Abstract
A general growth is being seen in the use of renewable energy resources, and photovoltaic cells are becoming increasingly popular for converting green renewable solar energy into electricity. Since the voltage produced by photovoltaic cells is DC, an inverter is required to connect them to the grid with or without transformers. Transformerless inverters are often used for their low cost and low power loss, and light weight. However, these inverters suffer from leakage current in the system, a challenge that needs to be addressed. In this paper, a topology with two alternative connection models is presented to stabilize the common mode voltage and reduce the leakage current. The output voltage characteristic of the proposed inverter is five-level, which reduces the harmonic distortion in the output current compared to the two- and three-level inverters. The operation modes and output of the proposed topology are described and analyzed. The structures of the proposed inverter are simulated in MATLAB/Simulink and are compared with some well-known structures. Results show that the proposed structure with both connection models effectively reduces leakage current and improves grid current THD.
Similar content being viewed by others
1 Introduction
Solar energy is one of the fastest growing sources of energy. There have been significant growth trends in both developing and using photovoltaic (PV) systems for harnessing green energy from the sun over the last few decades. Unlike fossil fuels, renewable sources of energy such as solar do not pollute the environment during their production and consumption [1].
In PV systems, voltage source inverters installed between the PV cells and the grid are required to connect the outputs to the electrical grid [2, 3]. These inverters can be connected to the grid with or without a transformer.
In recent years, grid-connected transformerless inverters have been widely used because of their higher efficiency and lower cost and weight when compared to systems with a transformer [4,5,6]. However, the problem with the transformerless inverters is the galvanic connection of the solar panels to the ground. This can cause leakage current [7]. Despite the generally acceptable efficiency of new inverters, issues such as grounding cells are still required to be addressed as they are essential in reducing leakage current. In transformerless inverters, the ground of the cells is not isolated from the ground of the grid and thus a parasitic capacitor exists between the cells and the ground. The presence of this capacitor introduces a leakage current in the system. This can flow through a human body and pose serious risks if exceeding a specific value. Also, the leakage current can cause efficiency reduction, harmonic injection, and increased total harmonic distortion (THD) in the grid current [8]. Figure 1 shows an overview of the PV system, including the inverter, output inductor and grid.
Many topologies have been proposed in the literature to reduce leakage current. The most prominent topologies are the full-bridge structure with bipolar switching method, H5 structure [9], H6 [10, 11], and HERIC [12] etc. A full-bridge structure with bipolar switching method has a fixed common mode voltage and therefore results in very low leakage current. However, because of the two-level output voltage, large output filters are required and this increases losses. The advantages of a full-bridge inverter with a unipolar switching method include excellent differential characteristic, low inductance current ripple, and higher efficiency. However, the drawbacks are the unsuitable common mode characteristics and very high leakage current [13].
Another approach is to disconnect the AC side from the DC side in the freewheeling modes. The structure proposed in [14] uses a connection between the negative terminal of the solar cell and the neutral point of the grid to reduce the leakage current. The input voltage of this structure is the same as that of the full-bridge structure, though in spite of ease of operation, this structure requires more devices. Also, in this structure, one of the output inductors is taken out and only one inductor is used. For this reason, H5, H6, and HERIC structures were designed based on the full-bridge structure and unipolar modulation. In this type of inverter, the weight and cost of the filters are higher because the cores of the filter inductors must be separated.
