Abstract
Background
The incidence of radiation-associated angiosarcoma (RAA) of the breast has been increasing, and its prognosis is reportedly poor. It is important to remove tumor tissues completely to prevent recurrence.
Case presentation
We report two cases of patients with RAA of the breast. Both patients had a nodule in their remaining breast a few years after undergoing breast-conserving surgery and radiation therapy for breast cancer. The nodules were diagnosed as angiosarcoma by skin biopsy and open biopsy, respectively. To determine the extent of lesion spread, mapping biopsy was performed before surgery. Both patients underwent mastectomy, extensive skin resection, and split skin grafting. Pathological findings showed that their tumors could be completely resected. After surgery, chemotherapy was performed.
Conclusion
In our cases, no local or distant recurrence has been detected in either patient for over 4 years. We identified the range of tumor invasion by preoperative mapping biopsy and completely resected all tumor tissue.
Similar content being viewed by others
Introduction
Radiation-associated angiosarcoma (RAA) of the breast is an unpleasant complication of radiation therapy for breast cancer. In the last few decades, breast-conserving surgery (BCS) with radiation therapy has replaced mastectomy as the standard of care for early-stage breast cancer [1]. Consequently, the incidence of RAA of the breast has been increasing, with the cumulative incidence reported to be 0.9 per 1,000 breast cancer cases in the past 15 years [2]. The prognosis of patients with RAA is reportedly poor. The recommended treatment for RAA of the breast is surgical resection. Although several reports about RAA of the breast have been published, methods for determining the resection range are not clearly described in these reports.
Here, we report two cases in which we identified the range of tumor invasion by preoperative mapping biopsy and resected the tumor tissue completely.
Case report
Case 1
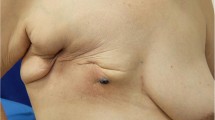
A 64-year-old woman visited our hospital with a 1-month history of a 1-cm dark red nodule in her right breast. Four years before, she underwent BCS and axillary lymph node dissection for right breast cancer followed by endocrine therapy and radiation therapy. The nodule was diagnosed as angiosarcoma by skin biopsy. A variety of image examination revealed a mass of 27 × 13 mm in outer lower lesion of her right breast, and the surrounding skin was markedly thickened (Fig. 1). Mapping biopsy 2 cm from the edge of the nodule revealed tumor invasion in all five sites examined, while mapping biopsy at 5 cm or 10 cm revealed no tumor invasion in any of the six sites examined (Fig. 2a).
Macroscopic and pathological findings (case 1). a Mapping biopsy was performed at 2 cm and 10 cm from the nodule. Red dots indicate positivity for tumor cells, and blue dots indicate negativity. b Pathological image of the resected specimen. It was diagnosed as angiosarcoma (hematoxylin-eosin [H.E.] staining: × 400). c Red dots indicate where tumor cells were observed. Tumor invasion was observed in a wider area outside the nodule
Total mastectomy with extensive skin resection (30 × 22 cm) was performed. The resection line was 10 cm from the edge of tumor. To repair a large skin defect, a wide skin graft using abdominal skin was performed. The pathological diagnosis was angiosarcoma, 45 × 40 × 20 mm in size (Fig. 2b, c). The surgical margins were completely free from tumor cells. Postoperative chemotherapy (weekly paclitaxel, 80 mg/m2 × 6 cycles) was administered, and the patient has experienced no recurrence for 6 years, 3 months.
Case 2
A 67-year-old woman had undergone BCS and sentinel lymph node biopsy for left breast cancer followed by chemotherapy, anti-HER2 therapy, and radiation therapy 3 years before. She visited another hospital with a 3-month history of a dark red nodule in her left breast. The nodule had been diagnosed as angiosarcoma by open biopsy by a dermatologist (Fig. 3a). Immunohistochemistry such as CD31 and CD34 were positive. She then consulted our department for surgical treatment. We could not point out obvious abnormal findings in imaging findings.
