Abstract
Background
Two Trichogramma spp., Trichogramma evanescens Westwood and Trichogrammatoidea bactrae Nagaraja (Hymenoptera: Trichogrammatidae), were studied to control one of the most cereal pests attacking various grains, Sitotroga cerealella (Olivier) (Gelechiidae: Lepidoptera). Experiments were carried out to evaluate S. cerealella egg-ages, parasitoids’ emergence time and cold storage host eggs on rearing the two tested parasitoids’ spp.
Results
The age of S. cerealella eggs had significantly influenced the parasitization and adult emergence rates of the two parasitoid species. Parasitism rate resulted from old host eggs (32 h old) (44.93%) decreased than those of the fresh ones (2 h old) (95.85%). Emergence rate ranged between (62.64–97.85%) for T. evanescens and (62.90–95.54%) for T. bactrae from different S. cerealella egg-ages (0–32 h). Regardless to late emerged parasitoids, their population affected. T. evanescens parasitized rate ranged (73.79–95.06%), which comparatively lower than those of T. bactrae (88.81–96.90%), at parasitoid emerging times (0–64 h), respectively. Emergence times had significantly differences in the emergence rate of T. evanescens and/or T. bactrae. On the other hand, percentage of parasitism of the non-stored S. cerealella eggs was higher than the other cold-stored ones. The emergence rate of adult parasitoids, T. evanescens (66.00–91.16%) and T. bactrae (71.16–94.11%), was decreased at the cold storage durations (5–40 days) increased. In comparison to the tested biological aspects between the two parasitoid species, non-significant differences were recorded, at the three assessment parameters, which include host egg-ages, parasitoid emergence time and cold-stored eggs. Meanwhile, there were significant differences between F1 emerged rates for T. evanescens and T. bactrae obtained at each of the three tested parameters.
Conclusion
It was concluded that low emergence time of the parasitoids, T. evanescens and T. bactrae, was relatively more effective when they parasitized the fresh egg-age and less cold storage periods of S. cerealella.
Similar content being viewed by others
Background
Angoumois grain moth, Sitotroga cerealella (Olivier) (Gelechiidae: Lepidoptera), is one of the most cereal pests that attacks various grains such as wheat, corn, barley and rice (Salim et al. 2023). The larvae as a destructive stage cause infestation and damage to field crops and an additional damage to grains after harvest (Kumar et al. 2022). Jena et al. (2023) indicated that infested seeds are usually unable to germinate where significant quantitative and qualitative economic losses, decrease in the weight and nutritional value of the grains were estimated. S. cerealella causes an internal infestation of grains, so it is difficult to be controlled with usual chemical pesticides, adding to the risks of uses pesticides.
Biological control, especially parasitoids, is considered one of the most successful controlling methods against stored grain pests (Tripathi 2018). Genus Trichogramma (Hymenoptera: Trichogrammatidae) as a biological control agent presented natural enemies for many of the stored grain moths (Flinn and Schöller 2012). Trichogrammatoidea bactrae Nagaraja and Trichogramma evanescens Westwood are common egg parasitoid species, which is extremely important in controlling cereal pests to prevent the damage from entering larvae into grains.
Certain biological aspects affect the effectiveness and ability of the Trichogramma parasitoids to parasitize. The host age is one of the most factors affected parasitism and parasitoid’s ability to parasitize. Parasitoids showed a strong preference for young host eggs compared to older ones (Perveen et al. 2012). Developmental period of female parasitoids increases without the presence of a host and minimizes the ability to parasitize (Ksentini et al. 2018).
The objective of the present study was to evaluate different biological aspects on rearing of two tested parasitoid species, T. evanescens and T. bactrae: as the effect of host egg-ages, the old of parasitoids’ emergence and the cold storage of S. cerealella eggs.
Methods
Rearing of Sitotroga cerealella
The mass rearing of S. cerealella was under controlled temperature of 28 ± 1ºC and 65 ± 5% RH. Wheat grains boil and then spread to left them dry. Dried wheat grains were placed into wire trays (6kg wheat grains /tray). The wheat grains were infested with S. cerealella eggs by homogenously sprinkled on trays (1 g eggs/1 kg wheat grains) placed in horizontal positions. After 10 days later, wire trays were placed vertically in cages, and then, after 25–30 days, S. cerealella moths started to emerge and falling in plastic jars fitted under each cage. Daily, moths were collected into wire cylinders and new plastic jars replaced daily. Wire cylinders filled with moths were replaced in a device till the moth’s eggs extracted to use fresh or stored ones at 8ºC.
