Abstract
Background
Extracellular superoxide dismutase (ECSOD) protects nitric oxide (NO) bioavailability by decreasing superoxide levels and preventing peroxynitrite generation, which is important in maintaining renal blood flow and in preventing acute kidney injury. However, the profile of ECSOD expression after sepsis is not fully understood. Therefore, we intended to evaluate the content and gene expression of superoxide dismutase (SOD) isoforms in the renal artery and their relation to renal blood flow.
Methods
Sepsis was induced in Wistar rats by caecal ligation and perforation. Several times after sepsis induction, renal blood flow (12, 24 and 48 h); the renal arterial content of SOD isoforms, nitrotyrosine, endothelial and inducible nitric oxide synthase (e-NOS and i-NOS), and phosphorylated vasodilator-stimulated phosphoprotein (pVASP); and SOD activity (3, 6 and 12 h) were measured. The influence of a SOD inhibitor was also evaluated.
Results
An increase in ECSOD content was associated with decreased 3-nitrotyrosine levels. These events were associated with an increase in pVASP content and maintenance of renal blood flow. Moreover, previous treatment with a SOD inhibitor increased nitrotyrosine content and reduced renal blood flow.
Conclusions
ECSOD appears to have a major role in decreasing peroxynitrite formation in the renal artery during the early stages of sepsis development, and its application can be important in renal blood flow control and maintenance during septic insult.
Similar content being viewed by others
Background
Sepsis is a complex syndrome characterized by an imbalance between pro-inflammatory and anti-inflammatory responses to a pathogen [1, 2]. During its development, a large amount of reactive oxygen species (ROS) and nitric oxide (NO) are produced [3, 4]. In this context, superoxide radicals can react with NO to produce peroxynitrite [5, 6]. Peroxynitrite is a powerful oxidizing agent that is more cytotoxic than NO and is implicated in endothelial dysfunction [7].
The control of peroxynitrite levels and the bioavailability of NO depend, at least in part, on SOD activity [5, 6]. Superoxide dismutases (SODs) are metalloenzymes that catalyse the dismutation of the superoxide radical to hydrogen peroxide and oxygen. Mammals have three distinct isoforms of SOD; copper/zinc-SOD (Cu/ZnSOD, SOD1), manganese-SOD (MnSOD, SOD2) and extracellular (ECSOD, SOD3). ECSOD is predominantly localized in the extracellular matrix and the extracellular fluids depending on the presence of a carboxy-terminal heparin-binding domain [5, 6]. ECSOD is secreted by various cells and binds to glycosaminoglycans in the vascular extracellular matrix [8–10], maintaining NO bioavailability [11, 12]. Since the production of peroxynitrite is associated with decreased renal blood flow and acute kidney injury [13, 14], ECSOD could play a major protective role in this context, but little is known about its modulation during sepsis.
Recently, we have demonstrated the role of ECSOD in lung injury after sepsis development [15]. In a second set of experiments, we hypothesized that sepsis induces a decrease in ECSOD levels in the renal artery and that this effect is associated with nitrosative stress that decreases global renal blood flow and promotes acute kidney injury.
Methods
Animals
Male Wistar rats (350–400 g) were obtained from our own breeding colony. They were caged in groups of five with free access to food and water and were maintained on a 12-h light–dark cycle (6:00–18:00 h) in a temperature-controlled colony room (22 ± 1 °C). These conditions were maintained constantly throughout the experiments. The research protocol was approved by the Ethical Committee for Animal Experimentation of Universidade do Extremo Sul Catarinense under protocol number 21/2011, and the procedures are in accordance with the National Institutes of Health guidelines for animal care.
Caecal ligation and perforation (CLP) surgery
The animals were subjected to CLP as previously described [15]. Briefly, rats were anaesthetized with ketamine and, under aseptic conditions, a 3-cm midline laparotomy was performed to allow for exposure of the caecum with the adjoining intestine. The caecum was tightly ligated with a 3.0-silk suture at its base, below the ileocaecal valve, and was perforated once with a 14-gauge needle. The caecum was then gently squeezed to extrude a small amount of faeces, returned to the peritoneal cavity, and the laparotomy was closed with 4.0-silk sutures. Animals were resuscitated with normal saline (50 mL/kg subcutaneous) immediately, 12 and 24 h after CLP, and were given antibiotics (ceftriaxone at 30 mg/kg and clindamycin 25 mg/kg) every 6 h and SC for the entire duration of the experiments. In a set of experiments, a non-specific SOD inhibitor, diethyldithiocarbamic acid diethylammonium (DETC, i.v. 7.5 mg/kg) [16, 17], was administered immediately after sepsis induction. All animals were returned to their cages with free access to food and water. In the sham-operated group, the rats were submitted to all surgical procedures, but the caecum was neither ligated nor perforated. All animals were observed and developed signs of infection (piloerection, lethargy, tachypnea or weight loss). The number of animals that survived is consistent with our previous reports.
