Abstract
Background
Allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation and checkpoint blockade therapy are immune-based therapies that have activity in selected refractory hematologic malignancies. Interest has developed in combining these treatments for high-risk hematologic diseases. However, there is concern that checkpoint blockade could augment graft-versus-host disease, and very few studies have evaluated the safety of checkpoint blockade in the post-allogeneic setting. Here, we report the outcomes of three patients with relapsed classical Hodgkin’s lymphoma following allogeneic transplant that were treated with the anti-PD-1 antibody, nivolumab.
Case presentations
Three patients with Hodgkin’s lymphoma relapsed following allogeneic transplant received nivolumab therapy at our institution. All patients were free of graft-versus-host disease and were off of all systemic immunosuppressive medications at the time of nivolumab treatment. Nivolumab was well-tolerated in two of the patients. However, nivolumab had to be discontinued in one patient due to development of immune-related polyarthritis requiring treatment with systemic corticosteroids and methotrexate. Objective responses were observed in all three patients.
Conclusions
Our case series demonstrates that anti-PD-1 therapy with nivolumab can be highly effective following allogeneic transplant for Hodgkin’s lymphoma, but serious immune-related adverse events can occur, requiring very close monitoring and interruption of therapy.
Similar content being viewed by others
Background
Allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (alloHSCT) can be a curative treatment for high-risk and recurrent hematological malignancies [1]. A major therapeutic effect of alloHSCT lies within the graft-versus-tumor (GVT) response, where donor-derived lymphocytes recognize antigens expressed on the surface of malignant cells, and eliminate them from the host [2]. However, it has become clear that disease relapse following alloHSCT can be associated with immune evasion and loss of GVT effects [3]. Concrete examples include upregulation of programmed death-ligand 1 (PD-L1) on leukemia cells, and programmed death-1 (PD-1) on donor-derived T cells at the time of post-alloHSCT relapse, as well as deletion of human leukocyte antigen alleles in some leukemia patients relapsing after haploidentical alloHSCT [4, 5]. New strategies to restore GVT effects in these patients are needed because patients who relapse after alloHSCT have few treatment options and dismal outcomes [6].
Recently, the defined activity of checkpoint blockade therapy (CBT) with anti-PD-1 and anti-cytotoxic lymphocyte antigen-4 (CTLA-4) antibodies in a number of malignancies has generated interest in their use to treat disease relapse following alloHSCT. Preclinical studies of CBT have demonstrated augmentation of GVT effects [7–9], and two phase I studies of the anti-CTLA-4 antibody, ipilimumab, have been reported in patients with relapse after alloHSCT, where objective responses were observed [10, 11]. In the most recently published study, ipilimumab treatment was associated with a 31% objective response rate, including complete responses in patients with leukemia cutis, myeloid sarcoma, and myelodysplastic syndrome [11].
However, there is concern that enhancing the GVT effect through administration of CBT might also induce or exacerbate graft-versus-host disease (GVHD). Indeed, ipilimumab treatment was discontinued in 4 of 29 patients due to GVHD in the aforementioned study, and 6 patients had other immune-related adverse advents (IrAE) including one treatment-related death [11]. Further, PD-1 blockade has also been associated with induction of severe GVHD in murine models, and a report of fatal GVHD in a patient treated with the anti-PD-1 antibody, pembrolizumab, was recently published [12, 13]. These observations have somewhat tempered enthusiasm for the exploration of PD-1 blockade after alloHSCT to anecdotal reports and a retrospective case series which has been published in abstract form [14–16]. However, PD-1 blockade has been associated with a lower incidence of severe IrAE in non-transplant settings compared to CTLA-4 blockade, and is clearly more effective across a number of malignancies, including classical Hodgkin lymphoma (cHL) [17, 18]. We therefore sought to examine the safety and efficacy of PD-1 blockade following alloHSCT, and present data summarizing our experience with nivolumab for the treatment of relapsed cHL after alloHSCT.