Rearing of Trichogramma spp. parasitoids
Two parasitoid species, T. evanescens and T. bactrae, were used. T. bactrae was imported from an American University, by Dr. A. H. El Heneidy (Plant Protection Research Institute, ARC) and adapted under Egyptian natural conditions. The mass rearing of the 2 Trichogramma spp. was prepared by gluing S. cerealella eggs < 24 h old on hard paper cards (9 × 13cm), and then, the host egg cards were introduced into plastic jars for exposing newly emerged (< 24 h) to Trichogramma adults. Afterward, the parasitized egg cards were removed and other fresh ones were replaced. The jars were maintained at 27ºC.
Experiments
Effect of host egg-ages on the rearing of two parasitoid spp. T. evanescens and T. bactrae
Five different ages of S. cerealella eggs (0, 2, 4, 8, 16 and 32 h.) were studied. Each age of host eggs was glued on cards, introduced individually into 250 ml plastic jars, each containing male/female pairs of freshly emerged parasitoid adults (< 24 h.). Jars were covered with cloth-wrapped cotton. Experiments were repeated in 4 replicates for each age. The total number of parasitized and emergence of the parasitoid species was recorded and their percentages calculated. Also, the parasitoids’ developmental periods at each age of host eggs were studied.
Effect of parasitoids’ emerging time on Trichogramma spp. parasitism
The experiment was carried out at 27 ± 1ºC and 60 ± 5 RH. Hard paper cards (1 × 1cm), contained glued S. cerealella eggs (< 24 h. old), were exposed to each of the parasitoid adults of T. evanescens and T. bactrae and then waited until the hatching of the newly emerged parasitoids. Paper cards with different ages of parasitoids’ adults (0, 4, 8, 16, 32 and 64 h.) were transferred, each to a new plastic jar. Each emergence time was repeated in 4 replicates. Parasitism rate and emerging rate were calculated.
Effect of cold storage S. cerealella eggs on Trichogramma spp. parasitism
Eggs of S. cerealella were incubated at 8 °C to 5, 10, 20 and 40 days. Eggs (> 24 h.) were used as control. Cold-stored eggs, at each period of storage and those of control, were placed on square paper card covered with a thin layer of glue and then tested by exposing them separately to each of the two Trichogramma parasitoids at 27 ± 1ºC and 60 ± 5 RH. Four replicates were carried out per test. Parasitized eggs were incubated at 27 ± 1ºC and 60 ± 5 RH. The number of parasitized eggs (blackened host eggs) was recorded in each treatment. Percentage of emerged adults was calculated: Number of emerged adults/N number of parasitized eggs × 100.
F1 progeny of T. evanescens and T. bactrae
F1 progeny of T. evanescens and T. bactrae was obtained from the previous 3 experiments as the same way of each one was studied. Parasitoid adults exposed to a paper card (1 × 1 cm) with S. cerealella eggs (> 24 h.) into a plastic jar and waited until the newly emerged adults of parasitoid species. Four replicates were carried out per test for experiment. The number of emerged adults was recorded and the correspondence percentage calculated.
Statistical analysis
Based on the data of percentage of parasitism, an emergence for each parasitoid sp. was analyzed using of one-way ANOVA and means were compared using Duncan test. The LSD test compared between percentage of significant results was used at P < 0.05. T test analysis of variance was used to analyze the biological aspects’ data between the two parasitoid spp. (at P < 0.05).
Results
Effect of host egg-ages on the cultures of the two parasitoid spp., T. evanescens and T. bactrae
Rate of parasitized eggs (RP)
Parasitization was recorded for blackened eggs due to the deposition of black stain in their inner surface. The age of S. cerealella influenced the parasitization rate of the two parasitoid spp. Parasitization of newly collected host eggs (> 24 h.) (control) was significantly higher than any of the other egg-ages. Parasitism rate of old host eggs (32 h old) (44.93%) decreased than those of fresh ones (2 h old) (95.85%) (F = 29.7426, P > 0.0001, df = 5, LSD5% = 10.5703) (F = 14.9537, P > 0.0001, df = 5, LSD5% = 13.8463) after exposing to T. evanescens and T. bactrae, respectively. This expected that old host eggs were less preferable for parasitoids to complete their development (Table 1).
