Abstract
Aim
We aimed to evaluate the prevalence of incidental 68 Ga-DOTA-conjugated somatostatin receptor-targeting peptide PET/CT (SSTR PET/CT) findings, their clinical significance in the need for follow-up, and their risk of malignancy.
Materials and methods
Studies reporting incidental SSTR PET/CT findings were systematically searched in PubMed, Cochrane, Embase and Web of Science literature published prior to 1st of May 2020. Studies were filtered by two independent readers for eligibility based on title and abstract, and subsequently on full text. The main exclusion criteria were: 1) pathological findings that matched scan indication, 2) known organ specific disease and/or incidental findings confirmed on other scan modality prior to SSTR PET/CT, 3) lack of diagnosis and/or follow up, and 4) results published in proceedings or conference abstracts.
Results
Twenty-one studies, comprising a total of 2906 subjects, were eligible for the analysis. Studies included were retrospective cohort studies on incidental SSTR PET/CT findings in a specific organ (n = 2888, 7/21) or case reports (n = 18, 14/21). A total of 133 subjects had incidental SSTR PET/CT findings. Incidental findings were predominantly seen in the thyroid gland (n = 65), spine (n = 30), brain (n = 26) and breast (n = 6). Seventeen of 133 (13%) incidental findings were malignant on final diagnosis. Incidental breast findings were associated with the highest risk of malignancy (67%). In the thyroid, incidental SSTR uptake was caused by malignancy in 8%, all presenting as focal uptake. The lowest risk was seen in the spine with a malignancy rate of 3% in patients with incidental SSTR uptake and benign cases were interpreted as vertebral hemangiomas on CT. Incidental SSTR PET/CT findings in other locations were of malignant etiology in two out of six cases (33%) and should be evaluated individually.
Conclusion
The most incidental SSTR PET/CT findings were found in the thyroid gland, spine, and brain. The risk of malignancy was greatest in incidental SSTR PET/CT findings in the breast, cranially, and thyroid gland. The results of the present study can prove useful in the interpretation of atypical findings on SSTR PET/CT and in the counseling of clinicians.
Similar content being viewed by others
Explore related subjects
Find the latest articles, discoveries, and news in related topics.Introduction/background
Somatostatin receptors (SSTR) subtype 1–5 belong to the G-protein coupled receptor superfamily and normally have a wide variety of physiological functions in the body, from the regulation of various hormones and neuropeptides, gastric emptying, and intestinal blood flow [1]. Neuroendocrine tumors (NET), a relatively heterogeneous group of tumors mainly arising in the gastro-entero-pancreatic tract (75%) and lungs (25%), are known to express SSTR, most abundantly SSTR2 that is expressed in 70–90% of all NETs [2]. This phenomenon has been utilized in diagnostic imaging with positron emission tomography (PET) and also in SSTR-targeting radionuclide treatment [3]. SSTR-targeting peptides linked with the 1,4,7,10-tetraazacyclodecane-1,4,7,10-tetraacetic acid (DOTA) with a chelated positron emitting radioactive isotope enables PET imaging of NET with high sensitivity and specificity [4, 5]. Gallium-68 is the most commonly used isotope since it has favorable properties for diagnostic imaging and can be produced onsite from a generator without a cyclotron. Different tracers have been developed by modifications of the SSTR binding Tyr3-Octreotide with different affinities towards the SSTR subtypes [2, 6]. Although DOTA-tracers show a reliable specificity in oncologic PET-imaging on known or suspected NETs, physiological uptake of DOTA-tracers is considerable in the liver, adrenal glands, urinary tract, pancreas, spleen, and pituitary gland, and modest in the gastrointestinal tract, thyroid- and salivary glands [7,8,9,10].
In the last decade SSTR PET/CT scans are increasingly performed and therefore, encountered atypical or incidental findings (or incidentalomas) are expected to increase in the future [2]. The understanding of SSTR-PET/CT incidentalomas is important for the evaluation and interpretation of SSTR-PET/CT. Additionally, clinicians need to know how to deal with unexpected findings to avoid unintended consequences. However, literature on the incidence as well as outcomes of SSTR PET/CT incidentalomas are scarce and has predominantly focused on incidental SSTR uptake in specific organs such as the thyroid gland [11, 12].
