Abstract
Depending on a field study for one of the largest iron and paints warehouses in Egypt, this paper presents a new multi-item periodic review inventory model considering the refunding quantity cost. Through this field study, we found that the inventory level is monitored periodically at equal time intervals. Returning a part of the goods that were previously ordered is permitted. Also, a shortage is permissible to occur despite having orders, and it is a combination of the backorder and lost sales. This model has been applied in both crisp and fuzzy environments since the fuzzy case is more suitable for real-life than crisp. The Lagrange multiplier technique is used for solving the restricted mathematical model. Here, the demand is a random variable that follows the normal distribution with zero lead-time. Finally, the model is followed by a real application to clarify the model and prove its efficiency.
Similar content being viewed by others
Introduction
Analysis of the inventory system has appeared from more than one hundred years ago. Due to the importance of this branch of sciences, it has attracted the researchers' attention. For instance, Iida [1] investigated the non-stationary periodic review production model with uncertain production capacity and uncertain demand. Silver and Robb [2] studied the periodic review inventory model with some thoughts regarding the optimal reorder period. Hollah and Fergany [3] introduced a constrained periodic review inventory model for deteriorating items when the lead-time is zero. Lin and Lin [4] presented the periodic review integrated model with the optimal ordering and recovery policy. Fergany [5] studied a multi-item continuous review model with varying mixture shortage cost under restrictions. Jaggi et al. [6] introduced the periodic review inventory model with controllable lead-time when the backorder rate depends on a protection interval. Thomas et al. [7] studied a periodic review inventory policy with the lost sales and zero lead-time. Fergany [8] introduced a periodic review inventory model with zero lead-time and varying ordering cost.
The cost parameters in real inventory systems and other parameters are uncertain in nature, such as prices, marketing, production, and inventory. In recent years, many researchers have contributed many articles by applying the fuzzy sets theory as a mathematical way to deal with these uncertainties. For example, Dey and Chakraborty [9] developed a fuzzy random periodic review model with variable lead-time. Rong et al. [10] studied a multi-objective inventory model with controllable lead-time and triangular fuzzy numbers. Jauhari et al. [11] introduced a fuzzy periodic review model involving stochastic demand. Xiaobin [12] developed a continuous review inventory model with variable lead time in a fuzzy environment. Sadjadi et al. [13] studied the fuzzy pricing and marketing planning model using a geometric programming approach. Biswajit and Amalendu [14] introduced the periodic review inventory model with variable lead time and fuzzy demand. Priyan and Uthayakumar [15] studied a multi-echelon inventory model under a service level constraint in a fuzzy cost environment. Khurdi et al. [16] introduced a fuzzy collaborative supply chain model for imperfect items and a service level constraint.
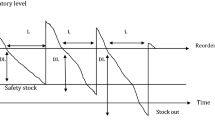
Based on a realistic study for one of the biggest irons and paints warehouses in Egypt, some adjustments have been made to the multi-item periodic review inventory model. In this model, the inventory level is reviewed periodically at equal time cycles. The warehouse allows the customers to return part of the goods they previously ordered; therefore, an extra cost is paid and added to the expected total cost (the refunding quantity cost). Shortage can occur despite having orders, and then a part of these orders is fulfilled in the next cycle at the same price at the request time (backorder), while the other part is lost forever and a penalty clause is paid. There is a constraint on the expected varying lost sales cost, for if this cost exceeds a certain limit, it may lead to loss or increase the expected total cost. The constrained problem is solved by using the Lagrange multiplier technique. The demand is a random variable that follows the normal distribution with zero lead-time. This model has been applied in both crisp and fuzzy environments since the fuzzy environment is closer to real-life than crisp. The main goal is to find the minimum expected annual total cost by finding the optimal maximum inventory level and the optimal time between reviews. The results in this paper have been derived by Mathematica program V. 12.0. Figure 1 shows the multi-item periodic review model with zero lead-time.
The following assumptions are made for developing the mathematical model
-
The warehouse allows refunding a part of the goods that were previously ordered.
-
The demand is a random variable, and the replenishment is instantaneous (lead-time is zero).
-
The stock level decreases at a uniform rate over the cycle.
-
\(f\left( {x_{r} } \right)\) is the density function for the demand \(x_{r}\).
-
A fraction of unsatisfied demand that will be backorder is \({\upgamma }_{r}\), while the remaining fraction \((1 - \gamma_{r} )\) is completely lost.
