Abstract
Background
Currently, there are few established pharmacogenetic predictors of response to treatment in multiple sclerosis (MS) patients. Commonly used second line treatments include natalizumab that has proven to be successful in slowing MS progression in a subset of patients. Our aim was to identify pharmacogenetic factor(s) associated with MS patients’ response to natalizumab.
Methods
Ten MS patients not responding to natalizumab and 23 MS patients responsive to natalizumab were selected for exome sequencing. Exome sequences were analyzed and resultant variant was assessed in an additional cohort of 86 MS patients.
Results
Exome analysis revealed a missense polymorphism (rs2304166) in glycoprotein VI (GP6) gene (19q13.42, c.940C > G, p.P314A) associated in homozygosity with MS poor response to natalizumab (p = 0.0012). An additional cohort of 86 MS patients of which 19 were natalizumab unresponsive and 67 responsive confirmed rs2304166 CC significant association with poor response to natalizumab (p = 0.0000027). In addition, rs2304166 CC MS patients had increased MS disability despite taking natalizumab (Odds ratio 22.18, 95% CI: 5.758–95.88, p = 0.00000001).
Conclusion
Natalizumab is a commonly used second line treatment for MS, and poor response to natalizumab appears to be associated with rs2304166 CC genotype in MS patients. Our findings suggest the need to investigate GP6’s rs2304166 role as a potential pharmacogenetic predictor for MS patients’ response to natalizumab.
Similar content being viewed by others
Background
Multiple sclerosis (MS) treatments are being developed at a rapid pace in tandem with increasing prevalence of MS worldwide [1]. MS worldwide prevalence is estimated to be 2500,000 cases, with a projected future increase in some countries [2]. MS management regimens involve treating MS-related symptoms in conjunction with available targeted MS disease-modifying drugs that can be broadly classified into anti-inflammatory and immunosuppressive treatments. Despite the wide selection of MS therapeutics available, disease progression and relapse are frequent. Several factors influence MS treatment success that can either be environmental or genetic [3]. Environmental factors such as trauma, patient adherence or life style can influence drug response. Genetic factors whilst very few are known are thought to contribute to MS co-morbidities, drug detoxification, adverse effects, and overall drug response. The disparity in patient response to MS disease-modifying drugs have gravitated MS research towards discovery of novel treatments and advocacy for personalized MS treatment research [4, 5]. In recent years, second-line treatments have been developed to target MS patients that do not respond to first-line treatments such as beta-interferon derivatives and glatiramer acetate [6]. Among the most effective second-line treatments for MS is Natalizumab (commercial name Tysabri©) [7]. Natalizumab (NTZ) is a monoclonal antibody against alpha-4-integrins expressed on lymphocytes. Alpha-4 integrins facilitate the attachment of myelin-reactive lymphocytes to endothelial cell walls and their transmigration across the blood brain barrier into the MS brain. Lymphocyte migration to the brain initiates the myelin targeted autoimmune inflammatory reaction characteristic of MS. NTZ’s successful treatment of MS relies on several factors including; adherence to treatment, starting in an active MS phase, having a relapsing-remitting MS course, and a mild to moderate expanded disability score [8,9,10]. Natalizumab’s success is hampered by the adverse effect associated with long-term use; as it associates with increased risk of progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy (PML) [11]. Moreover, a small percent of MS patients seemingly suitable for NTZ treatment fail to respond positively with apparent relapses, additional disability and new lesions on magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) indicative of disease activity [12, 13]. Here we show that a single nucleotide polymorphism (rs2304166, c.940C > G, p.P314A) in exon 8 of glycoprotein VI gene located on chromosome 19q13.42 can predict poor response to NTZ.