We aimed at evaluating the overall prevalence and risk of malignancy in incidental SSTR PET findings published in the literature.
Materials and methods
Study design
We conducted a systematic review of observational studies describing the prevalence and outcomes of incidental findings reported on 68 Ga-SSTR PET/CT or PET/MRI. The systematic review was performed in accordance with the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analysis (PRISMA) guideline [13].
Search strategy and eligibility criteria
A comprehensive literature search of PubMed, Embase, Web of Science, and The Cochrane Library was conducted. The search period was from the start of each database until 1st of May 2020. Databases were searched by using headings under the terms: incidental finding, unexpected finding AND DOTA-ligand PET/CT or PET/MRI (search profiles are presented in supplementary material). To expand our search, references of the retrieved articles were also screened for additional studies. All data were managed using the reference managing tool EndNote Web 3.3.
According to the report characteristics such as year of publication, language and country of first author, and according to the study characteristics such as PICOS concept (patient, intervention, comparator, outcome, study type), the following inclusion criteria were used: 1. Incidental 68 Ga-DOTA-conjugated Somatostatin Receptor-Targeting (SSTR) Peptide PET/CT finding, 2. Original articles published in peer reviewed journals, 3. No restrictions with respect to language, geographical limits or date, and 4. No restrictions regarding study design, single cases (including illustrative examples in reviews and editorials) were included. A SSTR PET incidentaloma was defined as findings unknown prior to SSTR PET or conditions with unknown potential uptake of SSTR-targeting tracers.
The following predefined exclusion criteria were used: 1. Pathological findings that matched scan indication, 2) Known organ specific disease and/or incidental findings confirmed on other scan modality prior to SSTR PET, 3. Studies not published in peer review (i.e., conferences, annual meetings etc.), and 4. Articles and/or cases with insufficient information and/or lack of confirmed diagnosis/pathology.
The inclusion and exclusion criteria were utilized on both a study and case level.
Two physicians (MB and FG) independently reviewed the titles and abstracts of the retrieved articles. The same two physicians then independently reviewed the full-text version of the remaining articles to determine their eligibility for inclusion. Disagreements were resolved by a third author (CA or HZ).
Data extraction
The following data were extracted from the included studies: author, publication year, impact factor of journal, country, study design, imaging indication, choice of tracer, organ of incidental findings, number of patients included in respective study, number of patients with sufficient follow-up, and the confirmed diagnosis. This data was extracted by one reviewer (MB) and controlled by a second reviewer (FG).
In cases where it was unclear whether a reported finding was incidental, or there was a lack of confirmational diagnostics, the reported finding was excluded from the analysis. These unclear cases were discussed between all of the authors (MB, FG, CA and HZ).
Synthesis
Incidental findings were grouped based on the anatomical location of the respective incidental findings. Incidental findings were then grouped as malignant or benign based on final confirmed diagnosis and/or pathology.
Statistics
Statistics in this review are descriptive. Due to many included case-studies and small sample size studies, no analysis of quality of evidence was conducted. Regarding reported incidental findings, no statistical meta-analysis was conducted due to few cohort studies and due to heterogeneity in study design.
Results
Included studies and study demographics
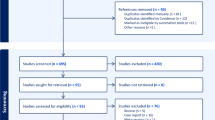
The systematic literature search identified 395 individual publications from four databases, which was reduced to 259 papers after removal of duplicates. A total of 195 papers were rejected based on title and abstract, and 64 reports were retrieved for full-text reading.
Forty-three studies were excluded after a full text readthrough.
Finally, 21 papers were included in the present systematic review. The search and inclusion process are summarized in Fig. 1. All studies were published in English. The majority of the studies were conducted in Europe and North America. Studies included were retrospective cohort studies on incidental SSTR PET/CT findings in a specific organ (n = 2888, 7/21) or case reports (n = 18, 14/21). A total of 2906 study subjects were included. Most included study subjects (n = 2888, 99%) were from cohort studies, the remaining subjects were from case reports (n = 18, 1%). Among the study subjects, incidental findings were reported in 187 patients (6%). Finally, a total of 133 patients had sufficient diagnostic follow-up and were included in the final analysis: 16 patients were from case reports and 117 patients were from cohort studies (Tables 1 and 2).