Direct measurement of renal blood flow
In this set of experiments, the animals were anaesthetized with ketamine/xylazine (90/15 mg/kg, i.m.) and a transverse abdominal incision was performed to assess the posterior right subhepatic space, allowing for the visualization of the right kidney. A laser probe (model VP1) connected to a laser Doppler blood flow monitor (moorVMS-LDF2, Moor Instruments, England) was carefully placed directly onto the kidney, allowing for the measurement of renal blood flow (in arbitrary units). The probe was kept in this position, and the surgical incision was covered with gauze sponges soaked in sterile phosphate-buffered saline to protect the kidney from drying out. The laser probe remained tightly fixed on the kidney surface, and very stable and constant trace recordings of renal blood flow were obtained. During the experiments, the animals were maintained on a warming pad and allowed to breathe spontaneously. An interval of 20 min was observed before the measurement of basal values and renal blood flow was measured for an additional 15 min [18].
Renal artery extraction and sample preparation
The animals were anaesthetized with ketamine and killed by decapitation at different times after surgery. The renal arteries were dissected out under ×4 magnification on ice and stored at −80 °C for posterior analyses.
Total SOD activity
SOD activity was measured by the inhibition of adrenaline auto-oxidation followed spectrophotometrically as previously described [19].
Immunoblotting
Samples were lysed in Laemmli buffer (62.5 mM Tris-HCl, pH 6.8, 1% (w/v) SDS, 10% (v/v) glycerol), and equal amounts of protein were fractionated by SDS-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (SDS-PAGE) and electroblotted onto nitrocellulose membranes. Protein loading and electroblotting efficiency were verified through Ponceau S staining, and the membrane was blocked in Tween–Tris-buffered saline (TTBS: 100 mM Tris-HCl, pH 7.5, containing 0.9% NaCl and 0.1% Tween-20) containing 5% albumin. Membranes were incubated overnight at 4 °C with rabbit polyclonal antibodies against SOD1 (1:400), SOD2 (dilution range, 1:400), SOD3 (dilution range, 1:750), iNOS (1:750), eNOS (1:750), pVASP (1:600) or β-actin (1:2000) and then washed with TTBS. Anti-rabbit immunoglobulin G (IgG) peroxidase-linked secondary antibody was incubated with the membranes for 1 additional hour (1:10000 dilution range). The membranes were washed again, and the immunoreactivity was detected by enhanced chemiluminescence using an ECL Plus kit. Densitometric analysis of the films was performed with ImageQuant software. Blots were developed to be linear in the range used for densitometry. All results were expressed as relative ratios between SOD1, SOD2, SOD3, iNOS, eNOS and pVASP immunocontent and the β-actin internal control immunocontent.
Analysis of gene expression by semi-quantitative RT-PCR
All transcriptional analyses were performed in samples that were different between groups in the immunocontent in the blotting analysis with the goal of evaluating the contribution of each gene to the immunocontent of each enzyme. Total RNA was isolated from rat renal arteries using TRIzol® reagent (Invitrogen, Carlsbad, CA, USA) in accordance with manufacturer instructions. The purity of the RNA was spectrophotometrically quantified by calculating the ratio between absorbance values at 260 and 280 nm, and its integrity was confirmed by electrophoresis through a 1.0% agarose gel. Afterwards, cDNA species were synthesized using ImProm-II™ Reverse Transcription System (Promega®) following the supplier's instructions. The cDNA products (1 μL) were used as a template for each PCR amplification. PCR parameters were first optimized, and then reactions were performed allowing for product detection within the linear phase of mRNA transcript amplification for each primer pair. PCR for the β-actin gene was performed in a total volume of 20 μL using 0.1 μM of each primer, 0.2 μM dNTP, 1.6 mM MgCl2 and 0.2 U Taq platinum DNA polymerase (Invitrogen). In the PCR for SOD1, SOD2 and SOD3, the reaction was performed in a total volume of 25 μL using 0.2 μM of each primer, 0.2 μM dNTP, 1.6 mM MgCl2 and 0.25 U Taq platinum DNA polymerase (Invitrogen). Conditions for sod 1, sod 2 and sod 3 PCR were as follows: an initial 1-min denaturation step at 94 °C; 1 min at 94 °C, a 1-min annealing step at 60 °C, and a 1-min extension step at 72 °C for 30 cycles; and a final 10 min extension at 72 °C. Conditions for β-actin PCR were as follows: an initial 1-min denaturation step at 94 °C; 1 min at 94 °C, a 1-min annealing step at 54 °C, and a 1-min extension step at 72 °C for 35 cycles; and a final 10-min extension at 72 °C. For each PCR set, a negative control was included. PCR products were analysed on a 1% agarose gel containing GelRed® and visualized with ultraviolet light. The Low DNA Mass Ladder (Invitrogen) was used as a molecular marker, and samples were normalized by employing β-actin as a constitutive gene. The band intensities were measured by optical densitometry analysis, and the enzyme/β-actin mRNA ratios were established for each treatment using the freeware Image J 1.37. Each experiment was repeated at least four times using RNA isolated from independent extractions.
Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) for 3-nitrotyrosine contents
An indirect ELISA assay was performed according to the manufacturer’s instructions. Briefly, microtiter plates were coated for 24 h with the samples diluted 1:2 in PBS with 5% albumin. Plates were then washed four times with wash buffer (PBS with 0.05% Tween-20), and the antibody was added to each plate for 2 h at room temperature. After washing, a second incubation with anti-rabbit antibody peroxidase conjugated (diluted 1:1000) for 1 h at room temperature was carried out. After the addition of substrates (hydrogen peroxide and tetramethylbenzidine 1:1, v/v), the samples were read at 450 nm in a plate spectrophotometer.
Statistical analysis
Data are expressed as the mean ± S.E.M and compared by the independent t test or ANOVA followed by the Tukey post hoc test depending on the sample characteristics. Statistical significance was set at p < 0.05.
Results
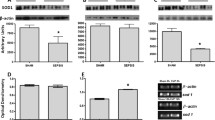
In this model, renal blood flow was maintained at early stages after sepsis induction (Fig. 1). Compared to sham animals, renal blood flow remained unchanged at least until 48 h after CLP (Fig. 1). Since SOD is a factor in renal blood flow control, we further investigated the protein content and expression of SOD in the renal arteries. Cu/ZnSOD protein content decreased at 6 h, but not at 3 or 12 h, after the induction of sepsis (Fig. 2a–c), which was not secondary to the downregulation of its gene expression (Fig. 2d). MnSOD content decreased from 6 to 12 h (Fig. 3a –c), but there was no downregulation of its gene expression (Fig. 3d, e). In contrast, ECSOD increased at 6 and 12 h after surgery (Fig. 4a –c), which could be partially secondary to an increase in its gene expression (Fig. 4d, e). The total SOD activity in the renal arteries was increased in septic animals when compared to sham animals at 6 and 12 h after sepsis (2.3 ± 0.9 vs 30.1 ± 9, p < 0.01; 2.6 ± 1.1 vs 34.1 ± 12, p < 0.01, respectively).
Superoxide dismutase 1 (SOD1) immunocontent and gene expression after sepsis induction by CLP. Three times, 3 h (a), 6 h (b) and 12 h (c), after sepsis, the renal arteries were isolated, and the content of SOD1 was quantified by immunoblot. Representative western blots show samples from shams in the first bands and samples from sepsis in the last bands, represented in equal number. The densitometric analysis quantification is depicted in bar graphs. Gene expression of SOD1 was measured by RT-PCR, with b-actin as control, 6 h (d) after the induction of sepsis. The results are expressed as optical densitometry for the mean ± S.E.M. (n = 6 animals each group). *p < 0.05 compared to the sham group
Superoxide dismutase 2 (SOD2) immunocontent and gene expression after sepsis induction by CLP. Three times, 3 h (a), 6 h (b) and 12 h (c), after sepsis, the renal arteries were isolated, and the content of SOD2 was quantified by immunoblot. Representative western blots show samples from shams in the first bands and samples from sepsis in the last bands, represented in equal number. The densitometric analysis quantification is depicted in bar graphs. Gene expression of SOD2 was measured by RT-PCR, with b-actin as control, 6 h (d) and 12 h (e) after the induction of sepsis in sham and sepsis groups. The results are expressed as optical densitometry for the mean ± S.E.M. (n = 6 animals in each group). *p < 0.05 compared to the sham group
Superoxide dismutase 3 (SOD3) immunocontent and gene expression after sepsis induction by CLP. Three times, 3 h (a), 6 h (b) and 12 h (c), after sepsis, the renal arteries were isolated, and the content of SOD3 was quantified by immunoblot. Representative western blots show samples from shams in the first bands and samples from sepsis in the last bands, represented in equal number. The densitometric analysis quantification is depicted in bar graphs. Gene expression of SOD3 was measured by RT-PCR, with b-actin as control, 6 h (d) and 12 h (e) after the induction of sepsis in sham and sepsis groups. The results are expressed as optical densitometry for the mean ± S.E.M. (n = 6 animals in each group). *p < 0.05 compared to the sham group
We further measured the levels of nitrotyrosine, which decreased at 6 and 12 h after sepsis (Fig. 5a –c). However, the immunocontent of iNOS was decreased only 6 h after sepsis (Fig. 5d –f), and there were no differences in the content of eNOS between the groups and time (data not shown). To further evaluate the mechanisms involved in the preservation of renal blood flow, we analysed the content of pVASP, which increased at 6 and 12 h after sepsis induction (Fig. 6).
