Abstract
Background
Cardiac troponin assays have improved the ability to detect myocardial damage. However, ascertaining whether troponin elevation is due to myocardial infarction (MI) or secondary to another process can be challenging. Our aim is to evaluate provider-level variation in the diagnosis of MI and the use of invasive coronary angiography (ICA) among patients with undifferentiated elevations in cardiac troponin.
Methods
We analyzed data from all patients with elevated troponin levels in a single Veterans Affairs (VA) Medical Center between 2006 and 2007. One of several cardiologists prospectively evaluated each patient’s presentation and course of care. We compared the frequency of MI diagnosis and ICA use between physicians using univariate odds ratios (OR).
Results
Among 761 patients, 34.0 % were diagnosed with MI and 25.9 % underwent ICA. The unadjusted rates of MI (23.9 to 56.7 %, P = 0.02) and ICA (17.3 to 73.3 %, P < 0.001) differed between physicians. Comparing the patient cohorts for each physician, baseline characteristics were similar except for chest pain. In multivariate regression, factors associated with the use of cardiac ICA included an abnormal electrocardiograph (ECG) (OR = 1.89, P = 0.014), level of troponin (OR = 1.71, P = 0.004), chest pain (OR = 8.60, P < 0.001), and care by non-VA physicians (OR = 4.45, P = 0.006). One physician had a lower ICA use (OR = 0.56, P = 0.017). In multivariate regression of MI, no physician-level variation was observed.
Conclusion
Among patients with elevated troponin, the likelihood of being diagnosed with MI and undergoing ICA is dependent on their clinical presentation. After adjustment, physician-level variation in care was observed for the use of ICA, but not for the diagnosis of MI.
Similar content being viewed by others
Background
Cardiac troponin (Tn) is a sensitive marker of myocardial necrosis [1], but Tn can be elevated in many disease states without clinical evidence of myocardial infarction (MI) [2, 3]. The universal definition of myocardial infarction is a rise and/or fall of a cardiac biomarker, preferably Tn, in addition to a clinical presentation consistent with MI [4]. Despite this, physicians may disagree when applying this definition to individual patients. Accurate clinical diagnosis of MI is important to guide appropriate utilization of diagnostic procedures and risk modifying therapies.
Variation in the use of medical testing and the interpretation of a diagnostic test is well documented in the medical literature and extends to the level of the individual provider [5, 6]. The use of cardiac testing and the interpretation of cardiac tests is also subject to significant variation [7–9]. Indeed, there is approximately a 2-fold regional variation in the use of invasive coronary angiography (ICA) after acute myocardial infarction within the United States [10, 11].
As part of a local quality improvement effort, our facility tracked all patients with elevated Tn for a one-year period. This provided a unique opportunity to evaluate patterns of MI diagnosis and the use of ICA in response to elevated Tn. We analyzed that database to determine if the care of patients with elevated Tn differed among providers.
Methods
We conducted a single center retrospective cohort study at our Veterans Affairs (VA) Medical Center. Data were obtained from a quality improvement program conducted on patients with elevated Tn who were seen in our facility between February 2006 and February 2007. The study protocol was reviewed by the Institutional Review Board-01 Gainesville Health Science Center, and the requirement for informed consent was waived. During that time frame, a “troponin team” evaluated every patient with an elevated Tn, defined as being greater than 0.03 ng/ml on our Tn-T assay. The team was led by a clinical coordinator who received a daily list from the facility’s core laboratory of all patients who had an elevated Tn. This coordinator evaluated each patient based on their chart documentation and presented all patients to a cardiologist who determined if the patient’s presentation was consistent with a MI and whether ICA should be performed. No formal definition of MI was applied, and physicians were free to make the diagnosis based on their clinical assessment of the patient. Because our facility does not have an inpatient service led by a cardiologist, all other care decisions were left to the admitting team with input from the cardiology consultation service. Several cardiologists shared responsibility for oversight of the “troponin team” including general/noninvasive, interventional, and electrophysiology cardiologists. Data were blinded as to the physician, and therefore could not be analyzed at the level of subspecialty within cardiology. Data, including each patient’s baseline clinical characteristics, clinical course, thrombolysis in myocardial infarction (TIMI) score, electrocardiogram (ECG) results, and follow-up, were recorded by the clinical coordinator.