Imaging characteristics
68 Ga-DOTATATE was the most common tracer (15 out of 21 studies. 71%) followed by 68 Ga-DOTATOC (n = 4, 19%) and 68 Ga-DOTANOC (n = 2, 10%). All studies were conducted using a PET/CT-system.
In most studies, the scan indication was known or suspected neuroendocrine tumor (NET) (n = 15, 71%), comprising a total of 2896 patients (99.7%). In the final patient selection, 125 out of 133 patients with incidental SSTR PET findings (94%) were scanned on this indication. In the remaining 8 cases, the scan indication was not presented in the paper.
Results: incidental findings
On a case level, most incidental SSTR PET findings were seen in the thyroid gland (n = 65, 49% of all incidental findings), followed by spine (n = 30, 23%), cranial findings (n = 26, 20%), breast (n = 6, 4%) and miscellaneous locations (n = 6, 4%) (Table 2).
Thyroid
Four studies (19%) assessed or contained cases of incidental thyroid SSTR PET/CT uptake [11, 12, 14, 15]. Incidental uptake in the thyroid gland was the most prevalent of all included incidental SSTR PET/CT findings. A total of 65 patients had incidental uptake in the thyroid gland: 25 patients had focal uptake and 40 patients had diffusely elevated uptake (Table 3). In the retrospective cohort studies by Nockel et al. and Kunikowska et al. the incidence of thyroid incidental findings on SSTR PET was estimated to be 11% (26/237) and 4% (46/1150), respectively [11, 12].
Incidental focal SSTR-uptake was proven to be due to malignancy in five of 25 cases with focal uptake (20%): Four cases of papillary carcinomas and 1 case of medullary carcinomas were revealed [11, 12, 14]. The remaining patients with focal incidental SSTR-uptake were consistent with adenoma (n = 7, 28%), multinodular goiter (n = 5, 20%), Hashimotos and coexisting multinodular goiter (n = 6, 24%), Hashimotos (n = 1, 4%), and finally physiological, nodular thyroid gland (n = 1, 4%) [11, 12, 15]. No malignancy was found with supplementary diagnostics in patients with diffuse elevated uptake (Table 3) [11, 12, 15].
Cranial
A total of 26 cranial SSTR PET incidentalomas (20%) were reported. Five cases (19%) were proven to be malignant: 4 cases of skull base paragangliomas (15%) and 1 case of cerebellar medulloblastoma (4%) [16, 17].
In benign cases, meningiomas were the most frequent finding (n = 12, 46%) [8, 17,18,19]. In the study by Cleary et al. (2016), six incidental SSTR PET findings were without clear anatomical structures on supplementary diagnostic imaging and were hypothesized to be due to physiological uptake in veins (n = 3) and sinuses (n = 2); however, the last incidental finding was of unknown etiology in the right frontal lobe (SUVmax 5.82) without correlating lesion on non-contrast MRI (Table 4) [20].
Breast
Our search revealed four studies reporting a total of six cases of incidental SSTR PET uptake in the breast with sufficient follow-up. On further diagnostics, four out of six incidentalomas (67%) were of malignant origin (two invasive ductal carcinomas and two patients with breast cancer not further specified), and in one of these cases, metastases to axillary lymph nodes were visible on SSTR PET/CT [15, 21, 22]. Benign incidental findings were asymmetric idiopathic gynecomastia (n = 1) and breast fibroadenoma (n = 1) [8, 23].
Spine
Regarding incidental spine SSTR PET findings, our study revealed 1 cohort study and 2 case reports.
In the case study by Has Simsek et al., the lesion of the spine was proven to be a malignant solitary bone plasmacytoma on further diagnostics [24]. In the single center cohort studies by Gauthe et al. (2018), a total of 28 patients with incidental spine SSTR PET findings were consistent with vertebral hemangiomas on diagnostic imaging [25]. The case report by Skoura et al. had similar results with a spine-lesion proven to be vertebral hemangioma [26].