Macroscopic and microscopic pathological findings (case 2). a The nodule was diagnosed as angiosarcoma by open biopsy (H.E. staining: × 20). b Mapping biopsy 5 cm from the surgical trace (H.E. staining: × 20). Arrow: atypical endothelial cells. c Mapping biopsy 10 cm from the surgical trace (H.E. staining: × 20). Arrow: atypical endothelial cells. d Mapping biopsy was performed 5 cm and 10 cm away from the surgical trace. The red dots indicate areas where atypical endothelial cells were observed, and blue dots indicate areas where no atypical endothelial cells were observed
Seven out of nine points of a mapping biopsy 5 cm from the surgical trace revealed atypical endothelial cells (Fig. 3b), while three out of ten points of mapping biopsy at 10 cm revealed atypical endothelial cells (Fig. 3c).
She underwent left mastectomy with extensive skin resection (25 × 20 cm). The resection range exceeded the three sites at which atypical endothelial cells were observed, and in other places, a range of 10 cm from the surgical trace was used. To repair a large skin defect, a wide skin graft from the thigh was performed.
Atypical endothelial cells were observed in resected specimens, but the degree of atypia was less than that of the primary tumor. Atypical endothelial cells were not observed in the resection margin (Fig. 4).
Macroscopic findings of mapping biopsy and pathological examination (case 2). a A red dot indicates the surgical trace. Yellow dots indicate locations at which atypical endothelial cells were observed. b Atypical endothelial cells, in which the degree of atypia was less than that of the primary tumor (H.E. staining: × 20). Arrow: atypical endothelial cells
Postoperative chemotherapy (nab-paclitaxel, 260 mg/m2 × 4 cycles) was administered, and the patient has experienced no recurrence for 5 years.
Discussion
The mean latency period of RAA of the breast after radiation therapy is approximately 5–7 years [3]. Clinically, it presents as violaceous, erythematous plaques; nodes; areas of ecchymosis; and skin thickening [4, 5].
Cahan et al. and Arlen et al. proposed the following criteria for diagnosis of RAA of the breast: (1) a sarcoma arising within the field of previous radiotherapy, (2) differing histology between the secondary sarcoma and primary tumor, and (3) at least a 3-year latency period between radiation therapy and development of the sarcoma [6, 7]. The two present cases fulfilled all of those criteria.
Standard therapy for RAA of the breast is simple mastectomy and/or wide local excision [8], because disease-free survival is significantly shortened if the resected stump is positive for cancer cells [9]. Seinen et al. reported that the cause of high recurrence is due to multifocal growth of angiosarcoma and residual tumor tissue. These investigators reported that even if the surgical margins are considered to be clear, it is preferable to resect all irradiated skin [10]. The suggested treatment is aggressive surgery with removal of the pectoral muscle and subsequent reconstruction to achieve clear margins [11]. For deciding the area of resection, mapping biopsy is useful. Mapping biopsy is multiple skin biopsy at a certain distance from the tumor for detecting tumor invasion. By this method, it is possible to confirm the range of tumor spreading. In case 1, we confirmed the range free from invasion of tumor cells by mapping biopsy, and we resected skin with a 10-cm margin. In case 2, atypical endothelial cells were confirmed both inside and outside of the irradiation range. Atypical post-radiation vascular lesions (AVLs) have been described to arise within previously irradiated skin [12]. Therefore, we considered the possibility of tumor invasion rather than AVLs. Although skin transplantation was required, we were able to resect the tumor completely. Both case 1 and case 2 omitted the axillary operation because there was no metastasis to the axillary lymph node in the preoperative image examination.
Regarding radiation therapy for angiosarcoma, Depla suggested that the addition of reirradiation to surgery may help in local control of RAA [13]. On the other hand, Torres suggested that the use of radiation therapy remains controversial, as repeat radiation exposure to an area that has already been irradiated may result in toxicity [14]. Therefore, we did not perform postoperative radiation therapy for RAA.