The co-primary outcomes were the rates of MI diagnosis and ICA use between individual physicians, which were compared using chi square analysis. We conducted a multivariate logistic regression to determine how the diagnosis of MI and the use of ICA were affected by the following variables: age by year, sex, coronary artery disease, hypertension, diabetes mellitus, hyperlipidemia, prior coronary intervention, prior coronary bypass surgery, ECG changes, new ECG changes, primary symptom of chest pain / dyspnea / other, serum creatinine, level of 1st Tn measurement. Each physician was included as an independent variable with the remainder of the physicians for comparison. We considered attempting an additional hierarchical multi-level model to compare odds ratios for MI diagnosis and ICA use between physicians after accounting for clustering of patients within their physician-based cohort. Due to the small sample sizes, however, this model was not considered statistically valid [12–14]. Odds ratios (OR) and 95 % confidence intervals (CI) were reported. Because we used an existing dataset, no formal a priori power calculation was performed. Baseline variables were compared by parametric and nonparametric tests as appropriate. Analysis was performed using SPSS version 21 (IBM, Armonk, NY).
Results
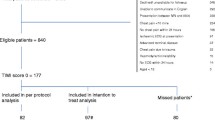
A total of 761 patients were included. Patient characteristics and their clinical course were compared between the different physicians. Occasionally (i.e., weekends and holidays) inpatient services were provided by physicians from our affiliated academic medical center. Patients seen by these physicians were grouped under “non-VA Physician” (Table 1). While not randomly assigned, patient characteristics of the cohorts seen by each of the physicians were similar, except for chest pain (P<0.01). MI was diagnosed in 34.0 % of patients with positive Tn and in 25.9 % patients who underwent ICA. The rates of diagnosing MI (P = 0.02) and ICA use (P < 0.0001) differed between physicians, ranging from 23.9 to 56.7 % and 17.3 to 73.3 %, respectively (Figs. 1 and 2).
Multivariate regression for the diagnosis of MI was associated with the 1st Tn level (OR = 11.44, 95 % CI 4.60-28.48, P < 0.0001), chest pain (OR = 4.25, 95 % CI 2.84–6.37, P < 0.0001), and new ECG changes (OR = 3.88, 95 % CI 2.34–6.43, P < 0.0001). Creatinine was associated with a lower likelihood of MI diagnosis (OR = 0.68, 95 % CI 0.57–0.81, P < 0.0001) (Table 2). None of the physicians were independently associated with the diagnosis of MI. In multivariate regression, cardiac ICA was associated with several factors (Table 3), including chest pain (OR = 8.60, 95 % CI 5.2–14.2, P < 0.0001), thrombolysis in myocardial infarction (TIMI) score greater than 2 (OR = 3.27, 95 % CI 1.64–6.52, P = 0.001), abnormal ECG (OR = 1.89, 95 % CI 1.13–3.13, P = 0.014), and the 1st Tn level (OR = 1.71, 95 % CI 1.19–2.47, P = 0.004). Increasing creatinine levels were associated with a lower likelihood of ICA (OR = 0.70, 95 % CI 0.58–0.85, P < 0.0001). Physician 2 was associated with a lower likelihood of ICA (OR = 0.56, 95 % CI 0.34–0.90, P = 0.017), while care by a non-VA physician was more likely to result in ICA (OR = 4.45, 95 % CI 1.54–12.89, P = 0.006).
Discussion
In this investigation, we demonstrated that the diagnosis of MI and the use of ICA vary by individual cardiology physicians within a single facility. After adjusting for differences in patient characteristics, physician-level variation in ICA use persisted. Because this was not a randomized trial and our sample size of providers was not adequate for hierarchical modeling, we cannot be certain that the observed variation was due to differences in the patient panel or to clinical decisions made by individual providers. For example, the non-VA physician category saw more patients with chest pain, a strong predictor of ICA use. Conversely, in our logistic regression model, we did not observe any differences between individual physicians with regard to the diagnosis of MI. While no formal definition of MI was applied, this would suggest that our physicians did use similar diagnostic criteria.