Miscellaneous
Studies reporting incidental SSTR PET uptake in other locations were case studies (n = 7). Two cases proved to be malignant (29%), including retiform hemangioendothelioma in soft tissue and a non-Hodgkins lymphoma in a lymph node [15, 27]. The remaining five benign cases revealed a pleomorphic adenoma in the parotid gland, parathyroid adenoma in close relation to the thyroid gland, elastofibroma dorsi in soft tissue, a uterine leiomyoma, and fibrous dysplasia in the femoral bone [8, 28,29,30,31].
Discussion
This is – to the best of the authors’ knowledge—the first review that aimed to assess incidental SSTR PET/CT findings. Based on the cohort studies, the overall incidence of incidental SSTR PET findings was approximately 4%.
The thyroid gland was the most frequently reported location of incidental SSTR uptake with an estimated incidence of between 4 and 11% in patients with known or suspected NET. In almost two thirds of the cases with unexpected thyroid uptake, the SSTR uptake was diffusely elevated, and no malignant cause was found on further investigations. In contrast, focal uptake in the thyroid carried a 20% risk of malignancy. These results imply that all incidental focal thyroid findings should be further investigated. Incidental thyroid uptake is also detected in approximately 2% of all FDG PET/CTs and 4% of all PSMA PET/CTs [32, 33]. Similarly, focal thyroid uptake on FDG PET/CT is associated with a high risk of malignancy (35%) whereas it is approximately 4% in diffuse uptake. For PSMA PET/CT, the risk of malignancy for focal uptake is 15% and no cases of malignancy in diffuse uptake have been reported [32,33,34].
Many of the included patients with incidental thyroid SSTR uptake had known disease of the thyroid gland prior to SSTR PET/CT. This may cause bias in the population, however, we only included cases included in the review which exhibited much higher SSTR uptake than normal physiologic thyroid uptake which had been deemed as abnormal by the interpreting nuclear medicine physician, for example Nockel et al. defined increased thyroid SSTR uptake as SUVmax above liver or salivary gland [12]. If such information was not available the cases were excluded. Likewise, cases of known thyroid disease were excluded if they were reported to have been confirmed with another scan modality prior to SSTR PET and/or known to be malignant prior to PET.
It is worth mentioning that a few studies were not included in the final synthesis due to their results not being published in peer reviewed journals or due to insufficient information. These studies reported additional incidental thyroid findings e.g. Sobral-Violante et al., found seven cancers among 16 incidental thyroid findings [35].
Following incidental thyroid uptake, SSTR uptake in the spine and cranial region were the most common localizations of incidental findings. Not surprisingly, meningiomas were the most frequent intracranial finding. In our study, we defined meningiomas as benign findings since in most cases they are low grade type 1 neoplasms, as defined by the World Health Organisation, and only very few are atypical, higher grade meningiomas [36]. It should therefore be stressed that incidental findings resembling meningiomas should always be followed up in accordance with standard regimens. Similarly, pituitary adenomas were defined as benign with elevated SSTR uptake on PET, however no further details regarding the incidental pituitary findings were reported. In other studies, pituitary adenomas and non-functioning pituitary adenomas have lower uptake on SSTR PET/CT indicating that elevated SSTR uptake is common in normal pituitary tissue [37, 38]. Of interest, SSTR PET/CT has also been valuable in localizing ectopic Cushing syndrome, however our search did include any studies with incidental uptake in ectopic ACTH producing tumors on SSTR PET/CT [39]. One study by Parghane et al. reported four patients with SSTR uptake in skull base paragangliomas in a study population of NET patients referred to 177Lu-DOTATATE Peptide Receptor Radionuclide Therapy (PRRT), a study population we suspect has a higher prevalence of paraganglioma of unknown malignant potential. We therefore suspect our calculated risk of malignancy of cranial incidental findings to be higher than in a general population undergoing a SSTR PET-scan.
Incidental spine SSTR PET/CT findings were seldom malignant when excluding known NET metastases. It should be noted that almost all cases included in our study were from the study by Gauthe et al. and represent cases of vertebral hemangioma (93%). In this study the authors reported even more incidental findings in degenerative spinal lesions, but unfortunately these cases could not be included in our final synthesis as the DOTATOC-avidity and exact number of study subjects with benign non-vertebral hemangioma lesions were unclear.