Regarding chemotherapy for angiosarcoma, Sinnamon performed retrospective analysis of cutaneous angiosarcoma, and the analysis indicated both adjuvant and neoadjuvant therapy after surgery did not show any survival benefit on univariate and multivariate [15]. On the other hand, there are several reports showing the possibility that taxanes are useful for angiosarcoma [16, 17].
Angiosarcomas express VEGFR [18]. Several studies using anti-VEGF monoclonal antibody have shown antitumor activity in angiosarcoma [19, 20]. On the basis of this background, Ray-Coquard conducted a non-comparative, open-label, randomized phase 2 trial to explore the activity and safety of bevacizumab and paclitaxel therapy for patients with advanced angiosarcoma. Fifty patients were randomized and assigned to two arms: (1) the paclitaxel alone or (2) the paclitaxel and bevacizumab arm. From the findings, they concluded that there is no benefit from adding bevacizumab to paclitaxel [21].
Therefore, it is thought that chemotherapy/molecular target treatment for angiosarcoma has not yet been determined. We used a taxane for two patients, taking into account the fact that the taxane may be effective and that they did not use anthracycline after the initial breast cancer surgery.
In general, the prognosis of patients with RAA of the breast is poor. The 5-year local recurrence-free survival rate is 41–47%, and the 5-year overall survival rate is 10–54% [14, 22, 23]. The median time to local recurrence after diagnosis has been reported to be 6 months (range, 1–89 months) [10, 24]. Poor prognosis is reported to be associated with large tumor size, high histologic grade, and positive surgical margins [25].
To the best of our knowledge, several case reports of RAA in the breast have been published since 1990. In those reports, mastectomy and/or wide excision were conducted; however, no reports have clearly described a method for determination of the surgical margin.
We identified the range of tumor invasion by preoperative mapping biopsy. This technique could potentially lead to complete resection of tumor tissues and a good prognosis.
Conclusion
Mapping biopsies are useful for confirming the invasion range of RAA of the breast. If tumor cells are completely resected, a long-term good prognosis can be achieved.
References
Veronesi U, Cascinelli N, Mariani L, Greco M, Saccozzi R, Luini A, et al. Twenty-year follow-up of a randomized study comparing breast-conserving surgery with radical mastectomy for early breast cancer. N Engl J Med. 2002;347:1227–32.
Yap J, Chuba PJ, Thomas R, Aref A, Lucas D, Severson RK, et al. Sarcoma as a second malignancy after treatment for breast cancer. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2002;52:1231–7.
Chesebro AL, Chikarmane SA, Gombos EC, Giardino AA. Radiation-associated angiosarcoma of the breast: what the radiologist needs to know. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2016;207(1):217–25.
Chikarmane SA, Gombos EC, Jagadeesan J, Raut C, Jagannathan JP. MRI findings of radiation-associated angiosarcoma of the breast (RAS). J Magn Reson Imaging. 2015;42:763–70.
Brenn T, Fletcher CD. Postradiation vascular proliferations: an increasing problem. Histopathology. 2006;48:106–14.
Cahan WG, Woodard HQ, Higinbotham NL, Stewart FW, Coley BL. Sarcoma arising in irradiated bone: report of eleven cases. Cancer. 1948;1:3–29.
Arlen M, Higinbotham NL, Huvos AG, Marcove RC, Miller T, Shah IC. Radiation-induced sarcoma of bone. Cancer. 1971;28:1087–99.
Kelly NP, Siziopikou K. A 68-year-old woman with bluish discoloration of the skin of the breast. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2002;126(8):989–90.
Monroe AT, Feigenberg SJ, Mendenhall NP. Angiosarcoma after breast-conserving therapy. Cancer. 2003;97:1832–40.
Seinen JM, Styring E, Verstappen V, Vult von Steyern F, Rydholm A, Suurmeijer AJ, et al. Radiation-associated angiosarcoma after breast cancer: high recurrence rate and poor survival despite surgical treatment with R0 resection. Ann Surg Oncol. 2012;19:2700–6.