The mathematical model for crisp environment
-
The expected order cost for the cycle is given by
$$E({\text{OC}}) = \mathop \sum \limits_{r = 1}^{n} C_{or}$$(1) -
The expected varying holding cost for the cycle is given by
$$E\left( {{\text{HC}}\left( {N_{r} } \right)} \right) = \mathop \sum \limits_{r = 1}^{n} C_{hr} \left( {N_{r} } \right){ }\overline{I}_{r} = \mathop \sum \limits_{r = 1}^{n} C_{hr} { }N_{r}^{1 - \beta } \left( {Q_{mr} - \frac{{{\overline{D}}_{r} { }N_{r} }}{2} + \left( {1 - {\upgamma }_{r} } \right)\mathop \smallint \limits_{{Q_{mr} }}^{\infty } \left( {x_{r} - Q_{mr} } \right){ }f\left( {x_{r} } \right){\text{d}}x_{r} } \right)$$(2)where the expected average amount in inventory is given by
$$\overline{I}_{r} = N_{r} \left( {Q_{mr} - \frac{{{\overline{D}}_{r} { }N_{r} }}{2} + \left( {1 - {\upgamma }_{r} } \right)\mathop \smallint \limits_{{Q_{mr} }}^{\infty } \left( {x_{r} - Q_{mr} } \right){ }f\left( {x_{r} } \right)dx_{r} } \right).$$ -
The expected varying backorder cost for the cycle is given by
$$E({\text{BC(}}N_{r} {)}) = \mathop \sum \limits_{r = 1}^{n} C_{br} \;\gamma_{r} \;N_{r}^{\beta } \overline{S}(Q_{mr} ) = \mathop \sum \limits_{r = 1}^{n} C_{br} \;\gamma_{r} \;N_{r}^{\beta } \mathop \smallint \limits_{{Q_{mr} }}^{\infty } (x_{r} - Q_{mr} )\;f(x_{r} )\;{\text{d}}x_{r}$$(3)where \(\overline{S}\left( {Q_{mr} } \right)\) represents the expected shortage quantity.
-
The expected varying lost sales cost for the cycle is given by
$${ }E\left( {{\text{LC}}} \right) = \mathop \sum \limits_{r = 1}^{n} C_{Lr} \left( {1 - \gamma_{r} } \right) N_{r}^{\beta } \overline{S}\left( {Q_{mr} } \right) = \mathop \sum \limits_{r = 1}^{n} C_{Lr} \left( {1 - \gamma_{r} } \right)N_{r}^{\beta } \mathop \smallint \limits_{{Q_{mr} }}^{\infty } \left( {x_{r} - Q_{mr} } \right){ }f\left( {x_{r} } \right){\text{d}}x_{r} { }$$(4)
And the expected varying refunding quantity cost for the cycle is given by
The expected annual total cost will be the sum of the expected order cost, the expected varying holding cost, the expected varying backorder cost, the expected varying lost sales cost, and the expected varying refunding quantity cost
Then from Eqs. (1), (2), (3), (4) and (5), the expected annual total cost is given by
Note: Obviously, the expected order cost \(\left( {\sum\nolimits_{r = 1}^{n} {C_{or} } } \right)\) is fixed, so it can be temporarily neglected in calculating the minimum expected annual total cost and eventually added to it.
Now, the main objective is to determine the optimal values \({Q}_{mr}^{*}\) and \({N}_{r}^{*}\) that minimize the expected annual total cost \(\mathrm{min }E\left(\mathrm{TC}\right)\). This paper puts a constraint on varying lost sales cost. The Karush–Kuhn–Tucker (KKT) conditions (Kuhn and Tucker [17]) are first-order necessary conditions for a solution of nonlinear programming to be optimal if some regularity conditions are satisfied. The Lagrange multiplier method is suitable to solve this constraint problem.
Consider a limitation on the expected varying lost sales cost, i.e.
To solve this primal function which is a convex programming problem, Eqs. (6) and (7) can be written in the following form
\({\text{Subject to:}}\)
To find optimal values \(Q_{mr}^{*} { }\) and \({ }N_{r}^{*}\) which minimize Eq. (8) under the constraint (Eq. (9)), the Lagrange multipliers function with the Kuhn-Tucker conditions is given by
where \({ }\lambda_{Lr}\) is a Lagrange multiplier.