Rate of emerged adults (RE)
Out of parasitized eggs, the number of emerged parasitoid adults was counted and their percentages were determined. Parasitoid emergence rate ranged between (62.64–97.85%) for T. evanescens and (62.90–97.13%) for T. bactrae as a result of different S. cerealella egg-age (0–32 h.). This rate was varied significantly (F = 46.2514, P < 0.0001, df = 5, LSD5% = 5.9554) and (F = 12.1956, P > 0.0001, df = 5, LSD5% = 10.9192) for the two parasitoid spp. (T. evanescens and T. bactrae, respectively), obtained from different host egg-ages (Table 1).
Developmental periods of parasitoid adults (DP)
Total developmental period was counted from parasitoids exposed to host eggs till their emergence. Developmental time of parasitoids was non-significantly varied between hot egg-ages, but longer in older eggs than in younger ones. The developmental period of T. evanescens and T. bactrae was ranged between (7.25 ± 0.25–7.50 ± 0.29 days) and (8.50 ± 0.25–8.75 ± 0.29 days), respectively, for tested host egg-ages (0–32 h) at 27 ± 1ºC (Table 1).
Effect of parasitoids’ emerging time on Trichogramma spp. parasitism
Rate of parasitized eggs (RP)
S. cerealella eggs parasitized by T. evanescens with a parasitism rate ranged (73.79–95.06%), which was comparatively lower than those by T. bactrae (88.81–96.90%), for parasitoid emerging time (0–64 h.), respectively (Table 2). There were significant differences between parasitism percentage at the tested emergence time of T. evanescens (F = 7.1902, P > 0.0007, df = 5 LSD5% = 8.1697) or for T. bactrae (F = 4.4252, P > 0.0084, df = 5 LSD5% = 4.2342).
Rate of parasitized eggs (RP)
Emergence time (4–64 h.) had significant differences on the rate of emerged parasitoids. The emergence rate was gradually decreased as the emergence time increased. The highest emergence rate was obtained at 4 h. of emerged T. bactrae (90.92%) as compared to (88.45%) of T. evanescens at the same emerged time. It decreased to make the lowest rates 70.00 and 72.94% for T. evanescens and T. bactrae, respectively, at 64 h. of emergence (Table 2).
Developmental periods (DP)
T. evanescens lived about (7.25–8.50 days) for parasitoid emerging times (0–64 h.); however T. bactrae reared (8.50–8.75days) for the same tested parasitoid emerging times at 27 ± 1 ºC (Table 2). Non-significant differences of parasitoids lifespan were found among times’ emergences.
Effect of cold storage S. cerealella eggs on Trichogramma spp. parasitism
Rate of parasitized eggs (RP)
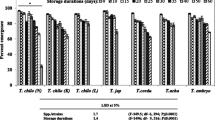
Percentage parasitism of the non-stored S. cerealella eggs was higher than the other cold-stored ones. Parasitization rate was significantly decreased with increasing the period of host-stored eggs. T. evanescens adults caused the highest parasitization rate (93.84%) from the non-cold-stored eggs (0 day). The egg cold storage periods (5, 10, 20 and 40 days) resulted parasitization rates of T. evanescens (87.78, 87.50, 79.71 and 61.41%), respectively. In the control, percentage parasitism of T. bactrae attained 97.08%, but it was 91.69, 89.64, 81.57 and 65.48% for the same storage periods, respectively (Table 3).
Rate of parasitized eggs (RP)
Emergence percentage of each of the 2 tested parasitoids’ adults varied significantly among the cold storage periods than those of non-stored host eggs (control). The emergence rate of T. evanescens adults ranged between (66.00–91.16%) in the cold storage durations of (5–40 days), respectively. Compared to the non-cold-stored eggs (97.07%), T. bactrae emergence rate decreased to 94.11, 89.03, 80.09 and 71.16% in cold-stored eggs 5, 10, 20 and 40 days, respectively (Table 3).