Case presentation
We treated three cHL patients who had relapsed after alloHSCT with off-label nivolumab at a dose of 3 mg/kg every 2 weeks. Patient and disease characteristics are summarized in Table 1. Briefly, all patients had multiply relapsed cHL despite treatment with conventional chemotherapy regimens and autologous hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Patients received T cell-depleted grafts after reduced-intensity conditioning regimens. None developed acute GVHD, although two patients developed limited-stage chronic GVHD requiring short courses of steroids. Disease relapse occurred at an average of 1,008 days from alloHSCT (181, 389, and 2456 days), and was histologically confirmed in all cases. One patient received a donor lymphocyte infusion (DLI) at the time of relapse, but failed to achieve an objective response. After exhausting all conventional treatment options, patients were consented to treatment with nivolumab after discussing potential risks including life-threatening GVHD.
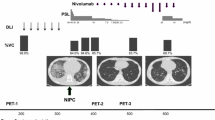
All three patients had no clinical evidence of acute or chronic GVHD at the time of initiating nivolumab, and immunosuppressive medications had been discontinued at least a year prior to starting therapy. Observed nivolumab IrAE are listed in Table 1, and included grade 2 keratoconjunctivits in 2 patients, responsive to corticosteroid eye drops in both, grade 1 rash (possibly representing limited-stage chronic GVHD) in 1 patient, successfully treated with topical steroids, and one grade 3 episode of inflammatory polyarthritis, that required treatment discontinuation and administration of systemic corticosteroids and methotrexate to control. Mean duration of therapy is 8.3 months and is continuing in two patients. All patients had objective partial responses to treatment based on the results of interim PET scans (Fig. 1a). Responses are ongoing in all patients at the time of publication. In addition to radiographic responses, one patient with severe pancytopenia due to marrow involvement by cHL achieved a marked improvement in peripheral blood counts, as well as an objective improvement in bone marrow involvement by cHL (Fig. 1b). Immunohistochemistry studies on bone marrow biopsy samples before and after 5 cycles of nivolumab therapy in this patient demonstrated abundant PD-L1 expression in Hodgkin cells, with an increase in tumor-infiltrating CD8+ T cells and decreased CD4+ T cells with therapy (Fig. 2). Furthermore, bone marrow chimerism studies demonstrated an increase in the donor CD3+ compartment from 18 to 49% with treatment.
Radiographic and hematologic responses with therapy. a Response as assessed by sequential PET scan images. Images are shown for Patients 2 and 3. The response for Patient 1 was more difficult to illustrate on PET scan as his disease was primarily confined to the bone marrow. b Serial complete blood counts during treatment with nivolumab demonstrating significant tri-lineage improvement for Patient 1. *Platelet units (×10^3/uL) are provided on the left y-axis, while hemoglobin (g/dL) and white blood cell count units (×10^3/uL) are on the right y-axis
Immunohistochemistry changes with therapy. Immunohistochemistry results on bone marrow biopsies from patient 1 before and after 5 cycles of nivolumab. There is an increase in tumor-infiltrating CD8+ T cells and a decrease in CD4+ T cells with treatment. PD-L1 staining was positive both before and after treatment. Images were captured using a Jenoptik ProgRes® Speed XT core 5 series camera on an Olympus BX53 microscope at 50× magnification using Adobe Photoshop Software
Discussion and Conclusions
Our data conclusively demonstrate that anti-PD-1 therapy with nivolumab is effective for relapsed cHL following alloHSCT. All three patients have achieved objective and ongoing responses to treatment. These findings are consistent with previous observations demonstrating immune escape as a mechanism of relapse following alloHSCT, and that immune activating therapies such as DLI and CBT have the potential to restore GVT effects [3–5, 7–11, 19]. The finding of an objective response in a patient refractory to DLI, also demonstrates that PD-1 blockade reinvigorates GVT responses through distinct pathways that potentially more effectively activate GVT effects.
The toxicity of PD-1 blockade following alloHSCT will be an important measure to continue to assess in prospective studies. We did not observe any GVHD; however, several IrAEs occurred among the three patients reported here, none of which was life-threatening. It is expected, as has recently been reported [13], that the use of anti-PD-1 antibodies may result in severe immune-related toxicities in the post-allo-HSCT setting.