Methods
Sample collection
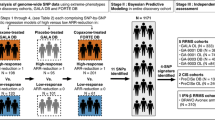
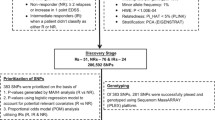
All MS patients included in this study were recruited at Dasman Diabetes Institute while attending their routine monthly appointments. All study protocols were approved by Dasman diabetes institute ethical review committee which adheres to the declaration of Helsinki’s Ethical Principles for Medical Research Involving Human Subjects. Information pertinent to study protocols was explained to all participants prior to procurement of their informed written consent. MS patients’ inclusion criteria were; a detailed clinical history (demographics, age of onset, disease duration, expanded disability status scale (EDSS) score, and treatment history), MS disease duration of ≥2 years, currently on NTZ, being adherent to NTZ for at least 1 year, and the agreement to provide a blood sample. Exclusion criteria included; having an EDSS score of 0, and MS disease duration of less than 2 years. The first sample collection identified 33 MS patients on NTZ. Of the 33 MS patients, 23 were classified as NTZ responsive and 10 were unresponsive when their MS clinical characteristics at the end of this part of the study’s duration of two years were compared to their pre-NTZ treatment clinical characteristics. Criteria used to categorize NTZ treated MS patients as responsive included; having a stable or reduced EDSS, no occurrence of relapse, and regression or lack of new MS-related CNS lesions on MRI. Whereas, NTZ unresponsive MS patients were identified based on the following; having an increased EDSS despite treatment, occurrence of a relapse during treatment course, and detection of new MS-related lesions on MRI compared to pre-treatment MRI results. These patients were selected for exome sequencing to investigate the genetic factor affecting their response to NTZ. The second sample collection cohort of 86 MS patients on NTZ was collected after the completion of the exome sequencing part of the study as a validation cohort using the same exclusion/inclusion criteria as above except for duration of NTZ adherence which was adjusted to > 2 years to allow detection of sufficient physical evidence of MS disease activity. The validation cohort included 19 NTZ unresponsive patients after an average of 4 years of NTZ treatment.
Exome sequencing
Whole blood was withdrawn in EDTA vacutainers and centrifuged at 2500 rpm at room temperature for fractionation. Plasma fractions were retained and stored at − 80 °C, and buffy coat fractions were collected for DNA extraction. DNA extraction was performed using Qiagen DNA mini kit (Qiagen, Germany) according to manufacturer’s standard protocol. DNA concentration and quality were assessed using spectrophotometry and agarose gel electrophoresis. Exome sequencing was performed on an Illumina HiSeq2000 platform using SureSelectXT v5 library preparation with target coverage of 50X (Illumina, CA, USA). Sequences were checked for quality using FASTQC software, and BWA software was used to map and align sequences to reference hg19 sequences. Picard was used to remove duplicate reads, and SAMtools was used to convert sequences from SAM format to sorted and indexed BAM files. GenomeAnalysisTK (GATK) was used to analyze the sequences for genotype calling and SnpEff was used to annotate variants and predict their effects. Resultant exomes were uploaded for comparative analysis using Tute Genomics application (Tute Genomics, Inc., UT, USA). Variants that have a Fisher exact test p-values of highest significance were prioritized and one was selected for further analysis in a secondary MS cohort.
Rs2304166 genotyping
Blood samples of the validation MS cohort were processed according to the same protocol mentioned above for DNA extraction. A genetic variant (rs2304166) in GP6 had the most significant association with NTZ response as detected by exome sequencing and was further investigated in the validation cohort. Taqman genotyping assay for single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) rs2304166 was used to genotype all samples. In summary, 50 ng of DNA from every sample were used for genotyping using ABI7500 Fast Real-time PCR system (Applied Biosystems, CA, USA). Genotype allelic discrimination was determined by SDS v1.4.1 software (Applied Biosystems, CA, USA).
GP6 enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay
Human GP6 sandwich enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay was used (LifeSpan Biosciences, Inc., WA, USA) according to manufacturer’s protocol. In summary, plasma samples were diluted in provided sample diluent at 1:10 and 1:20 dilutions and run in duplicates to ensure all samples’ readings fall within standard curve concentrations. Standards were prepared and 100 μl of blank, standards and samples were added to a 96-well plate in duplicates. Plates were sealed and incubated at 37 °C for 1 h followed by standard and sample aspiration from each well. Detection reagent A was added to each well and mixed thoroughly followed by incubation at 37 °C for 1 h. Following incubation, detection reagent was aspirated and wells were washed three times with kit supplied wash buffer and dried on absorbent paper. Detection reagent B was added to each well and plates were incubated for 30 min at 37 °C. After incubation, reagent B was aspirated and wells were washed five times with wash buffer, dried, and TMB solution was added into each well. Plates were incubated in the dark for 20 min at 37 °C and upon optimal color development incubation was terminated by adding kit provided stop solution. Optical density (OD) readings were immediately recorded on a microplate reader set at 450 nm wavelength. A standard curve was generated using a four-parameter logistic curve-fit and samples’ GP6 concentrations were corrected for dilution factors and recorded accordingly.