Many structures have been developed based on these topologies. For instance, a group of inverters based on the HERIC topology are designed by connecting the middle point of the two capacitors on the input side to the inverter output. This allows them to keep the common mode voltage constant in the freewheeling mode that further reduces leakage current [15,16,17,18]. In [19], a structure with six switches and two diodes is proposed, in which two additional switches are placed between the legs of the full-bridge structure. The inverter output is a short circuit in the freewheeling mode which prevents large fluctuations in the common mode voltage resulting in reduced leakage current. In another study, a HERIC-based cascade structure is introduced in [20] with a 9-level inverter connecting several PV cells. This topology, in addition to being multilevel, is able to reduce leakage current by separating the grid from PV cells in freewheeling mode. However, the large numbers of switches used in this structure increase the costs. Also, the additional switches in the current path during operation increase the conduction losses. In [21], a 5-level inverter is proposed consisting of six switches, two capacitors, and one diode. Only one inductor is used in the output of this inverter while its switching is controlled using Space Vector (SV) modulation. Furthermore, a transformerless five-level inverter is designed in [22] with a grid-tied single-phase PV system to reduce leakage current. The neutral of the grid links to a common node in which the negative and positive terminals of the DC-link are connected via parasitic capacitors to eliminate the leakage current. In this structure, eight switches and six diodes are used. This increases losses, while it also requires a high DC voltage level at the input. Another new structure of a single-phase transformerless grid connected multilevel inverter is presented in [23] based on a switched-capacitor structure. In this structure, the series–parallel switching conversion of the integrated switched-capacitor module is employed in a packed unit. In [24] a new topology of the switched-capacitor multilevel inverter (SCMLI) is proposed for PV systems, one which can eliminate the leakage current. Nevertheless, this structure uses more capacitors than similar structures and is less efficient than many other competing structures. The transformerless PV inverter proposed in [25] uses a cascaded 5-level H-bridge (CHB), which can also be developed into higher levels. However, leakage current circulation between PV panels in each 5-level block is a disadvantage. Finally, a single-phase three-level split-inductor neutral point clamped inverter is developed in [26] for transformerless PV application. However, the inverter also requires a high DC voltage at the input.
This paper presents a high-efficiency 5-level inverter with two structures capable of reducing leakage current. These structures reduce common-mode voltage oscillation and leakage current by connecting the inverter outputs to the midpoint of the DC bus in the freewheeling mode. In addition, the structures are designed so that the inverter output voltage is five-level leading to improved quality in the output current and reduced total harmonic distortion in the inverter output. The performance of the proposed topology is evaluated through comparisons with the HERIC topology [15,16,17,18] and the MOSFET neutral-point-clamped (M-NPC) structure presented in [16]. The study shows the advantages of the proposed inverter in terms of common mode voltage stabilization, leakage current reduction, multilevel output in the inverter, and improved THD, as well as a higher efficiency than other topologies proposed in the literature.
After reviewing the literature extensively in Sect. 1, the concept of leakage current in a HERIC inverter is described in Sect. 2. The proposed topology is presented and described with two connection models in Sect. 3. Section 4 presents the simulation results, and Sect. 5 concludes the paper.
2 Leakage current in inverters
In transformerless inverters, leakage current flows through the parasitic capacitor (between the ground and the PV panel (CPV)), the output inductors (L1, L2), and the ground impedance (ZG) as shown in Fig. 2. The detailed model of the corresponding common-mode noise is shown in Fig. 2a, while the simplified model is shown in Fig. 2b irrespective of ZG. The value of the parasitic capacitor depends on many factors such as the surface of the solar array, weather conditions, the distance of the plate from the ground, humidity, and dust [27], and is often considered to be between 50 and 150 nF/kW [8]. A full-bridge inverter has a relatively high leakage current with unipolar switching. Therefore, the AC separation method is recommended to avoid increasing the common mode voltage by creating a freewheeling path between AC and DC. Here, freewheeling is when the inverter output is short circuited. Figure 3 shows one of the most common AC separation structures, namely, the HERIC inverter. This topology is usually used to test leakage current behavior.
The HERIC topology [12]
According to the definitions in [28], the equivalent common-mode voltage VECM, differential and common mode voltages as well as leakage currents are calculated as:
where VAN and VBN are the respective potential differences between points A and B relative to the negative terminal of the PV array (point N in Fig. 3). If the values of L1 and L2 are equal, the second part of (1) is eliminated.
As noted from (4), the leakage current depends on the changes in the common mode voltage. In order to control the common mode voltage in the freewheeling mode in the HERIC inverter, two switches (S5 and S6) are placed on the AC side. This is achieved by turning on S5 and the diode parallel to S6 in the positive half cycle, and by turning on S6 and the diode parallel to S5 in the negative half cycle. The other switches are OFF in the freewheeling mode.