Developmental periods (DP)
Periods of T. evanescens development ranged between (7.25–8.25 days) for (0–40 days) host storage eggs, while for T. bactrae, those periods were 9.25, 9.25, 9.75, 9.25 and 9.25% for egg stored to 0, 5, 10, 20 and 40 days, respectively, at 27± 1ºC (Table 3). Results indicated that the developmental periods of both parasitoid species had non-significant differences in tested cold-stored eggs (Table 3).
Statistically, each of the biological aspects, non-significant difference was obtained between the 2 parasitoids, T. evanescens and T. bactrae, for the three tested parameters (host egg-ages, parasitoids’ emerging time, cold host storage) (Table 4).
Effect of host egg-ages, parasitoids’ emerging time, cold host storage on T. evanescens and T. bactrae emergence percentage of F1 progeny
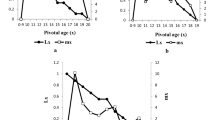
Figure 1 shows that 0 h.-old eggs of the host S. cerealella were the most age caused emergence of F1 progeny for T. evanescens (80.65%) and T. bactrae (87.66%). The emergence rate was decreased gradually by increasing the host egg-ages (2, 4, 8, 16 and 32 h.). It was (78.26, 70.88, 66.12, 54.49 and 41.97%) for T. evanescens and (81.41, 71.76, 68.58, 59.51 and 48.33%) for T. bactrae, at the same host egg-ages, respectively. There were significant differences among the emergence rate resulted from different host egg-ages (F = 8.91347, P > 0.0002, df = 5, LSD5% = 14.8376) for T. evanescens and (F = 4.3405, P > 0.0091, df = 5, LSD5% = 20.4244) for T. bactrae.
Percentage of F1 progeny emerging was an indicator for the suitable emerged parasitoids’ time. Rates differed according to the tested emerged parasitoids’ times (0, 4, 8, 16, 32 and 64 h.) for T. evanescens (91.10, 90.79, 80.97, 72.36, 72.36, 49.50 and 18.29%, respectively) and T. bactrae (93.04, 85.29, 86.35, 77.77, 54.98 and 21.58%, respectively). Results observed that the shortest emergence time was more suitable for rearing both parasitoids’ species (Fig. 2). Emergence rate differed significantly for T. evanescens (F = 39.7754, P > 0.0001, df = 5, LSD5% = 13.9057) or T. bactrae (F = 27.0475, P > 0.0001, df = 5, LSD5% = 16.0351) between the tested emerged times.
Figure 3 shows the emergence rate of T. bactrae in F1 progeny. It was more than T. evanescens along the cold storage durations at 8°C. Comparing to the non-stored S. cerealella eggs, the emergence rate of F1 progeny declined (89.67, 81.42, 75.19, 62.01 and 45.06%) for T. evanescens and (91.71, 88.80, 79.43, 67.13 and 51.83%) T. bactrae as the cold-stored host eggs increased (0, 5, 10, 20 and 40 days), respectively. F1 emergence rate had significant differences at cold host-stored S. cerealella eggs (F = 12.3237, P > 0.0001, df = 4, LSD5% = 15.0423) and (F = 10.50375, P > 0.0003, df = 4, LSD5% = 15.3141) of T. evanescens and T. bactrae, respectively.
