Abstract
Background
Ischemic stroke (IS) constitutes a relevant health concern recently in younger population causing permanent cognitive and function-limiting disability and ranks as the 3rd cause of death in Egypt after cardiac and hepatic diseases. Platelet activation has a crucial mechanism in arterial thrombogenesis, thus in pathophysiology of IS. Surface expression of P-selectin (CD62P) reflects platelet activation and measured by flowcytometry. The purpose of the study is to evaluate whether platelet activity and reactivity are considered risk factors for IS so more restrict antiplatelet protocols could be implemented for management and recurrence prevention.
Results
Study population was 60 IS patients and 60 apparently healthy age and gender-matched controls. Patients were subdivided into 37 patients without classical risk factors, aged 46.1 ± 8.2, and 23 patients with > 1 vascular risk factors, aged 52 ± 9.9. The percentage of platelets expressing CD62P reflecting ex vivo baseline activity was significantly higher in stroke patients to controls (p = 0.001), also platelet reactivity (CD62P expression after ADP provocation) was statistically significantly elevated in patients than in controls (p < 0.0001) and was significantly higher in IS patients with vascular risk factors compared to patients without risk factors (p = 0.02).
Conclusion
Both baseline platelet activity and reactivity were significantly higher in IS patients, and were also higher in IS patients with other vascular risk factors than in cryptogenic stroke and considered risk factors for IS.
Similar content being viewed by others
Background
In North Africa and the Middle East, stroke has become a major health problem, especially in younger population with estimates that deaths attributed to it will nearly double by 2030 [1]. The increasing prevalence of stroke and its risk factors in Egypt are alarming rendering it as an emerging public health problem. So understanding its risks, etiologies and management is of a great importance. Generally, stroke is classified into hemorrhagic and ischemic types (IS), IS constitutes ~ 80% of all stroke types.
IS is a consequence of thrombosis, rupture of atherosclerotic plaque or embolism. Thrombus and embolus formation are initiated by platelet activation, aggregation and fibrin generation via coagulation cascade [2]. Platelet activation and hyperreactivity contribute to cerebrovascular events significantly [3]. Many studies assumed that in acute and convalescent phases after cerebral ischemia, platelets are excessively activated or hyper-reactive [4, 5]. Platelet effects are not only augmenting the growth of an atherosclerotic lesion, but also worsening the impact of atherothrombosis [6]. They are loaded with a large array of procoagulant factors and receptors which can consequently lead to thrombosis and IS [6]. In spite of that, it is unclear whether platelet activation constitutes a cause of or a sequel to IS [7].
As an alternative method flowcytometry is used to assess platelet function by quantifying fibrinogen binding to integrin aIIbb3, expression of P-selectin (CD62P) or CD63 on platelet surface after stimulation. It has many benefits over that of traditional light transmission aggregometry (LTA). Estimation of platelet activation markers, such as CD62P, CD63, and CD40L by flowcytometry reflects platelet activation and reactivity (functional response to agonists) [8]. LTA is time consuming, operator dependent, labor intensive, needs large volumes of blood and preparing PRP as well as not being sensitive in thrombocytopenia. On the other hand, flowcytometry analysis requires a small volume of blood and permits the evaluation of platelet function in thrombocytopenia; however, unfortunately it cannot be used widely as it lacks standardization.
Methods
This case–control cross-sectional study was approved by the Ethics Committee of the University; Faculty of Medicine, and was carried out in concordance with Declaration of Helsinki. This study involved 60 adult patients with acute non-embolic ischemic stroke. Patients were recruited from neurology department, between 18 and 55 years old. Diagnosis of acute IS was based on clinical evidence of neurological deficit attributed to focal cerebral ischemia and detected by history (including demographics, drug intake and cardiovascular risk factors), detailed neurological examination in addition to neuroimaging by computed tomography (CT) scan (16 row multi-detector, Toshiba scanner, Shimoishigami, Japan) and/or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) (MRI scanner Achieva, Philips Medical Systems, Best, the Netherlands) according to Stroke Council of the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association. We excluded patients with potential source of emboli including major and minor risk; non-thrombotic cardiogenic emboli due to cardiac valvular disease as septic vegetation, calcified valvular fragments, mitral prolapsed, aortic stenosis, mechanical valves, cardiac tumors, AF, cardiac chamber embolism as left ventricle thrombus or regional dysfunction after MI. In addition, patients with stenotic carotid atherosclerotic plaques were excluded as being a potential source of atherosclerotic angiogenic emboli. Also, paradoxical emboli through patent foramen (PFO) were secluded. We excluded patients with hepatic, renal, endocrinological disorders, malignant diseases, trauma, major surgery, acute or chronic inflammatory disorders or infectious diseases. Patients were subdivided into 2 subgroups: 37 patients without traditional vascular risk factors, and 23 patients with one or more vascular risk factors. Sixty apparently healthy age and gender-matched control group who were recruited from the hospital blood bank. All individuals were interviewed using a questionnaire and routine lab investigations were done. By using BD-Bioscience four colors flowcytometry, both platelet activity and reactivity were assessed. Blood samples were collected at 9 PM. Phlebotomy was performed in supine or sitting position, 2 mL were withdrawn using 19-gauge needle by direct, single venepuncture of the antecubital vein with a tourniquet lightly applied just before venepuncture, first 2–3 mL of blood was discarded and the rest was evacuated into sterile tubes containing 0.109 M (3.2% w/v) sodium citrate anticoagulant and very gently mixed.
