maintained between 6.9 and 7.2 during the test. The initial depth of a crack is the sum of the depths of a saw-cut notch and the subsequent fatigue pre-crack (Fig. 3). The crack length (i.e. in the pipe axial direction) was made far greater than the depth during saw cutting to ensure that the crack propagates primarily in the depth direction with negligible length growth. According to BS7910 [64], two coplanar surface flaws with a1/l1 ≤ 1 and a2/l2 ≤ 1 are considered to interact if s ≤ max{a1/2, a2/2}, where a1 and a2 are depths of the two cracks, respectively, and l1 and l2 are half-lengths of the cracks, respectively. Since s for the cracks considered in the present study is far greater than the maximum crack depths (ranging from 2 to 5 mm in general), the cracks at the same clock position do not interact with each other. The initial crack depth was measured using a direct current potential drop (DCPD) system, which has a resolution of about 30 μm.
Each specimen was subjected to a series of different load spectra, referred to as the “test periods”, over the duration of the test. Fig. 4 illustrates the stress cycle applied within a given test period, which consists of a saw-tooth-shaped dynamic component and a static component. The unloading rate is twice the loading rate in the dynamic component. The inclusion of both the dynamic and static components in a stress cycle is intended to gain understanding of their respective effects on the crack growth rate. This can be achieved by comparing the crack growth rate obtained from the load spectrum illustrated in Fig. 4 with that corresponding to a reference load spectrum consisting only of the dynamic component in a stress cycle. The test data corresponding to such a reference load spectrum are, however, unavailable. During the test, the crack depth was measured by DCPD at different times such that the total crack growth (i.e. difference between the crack depth at the time of measurement and initial crack depth) was tracked throughout the test. Note that due to the uncertainties associated with the DCPD measurement as well as generally slow growths of cracks, the DCPD-measured crack depth did not monotonically increase with time.
Once the test was completed, the actual final depth of each crack on pipe #1 was physically measured by breaking open the pipe specimen at the location of the crack and compared with the corresponding final crack depth measured by DCPD to validate the accuracy of the DCPD measurement. Researchers at Canmet considered the DCPD-measured final depths of 9 cracks on pipe #1 to be close to the corresponding physically-measured crack depths, i.e. the measurement error of DCPD is considered acceptable. The final depths of the cracks on pipe #2 were not physically measured. The four cracks at the 9 o’clock position on pipe #2 are in the seam weld of the specimen and excluded in the present study because it is unclear if the growth models described in Section 3 are applicable to cracks in the weldment. It is assumed in this study that the DCPD-measured depths of the remaining 12 cracks on pipe #2 (i.e. at the 3, 6 and 12 o’clock positions) are associated with acceptable measurement errors. Therefore, a total of 21 cracks (9 from pipe #1 and 12 from pipe #2) are considered in the subsequent analysis to evaluate the accuracy of the crack growth models as detailed in Section 4.2. Table 1 summarizes the initial and final depths, and lengths of these 21 cracks. Tables 2 and 3 summarizes the relevant information of the test periods associated with the two pipe specimens, including the maximum hoop stress (σhmax) within a given stress cycle, R (= σhmin/σhmax), durations of the dynamic and static components of one stress cycle (t1 and t2), and duration of each test period.
Evaluation of crack growth rates based on test data
All of the 21 cracks listed in Table 1 except cracks 1–9-1 and 1–9-2 grew slowly during the test. Fig. 5 depicts the crack growth over the duration of the test for a representative crack, 2–3-2, as well as cracks 1–9-1 and 1–9-2. Cracks 1–9-1 and 1–9-2 differ from the other 19 cracks in that they exhibited fast growths during the test: the final crack depths (5.20 and 5.93 mm) are approximately twice the initial crack depths (2.80 and 2.73 mm). Figure 5b and c reveal that the fast growths of cracks 1–9-1 and 1–9-2 during the test are due entirely to their growths in test period VII, which should be considered separately. On the other hand, cracks 1–9-1 and 1–9-2 grow slowly in all test periods other than VII. For each of the 21 cracks in Table 1, the crack growth rate is evaluated for a selected number of test periods during which the crack growth trend is reasonably clear from the DCPD measurements. Since it is very difficult to quantify the change in the crack growth rate of a given slowly-growing crack within a given test period due to the relatively large scatter in the DCPD measurements, a constant crack growth rate, da/dt (mm/s), is evaluated for a given test period based on the linear regression analysis of the DCPD data. This results in a total of 39 da/dt values for the 21 cracks within the selected test periods (see Table 7 of Appendix). These 39 growth rates are referred to as the dataset hereafter. The linear regression results corresponding to the da/dt values are included in Figure 7 of Appendix. Note that the crack growth rates included in the dataset are generally in the order of 10− 8 mm/s (0.32 mm/year). This is consistent with typical growth rates of NNpHSCC observed on in-service pipelines [4].