Data analysis
To assess the impact of our resultant variant we chose the following prediction program tools; Polyphen2 both HDIV and HVAR (a score of > = 0.957 is probably damaging), SIFT (deleterious if score is <=0.05), Mutation Taster, FATHMM, Genome Evolutionary Rate Profiling++ (GERP++) for which higher scores are probably deleterious, and SiPhy log Odds which is a probabilistic framework that uses data from 29 species and higher scores are more deleterious. For exome and genotype analysis Fisher’s exact-test, chi-square test, and linear regression analyses were used. For ELISA data D’Agostino and Pearson normality tests were performed prior and non-parametric data Mann-Whitney U-test, and Kruskall-Wallis test were used if data was non-normally distributed, whereas t-test and one-way ANOVA tests were used when variables analyzed were normally distributed. All statistical analyses were performed using SPSS v.25 (IBM, NY, USA).
Results
Exome sequencing data coverage shows an average of 99.82% 1x coverage rate and an average depth of 57.63 reads per probe. Fisher’s exact test analysis of exome sequences of the two cohorts showed nine variants with a p-value < 0.005, which is less than the accepted p-value for exome sequencing association results (p-value ≤2.5 × 10− 6) (Additional file 1: Table S1). However, given the small sample size we pursued the top hit for possible association with response to NTZ. Of the nine variants seven were silent therefore ignored, and two were missense. The missense variants were rs2304166 in glycoprotein VI (GP6) (p = 0.0012) and rs3748229 in phosphoinositide 3-kinase adapter protein 1 (OIK3AP1) (p = 0.0049). We prioritized the variant rs2304166 in GP6 as it was homozygous CC in 100% of NTZ unresponsive MS patients, and 41% heterozygous (CG) and 59% homozygous wild-type (GG) in MS patients responsive to NTZ (Table 1). This variant’s minor allele C occurs at a frequency of 38% in the 1000 genomes project, and is considered to be benign in ClinVar database. In our Kuwaiti population, rs2304166 allelic distribution was investigated in 319 healthy control exomes and found to be 63.47% for allele G and 36.53% for the minor allele C. Prediction program tools gave contradicting predictions for this variant. Polyphen2 predicted it to be probably damaging, and polyphen2 HDIV prediction was probably damaging as well. SIFT predicted rs2304166 to be deleterious with low confidence, mutation taster and FATHMM both predicted it to be tolerable. Whereas, genome evolutionary rate profile (GERP++) prediction gave a moderate score of 2.65 suggesting a moderately deleterious prediction, and cross species prediction program SiPhy29way had a score of 8.956 suggestive of high conservation and a probably deleterious rs2304166 effect. Rs2304166 is a nonsynonymous conserved amino acid substitution (p.P314A) which may alter protein function. This variant was assessed further in a replicate cohort longitudinally followed for an average of 4 years after patient’s first NTZ drug administration and adherence to treatment. The replicate cohort composed of 19 MS patients poorly responding to NTZ based on disease progression assessments, and 67 patients responding to NTZ. Replicate cohort rs2304166 genotyping results show that allele C significantly associated with poor response to NTZ (Odds ratio 22.18, 95%CI: 5.758–95.88, p = 0.000000011). Homozygous CC patients were at greatest risk of disease progression while taking NTZ as assessed by worse EDSS, occurrence of relapse, and new CNS lesion detection on MRI (p = 0.0000027). Analysis of both exome and replicate MS cohorts collectively demonstrated NTZ unresponsive MS patients had significantly worse EDSS after the completion of follow-up assessment (p < 0.001), whereas NTZ responsive patients had significantly better EDSS (p < 0.001) (Table 2). In addition, linear regression analysis adjusted for sex, age, MS type, and disease duration result shows initiating NTZ treatment in MS patients at mild or intermediate EDSS scores affects positive response to NTZ (β = 0.089, 95% CI: 0.164 - 0.036, p = 0.003) as previously reported. However, rs2304166 CC had a strong predictive potential of negative response to NTZ when adjusted for the above mentioned variables including EDSS (β = 0.274, 95% CI: 0.166–0.379, p < 0.0001). We next investigated whether rs2304166 influences GP6 levels in our cohort. Genotype CC patients’ GP6 levels were normally distributed, whereas genotype GG and GC patients’ GP6 levels were non-normally distributed. Log transformed GP6 levels were used to assess the effect of rs2304166 genotypes and we found no significant effect of rs2304166 on plasma GP6 levels (p = 0.46, Fig. 1).