In the present study, in addition to the HERIC structure, other proposed structures [16, 23, 25] are considered for comparison. The structure of the MOSFET neutral-point-clamped (M-NPC) inverter [16] is shown in Fig. 4a. This consists of seven switches and four diodes. It also has two operations in freewheeling mode. In the positive freewheeling cycle, D1, D2, S2, and S5 are ON, while D1, D3, D4, and S7 are ON in the negative freewheeling cycle. This structure is not symmetrical in the positive and negative cycles of the conduction modes since in the positive cycle, S1, S2, S5, and S6 are ON, whereas in the negative cycle only S3 and S4 are ON.
The structure of [23] is shown in Fig. 4b, which consists of six switches, two diodes and capacitors. It has six operation modes that generate a five-level output voltage. The structure of [25] provides a multilevel cascaded H-bridge inverter, which can also be generalized to higher levels. Its five-level structure consisting of eight switches is shown in Fig. 4c.
3 The proposed topology
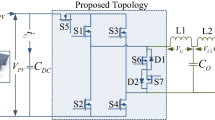
Here, a new five-level topology which contains 11 switches is proposed. This has the ability to reduce leakage current. This topology is presented in two structures. The main difference between them is the way the inverters are connected to the PV panels. The different connections provide choices in connecting the inverter to the solar panels based on the existing panels, with each connection option offering unique features. In the first structure, the THD of the output current is lower than the second, while the second structure has lower leakage current of each panel (not the grid leakage current) than the first structure. This increases the safety of using the panels.
3.1 The topology with the first structure
The first structure is illustrated in Fig. 5. The voltage level of PV1 is twice that of PV2 (VPV1 = 2VPV2). Using capacitors parallel to the panels (Cdc), a voltage division is performed and different voltage levels relative to point N at the input side are obtained. Among different PWM methods, SPWM is mostly used for multilevel inverters, because of simple implementation with good performance. In this paper, a type of level-shifted carrier PWM (LSC-PWM) method is selected which includes two high frequency carriers that have the same phase, amplitude and frequency.
According to this method, the amplitude of the carriers is 1/(Number of carriers), which in this paper is equal to 0.5 with 2 carriers. The switching of this method is based on the comparison of two high frequency triangular waves with a grid frequency modulation wave as shown in Figs. 6 and 7. The frequency of the carrier waves is 16 kHz.
The control rules are defined as follows:
The proposed inverter is comprised of five operation modes, two of which are in the positive cycle (Modes 1 and 2), two are in the negative cycle (Modes 3 and 4), and one is in the freewheeling cycle (Mode 5). In the positive or negative cycle, four switches are ON, while in the freewheeling mode, three switches are ON. The circuit diagram with switch status demonstrating different operational modes is shown in Fig. 8.
Mode 1: S1, S4, S9, and S10 are ON while the other switches are OFF. In this case, the positive and negative terminals of PV2 are connected to points A and B, respectively. Figure 8a shows the circuit diagram with the corresponding switch status. Differential (output voltage) and common mode voltages are calculated as:
Mode 2: S1, S4, S8, and S11 are ON while the other switches are OFF. In this case, the positive and negative terminals of PV1 are connected to points A and B, respectively (shown in Fig. 8b). Differential (output voltage) and common mode voltages are calculated as:
Mode 3: S2, S3, S9, and S10 are ON while the other switches are OFF. In this mode, the positive and negative terminals of PV2 are connected to points B and A, respectively (shown in Fig. 8c), and the voltages are calculated as:
Mode 4: S2, S3, S8, and S11 are ON while the other switches are OFF. In this mode, the positive and negative terminals of PV1 are connected to points B and A, respectively (as shown in Fig. 8d), and the voltage are defined as:
Mode 5: This mode is the freewheeling cycle, so S5, S6, and S7 are ON, while the midpoint of the PV panels is connected to both points A and B (shown in Fig. 8e). In this case, the voltages are determined as:
The voltages in points A and B relative to the reference point (N), and the voltages in the common and differential modes in each of the operation modes are given in Table 1. As observed in all the equations above, the common mode voltages in all the operating modes are constant and equal to VPV1/2. In this structure, the leakage current is reduced by stabilizing the common mode voltage in all modes to VPV1/2. There are five levels of output voltage, including − VPV1, − \(\frac{1}{2}\) VPV1, 0, + \(\frac{1}{2}\) VPV1, + VPV1, which are more than other structures such as HERIC.