Crack growth over the test duration for cracks 2–3-2, 1–9-1 and 1–9-2 [63]. a Crack 2–3-2. b Crack 1–9-1. c Crack 1–9-2
Quadratic equations are found to fit very well the growth paths of cracks 1–9-1 and 1–9-2 within test period VII. It follows that multiple da/dt values can be obtained for cracks 1–9-1 and 1–9-2 within test period VII by evaluating the slopes of the two fitted quadratic equations at different times. However, the obtained growth rates are generally in the order of 10− 7 – 10− 6 mm/s (3.2–32 mm/year), which are order-of-magnitude higher than typical NNpHSCC growth rates observed in practice. Therefore, these growth rates are not considered in the subsequent analysis.
Model predicted crack growth rates
The four growth models described in Section "Growth models for NNpHSCC defects on pipelines", i.e. the SwRI and modified SwRI models, Xing et al.’s and Chen et al.’s models, are employed to predict the growth rates included in the dataset. Analysis results however revealed that the crack growth rates predicted by Chen et al.’s model are drastically different from the corresponding growth rates obtained in the test. Therefore, Chen et al.’s model is not discussed further in the following sections, and predictions by the other three growth models are described in detail. In applying the modified SwRI model, the threshold value (ΔKeq/f1/24)th is not considered in the calculation since crack growths had been observed during all 39 collected test periods. In applying Xing et al.’s model, the value of n in Eq. (8) is set to 0.88 corresponding to the X52 pipe steel. Furthermore, the values of (da/dN)HEDE in Xing et al.’s model, i.e. Eq. (6), are also evaluated for the dataset. The crack growth rate per cycle, i.e. da/dN, predicted by the growth model is converted to da/dt using the following equation:
where f is the frequency of the cyclic load, which is a constant within a given test period and equals 1/(t1 + t2) (Fig. 4). The values of f in various test periods for pipes #1 and #2 range from 9.6 × 10− 5 to 1.1 × 10− 3 Hz. It is noteworthy that the stress cycle applied to the pipe specimen consists of the dynamic and static components. Previous studies [32, 65] suggest that the static load does not cause the growth of NNpHSCC. Further studies are therefore needed to investigate if the stress cycle shown in Fig. 4 could be converted to an equivalent stress cycle that consists of the dynamic component only.
All three growth models involve the evaluation of the maximum stress intensity factor within a stress cycle (Kmax) to predict the crack growth rates. To this end, a given crack is assumed to have a semi-elliptical profile and grows in the depth direction only. The Raju-Newman equation [66] is then employed to evaluate the stress intensity factor at the deepest point of the crack front. Since each of the da/dt values included in the dataset is considered the average observed crack growth rate of a given crack within a certain test period, the corresponding predicted da/dt is evaluated by using a single Kmax value in the crack growth model, which is the average of the Kmax values corresponding to all the crack depth measurements included in the test period for the crack. This simplification is justified by the fact that the increase in Kmax within a given test period is generally less than 5% for the cracks included in the dataset.
For clarity and easy reference, Table 4 summarizes values of parameters of the three growth models, i.e. B0, B′ 0, CLat cr, CB, D, rp, Req, Ω and c0, adopted in the present study as well as the corresponding sources for the values.
Comparison of observed and predicted crack growth rates
Predictions by the three growth models are shown in Fig. 6 for the dataset by plotting ratios of observed to predicted growth rates versus the observed growth rates. Let ZSwRI and ZMSwRI denote the observed-to-predicted growth rates corresponding to the SwRI and Modified SwRI models, respectively; let ZX-HEDE and ZX denote the observed-to-predicted growth rates corresponding to the HEDE component of Xing et al.’s model (Eq. (6)) and Xing et al.’s model (Eq. (8)), respectively. The mean and coefficient of variation (COV) of ZSwRI, ZMSwRI, ZX and ZX-HEDE for the dataset are shown in Table 5.