Discussion
NTZ targets alpha-4 integrin subunits on lymphocytes. Leukocytes require alpha-4 integrins for trafficking to sites of inflammation. The alpha-4 integrins and their receptors are widely involved in fetal and adult lymphopoiesis and hematopoiesis in addition to leukocyte activation and survival [14, 15]. Treatment with NTZ has been shown to increase leukocyte counts, nucleated red blood cell counts and spleen weight as it limits leukocytes to the circulation inhibiting extravasation through alpha-4 integrin and adhesion molecules’ interactions in the endothelium [16]. Here we have shown that a variant in GP6 appears to reduce the efficacy of NTZ’s therapeutic potential in MS patients homozygous CC for rs2304166. GP6 is composed of two extracellular immunoglobulin (Ig)–homology domains, a transmembrane domain, and a 51-amino acid cytoplasmic domain. GP6 shares ~ 44.1% amino acid similarities with leukocyte immunoglobulin-like receptors. GP6 is a collagen receptor found on the surface of platelets that dimerizes to activate thrombotic signaling pathways, and its ectodomain can be found in soluble form during platelet shedding [17]. Upon GP6 binding to exposed collagen at injured vascular sites it induces platelet activation and aggregation leading to thrombus formation at site of injury [18]. In hemostasis and thrombosis, GP6 is pivotal for the maintenance of vessel wall integrity during inflammation by inhibiting neutrophil-induced vascular damage. Mutations in GP6 that result in loss of GP6 protein, or an abnormally short or nonfunctional GP6 are associated with an autosomal recessive hereditary bleeding disorder due to the inability to produce clots (OMIM ID 614201). Although our reported variant (rs2304166) in the GP6 gene is a missense variant, this variant changes an amino acid (Proline) that is evolutionarily conserved across primates. Proline change into alanine occurs in a peptide palindrome (PPAPP) that might be critical for the protein’s secondary structure. Alanine is a non-polar amino acid with a methyl side chain, whereas proline is also non-polar but has a pyrrolidine side chain characteristic of transmembrane domains. It is plausible that this variant produces a less stable GP6 monomer or dimer on the surface of platelets that alters its shedding potential which is considered a thrombus growth limiting event [19].
While the mechanism by which this GP6 variant lessens the efficacy of NTZ treatment of MS is currently unknown, it should be noted that only 10.5% NTZ unresponsive MS patients had new MRI activity, while 89.5% showed significant disease progression assessed by worsening EDSS. Based on what is known about GP6 and NTZ it is possible that the efficiency of platelet response to vascular injury is reduced due to GP6 reduced surface stability resulting in poor vascular homeostasis causing accumulation of cerebral vascular injury and reductions in cerebrovascular reactivity shown to cause additional neurodegeneration in MS [20, 21]. Moreover, moderately low GP6 levels in rs2304166 CC MS patients reflect this possibility pointing towards the occurrence of thrombocytopenia. Sporadic case reports have documented immune thrombocytopenia development secondary to NTZ treatment in MS patients [22,23,24]. It is possible that NTZ induced thrombocytopenia in conjunction with GP6 reduced functionality inflicts a clotting disorder that counteracts the beneficial impact of NTZ on MS related disability. GP6 is not the only factor involved in initiating thrombosis, integrin alpha-IIb beta3 is another factor that has similar functions and share similar pathways. Our reported GP6 variant’s effects might not be substantial under normal conditions, but come into effect when NTZ hematological changes take place. Whether thrombocytopenia development in GP6 rs2304166 CC MS patients limits their response to NTZ remains to be investigated.