Immediately, direct staining of platelets was performed after sampling (within 20 min) in order to limit spontaneous platelet activation. Direct immunofluorescence staining were performed by adding 20 μL of activation–independent, platelet-specific antibody (CD41) and 20μL of platelet activation-dependent monoclonal antibody (CD62P) to 40 μL of the diluted whole blood (according to manufacturer’s instructions). Platelet agonist was purchased: the P2Y1/P2Y12 agonist ADP (adenosine 5 di-phosphate, BIO/DATA corporation, EMERGO EUROPE, Netherlands) as no significant differences in the percentage or mean fluorescent intensity (MFI) of activated platelets were observed when different agonists were used; so, ADP was chosen regarding its availability.
ADP provocation for platelet reactivity assessment were done by adding 50 μL of ADP onto 450-μL diluted whole blood, then stained directly with 20 μL of CD41 and 20 μL CD62P. Both direct and ADP-provoked stained tubes were kept for 20 min in room temperature in dark then re-suspended in 200 μL PBS.
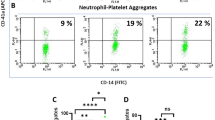
In vivo platelet activation was detected by measuring the percentage and MFI of membrane-bound CD62P in resting platelets without agonist stimulation (Figs. 1, 2). Platelet reactivity was detected by measuring both the percentage and MFI of CD62P after in vitro provocation using ADP as platelet agonist (Figs. 1, 2).
Statistical analysis
Data were collected, coded and entered as a spread sheets using Microsoft excel for windows office 2010. Data were managed using (SPSS) software (version 22.0) (IBM Corp. Released 2013, Armonk, NY). Data were presented as mean, standard deviation or numbers and percentages. Student’s t-test was used between two groups of quantitative variables, Chi-square test and Fisher’s exact test to compare between two groups or more regarding one qualitative variable. ANOVA test was used to compare means between the groups and Pearson’s correlation analysis was used to display strength and direction of association between two quantitative variables and Spearman correlation analysis was used to demonstrate strength and direction of association of nonparametric variables. Binary logistic regression analysis was used to assess platelet baseline activity and ADP provocation reactivity and Lab parameters (PLT, TLC, MPV, PDW, total cholesterol, TG and LDL). Statistical significance was considered at p-value < 0.05.
Results
IS patient group included 39 (65%) males and 21 (35%) females with average age of 48.48 ± 9.2 years compared with 32 (53.3%) males and 28 (46.6%) females with average age 40.72 ± 9 years in control group and age was found to be statistically significant higher in patients with modifiable vascular risk factors than cryptogenic stroke patients (Table 1). Also a statistically significant difference was found in WBC, MPV and PDW being higher in patients than in controls, but did not significantly differ between patients with and without risk factors subgroups, as well as significantly higher total cholesterol, TG and LDL and significantly lower HDL in patients than controls in addition to significantly higher RBS, serum creatinine and TG among patients with vascular risk factors (Tables 2, 3).
The percentage of platelets expressing CD62P reflecting ex vivo baseline activity was significantly higher in stroke patients to controls (32.82 ± 13 vs. 25.77 ± 10, p = 0.001), with MFI in IS patients was 103.6 ± 40.6 compared to 79.1 ± 35.2 in healthy controls, that difference was statistically significant (p = 0.001) (Table 4, Figs. 3, 4), and it was significantly higher in IS patients with vascular risk factors compared to patients without risk factors (34.2 ± 13.7 vs. 30.5 ± 12.4, p = 0.02) (Table 5). Platelet reactivity after stimulation with ADP showed that the percentage of platelets expressed CD62P was 72.95 ± 14.8 in patients compared to 62.2 ± 11.39 in controls, with MFI in patients was 248 ± 101 vs. 215 ± 75.8 in controls and both difference were statistically significant (Table 4, Figs. 1, 2).