Table 5 indicates that the accuracy of the predicted growth rates varies widely. The HEDE component of Xing et al.’s model leads to the best predictions for the dataset, with the mean and COV of ZX-HEDE equal to 1.06 and 61.2%, respectively. It is interesting to note that Xing et al.’s model performs much poorer than its HEDE component and results in on average almost one order of magnitude over-predictions of the growth rates in the dataset. Although the two SwRI models are on average somewhat accurate to predict the growth rates in the dataset, there is large variability associated with the predictions: the corresponding COVs are 200%, and the minimum and maximum observed-to-predicted ratios differ by two orders of magnitude. This can be explained by the strong dependence of the predicted growth rates on ΔK: for both the SwRI models, the predicted growth rates are proportional to ΔK4. An increase of R from 0.6 to 0.8 will lead to a 94% reduction in the predicted crack growth rate, all else being the same; however, such marked changes were not observed in the observed crack growth rates. These observations suggest that further research is needed to determine a more appropriate exponent on ΔK in both SwRI models.
While there is little room to adjust the value of a given parameter in both SwRI models as evident from the description in the previous Section, the possible value of a given parameter in Xing et al.’s model (e.g. D) may vary within a wide range. It is therefore valuable to investigate which input parameters have the most significant influences on the accuracy of Xing et al.’s model such that more efforts can be made to quantify those parameters more accurately. As the HEDE component of Xing et al.’s model leads to the best predictions for the dataset, analyses are carried out to investigate the sensitivity of ZX-HEDE to the values of different parameters. To this end, three parameters, namely D, Ω and c0, are considered in the sensitivity analysis as they have largely different recommended values from different sources: D varies from 2.7 × 10− 11 m2/s to 2.0 × 10− 9 m2/s [50, 52, 59]; Ω varies from 2.0 × 10− 30 m3 to 4.317 × 10− 30 m3 [52, 53, 57,58,59], and c0 varies from 0 to 5 × 10− 4 as suggested in [50, 52, 60]. For each parameter, three values are considered in the sensitivity analysis: one base case corresponding to the value indicated in Table 4 and two sensitivity cases as summarized in Table 6. In the sensitivity cases corresponding to a given parameter, values of all the other parameters are kept the same as those listed in Table 4. It is worth noting the relationship between fcrit and f for the dataset of the growth rates. For the base case, the majority of the data points (33 out of 39) have f < fcrit, indicating that the corresponding predicted growth rates are independent of f. Since fcrit is independent of c0, the two sensitivity cases for c0 are the same as the base case in terms of the relationship between fcrit and f for the dataset. On the other hand, fcrit is a function of D and Ω. The two sensitivity cases for D result in all 39 data points having f > fcrit, whereas the two sensitivity cases for Ω result in all 39 data points having f < fcrit. The results of the sensitivity analysis as summarized in Table 6 indicate that the COV of ZX-HEDE is only marginally affected by varying values of D, Ω and c0, whereas the mean of ZX-HEDE is somewhat influenced by varying values of D, Ω and c0. Overall, the base case values of D, Ω and c0, i.e. those listed in Table 4, result in relatively more accurate model predictions.
Conclusions
This study presents a review of four existing growth models for NNpHSCC defects on buried oil and gas pipelines, namely the two models developed at SwRI, Xing et al.’s model and Chen et al.’s model. All four models assume the main growth mechanism for NNpHSCC defects to be corrosion fatigue enhanced by hydrogen embrittlement. To investigate the predictive accuracy of the four models, a dataset consisting of 39 crack growth rates is established from a test program involving full-scale pipe specimens in NNpH environment under cyclic internal pressures conducted at Natural Resources Canada. The crack growth rates in the dataset are in the order of 10− 8 mm/s (0.32 mm/year), consistent with typical NNpHSCC growth rates observed on in-service oil and gas pipelines. The growth rates of the 39 cracks in the dataset are predicted using each of the four growth models, and the predicted growth rates are then compared with the corresponding observed growth rates.