Conclusions
A variant (rs2304166) in GP6 gene is associated with poor response to NTZ in homozygous CC genotype MS patients. Rs2304166 CC associated with progressive MS disability. Our findings support the need to investigate rs2304166 as a potential pharmacogenetic predictor of MS patients’ response to NTZ, and exploration of alternative therapeutics for this subset of MS patients.
References
Thompson AJ, Baranzini SE, Geurts J, Hemmer B, Ciccarelli O. Multiple sclerosis. Lancet. 2018. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(18)30481-1.
Amankwah N, Marrie RA, Bancej C, Garner R, Manuel DG, Wall R, et al. Multiple sclerosis in Canada 2011 to 2031: results of a microsimulation modelling study of epidemiological and economic impacts. Health Promot Chronic Dis Prev Can. 2017;37(2):37–48.
Golan D, Staun-Ram E, Miller A. Shifting paradigms in multiple sclerosis: from disease-specific, through population-specific toward patient-specific. Curr Opin Neurol. 2016;29(3):354–61. https://doi.org/10.1097/WCO.0000000000000324.
Ross CJ, Towfic F, Shankar J, Laifenfeld D, Thoma M, Davis M, et al. A pharmacogenetic signature of high response to Copaxone in late-phase clinical-trial cohorts of multiple sclerosis. Genome Med. 2017;9(1):50. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13073-017-0436-y.
Grossman I, Knappertz V, Laifenfeld D, Ross C, Zeskind B, Kolitz S, et al. Pharmacogenomics strategies to optimize treatments for multiple sclerosis: insights from clinical research. Prog Neurobiol. 2017;152:114–30. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pneurobio.2016.02.001.
Dorr J, Paul F. The transition from first-line to second-line therapy in multiple sclerosis. Curr Treat Options Neurol. 2015;17(6):354. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11940-015-0354-5.
Baroncini D, Ghezzi A, Annovazzi PO, Colombo B, Martinelli V, Minonzio G, et al. Natalizumab versus fingolimod in patients with relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis non-responding to first-line injectable therapies. Mult Scler. 2016;22(10):1315–26. https://doi.org/10.1177/1352458516650736.
Gajofatto A, Benedetti MD. Treatment strategies for multiple sclerosis: When to start, when to change, when to stop? World J. Clin. Cases. 2015;3(7):545–55. https://doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v3.i7.545.
Laroni A, Gandoglia I, Solaro C, Ribizzi G, Tassinari T, Pizzorno M, et al. Clinical baseline factors predict response to natalizumab: their usefulness in patient selection. BMC Neurol. 2014;14:103. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2377-14-103.
Prosperini L, Gianni C, Barletta V, Mancinelli C, Fubelli F, Borriello G, et al. Predictors of freedom from disease activity in natalizumab treated-patients with multiple sclerosis. J Neurol Sci. 2012;323(1–2):104–12. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jns.2012.08.027.
Bloomgren G, Richman S, Hotermans C, Subramanyam M, Goelz S, Natarajan A, et al. Risk of natalizumab-associated progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy. N Engl J Med. 2012;366(20):1870–80. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa1107829.
Hutchinson M, Kappos L, Calabresi PA, Confavreux C, Giovannoni G, Galetta SL, et al. The efficacy of natalizumab in patients with relapsing multiple sclerosis: subgroup analyses of AFFIRM and SENTINEL. J Neurol. 2009;256(3):405–15. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00415-009-0093-1.