Levels of 3-nitrotyrosine by ELISA and iNOS expression by blotting after sepsis induction by CLP. At times 3 h (a), 6 h (b) and 12 h (c) after sepsis induction, the renal arteries were isolated, and the content of 3-nitrotyrosine was quantified by ELISA and expressed in terms of nitrotyrosine concentration/absorbance. The content of iNOS was measured by immunoblot 3 h (d), 6 h (e) and 12 h (f) after sepsis. Representative western blots showed samples from shams in the first bands and samples from sepsis in the last bands, represented in equal number. The densitometric analysis quantification is depicted in bar graphs. The results are expressed as the mean ± S.E.M. in arbitrary units. (n = 6 animals in each group). *p < 0.05 compared to the sham group
Levels of phosphorylated vasodilator-stimulated phosphoprotein (pVASP) expression after sepsis induction. Three times, 3 h, 6 h, and 12 h after sepsis, the renal arteries were isolated and the content of pVASP was quantified by immunoblot. Representative western blots are positioned above the correspondent bar group, in each sham and sepsis group, and densitometric analyses quantification is depicted in bar graphs. The results are expressed as the mean ± S.E.M. in VASPSer239 phosphorylation (arbitrary units) (n = 6 animals in each group). *p < 0.05 compared to the sham group
To establish that the early increase in SOD content and activity was associated with the control of renal blood flow, a SOD inhibitor was injected early after sepsis. SOD inhibition induced a decrease in renal blood flow at 48 h after sepsis induction, but not at 12 and 24 h (Fig. 7a) and not in sham animals (data not shown). To determine whether this treatment truly interfered with SOD activity, we demonstrated that it induced a decrease in SOD activity (from 12 to 48 h after sepsis, Fig. 7b) but not in SOD protein content (data not shown). Since the working hypothesis proposes that SOD activity maintains NO bioavailability, we further measured the nitrotyrosine content that was increased by SOD inhibition from 24 to 48 h (Fig. 7c).
The effect of administration of a superoxide dismutase inhibitor on renal blood flow, superoxide dismutase activity and 3-nitrotyrosine content after sepsis induction. Immediately after sepsis induction, a SOD inhibitor, diethyldithiocarbamic acid diethylammonium (DETC, i.v. 7.5 mg/kg), was administered. Several times after sepsis induction (12, 24 and 48 h), renal blood flow was measured and (a) expressed as a percentage difference compared to the sham group; superoxide dismutase activity (b) was expressed in SOD (U/mg protein), and the 3-nitrotyrosine content (c) was expressed in nitrotyrosine content (arbitrary units). The dotted line represents sham renal blood flow. The values are presented as the mean ± S.E.M., n = 6 in each group. *p < 0.05, compared to CLP without SOD inhibitor at the same time point
Discussion
In a fluid-resuscitated model of sepsis, we have demonstrated that renal blood flow was maintained, at least in part, secondary to the upregulation of ECSOD and SOD activity in the renal arteries.
Acute kidney injury is a well-known, major complication in sepsis. In different models of sepsis, renal hypoperfusion occurs and is associated with the generation of peroxynitrite [20–22]. There are reports suggesting that peroxynitrite-induced PARP activation is involved in renal hypoperfusion and in impaired endothelium-dependent vasodilation [23]. In a model of endotoxaemia, ECSOD expression was decreased and was consequently associated with decreased renal blood flow [12, 24]. In general, in these models, the animals are not fully fluid resuscitated and antibiotic treatment is missing. Here, in a more clinically relevant model of sepsis, we demonstrated that renal blood flow could be maintained for at least 48 h, which is consistent with early goal-directed therapy to preserve microcirculation both in animal models and in humans [25–27]. In contrast, it was reported in a LPS model that, even when using fully balanced fluids, compromises in microvascular and renal functions occurred [28]. This unexpected result could be related to the regulation of NO production since peroxynitrite seems to be one of the most relevant mediators of sepsis-induced AKI [13, 20, 21].