The analysis reveals that Chen et al.’s model results in highly inaccurate predictions of the observed growth rates, whereas the SwRI model, Modified SwRI model and Xing et al.’s model lead to on average reasonably accurate predictions. However, predictions by both SwRI models are associated with high variability, with the COV of the observed-to-predicted growth rates equal to 200%. The HEDE component of Xing et al.’s model leads to the best predictions with the mean and COV of the observed-to-predicted ratios equal to 1.06 and 61.2%, respectively. Analyses further indicate that the accuracy of the HEDE component of Xing et al.’s model is somewhat sensitive to the values of three model parameters (i.e. D, Ω and c0). The findings of this study suggest that further research is needed to improve the existing NNpHSCC growth models or develop new growth models such that adequately accurate predictions of the NNpHSCC growth rates can be achieved in the pipeline integrity management practice.
Availability of data and materials
The dataset of the crack growth rates employed in the present study are already included in the manuscript. The raw data from which the crack growth rates are obtained are unavailable due to the non-disclosure agreement between the University of Western Ontario and Natural Resources Canada.
Abbreviations
- AD:
-
Anodic dissolution
- AIDE:
-
Adsorption-induced dislocation emission
- Canmet:
-
CanmetMATERIALS Lab
- CF:
-
Corrosion fatigue
- COV:
-
Coefficient of variation
- DCPD:
-
Direct current potential drop
- FPZ:
-
Fracture process zone
- HE:
-
Hydrogen embrittlement
- HEDE:
-
Hydrogen-enhanced decohesion
- HELP:
-
Hydrogen-enhanced localized plasticity
- NNpHSCC:
-
Near-neutral pH stress corrosion cracking
- SCC:
-
Stress corrosion cracking
- SwRI:
-
Southwest Research Institute
References
National Conference of State Legislatures (2021) Making state gas pipelines safe and reliable: an assessment of state policy. https://www.ncsl.org/research/energy/state-gas-pipelines.aspx. accessed 18 May 2021
Natural Resources Canada (2020) Pipelines across Canada. https://www.nrcan.gc.ca/our-natural-resources/energy-sources-distribution/clean-fossil-fuels/pipelines/pipelines-across-canada/18856. accessed 17 Aug 2020
National Energy Board (1996) Stress corrosion cracking on Canadian oil and gas pipelines. MH-2-95, NEB, Calgary
Transportation Safety Board of Canada (2018) Pipeline transportation safety investigation report P18H0088: pipeline rupture and fire, Westcoast energy Inc., 36-inch transmission south mainline loop, Prince George, BC
Transportation Safety Board of Canada (2009) Pipeline investigation report P09H0074: natural gas pipeline rupture, TransCanada Pipeline Inc., 914-millimeter-diameter pipeline, line 2-MLV 107–2 + 6.031 km, near Englehart, ON
Transportation Safety Board of Canada (2011) Pipeline investigation report P11H0011: TransCanada pipelines limited, 914.4-millimeter-diameter pipeline, line 100–2-MLV 76–2 + 09.76 km, near Beardmore, ON
Transportation Safety Board of Canada (2002) Pipeline investigation report P02H0017: natural gas pipeline rupture, TransCanada pipeline, line 100–3, 914-millimeter-diameter line, main-line valve 31–3 + 5.539 kilometers, near the village of Brookdale, ON
US Department of Transportation (2016) Failure investigation report: Williams partners L.P./Transco 24″ Leidy line B failure, Unityville, PA
US Department of Transportation (2011) Failure investigation report: Columbia gas transmission pipeline rupture
Jones RH (1992) Stress corrosion cracking: materials performance and evaluation, 1st edn. ASM International, Materials Park
Cheng YF (2013) Stress corrosion cracking of pipelines, 1st edn. Wiley, Hoboken
Leis BN, Bubenik TA, Nestleroth JB (1996) Stress corrosion cracking in pipelines. Pipeline Gas J 223(8):42–49
Justice J, Mackenzie J (1988) Progress in the control of stress corrosion in a 914mm O.D. gas transmission pipeline. Paper presented at the NG-18/EPRG 7th biennial joint meeting on line pipe research, Washington, D.C., the USA
Delanty B, O’Beirne J (1992) Major field study compares pipeline SCC with coatings. Oil Gas J 90(24):39–44