3.2 The second structure with a different connection in the DC-Link
In the first structure, two PV panels are used on the input side. In addition to the aforementioned configuration, the connections can be designed based on some other methods. The second structure uses four PV panels with equal voltage level. By series connection of these panels, different levels of voltage can be achieved, as shown in Fig. 9.
The switching pattern of this structure is the same as the previous structure (shown in Figs. 6 and 7). Also, this structure has five operation modes similar to the previous one. The circuit diagram with switch status for this topology in different operation modes is presented in Fig. 10, while VAN, VBN, differential voltage, and common mode voltage are summarized in Table 2. From Table 2, the common mode voltages in all the operating modes are constant and equal to 2VPV. Also, the output voltages (differential) in different operational modes have five levels: − 4VPV, − 2VPV, 0, + 2VPV, and + 4VPV.
4 Results and discussions
To evaluate the performance of the proposed topology, simulations are performed in MATLAB/Simulink. Data is obtained for the proposed topology (with two different structures), the HERIC topology, the M-NPC topology in [16], the topology in [23] and the CHB topology in [25]. The simulation results from MATLAB/Simulink are further validated by PSIM software with similar results obtained. In the simulations, for HERIC and M-NPC, a solar panel is considered with a voltage level of 400 V. For studies of the topologies in [23] and [25], one and two solar panels are considered, respectively, with a voltage level of 200 V. For the first structure of the proposed topology, the voltage levels of PV1 and PV2 are 400 V and 200 V, respectively, while the voltage level of each panel in the second structure of the proposed topology is 100 V. The grid voltage and frequency in all cases are 220 V and 50 Hz, respectively. The output filter inductors are 2 mH, and Cdc is 0.47 mF. The amount of radiation and temperature for these simulations are 1000 W/m2 and 25 ℃, respectively, while the value of parasitic capacitors (CPV) is 100 nF/kW. As several PV panels with different power are used in the proposed topology, the value of the leakage capacitance for each cell is proportional to the cell power (according to the ratio of 100 nF/kW). The simulations are carried out at 2 kW with unit power factor and the switching frequency is 16 kHz. The values of the simulation parameters are given in Table 3. In the simulations, the transient state is not considered and only the steady state of the systems is presented.
From the simulation, the behaviors of the two proposed structures are similar. Figure 11 shows the voltage waveforms of the two structures. As can be seen, the voltages in both structures are the same, while the main differences between the two proposed structures are the leakage current and total harmonic distortion, as previously discussed. Thus the first structure is used to compare the proposed topology with conventional topologies.
Figure 12 shows VAN and VBN in HERIC, M-NPC, and the proposed topology, where the five-level voltage in the proposed topology is evident. Figure 13 demonstrates the output voltage and the common mode voltage of the inverter in each topology, demonstrating that the common voltage variations in M-NPC and the proposed topology are much lower than that of the HERIC.
Figure 14 shows the grid and leakage currents in each topology. Unlike HERIC, in the proposed topology several PV panels are used at the input side, and therefore, the leakage current is divided between the PV panels. Accordingly, for a more accurate comparison, grid leakage currents in different topologies are compared. As seen from Fig. 14, M-NPC and the proposed topology perform better at reducing and improving leakage current than HERIC. The RMS of the leakage current is 34.8 mA in HERIC compared with 14.73 mA and 13.82 mA for M-NPC and the proposed topology, respectively.
For a better comparison of M-NPC with the proposed topology, the leakage current waveforms are shown in Fig. 15 with magnification. As it clearly illustrates, the leakage current in the proposed topology is better than that of M-NPC.
By using FFT analysis, THD is obtained for the output current of each structure. From this, THD values for HERIC, M-NPC, and the proposed structure with the first and second connections are 8.6%, 8.85%, 3.64% and 4.48%, respectively.
Figure 16 shows the variations in the efficiency of HERIC, inverters in [16] and [23], and the proposed structure for different loads. The overall performance of the topologies under investigation is presented in Table 4.
As mentioned earlier, the parasitic capacitor (CPV) capacitance value is often between 50 and 150 nF/kW. In the main simulations, 100 nF/kW is considered. To further investigate the effect of the capacitance value on the leakage current, simulations with values of 50 and 150 nF/kW are performed on the proposed topology and the results are given in Table 5. These results show that upon increasing the parasitic capacitance, leakage current increases.