SODs are the first defence system against superoxide anion radicals. Vascular smooth muscle cells secrete large amounts of ECSOD, and it is thought that these cells are the major source of the enzyme in the vascular wall [29]. Actually, ECSOD is widely expressed in the cardiovascular system and in the kidney [30], and it is critical to controlling 3-nitrotyrosine formation [31]. In addition, circulating microparticles from septic patients are able to increase ECSOD expression in the rat heart [32], which is consistent with our results. Therefore, despite the decreases in Mn and Cu/Zn SOD content after sepsis, there is an increase in total SOD activity that is probably associated with the observed increase in ECSOD. These results suggest that ECSOD is of major importance in maintaining kidney redox status early during sepsis. Actually, post-ischaemic renal vasoconstriction is associated with an impairment of endothelium-dependent NO-mediated vasodilation in renal vasculature [13, 33], but ECSOD overexpression prevents endothelial dysfunction and preserves blood flow [34]. It has also been demonstrated that a SOD mimetic decreased superoxide formation in the vascular compartment [35], which is consistent with our results. The maintenance of renal blood flow is probably mediated by SOD quenching of superoxide, causing a consequent decrease in peroxynitrite and improvement in vasorelaxation [36].
Therefore, if ECSOD is critical in regulating the redox state in the renal artery after sepsis, it can be expected that it could decrease 3-nitrotyrosine formation, which was, in fact, demonstrated in our model. Therefore, we propose that there is a decrease in the availability of superoxide early after sepsis due to an increase in ECSOD content, which in turn preserves NO levels to maintain renal blood flow. This is further supported by the fact that microparticles from septic patients did not change superoxide anion and nitric oxide production in the rat kidney [32]. It is suggested that, even without any detectable increase in NOS content, an increase in ECSOD would be sufficient to maintain NO levels in conditions where superoxide production is increased, such as in sepsis. NO plays a role in cyclic GMP-mediated smooth muscle relaxation leading to the production of pVASP [37–39]. We demonstrated an increase in pVASP at 6 and 12 h after sepsis induction, which was temporally related to the increase in ECSOD and the decrease in 3-nitrotyrosine, suggesting that NO signalling is preserved at these early stages of sepsis. Similarly, Fisher 344 rats are able to increase ECSOD in response to exercise as opposed to Sprague-Dawley rats, which indicates protection against acute kidney injury induced by ischaemia-reperfusion [40]. To ascertain that ECSOD plays a critical role in the control of renal blood flow, we administered a SOD inhibitor to septic animals. Inhibition of SOD not only induced an increase in nitrotyrosine levels but also resulted in decreased blood flow in later periods (48 h) of sepsis. One intriguing fact is that the SOD inhibitor did not affect renal blood flow at 12 and 24 h after sepsis. Actually, since the SOD inhibitor effectively inhibited SOD activity after 12 h, it was expected that nitrotyrosine levels and renal blood flow would also change, which occurs at 48 h. This probably reflects a steady state between NO and superoxide that could be affected by several other factors not assessed in our study. For example, it is well known that arginase activity could decrease NO synthesis by competing with NOS for arginine [41], and it has been demonstrated that arginase activity is modulated during sepsis development [42]. In addition, the role of SOD in the development of acute kidney injury was recently demonstrated in humans [43]. In septic shock patients, higher erythrocyte SOD activity was independently associated with protection from acute kidney injury [43]. However, the protective effects of ECSOD are also observed in other different tissues during sepsis development [15, 44].
Some limitations must be highlighted. First, renal blood flow was measured at three time points after sepsis, but renal blood flow may vary over time. Therefore, every hour time point measures for quasi-continuous monitoring would be required. This procedure would require a large number of animals (for each time point) or prolonged anaesthesia and mechanical ventilation, which could result in the generation of a different bias that could interfere with the results. Although the timeline of such changes remains to be further investigated by means of approaches that allow for the continuous measurement of renal blood flow, our results provide insight into the pharmacological use of an ECSOD mimetic to prevent kidney damage associated with sepsis. Second, we did not directly measure NO levels; therefore, we cannot determine if ECSOD activity truly preserved NO levels in our model. This was only indirectly measured by nitrotyrosine levels, pVASP content and renal blood flow.
Conclusions
In conclusion, ECSOD has a relevant role in decreasing ONOO- formation in the renal artery during early sepsis development, which can be an important step in the preservation of renal blood flow. These results provide insight into the pharmacological use of an ECSOD mimetic to prevent kidney damage associated with sepsis.