Engel DW (2017) Investigation of surface crack growth behaviour under variable pressure fluctuations in near-neutral pH environments. MSc Dissertation, University of Alberta, Edmonton, Alberta, Canada
Lu BT (2013) Crack growth model for pipeline steels exposed to near-neutral pH groundwater. Fatigue Fracture Eng Mater Struct 36(7):660–669. https://doi.org/10.1111/ffe.12033
Cui Z, Wang L, Liu Z, Du C, Li X, Wang X (2016) Anodic dissolution behavior of the crack tip of X70 pipeline steel in near-neutral pH environment. J Mater Eng Perform 25:5468–5476. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-016-2394-8
Mohtadi-Bonab MA (2019) Effects of different parameters on initiation and propagation of stress corrosion cracks in pipeline steels: a review. Metals 9(5):590. https://doi.org/10.3390/met9050590
Parkins RN, Blanchard WK, Delanty BS (1994) Transgraunlar stress corrosion cracking of high-pressure pipelines in contact with solutions of near-neutral pH. Corrosion 50(5):394–408. https://doi.org/10.5006/1.3294348
Gu B, Yu WZ, Luo JL, Mao X (1999) Transgranular stress corrosion cracking of X-80 and X-52 pipeline steels in dilute aqueous solution with near-neutral pH. Corrosion 55(3):312–318. https://doi.org/10.5006/1.3283993
Lu BT, Luo JL, Norton PR, Ma HY (2009) Effects of dissolved hydrogen and elastic and plastic deformation on active dissolution of pipeline steel in anaerobic groundwater of near-neutral pH. Acta Mater 57(1):41–49. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2008.08.035
Lu BT, Luo JL, Norton PR (2010) Environmentally assisted cracking mechanism of pipeline steel in near-neutral pH groundwater. Corros Sci 52(5):1787–1795. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.corsci.2010.02.020
Cheng YF, Niu L (2007) Mechanism for hydrogen evolution reaction on pipeline steel in near-neutral pH solution. Electrochem Commun 9(4):558–562. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.elecom.2006.10.035
Li MC, Cheng YF (2007) Mechanistic investigation of hydrogen-enhanced anodic dissolution of X-70 pipe steel and its implication on near-neutral pH SCC of pipelines. Electrochim Acta 52(28):8111–8117. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2007.07.015
Liu ZY, Li XG, Cheng YF (2012) Mechanistic aspect of near-neutral pH stress corrosion cracking of pipelines under cathodic polarization. Corros Sci 55:54–60. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.corsci.2011.10.002
Anderson TL (2017) Fracture mechanics: fundamentals and applications, 4th edn. CRC Press, Boca Raton
Oriani RA (1972) A mechanistic theory of hydrogen embrittlement of steels. Ber Bunsengesellschaft Phys Chemie 76(8):848–857. https://doi.org/10.1002/bbpc.19720760864
Xing X, Zhou J, Zhang S, Zhang H, Li Z, Li Z (2019) Quantification of temperature dependence of hydrogen embrittlement in pipeline steel. Materials 12(4):585–595. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12040585
Beachem CD (1972) A new model for hydrogen assisted cracking (hydrogen “embrittlement”). Metall Mater Trans B 3:441–455
Lynch SP (1988) Environmentally assisted cracking: overview of evidence for an adsorption-induced localised-slip process. Acta Metall 36(10):2639–2661. https://doi.org/10.1016/0001-6160(88)90113-7
Lynch S (2012) Hydrogen embrittlement phenomena and mechanisms. Corros Rev 30:105–123. https://doi.org/10.1515/corrrev-2012-0502
Zheng W, Revie RW, MacLeod FA, Tyson WR, Shen G (1996) Pipeline SCC in near-neutral pH environment: recent progress. Paper presented at the IPC-1996 Conference, Calgary. https://doi.org/10.1115/IPC1996-1854
Chen W, Sutherby R (2004) Environmental effect of crack growth rate of pipeline steel in near-neutral pH soil environments. Paper presented at the IPC-2004 Conference, Calgary, 4–8 October 2004. https://doi.org/10.1115/IPC2004-0449
Chen W, Sutherby R (2007) Crack growth behaviour of pipeline steel in near-neutral pH soil environments. Metall Mater Trans A 38A:1260–1268. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-007-9184-8