The overall rate of MI diagnosis Dx (34.0 %) and the use of ICA (25.9 %) were both low in this population despite the high risk of cardiovascular events. Approximately half the patients had prior CAD and diabetes, and a substantial majority had TIMI scores greater than 2. This observation is due, at least in part, to what appears to be widespread use among patients without typical symptoms of MI. Our observed rate of MI was even lower than the rate observed by Alcalai et al. [15]. We cannot accurately ascertain the reasons for this observation from our database. Given the high proportion of pre-existing CAD, type 2 myocardial infarctions or chronic, baseline elevation in Tn are plausible explanations. We did note in our logistic regression that an increased creatinine was associated with lower likelihood of both MI and ICA. Presumably, our physicians included elevated creatinine in their consideration of whether Tn elevation was due to MI. This also likely played a role in decisions concerning ICA use where consideration for avoiding iodinated contrast and preserving renal function are important factors.
In our analysis of ICA use, physician-level variation persisted within our regression model. One VA physician was associated with a lower likelihood of ICA perhaps reflecting a more conservative approach to MI management. The non-VA physician group had a higher propensity for ICA. This group was comprised of multiple physicians who do not practice regularly at our VA facility. We cannot determine if the difference in ICA use represents overuse by the non-VA physicians or underuse by those working at the VA. It is possible that the non-VA physicians, unfamiliar with a veteran population, felt that a more aggressive/invasive management strategy was warranted. VA physicians appeared to have similar rates of ICA use although this could represent widespread underuse.
The landscape of cardiology practice has changed substantially since the data for this investigation were first collected. The “troponin team” that once existed at our institution is no longer in use. The primary reason for its discontinuation was the high cost of the program (which involved tracking all patients with an elevated Tn and physician staffing). Furthermore, patient care was not substantially improved (i.e., short-term mortality tracked in the facility was not changed with the use of the troponin team). We no longer have physicians who share part-time staffing duties. All physicians are now full-time VA employees. As such, we do not have any immediate plans to alter our patterns of care based on the results of our investigation.
Our data were gathered as part of a clinical demonstration project and not primarily as a research investigation. As a result, definitions of MI and decisions to perform ICA were not standardized. Patients were not randomly assigned, and residual differences in patient populations after logistic regression may have occurred. A multi-level model controlling for patient characteristics within each physician cohort would have been a preferable statistical approach; however, our sample of physicians was too small for this to be a valid approach. This limited sample size and the blinding of the identities of individual physicians precludes any analysis based on subspecialty within cardiology. The strongest variation by an “individual physician” in our investigation was actually the group of non-VA physicians with too few encounters to analyze individually, limiting the ability to compare our data with other investigations of individual physician care variations.
Conclusion
The likelihood of a patient with an elevated Tn being diagnosed with MI and undergoing ICA is dependent on their clinical presentation and may possibly depend on the responsible physician. Whether this variation represents overuse or underuse is unclear.
Abbreviations
CI, confidence interval; ECG, electrocardiogram; ICA, invasive coronary angiography; MI, myocardial infarction; OR, Odds ratio; TIMI, Thrombolysis in myocardial infarction; Tn, Troponin; VA, Veterans affairs
References
Reichlin T, Twerenbold R, Reiter M, Steuer S, Bassetti S, Balmelli C, et al. Introduction of high-sensitivity troponin assays: impact on myocardial infarction incidence and prognosis. Am J Med. 2012;125:1205–13. e1.
De Gennaro L, Brunetti ND, Cuculo A, Pellegrino PL, Izzo P, Roma F, et al. Increased troponin levels in nonischemic cardiac conditions and noncardiac diseases. J Interv Cardiol. 2008;21:129–39.