Belachew S, Phan-Ba R, Bartholome E, Delvaux V, Hansen I, Calay P, et al. Natalizumab induces a rapid improvement of disability status and ambulation after failure of previous therapy in relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis. Eur J Neurol. 2011;18(2):240–5. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1468-1331.2010.03112.x.
Arroyo AG, Yang JT, Rayburn H, Hynes RO. Differential requirements for alpha4 integrins during fetal and adult hematopoiesis. Cell. 1996;85(7):997–1008.
Rose DM. The role of the alpha4 integrin-paxillin interaction in regulating leukocyte trafficking. Exp Mol Med. 2006;38(3):191–5. https://doi.org/10.1038/emm.2006.23.
Polman CH, O'Connor PW, Havrdova E, Hutchinson M, Kappos L, Miller DH, et al. A randomized, placebo-controlled trial of natalizumab for relapsing multiple sclerosis. N Engl J Med. 2006;354(9):899–910. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa044397.
Bender M, Hofmann S, Stegner D, Chalaris A, Bosl M, Braun A, et al. Differentially regulated GPVI ectodomain shedding by multiple platelet-expressed proteinases. Blood. 2010;116(17):3347–55. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2010-06-289108.
Poulter NS, Pollitt AY, Owen DM, Gardiner EE, Andrews RK, Shimizu H, et al. Clustering of glycoprotein VI (GPVI) dimers upon adhesion to collagen as a mechanism to regulate GPVI signaling in platelets. J Thromb Haemost. 2017;15(3):549–64. https://doi.org/10.1111/jth.13613.
Induruwa I, Jung SM, Warburton EA. Beyond antiplatelets: the role of glycoprotein VI in ischemic stroke. Int J Stroke. 2016;11(6):618–25. https://doi.org/10.1177/1747493016654532.
Marshall O, Lu H, Brisset JC, Xu F, Liu P, Herbert J, et al. Impaired cerebrovascular reactivity in multiple sclerosis. JAMA Neurol. 2014;71(10):1275–81. https://doi.org/10.1001/jamaneurol.2014.1668.
Stolp HB, Dziegielewska KM. Review: role of developmental inflammation and blood-brain barrier dysfunction in neurodevelopmental and neurodegenerative diseases. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol. 2009;35(2):132–46. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2990.2008.01005.x.
Stosic M, De Jesus P, McCarthy J, Hutton G, Rivera V. Immune thrombocytopenic purpura in a patient with multiple sclerosis treated with natalizumab. Neurology. 2011;77(5):505–7. https://doi.org/10.1212/WNL.0b013e318227b23f.
Midaglia L, Rodriguez Ruiz M, Munoz-Garcia D. Severe haematological complications during treatment with natalizumab. Mult Scler. 2012;18(11):1644–6. https://doi.org/10.1177/1352458512442262.
Cachia D, Izzy S, Berriosmorales I, Ionete C. Drug-induced thrombocytopenia secondary to natalizumab treatment. BMJ Case Rep. 2014;2014. https://doi.org/10.1136/bcr-2013-203313.
Funding
This work was funded by Kuwait University Research Sector Grant MG04/15.
Availability of data and materials
The datasets analysed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
MA performed the genotyping experiment, RAR facilitated sample collection and provided patients demographics and clinical data, TK performed ELISA experiments, MD performed the bioinformatics analysis and provided population frequency data, and RAT performed the exome sequencing, authored the manuscript and is the project’s principal investigator. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
All study protocols were approved by Dasman diabetes institute ethical review committee which adheres to the declaration of Helsinki’s Ethical Principles for Medical Research Involving Human Subjects. Informed written consent was secured from each participant prior to sample collection.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Additional file
Additional file 1:
Table S1. Exome sequencing significant (p < 0.005) results generated by comparing MS patients responding to NTZ (n = 23) and those unresponsive to NTZ (n = 10). (DOCX 14 kb)
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made. The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver (http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated.
About this article
Cite this article
Al-Mojel, M., Alroughani, R., Kannankeril, T. et al. GP6 rs2304166 polymorphism is associated with response to natalizumab in multiple sclerosis patients. Mult Scler Demyelinating Disord 4, 2 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1186/s40893-019-0039-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s40893-019-0039-0