Although rarely encountered, incidental breast SSTR PET/CT findings carried the highest risk of malignancy (67%). Based on our results, rapid diagnostic evaluation of incidental breast SSTR PET/CT is advised (Table 5). The study by Elgeti et al. is the only retrospective cohort study on incidental breast uptake on SSTR PET/CT with an estimated incidence of 6% which is higher than the reported incidental breast uptake by FDG PET of approximately 0.6% of all FDG PET/CT scans with a wide variety in reported malignancy risk ranging from 27–85% [40, 41].
Although SSTR-tracers has shown lymphomas to be SSTR-tracer avid, our search revealed only one case of incidentally detected of non-Hodgkin lymphoma. Lymphomas should therefore also be considered a potential pitfall although it is rarely incidentally encountered according to our systematic review [42, 43].
Our study has several limitations. Most importantly, the present systematic review revealed a lack of high-quality data preventing the planned meta analyses, the vast majority were single center studies on specific organs and case reports. Similarly, a publication bias is present: there are relatively few studies reporting SSTR PET/CT and—on a case level—there are even fewer studies reporting incidental SSTR PET findings. As highlighted above, some incidental findings could not be included in our final synthesis due to lack of information in the reported cases. One must suspect that SSTR PET incidental findings are heavily underreported leading to publication bias in our study. Also, the majority of included studies are case report which will most likely skew the results of our review towards malignant or rare pathologies. Additionally, some organs are more well-studied than others. Most of the included study subjects were from retrospective cohort studies conducted at single centers focusing on a single organ. These studies, although valuable, can result in a biased study population when conducting a systematic review on incidental findings on SSTR PET in general.
Also, due to limited patient information in some cases, it is doubtful whether these reported incidental findings were true SSTR PET incidental findings or represented already known or secondary lesions to the primary NET initially indicated on the SSTR PET. Therefore, on a case level, our study carries a risk of selection bias. As described above, some cases from excluded studies could have impacted our study if they had met the pre-defined inclusion and exclusion criteria.
Conclusion
We performed a systematic review of the available studies on incidental SSTR PET findings and found that most atypical findings of uptake on SSTR PET were located in the thyroid gland, spine, and cranially. The risk of malignancy was greatest for incidentalomas located in the breasts and in patients with focal uptake in the thyroid gland and in the brain. The present study can provide guidance in the interpretation of atypical findings on SSTR PET/CT and in the counseling of clinicians.
Availability of data and materials
All data generated or analysed during this study are included in the present article. Search strings are provided in supplementary materials.
Abbreviations
- PET/CT:
-
Positron emission tomography / computer tomography
- SSTR:
-
Somatostatin receptor
- SSTR PET/CT:
-
68 Ga-DOTA-conjugated somatostatin receptor-targeting peptide PET/CT
- NET:
-
Neuroendocrine tumors
- DOTA:
-
1,4,7,10-Tetraazacyclodecane-1,4,7,10-tetraacetic acid
- PRRT:
-
Peptide Receptor Radionuclide Therapy
References
Theodoropoulou M, Stalla GK. Somatostatin receptors: from signaling to clinical practice. Front Neuroendocrinol. 2013;34(3):228–52.
Johnbeck CB, Knigge U, Kjaer A. PET tracers for somatostatin receptor imaging of neuroendocrine tumors: current status and review of the literature. Future Oncol. 2014;10(14):2259–77.
Sanli Y, et al. Neuroendocrine Tumor Diagnosis and Management: (68)Ga-DOTATATE PET/CT. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2018;211(2):267–77.
Evangelista L, et al. Ga-68 DOTA-peptides and F-18 FDG PET/CT in patients with neuroendocrine tumor: a review. Clin Imaging. 2020;67:113–6.
Treglia G, et al. Diagnostic performance of Gallium-68 somatostatin receptor PET and PET/CT in patients with thoracic and gastroenteropancreatic neuroendocrine tumours: a meta-analysis. Endocrine. 2012;42(1):80–7.
Virgolini I, et al. Current knowledge on the sensitivity of the (68)Ga-somatostatin receptor positron emission tomography and the SUVmax reference range for management of pancreatic neuroendocrine tumours. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2016;43(11):2072–83.
Kunikowska J, et al. Semiquantitative analysis and characterization of physiological biodistribution of (68)Ga-DOTA-TATE PET/CT. Clin Nucl Med. 2012;37(11):1052–7.