A faint statistically significant negative correlation detected for age with baseline CD62P MFI and post-provocation platelet activation, and on the other hand a weak significantly positive correlation for MPV, TG and LDL with both platelet activity and reactivity were detected. Otherwise, there was no statistically significant correlation between both platelet activity and reactivity and other tested vascular risk factors (Table 6).
Discussion
Ischemic cerebrovascular stroke constitutes a very relevant public health concern recently in younger population with estimates that deaths attributed to it will nearly double by 2030 [9]. In agreement with our results, early aggregation studies demonstrated augmented platelet reactivity in acute phase of IS and larger platelet size signifying increased reactivity, a feature of stroke sufferers [10] as we found that PDW and MPV significantly higher in IS compared to healthy controls (p < 0.001 for both). Some authors verified enhanced platelet activation in acute IS and noted that platelets were hyper-reactive in the early, subacute or late and recovery phases [4, 5, 11,12,13,14]. Both platelet–granulocyte aggregates and platelet-derived microparticles appear to increase quantitatively [15,16,17] denoting increased platelet activity.
On the other hand, some researchers stated that platelet activity is increased only in acute phase of IS [18] and reduced during recovery and explained their results due to a rapid decrease in CD62P expression because of its shedding from cell surface [19]. From the literature reviews, it also appeared that lacunar strokes are related to enhanced platelet activity and that circulating P-selectin elevated in large-vessel infarction [20, 21]. Apparently, surface-bound P-selectin is not affected by aspirin intake, whether after agonists provocation or in non-stimulated platelets [22]. Also Sabra and colleagues, came to the same conclusion, that platelet aggregation in IS patients is more significantly higher than in healthy controls. However, it is difficult to be sure if that finding is due to underlying platelet hyperreactivity or is 2nd to the acute ischemic event [23], agreed to the previous results, Pawelczyk and colleagues, reported higher platelet reactivity in response to thrombin in all IS patients in the convalescence stage (at least 3 months later) and concluded that platelet hyperreactivity and susceptibility to agonist may contribute to atherothrombotic intensification and may constitute one of the mechanisms resulting in higher risk of IS and IS recurrence [8].
Regarding the correlation between platelet activation and vascular risk factors, we did not find correlation between platelet activity and reactivity with traditional vascular risk factors in IS patients except for a weak positive correlation between platelet activity and reactivity with TG and LDL, that partially agreed by Yamazaki and colleagues, and Marquardt and colleagues, who found that single vascular risk factors and clinical IS severity did not significantly modify the expression of CD62P and CD63 so stated that simultaneous presence of multiple classical risk factors were not associated with higher platelet activation concluding that markers of platelet activation may state relevant information independently from and in addition to the clinical risk factor assessment and added that different platelet inhibitors were not associated with lower expression of platelet activations antigens is in line with previous reports showing that platelet inhibitors such as aspirin do not modify α-granules excretion [19, 24].
On the other hand, some authors evaluated post-IS patient during convalescent phase and revealed that CD62P expression in resting circulating platelets, in addition to platelets activated in vitro with agonists (TRAP, ADP) still significantly lower than in that found in controls. In parallel, those patients showed a significantly higher PMPs [5], similar results to theirs had been earlier reported by Singh and colleagues, who evaluated unstable angina patients and confirmed an elevated PMPs, lower CD62P expression [25]. Schmalbach and colleagues, obtained same results as ours, and confirmed that PLA and percentage of activated platelet were significantly increased in acute IS patients compared to controls and by regression analyses demonstrated that platelet activation was independent determinant of IS [26]. Also, the results revealed by Serebruany and colleagues, were in consistent and demonstrated no differences between post-stroke patients and controls, and surprisingly lower aggregation analyses in post-stroke patients. Additionally, they reported lower CD62P expression in post-stroke group who received aspirin, compared to patients with no 2ry prophylaxis [27]. An explanation was platelet shape change does not necessarily lead to degranulation and aggregation, so formation of PMPs does not necessarily result in secretion of α granules or aggregation [28, 29], also enhanced shedding of platelet surface receptors, a phenomenon that can occur in their chronic and augmented, but incomplete activation lead to the secretion of microvesicles. Contradicted results were obtained by other scientists who had revealed no alterations or even a reduction in platelet reactivity in the acute phase of cerebral infarctions [7].
Limitation of the work
The main study limitation is the small sample size and conducting the study in single hospital. So, we recommend doing multicenter researches to evaluate larger numbers of patients to more evenly ensure patient distribution. In addition, we recommend using other platelet agonists, in addition to the ADP, to comprehensively assess platelet reactivity.