References
Hotchkiss RS, Karl IE (2003) The pathophysiology and treatment of sepsis. N Engl J Med 348:138–150. doi:10.1056/NEJMra021333
Bosmann M, Ward PA (2013) The inflammatory response in sepsis. Trends Immunol 34(3):129–136. doi:10.1016/j.it.2012.09.004
Andrades ME, Ritter C, Dal-Pizzol F (2009) The role of free radicals in sepsis development. Front Biosci 1:277–287
Lupp C, Baasner S, Ince C, Nocken F, Stover JF, Westphal M. Differentiated control of deranged nitric oxide metabolism: a therapeutic option in sepsis? Crit Care. 2013;17(3):311.
Dyson A, Bryan NS, Fernandez BO, Garcia-Saura MF, Saijo F, Mongardon N, Rodriguez J, Singer M, Feelisch M (2011) An integrated approach to assessing nitroso-redox balance in systemic inflammation. Free Radic Biol Med 51:1137–1145. doi:10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2011.06.012
Slosky LM, Vanderah TW (2015) Therapeutic potential of peroxynitrite decomposition catalysts: a patent review. Expert Opin Ther Pat 25(4):443–466. doi:10.1517/13543776.2014.1000862
Burgoyne JR, Rudyk O, Mayr M, Eaton P (2011) Nitrosative protein oxidation is modulated during early endotoxemia. Nitric Oxide 25(2):118–124. doi:10.1016/j.niox.2010.11.005
Oury TD, Day BJ, Crapo JD (1996) Extracellular superoxide dismutase in vessels and airways of humans and baboons. Free Radic Biol Med 20:957–965
Marklund SL (1982) Human copper-containing superoxide dismutase of high molecular weight. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 79:7634–7638
Fukai T, Ushio-Fukai M (2011) Superoxide dismutases: role in redox signaling, vascular function, and diseases. Antioxid Redox Signal 15(6):1583–1606. doi:10.1089/ars.2011.3999
Demchenko IT, Oury TD, Crapo JD, Piantadosi CA (2002) Regulation of the brain’s vascular responses to oxygen. Circ Res 91:1031–1037
Qin Z, Reszka KJ, Fukai T, Weintraub NL (2008) Extracellular superoxide dismutase (ecSOD) in vascular biology: an update on exogenous gene transfer and endogenous regulators of ecSOD. Transl Res 151(2):68–78. doi:10.1016/j.trsl.2007.10.003
Seija M, Baccino C, Nin N, Sánchez-Rodríguez C, Granados R, Ferruelo A, Martínez-Caro L, Ruíz-Cabello J, de Paula M, Noboa O, Esteban A, Lorente JA (2012) Role of peroxynitrite in sepsis-induced acute kidney injury in an experimental model of sepsis in rats. Shock 38:403–410. doi:10.1097/SHK.0b013e31826660f2
Wang Z, Holthoff JH, Seely KA, Pathak E, Spencer HJ 3rd, Gokden N, Mayeux PR (2012) Development of oxidative stress in the peritubular capillary microenvironment mediates sepsis-induced renal microcirculatory failure and acute kidney injury. Am J Pathol 180:505–516. doi:10.1016/j.ajpath.2011.10.011
Constantino L, Gonçalves RC, Giombelli VR, Tomasi CD, Vuolo F, Kist LW, de Oliveira GM, Pasquali MA, Bogo MR, Mauad T, Horn A Jr, Melo KV, Fernandes C, Moreira JC, Ritter C, Dal-Pizzol F (2014) Regulation of lung oxidative damage by endogenous superoxide dismutase in sepsis. Intensive Care Med Exp 2(1):17. doi:10.1186/2197-425X-2-17
Makino A, Skelton MM, Zou AP, Roman RJ, Cowley AW Jr (2002) Increased renal medullary oxidative stress produces hypertension. Hypertension 39:667–672. doi:10.1161/hy0202.103469
Fu P, Murley JS, Grdina DJ, Birukova AA, Birukov KG (2011) Induction of cellular antioxidant defense by amifostine improves ventilator induced lung injury. Crit Care Med 39(12):2711–2721. doi:10.1097/CCM.0b013e3182284a5f
Sant'Helena BD, Guarido KL, de Souza P, Crestani S, da Silva-Santos JE (2015) Reduction in renal blood flow following administration of norepinephrine and phenylephrine in septic rats treated with Kir6.1 ATP-sensitive and KCa1.1 calcium-activated K+ channel blockers. Eur J Pharmacol 765:42–50. doi:10.1016/j.ejphar.2015.08.014
Bannister JV (1987) Calaberese L (1987) Assays for SOD. Methods Biochem Anal 32:279–312
Wu L, Gokden N, Mayeux PR (2007) Evidence for the role of reactive nitrogen species in polymicrobial sepsis-induced renal peritubular capillary dysfunction and tubular injury. J Am Soc Nephrol 18:1807–1815. doi:10.1681/ASN.2006121402
Wang Z, Herzog C, Kaushal GP, Gokden N, Mayeux PR (2011) Actinonin, a meprin A inhibitor, protects the renal microcirculation during sepsis. Shock 35:141–147. doi:10.1097/SHK.0b013e3181ec39cc