Chen W, Kania R, Worthingham R, Van Boven G (2009) Transgranular crack growth in the pipeline steels exposed to near-neutral pH soil aqueous solutions: the role of hydrogen. Acta Mater 57:6200–6214. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2009.08.047
Tehinse O, Lamborn L, Chevil K, Gamboa E, Chen W (2021) Influence of load interaction and hydrogen on fatigue crack growth behaviour in steel pipelines under mean load pressure fluctuations. Fatigue Fracture Eng Mater Struct 44(4):1073–1084. https://doi.org/10.1111/ffe.13414
Revie RW (2011) Uhlig’s corrosion handbook, 3rd edn. Wiley, Hoboken
Zheng W, Bibby D, Li J, Bowker JT, Gianetto JA, Revie RW, Williams G (2006) Near-neutral pH SCC of two line pipe steels under quasi-static stressing conditions. Paper presented at the IPC-2006 Conference, Calgary, 25–29 September 2006. https://doi.org/10.1115/IPC2006-10084
Fang BY, Han EH, Wang JQ, Ke W (2007) Stress corrosion cracking of X-70 pipeline steel in near-neutral pH solution subjected to constant load and cyclic load testing. Corros Eng Sci Technol 42(2):123–129. https://doi.org/10.1179/174327807X196843
Jia YZ, Wang JQ, Han EH, Ke W (2011) Stress corrosion cracking of X80 pipeline steel in near-neutral pH environment under constant load tests with and without preload. J Mater Sci Technol 27(11):1039–1046. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1005-0302(11)60184-9
Kang J, Zheng W, Bibby D, Amirkhiz BS, Li J (2016) Initiation of stress corrosion cracks in X80 and X100 pipe steels in near-neutral pH environment. J Mater Eng Perform 25:227–240. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-015-1822-5
Zheng W, Bibby D, Li J, Williams G, Revie W, Tyson B (2009) Stress corrosion cracking of oil and gas pipelines: new insights on crack growth behaviour gained from full-scale and small-scale tests, Paper presented at the ICF 12 Conference, Ottawa 12–17 July 2009
Zheng W, Elboujdani M, Revie RW (2011) Stress corrosion cracking in pipelines. In: Raja VS, Shoji T (eds) Stress corrosion cracking: theory and practice, 1st edn. Woodhead Publishing Limited, Sawston, Cambridge
Song FM, Lu BT, Gao M, Elboujdaini M (2011) Development of a commercial model to predict stress corrosion cracking growth rates in operating pipelines. Report Prepared for U.S. Department of Transportation Pipeline and Hazardous Materials Safety Administration, Contract Number: DTPH 56-08-T-000001, Southwest Research Institute, San Antonio, TX United States 78238.
Lu BT, Song FM, Gao M, Elboujdaini M (2012) A phenomenological model for environmentally assisted cracking of pipeline steels in near-neutral pH groundwater. Paper presented at the CORROSION 2012 Conference, Salt Lake City
Gerberich WW, Livne T, Chen YF, Kaczorowski M (1988) Crack growth from internal hydrogen-temperature and microstructural effects in 4340 steel. Metall Trans A 19:1319–1334
Chen W, King F, Vokes E (2002) Characteristics of near-neutral-pH stress corrosion cracks in an X-65 pipeline. Corrosion 58(3):267–275
Parkins RN, Beavers JA (2003) Some effects of strain rate on the transgranular stress corrosion cracking of ferritic steels in dilute near-neutral-pH solutions. Corrosion 59(3):258–273
Gutierrez-Solana F, Valiente A, Gonzalez J, Varona JM (1996) A strain-based fracture model for stress corrosion cracking of low alloy steels. Metall Mater Trans A 27(2):291–304. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02648407
Xing X, Chen W, Zhang H (2015) Prediction of crack propagation under cyclic loading based on hydrogen diffusion. Mater Lett 152:86–89. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matlet.2015.03.045
Song J, Curtin WA (2011) A nanoscale mechanism of hydrogen embrittlement in metals. Acta Mater 59(4):1557–1569. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2010.11.019
Song J, Curtin WA (2013) Atomic mechanism and prediction of hydrogen embrittlement in iron. Nat Mater 12:145–151. https://doi.org/10.1038/NMAT3479
Song J, Curtin WA (2014) Mechanisms of hydrogen-enhanced localized plasticity: an atomistic study using α-Fe as a model system. Acta Mater 68:61–69. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2014.01.008