The optimal values \(Q_{mr}^{*}\) and \(N_{r}^{*}\) can be calculated by setting the corresponding first partial derivatives of Eq. (10) equal to zero. Then we obtain:
and
It can be determined the minimum expected annual total cost (min E(TC)), after finding the optimal values \(Q_{mr}^{*}\) and \({ }N_{r}^{*}\), substituting these in Eq. (8), then adding the fixed value \(\left( {\sum\nolimits_{r = 1}^{n} {C_{or} } } \right)\).
The mathematical model for fuzzy environment
The inventory cost coefficients and other coefficients are fuzzy in nature. Therefore, the decision variables and the objective function should be fuzzy as well. This model is resolved when the cost parameters are triangular fuzzy numbers (TFN), and the right and left shape functions of the objective function and its decision variables should be found by finding the upper and the lower bound of the optimal objective function, i.e., \({\tilde{L }}^{U}(\propto )\) and \({\tilde{L }}^{V}(\propto )\) (the left and right \(\propto \mathrm{cuts}\) of \(\tilde{L }\left(\propto \right)\)). For example, the approximated value of TFN of \({\tilde{C }}_{or}\), is observed in Fig. 2.
Consider the model when all parameters are triangular fuzzy numbers (TFN) as given below
where \(a_{ir}\),\({ }i = 1{,}2{,} \ldots {,}10\) are arbitrary positive numbers under the following restrictions:
The left and right limits of \(\propto \;{\text{cuts}}\) of \({ }C_{or} {, }C_{hr} {, }C_{br} {, }C_{Lr} {\text{ and }}{\overline{D}}_{r}\) are given by
Using the signed distance method, we have
The optimal values \(Q_{mr}^{*} { }\) and \({ }N_{r}^{*}\) for the fuzzy case can be determined as in crisp case except replacing the crisp costs \(C_{or} {, }C_{hr} {, }C_{br} ,C_{Lr} \;{\text{and }}\;{\overline{D}}_{r}\) by fuzzy costs \(\tilde{C}_{or} {, }\tilde{C}_{hr} {, }\tilde{C}_{br} ,\tilde{C}_{Lr} \;{\text{and}}\;{ }\widetilde{{{\overline{D}}}}_{r}\).
The demand follows normal distribution
When the mean μ and the standard deviation σ, i.e.
\(\mu_{r}\), continuous location parameter, \(\sigma_{r}\), continuous scale parameter \(\sigma_{r} > 0\) where \(E(x) = \mu_{r} { },\;V(x) = {\upsigma }_{r}^{2} { },\;{ }f\left( {Q_{mr} } \right) = \emptyset \left( {\frac{{Q_{mr} { } - \mu_{r} }}{{{\upsigma }_{r} }}} \right),\;\phi (z) = N(z;0,1)\) is the probability density function of the standard normal distribution, and \(\Phi \left( z \right)\) is the cumulative distribution function of the standard normal distribution.
But
The optimal values \(Q_{mr}^{*}\) and \(N_{r}^{*}\) for crisp case can be calculated as follows:
and the expected number of shortages incurred per cycle is the solution of the following equation
The decision variables and minimum expected annual total cost for a fuzzy case can be determined by the same way except replacing the crisp costs by fuzzy costs.
Application
A large store for iron and paints that sells its products wholesale follows a policy of reviewing all items periodically. Three items were selected (Tanner I, Lacquered II and, Plastic III). This store allows refunding a part of the goods previously ordered. The parameters with 36 samples indicate to the demand during the period 2016–2018 are estimated in Table 8 when α = 0.05 (see the “Appendix”). However, for some unexpected reasons in some cycles, the store faces shortage and pays at least 7% for backorder and 6% for a lost sale. Table 4 shows the allowable cost of lost sales \(K_{Lr}\). The store manager wishes to establish the optimal values \(Q_{mr}^{*} { }\) and \({ }N_{r}^{*} { }\) that achieve the minimum expected annual total cost for different values of \(\beta \in (0,1)\) when the demand follows the normal distribution \(- \infty < x_{r} < + \infty\).