Pathak E, Mayeux PR (2010) In vitro model of sepsis-induced renal epithelial reactive nitrogen species generation. Toxicol Sci 115:475–481. doi:10.1093/toxsci/kfq058
Vaschetto R, Kuiper JW, Musters RJ, Eringa EC, Della Corte F, Murthy K, Groeneveld AB, Plötz FB (2010) Renal hypoperfusion and impaired endothelium-dependent vasodilation in an animal model of VILI: the role of the peroxynitrite-PARP pathway. Crit Care 14(2):R45. doi:10.1186/cc8932
Wang W, Jittikanont S, Falk SA, Li P, Feng L, Gengaro PE, Poole BD, Bowler RP, Day BJ, Crapo JD, Schrier RW (2003) Interaction among nitric oxide, reactive oxygen species, and antioxidants during endotoxemia-related acute renal failure. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 284:F532–F537. doi:10.1152/ajprenal.00323.2002
Trzeciak S, McCoy JV, Phillip Dellinger R, Arnold RC, Rizzuto M, Abate NL, Shapiro NI, Parrillo JE, Hollenberg SM, Microcirculatory Alterations in Resuscitation and Shock (MARS) investigators (2008) Microcirculatory Alterations in Resuscitation and Shock (MARS) investigators. Early increases in microcirculatory perfusion during protocol-directed resuscitation are associated with reduced multi-organ failure at 24 h in patients with sepsis. Intensive Care Med 34:2210–2217. doi:10.1007/s00134-008-1193-6
Dubin A, Pozo MO, Casabella CA, Murias G, Pálizas F Jr, Moseinco MC, Kanoore Edul VS, Pálizas F, Estenssoro E, Ince C (2010) Comparison of 6% hydroxyethyl starch 130/0.4 and saline solution for resuscitation of the microcirculation during the early goal-directed therapy of septic patients. J Crit Care 25:659. doi:10.1016/j.jcrc.2010.04.007, e1-8
Saugel B, Trepte CJ, Heckel K, Wagner JY, Reuter DA (2015) Hemodynamic management of septic shock: is it time for “individualized goal-directedhemodynamic therapy” and for specifically targeting the microcirculation? Shock 43(6):522–529. doi:10.1097/SHK.0000000000000345
Ergin B, Zafrani L, Kandil A, Baasner S, Lupp C, Demirci C, Westphal M, Ince C (2016) Fully balanced fluids do not improve microvascular oxygenation, acidosis and renal function in a rat model of endotoxemia. Shock 46(1):83–91. doi:10.1097/SHK.0000000000000573
Stralin P, Karlsson K, Johansson BO, Marklund SL (1995) The interstitium of the human arterial wall contains very large amounts of extracellular superoxide dismutase. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 15:2032–2036. doi:10.1161/01.ATV.15.11.2032
Jung O, Marklund SL, Xia N, Busse R, Brandes RP (2007) Inactivation of extracellular superoxide dismutase contributes to the development of high-volume hypertension. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 27(3):470–477. doi:10.1161/01.ATV.0000254823.15843.1f
Schneider MP, Sullivan JC, Wach PF, Boesen EI, Yamamoto T, Fukai T, Harrison DG, Pollock DM, Pollock JS (2010) Protective role of extracellular superoxide dismutase in renal ischemia/reperfusion injury. Kidney Int 78:374–381. doi:10.1038/ki.2010.141
Mastronardi ML, Mostefai HA, Meziani F, Martínez MC, Asfar P, Andriantsitohaina R (2011) Circulating microparticles from septic shock patients exert differential tissue expression of enzymes related to inflammation and oxidative stress. Crit Care Med 39:1739–1748. doi:10.1097/CCM.0b013e3182190b4b
Guan Z, Gobe G, Willgoss D, Endre ZH (2006) Renal endothelial dysfunction and impaired autoregulation after ischemia-reperfusion injury result from excess nitric oxide. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 291:F619–F628. doi:10.1152/ajprenal.00302.2005
Obal D, Dai S, Keith R, Dimova N, Kingery J, Zheng YT, Zweier J, Velayutham M, Prabhu SD, Li Q, Conklin D, Yang D, Bhatnagar A, Bolli R, Rokosh G (2012) Cardiomyocyte-restricted overexpression of extracellular superoxide dismutase increases nitric oxide bioavailability and reduces infarct size after ischemia/reperfusion. Basic Res Cardiol 107(6):305. doi:10.1007/s00395-012-0305-1
Macarthur H, Westfall TC, Riley DP, Misko TP, Salvemini D (2000) Inactivation of catecholamines by superoxide gives new insights on the pathogenesis of septic shock. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 97:9753–9758. doi:10.1073/pnas.97.17.9753