Conclusion
It was found that IS patients had more ex vivo active platelets (resting baseline platelets) and also increased susceptibility to platelet agonist (reactivity). Enhanced platelet activity and reactivity may be one mechanism that takes part in atherothrombotic intensification, leading to a higher risk of ischemic stroke. CD62P could be used as a risk-predictive biomarker in IS patients, so more strict antiplatelet protocols could be implemented and tailored individually.
Availability of data and materials
Datasets used and analyzed during the current study are not publicly available due to patients’ privacy policy, but are available from the corresponding author.
Abbreviations
- IS:
-
Ischemic stroke
- LTA:
-
Light transmission aggregometry
- MFI:
-
Mean fluorescent intensity
- ADP:
-
Adenosine 5 di-phosphate
- WBC:
-
White blood cells
- MPV:
-
Mean platelet volume
- PDW:
-
Platelet distribution width
- TG:
-
Triglycerides
- LDL:
-
Low-density lipoproteins
- HDL:
-
High-density lipoproteins
References
Tran J, Mirzaei M, Anderson L, Leeder SR. The epidemiology of stroke in the Middle East and North Africa. J Neurol Sci. 2010;295:38–40.
Depta JP, Bhatt DL. New approaches to inhibiting platelets and coagulation. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 2015;55:373–97.
Bray PF. Platelet Hyperreactivity: predictive and intrinsic properties. Hematol Oncol Clin North Am. 2007;21:633–vi.
Cha JK, Jeong MH, Jang JY, Bae HR, Lim YJ, Kim JS, et al. Serial measurement of surface expressions of CD63, P-selectin and CD40 ligand on platelets in atherosclerotic ischemic stroke. A possible role of CD40 ligand on platelets in atherosclerotic ischemic stroke. Cerebrovas Dis (Basel, Switzerland). 2003;16:376–82.
Lukasik M, Rozalski M, Luzak B, Michalak S, Kozubski W, Watala C. Platelet activation and reactivity in the convalescent phase of ischaemic stroke. Thromb Haemost. 2010;103:644–50.
Anyanwu CHM, Nath M, Li J, Barone FC, Rosenbaum DM, Zhou J. Platelets pleiotropic roles in ischemic stroke. Austin J Cerebrovasc Dis Stroke. 2016;3:1048.
Järemo P, Eriksson M, Lindahl T, Nilsson S, Milovanovic M. Platelets and acute cerebral infarction2012.
Pawelczyk M, Chmielewski H, Kaczorowska B, Przybyła M, Baj Z. Platelet reactivity in patients with stroke and hyperlipidemia, GPIbα assessment. Clin Appl Thromb/Hemost. 2016;22:166–70.
O’Donnell MJ, Xavier D, Liu L, Zhang H, Chin SL, Rao-Melacini P, et al. Risk factors for ischaemic and intracerebral haemorrhagic stroke in 22 countries (the INTERSTROKE study): a case-control study. Lancet. 2010;376:112–23.
Mayda-Domac F, Misirli H, Yilmaz M. Prognostic role of mean platelet volume and platelet count in ischemic and hemorrhagic stroke. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis. 2010;19:66–72.
McCabe DJ, Harrison P, Sidhu PS, Brown MM, Machin SJ. Circulating reticulated platelets in the early and late phases after ischaemic stroke and transient ischaemic attack. Br J Haematol. 2004;126:861–9.
Yip H-K, Chen S-S, Liu JS, Chang H-W, Kao Y-F, Lan M-Y, et al. Serial changes in platelet activation in patients after ischemic stroke: role of pharmacodynamic modulation. Stroke. 2004;35:1683–7.
Cevik O, Baykal AT, Sener A. Platelets proteomic profiles of acute ischemic stroke patients. PLoS ONE. 2016;11:e0158287.
Kalmarova K, Kurca E, Nosal V, Dluha J, Ballova J, Sokol J, et al. Measurement of platelet p-selectin expression by flow cytometry in patients with acute ischemic stroke. Acta Medica Martiniana. 2018;18:14–20.
Marquardt L, Anders C, Buggle F, Palm F, Hellstern P, Grau AJ. Leukocyte-platelet aggregates in acute and subacute ischemic stroke. Cerebrovasc Dis (Basel, Switzerland). 2009;28:276–82.
McCabe DJ, Harrison P, Mackie IJ, Sidhu PS, Purdy G, Lawrie AS, et al. Platelet degranulation and monocyte-platelet complex formation are increased in the acute and convalescent phases after ischaemic stroke or transient ischaemic attack. Br J Haematol. 2004;125:777–87.