Sara TV, Rosa AF, Sara PF, Diego NG, Manolo La CM. Radiation-induced breast angiosarcoma: a case report. Ecancermedicalscience. 2016;10(697):29.
Fineberg S, Rosen PP. Cutaneous angiosarcoma and atypical vascular lesions of the skin and breast after radiation therapy for breast carcinoma. Am J Clin Pathol. 1994;102:757–63.
Depla AL, Scharloo-Karels CH, de Jong MA, et al. Treatment and prognostic factors of radiation associated angiosarcoma (RAAS) after primary breast cancer: a systematic review. Eur J Cancer. 2014;50:1779–88.
Torres KE, Ravi V, Kin K, Min Y, Guadagnolo BA, May CD, et al. Long-term outcomes in patients with radiation-associated angiosarcoma of the breast following surgery and radiotherapy for breast cancer. Ann Surg Oncol. 2013;20:1267–74.
Sinnamon AJ, Neuwirth MG, McMillan MT, Ecker BL, Bartlett EK, Zhang PJ, et al. A prognostic model for resectable soft tissue and cutaneous angiosarcoma. J Surg Oncol. 2016;114(5):557–63.
Fata F, O’Reilly E, Ilson D, et al. Paclitaxel in the treatment of patients with angiosarcoma of the scalp or face. Cancer. 1999;86:2034–7.
Casper ES, Waltzman RJ, Schwartz GK, Sugarman A, Pfister D, Ilson D, et al. Phase II trial of paclitaxel in patients with soft-tissue sarcoma. Cancer Investig. 1998;16(7):442–6.
Itakura E, Yamamoto H, Oda Y, Tsuneyoshi M. Detection and characterization of vascular endothelial growth factors and their receptors in a series of angiosarcomas. J Surg Oncol. 2008;97(1):74–81.
Agulnik M, Yarber JL, Okuno SH, von Mehren M, Jovanovic BD, Brockstein BE, et al. An open-label, multicenter, phase II study of bevacizumab for the treatment of angiosarcoma and epithelioid hemangioendotheliomas. Ann Oncol. 2013;24(1):257–63.
Koontz BF, Miles EF, Rubio MA, Madden JF, Fisher SR, Scher RL, et al. Preoperative radiotherapy and bevacizumab for angiosarcoma of the head and neck: two case studies. Head Neck. 2008;30(2):262–6.
Ray-Coquard IL, Domont J, Tresch-Bruneel E, Bompas E, Cassier PA, Mir O, et al. Paclitaxel given once per week with or without bevacizumab in patients with advanced angiosarcoma: a randomized phase II trial. J Clin Oncol. 2015;33(25):2797–802.
Morgan EA, Kozono DE, Wang Q, Mery CM, Butrynski JE, Baldini EH, et al. Cutaneous radiation-associated angiosarcoma of the breast: poor prognosis in a rare secondary malignancy. Ann Surg Onc. 2012;19:3801–8.
D’Angelo SP, Antonescu CR, Kuk D, Qin L, Moraco N, Carvajal RC, et al. High-risk features in radiation-associated breast angiosarcomas. Br J Cancer. 2013;109:2340–6.
Abbott R, Palmieri C. Angiosarcoma of the breast following surgery and radiotherapy for breast cancer. Nat Clin Pract Oncol. 2008;5:727–36.
Young RJ, Brown NJ, Reed MW, Hughes D, Woll PJ. Angiosarcoma. Lancet Oncol. 2010;11(10):983–91.
Acknowledgements
Not applicable.
Funding
Not applicable.
Availability of data and materials
Not applicable.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made.
About this article
Cite this article
Nomoto, Y., Kijima, Y., Shinden, Y. et al. Two cases of radiation-associated angiosarcoma of the breast. surg case rep 4, 132 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1186/s40792-018-0539-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s40792-018-0539-8