Ma L, Wang K, Shang J, Cao C, Zhen P, Liu X, Wang W, Zhang H, Du Y, Liu H (2014) Anti-peroxynitrite treatment ameliorated vasorelaxation of resistance arteries in aging rats: involvement with NO-sGC-cGKs pathway. Plos One 9(8), e104788. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0104788
Lindsay SL, Ramsey S, Aitchison M, Renné T, Evans TJ (2007) Modulation of lamellipodial structure and dynamics by NO-dependent phosphorylation of VASP Ser239. J Cell Sci 120:3011–3021. doi:10.1242/jcs.003061
Oelze M, Mollnau H, Hoffmann N, Warnholtz A, Bodenschatz M, Smolenski A, Walter U, Skatchkov M, Meinertz T, Münzel T (2000) Vasodilator stimulated phosphoprotein serine 239 phosphorylation as a sensitive monitor of defective nitric oxide/cGMP signaling and endothelial dysfunction. Circ Res 87:999–1005. doi:10.1161/01.RES.87.11.999
Davel AP, Victorio JA, Delbin MA, Fukuda LE, Rossoni LV (2015) Enhanced endothelium-dependent relaxation of rat pulmonary artery following β-adrenergic overstimulation: involvement of the NO/cGMP/VASP pathway. Life Sci 15(125):49–56. doi:10.1016/j.lfs.2015.01.018
Moningka NC, Cunningham MW Jr, Sterling M, West CA, Verlander JW, Croker BP, Ahlgren J, Hayward L, Baylis C (2013) Effects of voluntary wheel running on the kidney at baseline and after ischaemia-reperfusion-induced acute kidney injury: a strain difference comparison. J Physiol 591:1313–1324. doi:10.1113/jphysiol.2012.244327
Wijnands KA, Hoeksema MA, Meesters DM, van den Akker NM, Molin DG, Briedé JJ, Ghosh M, Köhler SE, van Zandvoort MA, de Winther MP, Buurman WA, Lamers WH, Poeze M (2014) Arginase-1 deficiency regulates arginine concentrations and NOS2-mediated NO production during endotoxemia. PLoS One 9, e86135. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0086135
Wijnands KA, Castermans TM, Hommen MP, Meesters DM, Poeze M (2015) Arginine and citrulline and the immune response in sepsis. Nutrients 7:1426–1463. doi:10.3390/nu7031426
Costa NA, Gut AL, Azevedo PS, Tanni SE, Cunha NB, Magalhães ES, Silva GB, Polegato BF, Zornoff LA, de Paiva SA, Balbi AL, Ponce D, Minicucci MF (2016) Erythrocyte superoxide dismutase as a biomarker of septic acute kidney injury. Ann Intensive Care 6:95. doi:10.1186/s13613-016-0198-5
Andrades M, Ritter C, de Oliveira MR, Streck EL, Fonseca Moreira JC, Dal-Pizzol F (2011) Antioxidant treatment reverses organ failure in rat model of sepsis: role of antioxidant enzymes imbalance, neutrophil infiltration, and oxidative stress. J Surg Res 167(2):e307–e313. doi:10.1016/j.jss.2009.08.005
Acknowledgements
We would like to acknowledge support from the Universidade do Extremo Sul Catarinense, Brazilian Council for Scientific and Technological Development and Fundação de Amparo a Pesquisa do Estado de Santa Catarina.
Funding
This work was supported by unrestricted grants from Universidade do Extremo Sul Catarinense, Brazilian Council for Scientific and Technological Development and Fundação de Amparo a Pesquisa do Estado de Santa Catarina.
Authors’ contributions
LC is responsible for substantial contributions to conception and design; LSG, FV, KLG, LWK, GMTO and MABP are responsible for the acquisition of data and statistical analysis; CTS, JESS, MRB, JCFM, CR and FDP are responsible for drafting the article or revising it critically for important intellectual content and for final approval of the version. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Authors’ information
There is nothing relevant to report.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests. All authors have read the journal’s authorship agreement and the policy on disclosure of potential conflicts of interest.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made.
About this article
Cite this article
Constantino, L., Galant, L.S., Vuolo, F. et al. Extracellular superoxide dismutase is necessary to maintain renal blood flow during sepsis development. ICMx 5, 15 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1186/s40635-017-0130-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s40635-017-0130-9