Abstract
Aims
This study aimed to evaluate the correlation between parental attachment, resilience, postpartum traumatic stress disorder (PTSD), and maternal-infant bonding at 1 to 3 months postpartum. The mediation effect of resilience and PTSD on the postpartum parental attachment and maternal-infant bond was also evaluated.
Design
A cross-sectional research design was used.
Methods
A total of 400 postpartum women examined at a tertiary hospital in Wuhan from January 2021 to June 2021 were enrolled in the study. At about 1 to 3 months after giving birth, the women were asked to complete the Postpartum Bonding Questionnaire (PBQ), Connor-Davidson Resilience scale(CD-RISC), PTSD CheckList-Civilian version (PCL-C), and the Parental Bonding Instrument (PBI). The data were summarized using descriptive statistics. Mediation analyse and the Spearman correlation (r) were used to correlate the resilience and PTSD questionnaire scores.
Results
The care attachment dimension was significantly associated with resilience (r = 0.24, p < 0.01), PTSD (r = − 0.27, p < 0.01), and maternal-infant bonding (r = 0.10, p < 0.01), and the overprotection attachment dimension was significantly associated with resilience (r = − 0.11, p < 0.01), PTSD (r = 0.33, p < 0.01), and maternal-infant bonding (r = 0.16, p < 0.01). Resilience and PTSD can mediate the relationship between attachment and maternal-infant bonding.
Conclusion
Parental attachment, resilience, and PTSD significantly affect maternal-infant bonding at 1 to 3 months postpartum.
Impact
This study demonstrated that new interventions aimed at addressing PTSD symptoms and improving resilience might increase parental attachment and maternal-infant bonding after birth. However, further research is required to evaluate the success of these interventions.
No patient or public contribution
Problem or Issue | Intergenerational transmission of maternal-infant bonding disorders and the occurrence of child abuse incidents frequently. |
• What is Already Known | While a range of factors influence mater-infant bonding, women’s resilience and PTSD also play a role. |
• What this Paper Adds | Parental attachment, resilience, and PTSD significantly affect maternal-infant bonding at 1 to 3 months postpartum, and resilience and PTSD play a mediation role in parental attachment and maternal-infant bonding. |
Similar content being viewed by others
Introduction
Maternal-infant bonding is the process in which a mother forms an affectionate attachment to her infant [1]. This process starts during pregnancy and continues over the next few years. Maternal-infant bonding disorders (or failure) is a emotion disorder characterised by a lack of maternal emotional response towards her infant [2, 3]. Which can cause frequent crying and infant gastroesophageal reflux (GER), harm the maternal psychological well-being [4], poor emotional management skills within the newborn, and a serious long-term negative impact on the child’s development and maternal-infant interactions. Negative maternal-infant bonding will hinder infants’ regulation, tolerance, and integration of their own emotions and harm the infants’ social and emotional development, leading to the formation of poor emotional management ability [5, 6]. Studies have shown that postpartum maternal-infant bonding directly predicts social-emotional development in infants at 12 months of age [5]. About 5.2–11.3% of pregnant women suffer from a mild maternal-infant bonding disorder in the early postnatal period. Moreover, about 0.3–2.0% of mothers develop a severe maternal-infant bonding disorder and eventually reject their newborns [7, 8]. Several factors have been found to contribute to the development of maternal-infant bonding disorders, including the mother’s personality and educational level, spousal relationship, support from family and friends, postpartum anxiety and depression, and the newborn’s temperament [9, 10]. Early interventions may improve the maternal-infant bond and reduce the psychosocial burdens of the disorder. However, to develop effective interventions, more research is required to understand the processes involved in the development of maternal-infant bonding.
Background
Parental attachment refers to the individual’s memories of the early years with their parents. Studies reported that a dual or disorganized attachment and anxious-ambivalent romantic, parental attachment styles tend to lead to increased bonding impairments [11, 12]. Protection and care are the main ways in which mothers care for their babies. In the attachment theory, parental attachment and maternal-infant bonding are intergenerational [13], meaning that the early attachment experience would create a prototype and provide a relationship engagement framework for later on in life [14]. As a result, numerous studies have found a positive association between parental attachment and maternal-infant bonding [11, 12]. More specifically, an insecure parental attachment was not only associated with the development of maternal-bonding difficulties [15,16,17,18,19], but also through the mediation effect of maternal sensitivity and emotional [20]. Further research is therefore required to understand the exact relationship between parental attachment and the onset of postnatal maternal-infant bonding.
Posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD) is a delayed psychopathology stress disorder. Which can occur after childbirth trauma, affect about 3 to 4% of mothers, but the incidence can increase 4 to 5 times in patients with emergency deliveries, postpartum complications, and mental health issues [21, 22]. MacKinnon et al. [23] evaluated the impact of parental attachment on the development of PTSD at 5 weeks, 2 months, and 6 months postpartum and found that parental attachment was associated with the onset and rate of PTSD development. Furthermore, numerous studies found an association between PTSD and the development of maternal-infant bonding disorders [21, 24, 25]. On the other hand, Handelzalts et al. [26] found that avoidant and anxious maternal-infant attachments may occur due to PTSD symptoms.
Resilience is an ability in life that can enable individuals to cope with traumatic events and can also help individuals recover faster from adversity and stress [27]. As a result, several studies tried to evaluate the relationship between resilience and PTSD. Connor [27] developed the Connor-Davidson Resilience scale (CD-RISC) to measure resilience and found that individuals with higher CR-RISC scores could cope better with stress and were less likely to develop PTSD. The cluster analysis of Travis et al. [28] showed that women with poor infant attachment could enhance maternal-infant bonding by improving resilience. Resilience may have a mediation role in attachment and maternal-infant bonding. Similarly, other studies found that resilience may have an important role in preventing the intergenerational transmission of negative parental attachment feelings from the mother to the infant and thus enable the mother to cope better with stress [29, 30]. In addition, Wang Meifang et al. [31] identified resilience as an independent predictive factor for developing PTSD after 30 days to 1 year postpartum.
In the attachment theory, the relationship engagement framework and internal working models are thought to influence the perception of and coping with stressful experiences [14]. Hence, women with secure attachment experience may have a strong ability to cope with stress, actively adapt to childbirth events, and have a good maternal-infant bonding after birth. They have better resilience ability to overcome pressure, reduce the psychological or physical trauma or negative emotions caused by childbirth, and reduce the occurrence of PTSD [11, 14, 27].
Although numerous studies have evaluated the interrelationship between parental attachment, resilience, PTSD, and maternal-infant bonding, very few studies have evaluated the relationship between resilience and PTSD in mediating parental attachment and maternal-infant bonding. Therefore, further research is required to evaluate the role of resilience in reducing the symptoms of PTSD and hence enable healthcare professionals to develop interventions to enhance the maternal-infant bond and enable them to develop healthy parental attachments.
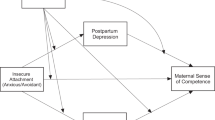
Based on the above, Resilience and PTSD may affect the effect of parental attachment on maternal-infant bonding. Besides, we suspect that resilience and PTSD may play a role of chain mediation. The present study constructed a chain mediation model (Fig. 1) to test the mediating role of resilience, PTSD in parental attachment and maternal-infant bonding. We proposed the following hypothesis:
Note: a1: direct effect of parental attachment on resilience, a2: direct effect of parental attachment on PTSD, b1: direct effect of resilience on maternal-infant bonding, b2: direct effect of PTSD on maternal-infant bonding, c: direct effect of parental attachment on maternal-infant bonding, d: direct effect of resilience on PTSD. Mediation model of the effect of parental attachment on maternal-infant bonding by resilience and PTSD
-
Hypothesis 1: Parental attachment positively predicts maternal-infant bonding among maternal of 1 ~ 3 months postpartum.
-
Hypothesis 2: Resilience plays a mediating role in the effect of parental attachment on maternal-infant bonding.
-
Hypothesis 3: PTSD plays a mediating role in the effect of parental attachment on maternal-infant bonding.
-
Hypothesis 4: Resilience and PTSD plays a chain mediating role in the effect of parental attachment on maternal-infant bonding.
The study
Aims
This study aimed to evaluate the correlation between parental attachment, resilience, PTSD, and maternal-infant bonding at 1 to 3 months postpartum. In addition, we also investigated whether resilience and PTSD can mediate parental attachment and the postpartum maternal-infant bonding.
Design
A quantitative cross-sectional research design was used.
Instrument
The assessment tool consisted of 7 sections as follows.