Discussion
The host age is one of the most important factors affected parasitism and parasitoid’s efficiency to parasitize. Trichogramma spp. parasitized and emerged from all S. cerealella egg-ages, but they were decreased significantly when the oldest host eggs were utilized. Developmental time of parasitoids was non-significantly varied between hot egg-ages, but longer in older eggs than in younger ones. This finding was in agreement with Atashi et al. (2021) when Trichogramma euproctidis (Girault) developed faster in small old eggs rather than the old ones. Also, the youngest host eggs were used than the oldest ones to ensure the persistence of parasitoid mass production. Godin and Boivin (2000) mentioned that Trichogramma spp. were unable to complete their development in the oldest eggs. The number of parasitized eggs (9.60 eggs) was the highest for host aged 24 h followed by those of 48 h (1.00 egg), while no parasitism occurred for 72 h host egg-age (de Queiroz et al. 2020). At 25°C, T. euproctidis parasitized one-day-old eggs of Ephestia kuehniella Zeller (Lepidoptera: Pyralidae) were developed through 8.9 days (Hansen and Jensen 2002) and 9.8 days (Tabebordbar et al. 2020). El-Mandarawy and Rizk (2002) found that parasitization percentage between the two studded parasitoids was significantly differed. Additionally, a disagreement with the present study was recorded where parasitization and fecundity were higher in T. evanescens than T. bactrae reared from two stored pests, Callosobruchus maculatus (Fabricius) (Coleoptera: Chrysomelidae) and Corcyra cephalonica (Stainton) (Lepidoptera: Pyralidae).
Parasitism and emergence rate was gradually decreased as the emergence time of the two tested parasitoid species increased. The rate of S. cerealella parasitized eggs decreased significantly with increasing parasitoids’ age. The rate of parasitism reached its peak in control and decline at the parasitoid ages of 8 and 16 h, and then, it began to decrease until reached the lowest rate at the age of 64 h. These results agree with Taha et al. (2022) who recorded a significant decrease in T. evanescens emergence percentages among parasitoid emerging times. Shawer et al. (2021) found that the emergence rate of T. evanescens was generally hosted egg-ages-dependent.
Parasitism rate was high in non-stored host eggs (control) compared to the cold host-stored eggs at different tested periods. Cold-stored eggs were affected significantly by the parasitism and emergence rate of Trichogramma spp. Results were in agreement with Rodrigues and Sampaio (2011) who observed that cold storage period at 8–10 °C had nonnegative effect. Lessard and Boivin (2013) observed negative effects on F1 progeny, where the period of cold storage host eggs increased the F1 emergence rate decreased. Age-dependent storage egg kept at either 4 or 9 °C was significantly influenced the parasitism percentages of Plodia interpunctella (Hübner) eggs by T. evanescens (Haque et al. 2021).
Percentage of F1 progeny emerging was an indicator for the suitable emerged parasitoids’ time. Aging of host eggs at the parasitism appears to affect emergence of progeny F1 where negative relationship between emerging time and the emerging percentages of F1 was recorded (Shawer et al. 2021). Emergence of progeny F1 of both the two parasitoids varied significantly according to the emergence time (Taha et al. 2022).
Conclusion
It was concluded that the egg-ages of S. cerealella influenced the parasitization and emergence rate of two Trichogramma parasitoid spp. The least parasitoid emergence time was more suitable for rearing both of the two parasitoid spp., T. evanescens and T. bactrae. Data revealed that S. cerealella eggs cold stored at 5 and 10 days at 8°C are more suitable for the rate productivity of Trichogramma spp. Developmental time of parasitoids was longer in older eggs than in younger ones. Under laboratory conditions, T. bactrae was less affected by the tested parameters than T. evanescens.
Availability of data and materials
All data and materials are available.