Kuyumcu S, et al. Physiological and tumoral uptake of (68)Ga-DOTATATE: standardized uptake values and challenges in interpretation. Ann Nucl Med. 2013;27(6):538–45.
Prasad V, Baum RP. Biodistribution of the Ga-68 labeled somatostatin analogue DOTA-NOC in patients with neuroendocrine tumors: characterization of uptake in normal organs and tumor lesions. Q J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2010;54(1):61–7.
Kroiss A, et al. 68Ga-DOTA-TOC uptake in neuroendocrine tumour and healthy tissue: differentiation of physiological uptake and pathological processes in PET/CT. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2013;40(4):514–23.
Kunikowska J, et al. How often do we see incidental 68Ga-DOTATATE thyroid uptake in PET/CT in patients with neuroendocrine tumours? Endokrynol Pol. 2015;66(3):231–6.
Nockel P, et al. The rate and clinical significance of incidental thyroid uptake as detected by gallium-68 DOTATATE positron emission tomography/computed tomography. Thyroid. 2016;26(6):831–5.
Moher D, et al. Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: the PRISMA statement. BMJ. 2009;339: b2535.
Mahajan S, Shaha A, Grewal RK. Incidental detection of medullary thyroid carcinoma by 68Ga-DOTATATE PET/CT in a patient with neuroendocrine tumor liver metastases. Clin Nucl Med. 2018;43(2):136–8.
Yamaga LYI, Wagner J, Funari MBG. 68Ga-DOTATATE PET/CT in nonneuroendocrine tumors: a pictorial essay. Clin Nucl Med. 2017;42(6):e313–6.
Chan M, Hsiao E. Incidental finding of cerebellar medulloblastoma on 68Ga-DOTATATE PET/CT in a patient with appendiceal carcinoid. Clin Nucl Med. 2016;41(11):886–7.
Parghane RV, Talole S, Basu S. Prevalence of hitherto unknown brain meningioma detected on (68)Ga-DOTATATE positron-emission tomography/computed tomography in patients with metastatic neuroendocrine tumor and exploring potential of (177)Lu-DOTATATE peptide receptor radionuclide therapy as single-shot treatment approach targeting both tumors. World J Nucl Med. 2019;18(2):160–70.
Lasocki A, et al. Cerebellar haemangioblastoma discovered incidentally on (68)Ga-DOTA-octreotate examination. Clin Neurol Neurosurg. 2016;144:20–2.
Law WP, et al. The ‘double pituitary hot spot’ sign of skull base meningioma on gallium-68-labelled somatostatin analogue PET. J Med Imaging Radiat Oncol. 2013;57(6):680–3.
Cleary JO, et al. The significance of incidental brain uptake on 68Ga-DOTATATE PET-CT in neuroendocrine tumour patients. Nucl Med Commun. 2016;37(11):1197–205.
Sampaio Vieira T, et al. Incidental finding of a breast carcinoma on Ga-68-DOTA-1-Nal3-octreotide positron emission tomography/computed tomography performed for the evaluation of a pancreatic neuroendocrine tumor: a case report. Medicine (Baltimore). 2018;97(36): e11878.
Elgeti F, et al. Incidental detection of breast cancer by 68Ga-DOTATOC-PET/CT in women suffering from neuroendocrine tumours. Nuklearmedizin. 2008;47(6):261–5.
Pandika V, Covington MF. Incidental uptake in Benign Gynecomastia on 68Ga-DOTATATE PET/CT. Clin Nucl Med. 2019;44(10):799–800.
Has Şimşek D, et al. An incidental solitary plasmacytoma of bone mimicking neuroendocrine tumor metastasis on 68Ga-DOTATATE positron emission tomography/computed tomography. Mol Imaging Radionucl Ther. 2016;25(3):147–9.
Gauthé M, et al. Vertebral metastases from neuroendocrine tumours: how to avoid false positives on (68)Ga-DOTA-TOC PET using CT pattern analysis? Eur Radiol. 2018;28(9):3943–52.
Skoura E, et al. Adolescent with 68Ga DOTATATE-avid vertebral hemangioma mimicking metastasis in PET imaging. Clin Nucl Med. 2015;40(7):e378–9.