While our results are encouraging, it is not known whether other hematologic cancers will also be responsive to PD-1 blockade in the post-alloHSCT setting. That being said, complete responses to ipilimumab were observed after alloHSCT in patients with relapsed leukemia cutis and myelodysplastic syndrome [11]. This is an important observation since single-agent ipilimumab has only modest activity in hematologic malignancies outside of the alloHSCT setting [20], and may indicate that CBT and alloHSCT have therapeutically synergistic effects. In support of this, our finding of increased donor CD3+ chimerism at the site of disease involvement in one of our patients, suggests that anti-tumor effects are preferentially driven by donor-derived T cells following PD-1 blockade. Biologically, the enhanced activity of combining CBT with alloHSCT could be related to the observation that immune responses generated by PD-1 blockade are likely restricted to tumor neo-antigens in the non-transplanted host [21], whereas immune responses from donor-derived T cells are targeted against minor histocompatibility antigens that are more uniformly expressed [22]. Furthermore, anti-PD-1 antibodies may enhance the efficacy of alloHSCT by reinvigorating the GVT effect in hematological cancers that acquire PD-L1 expression as an adaptive response to immune pressure. Therefore the complementary immune effects of alloHSCT and PD-1 blockade hold promise in both the prevention and treatment of relapse following alloHSCT.
Abbreviations
- AlloHSCT:
-
Allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplant
- CBT:
-
Checkpoint blockade therapy
- cHL:
-
Classical Hodgkin’s Lymphoma
- CTLA-4:
-
Cytotoxic T-lymphocyte associated protein-4
- DLI:
-
Donor lymphocyte infusion
- GVHD:
-
Graft-versus-host disease
- GVT:
-
Graft-versus-tumor
- IrAE:
-
Immune-related adverse event
- PD-1:
-
Programmed death receptor-1
- PD-L1:
-
Programmed death ligand-1
- PET:
-
Positron emission tomography
References
Stem Cell Trialists’ Collaborative Group. Allogeneic peripheral blood stem-cell compared with bone marrow transplantation in the management of hematologic malignancies: an individual patient data meta-analysis of nine randomized trials. J Clin Oncol. 2005;23(22):5074–87.
Zilberberg J, Feinman R, Korngold R. Strategies for the identification of T cell-recognized tumor antigens in hematological malignancies for improved graft-versus-tumor responses after allogeneic blood and marrow transplantation. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2015;21(6):1000–7.
Toffalori C, Riba M, Zito L, et al. Acute myeloid leukemia relapses after allogenenic HSCT display a distinctive immune-related signature, with frequent and functionally relevant alterations in HLA class II antigen presentation and T cell costimulation [abstract]. Blood. 2014;124(21):427.
Kong Y, Zhang J, Claxton DF, et al. PD-1(hi)TIM-3(+) T cells associate with and predict leukemia relapse in AML patients post allogeneic stem cell transplantation. Blood Cancer J. 2015;5:e330.
Vago L, Perna SK, Zanussi M, et al. Loss of mismatched HLA in leukemia after stem-cell transplantation. N Engl J Med. 2009;361(5):478–88.
van den Brink MR, Porter DL, et al. Relapse after allogeneic hematopoietic cell therapy. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2010;16(1 Suppl):S138–45.
Blazar BR, Taylor PA, Panoskaltsis-Mortari A, Sharpe AH, Vallera DA. Opposing roles of CD28:B7 and CTLA-4:B7 pathways in regulating in vivo alloresponses in murine recipients of MHC disparate T cells. J Immunol. 1999;162(11):6368–77.
Norde WJ, Maas F, Hobo W, et al. PD-1/PD-L1 interactions contribute to functional T-cell impairment in patients who relapse with cancer after allogeneic stem cell transplantation. Cancer Res. 2011;71(15):5111–22.