Results and discussion
Tables 1 and 2 show the crisp and fuzzy values of the cost parameters. Table 3 represents the crisp and fuzzy values of the average demand. Table 4 shows the maximum cost allowed (the limitations) for lost sales and its fraction. Table 5 represents parameter values for normal distribution. In Table 6, the results of crisp and fuzzy values for the normal distribution are calculated. Table 7 presents the optimal values of \(Q_{mr}^{*} , N_{r}^{*}\), and the minimum expected annual total cost for crisp and fuzzy values. Table 8 shows the demand during the period 2016–2018 for 36 samples. By using the SPSS program, Table 9 shows One-Sample Kolmogorov–Smirnov Test.
The optimal values \(Q_{mr}^{*} ,\) \(N_{r}^{*} ,\) and the minimum expected annual total cost min \(E({\text{TC}})\) for three items are deduced in Table 7. The results are calculated for the crisp and fuzzy environment. Figures 3, 4 and 5 are displayed to illustrate the crisp and fuzzy values of the expected annual total cost for the three items against the different values β.
Conclusion
By conducting a realistic study of a large warehouse for iron and paints in Egypt, this paper introduced a new multi-item inventory model where the warehouse allows the customers to return a part of the orders they previously ordered. The inventory level of the warehouse is monitored periodically at equal time cycles. Shortages can occur despite having orders, which are a mixture of backorder and lost sales. The demand is a random variable that follows the normal distribution with zero lead-time. It can be concluded that there is a restriction on the expected varying lost sales cost, for if this cost exceeds a certain limit, it may lead to loss or increase the expected total cost. After solving the model in a crisp environment, it resolved in a fuzzy sense, where the fuzzy environment is more suitable for real-life than crisp. Increasing the value of the varying β leads to a loss or an increase in the expected annual total cost. The minimum expected annual total cost is achieved at the minimum value of β (β = 0.1).
Availability of data and materials
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Abbreviations
- \(Q_{mr}\) :
-
The maximum inventory level of the rth item per period (decision variable)
- \(N_{r}\) :
-
The time between reviews for the rth item (decision variable)
- \(x_{r}\) :
-
The demand for the rth item during the period \(N_{r} { }\)(random variable)
- \({\overline{D}}_{r}\) :
-
The expected average demand for the rth item during the period
- \(C_{or}\) :
-
The order cost of the rth item per period
- \(C_{hr} (N)\) :
-
The varying holding cost of the rth item per period \(= \;C_{hr} { }N_{r}^{ - \beta }\)
- \(C_{br} (N)\) :
-
The varying backorder cost of the rth item \(= C_{br} { }N^{\beta }\)
- \(C_{Lr} (N)\) :
-
The varying lost sales cost of the rth item \(= C_{Lr} { }N^{\beta }\)
- \(C_{{{\text{RQ}}r}} (N)\) :
-
The varying refunding quantity cost of the rth item per period \({ } = C_{{\mathrm{RQ}}r} { }N_{r}^{ - \beta }\)
- \(Q_{mr}^{*}\) :
-
The optimal maximum inventory level of the rth item per period
- \(N_{r}^{*}\) :
-
The optimal time between reviews for the rth item (the period)
- \(E\left( {{\text{TC}}_{r} } \right)\) :
-
The expected annual total cost function of the rth item
- \(E({\text{TC}})\) :
-
The expected annual total cost function \(E\left( {{\text{TC}}\left( {Q_{mr} , N_{r} } \right)} \right)\) of the whole items
- \({\text{min}}\;E({\text{TC}})_{r}\) :
-
The minimum expected annual total cost function of the rth item
- \({\text{min}}\;E({\text{TC}})\) :
-
The minimum expected annual total cost function of the whole items
- \(\tilde{C}_{or}\) :
-
The fuzzy order cost of the rth item per period
- \(\tilde{C}_{hr} (N)\) :
-
The fuzzy varying holding cost of the rth item per period \(= \tilde{C}_{hr}\,N_{r}^{ - \beta }\)
- \(\tilde{C}_{br} (N)\) :
-
The fuzzy varying backorder cost \(= \tilde{C}_{br} { }N^{\beta }\)
- \(\tilde{C}_{Lr} (N)\) :
-
The fuzzy varying lost sales cost \(= \tilde{C}_{Lr} { }N^{\beta }\)
- \(\tilde{C}_{{{\text{RQ}}r}} (N)\) :
-
The fuzzy varying refunding quantity cost of the rth item per period \(= \tilde{C}_{{{\text{RQ}}r}} \;N^{ - \beta }\)