Vadrucci M, Vandoni A, Gilardi L. Incidental detection of retiform hemangioendothelioma by 68Ga DOTATOC PET/CT. Clin Nucl Med. 2017;42(2):149–51.
Laurens ST, Netea-Maier RT, Aarntzen EJHG. 68Ga-DOTA-TOC uptake in pleomorphic adenoma. Clin Nucl Med. 2018;43(7):524–5.
Ishiyama M, Vesselle H. 68Ga DOTATATE PET/CT imaging of elastofibroma dorsi. Clin Nucl Med. 2018;43(5):e154–5.
Liu H, Zhang W, Chen Y. Incidental 68Ga-DOTATATE uptake in uterine leiomyoma. Endocrine. 2020;68(1):233–4.
Arora S, et al. Incidental detection of parathyroid adenoma on somatostatin receptor PET/CT and incremental role of (18)F-fluorocholine PET/CT in MEN1 syndrome. Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2018;52(3):238–42.
Gossili F, Petersen LJ, Zacho HD. The frequency of thyroid incidental findings and risk of malignancy detected by (68)Ga-labeled prostate-specific membrane antigen PET/CT in prostate cancer. Hell J Nucl Med. 2020;23(3):240–5.
Soelberg KK, et al. Risk of malignancy in thyroid incidentalomas detected by 18F-fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography: a systematic review. Thyroid. 2012;22(9):918–25.
Gedberg N, et al. The frequency of focal thyroid incidental findings and risk of malignancy detected by 18F-fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography in an iodine deficient population. Diagnostics (Basel). 2018;8(3):46.
Sobral Violante LC, et al. Thyroid incidentalomas detected by 68Ga-dotanoc PET/CT-correlation of clinical findings and maximum standardized value uptake (SUVmax). Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2014;41:S189.
Louis DN, et al. The 2021 WHO classification of tumors of the central nervous system: a summary. Neuro Oncol. 2021;23(8):1231–51.
Wang H, et al. PET/MRI in the diagnosis of hormone-producing pituitary microadenoma: a prospective pilot study. J Nucl Med. 2018;59(3):523–8.
Tjörnstrand A, et al. Lower (68) Ga-DOTATOC uptake in nonfunctioning pituitary neuroendocrine tumours compared to normal pituitary gland-A proof-of-concept study. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf). 2020;92(3):222–31.
Santhanam P, et al. PET imaging in ectopic Cushing syndrome: a systematic review. Endocrine. 2015;50(2):297–305.
Aarstad EM, et al. Prevalence of focal incidental breast uptake on FDG-PET/CT and risk of malignancy: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur J Hybrid Imaging. 2019;3(1):16.
Andersen JD, Zacho HD, Petersen LJ. The frequency and malignancy rate of incidental focal breast lesions identified by 18F-fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography. Nucl Med Commun. 2021;42(1):93–100.
Bashir A, et al. Pearls and pitfalls in interpretation of 68Ga-DOTATOC PET imaging. Clin Nucl Med. 2020;45(6):e279–80.
Ruuska T, et al. Somatostatin receptor expression in lymphomas: a source of false diagnosis of neuroendocrine tumor at (68)Ga-DOTANOC PET/CT imaging. Acta Oncol. 2018;57(2):283–9.
Acknowledgements
NA
Funding
No funding was received to sponsor this project.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Authors are credited in the presented order of authorship. FG and HZ developed the concept. MB was responsible for the completion of the present project. FG searched databases. FG and MB screened literature and extracted data. CA and HZ was consulted in cases of disagreement (between MB and FG). MB pooled and synthesized the data, and created all figures and tables. Drafts were written by MB and FG. All authors (MB, FG, CA and HZ) revised manuscript drafts and contributed to the final content. The author(s) read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable (NA).
Consent for publication
NA
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/. The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver (http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
About this article
Cite this article
Bentestuen, M., Gossili, F., Almasi, C.E. et al. Prevalence and significance of incidental findings on 68 Ga-DOTA-conjugated somatostatin receptor-targeting peptide PET/CT: a systematic review of the literature. Cancer Imaging 22, 44 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1186/s40644-022-00484-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s40644-022-00484-0