We should mention that the findings presented in Table 4 are obtained at 1000 W/m2 and 25 ℃. In addition to these values, variations in the radiation and temperature and their effects on leakage current and THD are investigated in each topology and the results are illustrated in Tables 6 and 7. In Table 6, it can be seen that variations in the temperature and radiation change the leakage current in HERIC and M-NPC topologies. However, the leakage current in the proposed topology is not dependent on the environmental changes and has a desirable low value under different environmental conditions. Also, under varying temperatures and radiations as shown in Table 7, THD values of the previous two topologies are very high and undesirable while it is favorably low and acceptable in the proposed structure.
5 Conclusion
In this paper, a new inverter has been presented to reduce leakage current. HERIC and M-NPC inverters and their effects on reducing leakage current are discussed and compared with the proposed topology. In addition to reducing leakage current, the output voltage of the proposed topology has five levels. This is more efficient than HERIC in reducing the output current THD. Although the proposed topology is slightly complex in terms of structure and switching, the most notable advantages of the proposed inverter are:
-
Common mode voltage stabilization and leakage current reduction
-
Multilevel output with improved THD
-
Higher efficiency than the other competing topologies
Availability of data and materials
All data used or analyzed during this study are included in the published article.
Abbreviations
- THD:
-
Total harmonic distortion
- PV:
-
Photovoltaic
- HERIC:
-
Highly efficient and reliable inverter concept
- SV:
-
Space vector
- SCMLI:
-
Switched-capacitor multilevel inverter
- CHB:
-
Cascaded H-bridge
- M-NPC:
-
MOSFET neutral-point-clamped
- CPV :
-
Parasitic capacitor
- L1, L2 :
-
Output inductors
- ZG :
-
Ground impedance
- RG :
-
Ground resistance
- Cdc :
-
Capacitor parallel to the DC bus
- VECM :
-
Equivalent common-mode voltage
- VCM :
-
Common mode voltage
- VDM :
-
Differential voltage
- VPV :
-
Photovoltaic panel voltage
- ILeakage :
-
Leakage current
- IGrid :
-
Grid current
- POut :
-
Output power
- PF:
-
Power factor
- LSC-PWM:
-
Level-shifted carrier PWM
- FFT:
-
Fast Fourier transform
References
Romero-Cadaval, E., Spagnuolo, G., Franquelo, L. G., et al. (2013). Grid-connected photovoltaic generation plants: Components and operation. IEEE Ind Electron Mag, 7(3), 6–20.
Ozkan Z, Hava AM editors. Leakage current analysis of grid connected transformerless solar inverters with zero vector isolation. In 2011 IEEE energy conversion congress and exposition; 2011.
Cha, W. J., Kim, K. T., Cho, Y. W., et al. (2015). Evaluation and analysis of transformerless photovoltaic inverter topology for efficiency improvement and reduction of leakage current. IET Power Electron, 8(2), 255–67.
Faraji, F., Hajirayat, A., Birjandi, A. A. M., et al. (2017). Single-stage single-phase three-level neutral-point-clamped transformerless grid-connected photovoltaic inverters: Topology review. Renew Sustain Energy Rev, 80, 197–214.
Li, W., Gu, Y., Luo, H., et al. (2015). Topology review and derivation methodology of single-phase transformerless photovoltaic inverters for leakage current suppression. IEEE Trans Ind Electron, 62(7), 4537–51.
Poliseno M, Mastromauro R, Liserre M, et al., editors. High efficiency transformerless PV power converters. In: International symposium on power electronics power electronics, electrical drives, automation and motion; 2012. IEEE.
Gubia, E., Sanchis, P., Ursua, A., et al. (2007). Ground currents in single-phase transformerless photovoltaic systems. Prog Photovolt Res Appl, 15(7), 629–50.
Myrzik JM, Calais M, editors. String and module integrated inverters for single-phase grid connected photovoltaic systems-a review. In: 2003 IEEE Bologna Power Tech conference proceedings; 2003. IEEE.
Victor M, Greizer F, Bremicker S, et al. Method of converting a direct current voltage from a source of direct current voltage, more specifically from a photovoltaic source of direct current voltage, into a alternating current voltage. Google Patents; 2008.