- \(\widetilde{{{\overline{D}}}}_{r}\) :
-
The fuzzy expected average demand for the rth during the period
- \(\min \;E\left( {\widetilde{{{\text{TC}}_{r} }}} \right)\) :
-
The fuzzy minimum expected annual total cost function of the rth item
- \({\text{min}}\;E\left( {\widetilde{{{\text{TC}}}}} \right)\) :
-
The fuzzy minimum expected annual total cost function of the whole items
- \(k_{Lr}\) :
-
The goal associated with the available lost sales of the rth item
- β :
-
A constant real number selected to provide the best fit of estimated expected cost function such that \(0 < \beta < 1\)
References
Iida, T.: A non-stationary periodic review production–inventory model with uncertain production capacity and uncertain demand. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 140, 670–683 (2002)
Silver, E., Robb, D.: Some insights regarding the optimal reorder period in periodic review inventory systems. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 112, 354–366 (2008)
Hollah, O.M., Fergany, H.A.: Periodic review inventory model for Gumbel deteriorating items when demand follows Pareto distribution. Springer Plus 27(10), 1–13 (2019)
Lin, Y.J., Lin, H.J.: Optimal ordering and recovery policy in a periodic review integrated inventory model. Int. J. Syst. Sci. 3, 200–210 (2016)
Fergany, H.: Probabilistic multi-item inventory model with varying mixture shortage cost under restrictions. Springer Plus. 5(1), 1–13 (2016)
Jaggi, C., Ali, H., Arneja, N.: Periodic inventory model with controllable lead-time where backorder rate depends on protection interval. Int. J. Ind. Eng. Comput. 5(2), 235–248 (2014)
Thomas, D., Georges, A., Frank, W.: Determining the fill rate for a periodic review inventory policy with capacitated replenishments, lost sales and zero lead time. Oper. Res. Lett. 41, 726–729 (2013)
Fergany, H.: Periodic review probabilistic multi-item inventory system with zero lead-time under constraints and varying ordering cost. Am. J. Appl. Sci. 2(8), 1213–1217 (2005)
Dey, O., Chakraborty, D.: A fuzzy random periodic review system with variable lead-time and negative exponential crashing cost. Appl. Math. Model. 36, 6312–6322 (2012)
Rong, M., Mahapatra, N., Maiti, M.: A multi-objective wholesaler–retailers inventory-distribution model with controllable lead-time based on probabilistic fuzzy set and triangular fuzzy number. Appl. Math. Model. 32, 2670–2685 (2008)
Jauhari, W.A., Mayangsari, S., Kurdhi, N.A., Wong, K.Y.: A fuzzy periodic review integrated inventory model involving stochastic demand. Imperfect Prod. Process Insp. Errors Cogent Eng. 4, 1–24 (2017)
Xiaobin, W.: Continuous review inventory model with variable lead time in a fuzzy random environment. Expert Syst. Appl. 38, 11715–11721 (2011)
Sadjadi, S., Ghazanfari, M., Yousefli, A.: Fuzzy pricing and marketing planning model: a possibilistic geometric programming approach. Expert Syst. Appl. 37, 3392–3397 (2010)
Biswajit, S., Amalendu, S.M.: Periodic review fuzzy inventory model with variable lead time and fuzzy demand. Int. Trans. Oper. Res. 24, 1197–1227 (2017)
Priyan, S., Uthayakumar, R.: Economic design of multi-echelon inventory system with variable lead-time and service level constraint in a fuzzy cost environment. Fuzzy Inf. Eng. 8, 465–511 (2016)
Khurdi, N.A., Lestari, S.M.P., Susanti, Y.: A fuzzy collaborative supply chain inventory model with controllable setup cost and service level constraint for imperfect items. Int. J. Appl. Manag. Sci. 7, 93–122 (2015)
Kuhn, H.W., Tucker, A.W.: Nonlinear programming. In: Proceedings of 2nd Berkeley Symposium, pp. 481–492. University of California Press, Berkeley (1951)
Acknowledgements
Not applicable.
Funding
Not applicable.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
The author contributed in this paper and then read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The author declares that he has no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
About this article
Cite this article
Hollah, O.M. Variable demand model for periodically reviewing with allowing refunding parts of the orders. J Egypt Math Soc 29, 20 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1186/s42787-021-00129-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s42787-021-00129-4