Abbreviations
- RP:
-
Rate of parasitized eggs
- RE:
-
Rate of emerged adults
- DP:
-
Developmental periods of parasitoid adults
References
Atashi N, Shishehbor P, Seraj AA, Rasekh A, Hemmati SA, Riddick EW (2021) Effects of Helicoverpa armigera egg age on development, reproduction, and life table parameters of Trichogramma euproctidis. InSects 12(7):569
El-Mandarawy M, Salwa RA (2002) Comparative study between Trichogramma evanescens Westwood and Trichogrammatoidea bactrae Nagaraja as biological control agents against two irradiated and non-irradiated stored product pests. Pak J Biol Sci 5(5):563–565
Flinn PW, Schöller M (2012) Biological control: Insect pathogens, parasitoids, and predators. In: Hagstrum DW, Phillips TW, Cuperus G (eds) Stored Product Protection. Kansas State University, Manhattan, KS, pp 203–212
Godin C, Boivin G (2000) Effect of host age on parasitism and progeny allocation in Trichogrammatidae. Entomol Exp Appl 97:149–160
Hansen LS, Jensen KMV (2002) Effect of temperature on parasitism and host-feeding of Trichogramma turkestanica (Hymenoptera: Trichogrammatidae) on Ephestia kuehniella (Lepidoptera: Pyralidae). J Econ Entomol 95:50–56
Haque A, Islam S, Bari A, Hossain A, Athanassiou CG, Hasan M (2021) Cold storage-mediated rearing of Trichogramma evanescens Westwood on eggs of Plodia interpunctella (Hübner) and Galleria mellonella L. PLoS ONE 16(6):e0253287
Jena MK, Moharana RL, Gosavi S, Sahoo S (2023) Biology of Sitotroga cerealella (Olivier) (Lepidoptera: Gelechiidae) on stored wheat, Triticum aestivum L. Pharma Innov J 12(04):749–754
Ksentini I, Jardak T, Zeghal N (2018) Parasitoid age and host quality side effects on the parasitization behavior of Trichogramma oleae and Trichogramma cacoeciae (Hymenoptera: Trichogrammatidae). J Entomol Zool Stud 6(2):2004–2009
Kumar A, Yadav SS, Jat MK (2022) Approaches in pest management of stored grain pests Abiotic and biotic stress management in plants. Crc Press, London, pp 179–186
Lessard E, Boivin G (2013) Effect of low temperature on emergence, fecundity, longevity and host-feeding by Trichogramma brassicae. Biocontrol 58:319–329
Perveen F, Sultan R, Ul-Haque E (2012) Role of temperature and hosts (Sitotrogacerealella and Corcyra cephalonica) egg age on the quality production of Trichogramma chilonis. Arthropods 1(4):144
de Queiroz AP, Costa CO, Favetti BM, Silva GV, Bueno ADF (2020) Effects of parasitoid and host age on the parasitism of Trichogramma pretiosum on eggs of Anticarsia gemmatalis. Revista Brasileira De Entomologia 64(2):2–5
Rodrigues SMM, Sampaio MV (2011) Cold storage of Trichogramma pretiosum Riley (Hymenoptera: Trichogrammatidae). Biol Sci 78:45–51
Salim M, Ullah I, Saljoqi AR, Gökçe A, Ahmad S, Almutairi MH, Amany A, Sayed AL, Abdel-Daim MM, Kumar MS (2023) Life table study of Sitotroga cerealella on different cereals and its implications on the performance of the egg parasitoid (Trichogramma chilonis) under laboratory conditions. Sci Rep 13(1):1–13
Shawer MB, Sharshir FA, Taha EK, Shenishen EZ, Hassan MM, Elshazly H, Elnabawy ES (2021) The impact of cold storage durations on Trichogramma evanescens (Westwood) (Hymenoptera: Trichogrammatidae) during their pupal stage. Saudi J Biol Sci 28(12):7202–7206
Tabebordbar F, Shishehbor P, Ebrahimi E (2020) Suitability of different egg ages of Ephestia kuehniella (Lep.: Pyralidae) for the development, reproduction and life table parameters of Trichogramma evanescens (Hym.: Trichogrammatidae). J Crop Protect 9:89–99
Taha EK, Shawer MB, Sharshir FA, Shenishen EZ, Hassan MM, Elshazly H, Elnabawy ES (2022) Effect of emergence time on some biological aspects of Trichogramma evanescens (Westwood) (Hymenoptera: Trichogrammatidae). J King Saud Univ Sci 34(4):101981
Tripathi AK (2018) Pests of stored grains. Pests Manag. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-10-8687-8_10
Funding
Funding is by the authors.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Esraa M. Abdel Halim was involved in writing, El-Mandarawy M. R contributed to methodology, formal analysis, investigation and writing, Ahmed S.S. was involved in visualization and reviewing, and Magda contributed to visualization. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
About this article
Cite this article
Abdel Halim, E.M., El-Mandarawy, M.R., Naroz, M.H. et al. Studies of certain parameters affecting two parasitoid species, Trichogramma evanescens Westwood and Trichogrammatoidea bactrae Nagaraja (Hymenoptera: Trichogrammatidae), on egg host, Sitotroga cerealella (Olivier) (Gelechiidae: Lepidoptera). Egypt J Biol Pest Control 34, 35 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1186/s41938-024-00797-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s41938-024-00797-1