Xu M, Zhang L, Xing Y, et al., editors. A novel H6-type transformerless inverter for grid-connected photovoltaic application. In: 2012 7th IEEE conference on industrial electronics and applications (ICIEA); 2012. IEEE.
González, R., Lopez, J., Sanchis, P., et al. (2007). Transformerless inverter for single-phase photovoltaic systems. IEEE Trans Power Electron, 22(2), 693–7.
Schmidt H, Siedle C, Ketterer J. DC/AC converter to convert direct electric voltage into alternating voltage or into alternating current. Google Patents; 2006.
Guo, X., & Jia, X. (2016). Hardware-based cascaded topology and modulation strategy with leakage current reduction for transformerless PV systems. IEEE Trans Ind Electron, 63(12), 7823–32.
Vázquez, N., Rosas, M., Hernández, C., et al. (2015). A new common-mode transformerless photovoltaic inverter. IEEE Trans Ind Electron, 62(10), 6381–91.
Mei, Y., Hu, S., Lin, L., et al. (2016). Highly efficient and reliable inverter concept-based transformerless photovoltaic inverters with tri-direction clamping cell for leakage current elimination. IET Power Electron, 9(8), 1675–83.
Syed, A., Sandipamu, T. K., & Suan, F. T. K. (2017). High-efficiency neutral-point-clamped transformerless MOSFET inverter for photovoltaic applications. IET Power Electron, 11(2), 246–52.
Khan SA, Guo Y, Zhu J, editors. A high efficiency transformerless PV grid-connected inverter with leakage current suppression. In: 2016 9th International conference on electrical and computer engineering (ICECE); 2016. IEEE.
Hu S, Li C, Li W, et al., editors. Enhanced HERIC based transformerless inverter with hybrid clamping cell for leakage current elimination. In: 2015 IEEE energy conversion congress and exposition (ECCE); 2015. IEEE.
Tey, K. S., & Mekhilef, S. (2016). A reduced leakage current transformerless photovoltaic inverter. Renew Energy, 86, 1103–12.
Kukade P, Sonti V, Jain S, editors. A cascaded HERIC based multilevel inverter for reducing leakage current in the PV applications. In: IECON 2017–43rd annual conference of the IEEE industrial electronics society; 2017. IEEE.
Grigoletto, F. B. (2019). Five-level transformerless inverter for single-phase solar photovoltaic applications. IEEE J Emerg Sel Top Power Electron, 8(4), 3411–22.
Sabry, A. H., Mohammed, Z. M., Nordin, F. H., et al. (2019). Single-phase grid-tied transformerless inverter of zero leakage current for PV system. IEEE Access, 8, 4361–71.
Vosoughi, N., Hosseini, S. H., & Sabahi, M. (2019). A new transformer-less five-level grid-tied inverter for photovoltaic applications. IEEE Trans Energy Convers, 35(1), 106–18.
Samizadeh, M., Yang, X., Karami, B., et al. (2020). A new topology of switched-capacitor multilevel inverter with eliminating leakage current. IEEE Access, 8, 76951–65.
Shahabadini, M., & Imaneini, H. (2021). Leakage Current Suppression in Multilevel Cascaded H-bridge Based Photovoltaic Inverters. IEEE Trans Power Electron, 36, 13754–13762.
Faraji, F., Birjandi, A. A. M., Zhang, J., et al. (2020). An improved multilevel inverter for single-phase transformerless PV system. IEEE Trans Energy Convers, 36(1), 281–90.
Chen, W., Yang, X., Zhang, W., et al. (2016). Leakage current calculation for PV inverter system based on a parasitic capacitor model. IEEE Trans Power Electron, 31(12), 8205–17.
Ji, B., Wang, J., & Zhao, J. (2012). High-efficiency single-phase transformerless PV H6 inverter with hybrid modulation method. IEEE Trans Ind Electron, 60(5), 2104–15.
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to acknowledge the Imam Khomeini International University, Qazvin, Iran.
Funding
Not applicable.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
The paper was a collaborative effort among the authors. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
About this article
Cite this article
Hosseinkhani, V., Sarvi, M. A new five-level inverter with reduced leakage current for photovoltaic system applications. Prot Control Mod Power Syst 7, 19 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1186/s41601-022-00240-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s41601-022-00240-3