Melanson SE, Conrad MJ, Mosammaparast N, Jarolim P. Implementation of a highly sensitive cardiac troponin I assay: test volumes, positivity rates and interpretation of results. Clin Chim Acta. 2008;395:57–61.
Thygesen K, Alpert JS, Jaffe AS, Simoons ML, Chaitman BR, White HD, et al. Third universal definition of myocardial infarction. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2012;60:1581–98.
Harris BU, Miyake CY, Motonaga KS, Dubin AM. Diagnosis and management of pediatric brugada syndrome: a survey of pediatric electrophysiologists. Pacing Clin Electrophysiol. 2014;37:638–42.
Wijeysundera HC, Qiu F, Bennell MC, Natarajan MK, Cantor WJ, Smith S, et al. Impact of system and physician factors on the detection of obstructive coronary disease with diagnostic angiography in stable ischemic heart disease. Circ Cardiovasc Qual Outcomes. 2014;7:648–55.
Chassin MR, Brook RH, Park RE, Keesey J, Fink A, Kosecoff J, et al. Variations in the use of medical and surgical services by the Medicare population. N Engl J Med. 1986;314:285–90.
Kuhn EM, Hartz AJ, Baras M. Correlation of rates of coronary artery bypass surgery, angioplasty, and cardiac catheterization in 305 large communities for persons age 65 and older. Health Serv Res. 1995;30:425–36.
Lucas FL, Wennberg DE, Malenka DJ. Variation in the use of echocardiography. Eff Clin Pract. 1999;2:71–5.
Ko DT, Krumholz HM, Wang Y, Foody JM, Masoudi FA, Havranek EP, et al. Regional differences in process of care and outcomes for older acute myocardial infarction patients in the United States and Ontario, Canada. Circulation. 2007;115:196–203.
Stukel TA, Lucas FL, Wennberg DE. Long-term outcomes of regional variations in intensity of invasive vs medical management of Medicare Patients with acute myocardial infarction. JAMA. 2005;293:1329–37.
Tabachinick BG, Fidell LS. Using Multivariate Statistics. Upper Saddle River, NJ: Pearson Education; 2012.
Heck RH, Thomas S, Tabata L. Multilevel Modeling of Categorical Outcomes Using IBM SPSS. NY, NY: Routledge, Taylor and Francis Group; 2012.
Maas CJM, Hox JJ. Sufficient sample sizes for multilevel modeling. Methodology. 2005;1:86–92.
Alcalai R, Planer D, Culhaoglu A, Osman A, Pollak A, Lotan C. Acute coronary syndrome vs nonspecific troponin elevation: clinical predictors and survival analysis. Arch Intern Med. 2007;167:276–81.
Acknowledgements
Not applicable.
Funding
No VA research funds were used for this investigation. This work was supported by resources provided by the North Florida/South Georgia Veterans Health System, Gainesville, FL.
Authors’ contributions
DW was responsible for the design and oversight of the study. DW, NA, and LB collected the data and drafted the manuscript. DW and TS conducted the statistical analyses. All authors contributed to the interpretation of the data, contributed critically to drafting the manuscript, and approved the final submission.
Competing interests
Dr. Winchester received an unrelated grant from Roche Diagnostics after conducting this investigation. All other authors have no financial or other conflicts of interest to disclose.
Ethics approval and consent to participate
The study protocol was reviewed and approved by Institutional Review Board-01 Gainesville Health Science Center, and the requirement for informed consent was waived.
Data
The data supporting the conclusions of this article are not available publicly due to restrictions from our Institutional Review Board and US federal regulations. Dr. Winchester had full access to and accepts responsibility for the integrity of the data and analysis.
Declarations
The contents of this paper do not represent the views of the U.S. Department of Veterans Affairs or the United States Government.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made. The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver (http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated.
About this article
Cite this article
Winchester, D.E., Agarwal, N., Burke, L. et al. Physician-level variation in the diagnosis of myocardial infarction and the use of angiography among Veterans with elevated troponin. Military Med Res 3, 22 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1186/s40779-016-0090-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s40779-016-0090-5