Garlichs CD, Kozina S, Fateh-Moghadam S, Handschu R, Tomandl B, Stumpf C, et al. Upregulation of CD40-CD40 ligand (CD154) in patients with acute cerebral ischemia. Stroke. 2003;34:1412–8.
Htun P, Fateh-Moghadam S, Tomandl B, Handschu R, Klinger K, Stellos K, et al. Course of platelet activation and platelet–leukocyte interaction in cerebrovascular ischemia. Stroke. 2006;37:2283–7.
Marquardt L, Ruf A, Mansmann U, Winter R, Schuler M, Buggle F, et al. Course of platelet activation markers after ischemic stroke. Stroke. 2002;33:2570–4.
Tsai NW, Chang WN, Shaw CF, Jan CR, Chang HW, Huang CR, et al. Levels and value of platelet activation markers in different subtypes of acute non-cardio-embolic ischemic stroke. Thromb Res. 2009;124:213–8.
Ilhan D, Özbabalik D, Gulcan E, Özdemir Ö, Gülbaçs Z. Evaluation of platelet activation, coagulation, and fibrinolytic activation in patients with symptomatic lacunar stroke. Neurologist. 2010;16:188–91.
Halawani SHWD, Webster J, Greaves M, Ford I. Aspirin failure in patients presenting with acute cerebrovascular ischaemia. Thromb Haemost. 2011;106:240–7.
Sabra A, Stanford SN, Storton S, Lawrence M, D’Silva L, Morris RHK, et al. Assessment of platelet function in patients with stroke using multiple electrode platelet aggregometry: a prospective observational study. BMC Neurol. 2016;16:254.
Yamazaki M, Uchiyama S, Iwata M. Measurement of platelet fibrinogen binding and p-selectin expression by flow cytometry in patients with cerebral infarction. Thromb Res. 2001;104:197–205.
Singh N, Gemmell CH, Daly PA, Yeo EL. Elevated platelet-derived microparticle levels during unstable angina. Can J Cardiol. 1995;11:1015–21.
Schmalbach B, Stepanow O, Jochens A, Riedel C, Deuschl G, Kuhlenbaumer G. Determinants of platelet-leukocyte aggregation and platelet activation in stroke. Cerebrovasc Dis (Basel, Switzerland). 2015;39:176–80.
Serebruany VL, Malinin AI, Oshrine BR, Sane DC, Takserman A, Atar D, et al. Lack of uniform platelet activation in patients after ischemic stroke and choice of antiplatelet therapy. Thromb Res. 2004;113:197–204.
Brass LF. Thrombin and platelet activation. Chest. 2003;124:18s–25s.
Offermanns S. Activation of platelet function through G protein-coupled receptors. Circ Res. 2006;99:1293–304.
Acknowledgements
My great appreciation to all patients and individuals participated in the study; nothing could have been accomplished without their participation. I would like to thank my professors, staff and colleagues in Clinical Pathology, Neurology and genetic departments for their encouragement and advice.
Funding
I certify that all financial and material support for this research was supplied by the corresponding author and work is clearly identified in the title page of the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualization: ASab, ASAh, AH, AM, MAS. Methodology: ASab, ASAh, AH, AM, HN. Investigation: HN, AM. Data curation and statistical contribution: HN, MAS. Writing—original draft: HN. Writing—review and editing: ASab, ASAh, AH, AM. Funding acquisition: HN. Resources: HN, AM. Supervision: ASab, ASAh, AH, AM. All authors have read and approved the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval and consent to participate
The study was approved by the Ethics Committee of the Suez Canal University, Faculty of Medicine and was carried out in concordance with Declaration of Helsinki. Human rights statements and informed consent: All procedures followed were in accordance with the ethical standards of the responsible committee on human research (institutional and national) and with the Helsinki Declaration of 1964 and its later amendments. Informed consent was obtained from all patients for being included in the study. Research Ethics Committee, Faculty of Medicine, Suez Canal University. The proposal was reviewed by full board Committee at its meeting on: 15/6/2016. Research 2815#. An informed written consent was taken from all participants before enrollment. All patients received full explanation regarding study aim, objective as well as platelet tests, and all consented to participate.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no financial and non-financial competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
About this article
Cite this article
Nashaat, HA.H., Abdelhamid, A.ED.S., Ahmed, A.S. et al. Evaluation of platelets activity and reactivity as risk factors for acute ischemic non-embolic stroke in young adults. Egypt J Neurol Psychiatry Neurosurg 57, 133 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1186/s41983-021-00373-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s41983-021-00373-6