Koestner W, Hapke M, Herbst J, et al. PD-L1 blockade effectively restores strong graft-versus-leukemia effects without graft-versus-host disease after delayed adoptive transfer of T-cell receptor gene-engineered allogeneic CD8+ T cells. Blood. 2011;117(3):1030–41.
Bashey A, Medina B, Corringham S, et al. CTLA4 blockade with ipilimumab to treat relapse of malignancy after allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation. Blood. 2009;113(7):1581–8.
Davids MS, Kim HT, Bachireddy P, et al. Ipilimumab for patients with relapse after allogeneic transplantation. N Engl J Med. 2016;375(2):143–53.
Saha A, Aoyama K, Taylor PA, et al. Host programmed death ligand 1 is dominant over programmed death ligand 2 expression in regulating graft-versus-host disease lethality. Blood. 2013;122(17):3062–73.
Singh AK, Porrata LF, Aljitawi O, et al. Fatal GVHD induced by PD-1 inhibitor pembrolizumab in a patient with Hodgkin’s lymphoma. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2016;51(9):1268–70.
Angenendt L, Schliemann C, Lutz M, et al. Nivolumab in a patient with refractory Hodgkin’s lymphoma after allogeneic stem cell transplantation. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2016;51(3):443–5.
Villasboas JC, Ansell SM, Witzig TE. Targeting the PD-1 pathway in patients with relapsed classic Hodgkin lymphoma following allogeneic stem cell transplant is safe and effective. Oncotarget. 2016;7(11):13260–4.
Herbaux C, Gauthier J, Brice P, et al. Nivolumab is effective and reasonably safe in relapsed or refractory Hodgkin’s lymphoma after allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation: a study from the LYSA and SFGM-TC [abstract]. Blood. 2015;126(23):3979.
Armand P. Immune checkpoint blockade in hematologic malignancies. Blood. 2015;125(22):3393–400.
Ansell SM, Lesokhin AM, Borrello I, et al. PD-1 blockade with nivolumab in relapsed or refractory Hodgkin’s lymphoma. N Engl J Med. 2015;372(4):311–9.
Bachireddy P, Hainz U, Rooney M, et al. Reversal of in situ T-cell exhaustion during effective human antileukemia responses to donor lymphocyte infusion. Blood. 2014;123(9):1412–21.
Ansell SM, Hurvitz SA, Koenig PA, et al. Phase I study of ipilimumab, an anti-CTLA-4 monoclonal antibody, in patients with relapsed and refractory B-cell non-Hodgkin lymphoma. Clin Cancer Res. 2009;15(20):6446–53.
McGranahan N, Furness AJ, Rosenthal R, et al. Clonal neoantigens elicit T cell immunoreactivity and sensitivity to immune checkpoint blockade. Science. 2016;351(6280):1463–9.
Feng X, Hui KM, Younes HM, Brickner AG. Targeting minor histocompatibility antigens in graft versus tumor or graft versus leukemia responses. Trends Immunol. 2008;29(12):624–32.
Acknowledgements
Not applicable.
Funding
There were no funding sources used for the study.
Availability of data and materials
Not applicable.
Author contributions
JG, MRB and JK were responsible for the primary writing of the manuscript with the assistance of the other coauthors. JG, MRB and JK were the primary physicians caring for the 3 patients in the case series and assisted in collection of patient data. EH and SS performed the histological analysis of the bone marrow biopsy and provided the images demonstrating the immunohistochemical changes occurring with therapy. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Consent for publication
Written informed consent was obtained from all patients for publication of this case report and any accompanying images.
Competing interests
JK has research support from Merck. The remaining authors declare no other competing financial interests.
Ethics approval and consent to participate
The study was approved by the University of Chicago institutional review board, and all patients consented to participate in our study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made. The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver (http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated.
About this article
Cite this article
Godfrey, J., Bishop, M.R., Syed, S. et al. PD-1 blockade induces remissions in relapsed classical Hodgkin lymphoma following allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. j. immunotherapy cancer 5, 11 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1186/s40425-017-0211-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s40425-017-0211-z