Been J, Eadie R, Sutherby R (2006) Prediction of environmentally assisted cracking on gas and liquid pipelines. Paper presented at the IPC-2006 Conference, Calgary, 25–29 September 2006. https://doi.org/10.1115/IPC2006-10345
Marvasti MH, Chen W, Kania R, Worthingham R, Van Boven G (2010) Frequency dependence of fatigue and corrosion fatigue crack growth rate. Paper presented at the IPC-2010 Conference, Calgary, 27 September-1 October 2010. https://doi.org/10.1115/IPC2010-31007
Xing X, Cui G, Yang Z, Li Z (2019) A new model to predict crack growth rate in pipeline steel. Acta Pet Sin 40(6):740–747
Bockris JO’M, Beck W, Genshaw MA, Subramanyan PK, Williams FS (1971) The effect of stress on the chemical potential of hydrogen in iron and steel. Acta Metall 19(11):1209–1218. https://doi.org/10.1016/0001-6160(71)90054-X
Lee Y, Gangloff RP (2007) Measurement and modeling of hydrogen environment-assisted cracking of ultra-high-strength steel. Metall Mater Trans A 38:2174–2190. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-006-9051-z
Yu M, Xing X, Zhang H, Zhao J, Eadie R, Chen W, Been J, Van Boven G, Kania R (2015) Corrosion fatigue crack growth behaviour of pipeline steel under underload-type variable amplitude loading schemes. Acta Mater 96(1):159–169. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2015.05.049
Xing X (2016) Molecular dynamics simulations on crack growth behaviour of BCC Fe under variable pressure fluctuations. PhD Dissertation, University of Alberta
Chen W (2016) An overview of near-neutral pH stress corrosion cracking in pipelines and mitigation strategies for its initiation and growth. Corrosion 72(7):962–977. https://doi.org/10.5006/1967
Zhao J, Chen W, Yu M, Chevil K, Eadie R, Been J, Van Boven G, Kania R, Keane S (2017) Crack growth modelling and life prediction of pipeline steels exposed to near-neutral pH environments: stage II crack growth and overall life prediction. Metall Mater Trans A 48:1641–1652. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-016-3939-z
Zheng W, Revie RW, Tyson WR, Shen G, MacLeod FA (1996) Effects of pressure fluctuation on the growth of stress corrosion cracks in an X-52 linepipe steel. Paper presented at the ICPVT-8 Conference, New York
BSI (2015) BS 7910:2013+A1:2015: guide to methods for assessing the acceptability of flaws in metallic structures. The British Standards Institution, London
Yu M, Chen W, Chevil K, Van Boven G, Been J (2016) Retarding crack growth by static pressure hold for pipeline steel exposed to a near-neutral pH environment. Paper presented at the IPC-2016 Conference, Calgary, 27–30 September 2016. https://doi.org/10.1115/IPC2016-64627
Raju IS, Newman JC (1979) Stress-intensity factors for a wide range of semi-elliptical surface cracks in finite-thickness plates. Eng Fract Mech 11(4):817–829. https://doi.org/10.1016/0013-7944(79)90139-5
Acknowledgements
The authors thank Kayley Young and Matthew Lount at CanmetMATERIALS for their help with the development of an SCC database used in this study.
Funding
The study is funded by Natural Resources Canada and Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council of Canada (NSERC) through the Alliance grant (Grant No. ALLRP 548648–2019). The financial support provided to HS by the Faculty of Engineering at the University of Western Ontario is also acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
HS analyzed full-scale test data, implemented the crack growth models, compared the predicted and observed crack growth rates for the test data, and drafted the manuscript. WZ guided the research carried out in the project and revised the manuscript. JK provided the full-scale test data, guided the processing of the test data to extract the growth rates and reviewed the manuscript. The authors read and approved the submitted manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
About this article
Cite this article
Sun, H., Zhou, W. & Kang, J. A review of crack growth models for near-neutral pH stress corrosion cracking on oil and gas pipelines. J Infrastruct Preserv Resil 2, 28 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1186/s43065-021-00042-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s43065-021-00042-1