Section 1: Socio-demographic and pregnancy childbirth-related information
This section aimed to collect information about the participants’ socio-demographic background (i.e., age and educational level), post-partum child and maternal health (i.e., days postpartum, parental responsibilities) and pregnancy and postpartum complications (e.g., hypertension during pregnancy, anemia, gestational diabetes, and sleep quality during pregnancy), and relationship status and satisfaction.
Section 2: Postpartum Bonding Questionnaire (PBQ)
In Sect. 2, the PBQ was used to measure postpartum maternal-infant bonding. The PBQ consists of 25 items divided into 4 dimensions: impaired bonding, rejection and anger, concerned with anxiety, and concerned with abuse. Each item is rated using a 6-point Likert scale, ranging from always to never [3]. The PBQ score ranges from 0 to 125, and a higher score indicates a worse maternal-infant bond. In the current study, Cronbach’s alpha was 0.88.
Section 3: The Connor-Davidson Resilience scale (CD-RISC)
In this section, the CD-RISC was used to measure the patient’s resilience. This questionnaire consists of 25 items, all of which are answered on a 5-point Likert scale ranging from (0) not true at all to (4) true nearly all the time [32]. The 25 items are divided into 3 dimensions: tenacity, strength, and optimism. The total score ranges from 0 to 100, with higher scores reflecting greater resilience. In the current study, Cronbach’s alpha was 0.87.
Section 4: PTSD check list-civilian version (PCL-C)
In this section, the PCL-C was used to measure the presence and severity of PTSD symptoms. PCL-C consists of 17 items, all of which are answered on a 5-point Likert scale ranging from (1) not at all to (5) extremely. The 17 items are divided into 3 dimensions: reexperiencing, avoidance/numbing, and hyperarousal. The total score of the questionnaire ranges from 17 to 85, and a higher score indicates higher levels of PTSD. The scale has good reliability and validity for measuring posttraumatic stress disorder in mothers [33]. In the current study, Cronbach’s alpha was 0.89.
Section 5: Parental bonding instrument (PBI)
The paternal bonding instrument was used to measure the contribution of parental behavior to the development of appropriate bonds between parents and children. The PBI has a version for the father and the mother. Each edition contains 25 items divided into 2 dimensions: care and overprotection. The Cronbach’s alpha of care dimension was 0.80, The Cronbach’s alpha of overprotection dimension was 0.86 in the current study. For this study, the version designed for the mother was adopted [34]. Each item in the PBI tool is rated using a 4-point Likert scale ranging from 0 (very unlikely) to 3 (very likely).
Section 6: Edinburgh postnatal depression scale (EPDS)
The Edinburgh Postnatal Depression Scale instrument was used to measure postpartum depression [35]. The EPDS consists of 10 items, all of which are answered on on a 4-point Likert scale ranging from (0) Nothing or very little to (3) always. The total score of the questionnaire ranges from 0 to 30, and a total score of more than 13 is classified as depression in this study [36]. In the current study, Cronbach’s alpha was 0.84.
Section 7: Self-rating anxiety scale (SAS)
The Self-rating Anxiety Scale instrument was used to measure postpartum anxiety [37]. The SAS consists of 20 items, all of which are answered on on a 4-point Likert scale ranging from (0) Nothing or very little to (3) always. Calculate the total score of 20 items, and the standard score is an integer after the total coarse score *1.25. A total score of more than 50 is classified as anxiety in this study [37]. In the current study, Cronbach’s alpha was 0.82.
Sampling and recruitment
Convenience sampling was used to recruit the participants. Inclusion criteria:①≥18 years old; ②1 ~ 3 months postpartum and single live birth; ③Having the basic ability of reading and writing; ④Informed consent and voluntary participation. Women with a neurological or psychiatric disorder, serious pregnancy complications, a history of alcohol and drug abuse, and those with infectious diseases were excluded. In structural equation models, the minimum sample size is 10 times the number of items of the scale with the most items in the survey scale [38], The total of 25 items of the scale with the most items, so the sample size was expanded 10 times to 250, A total of 400 women participated in this survey.
The research team included trained obstetricians and gynecologists, pelvic floor rehabilitation specialists, and a graduate student. The researchers explained the purpose of the study, and written informed consent was obtained from all participants willing to participate. Another researcher explained the content of the questionnaire to those women who agreed to participate in the study.
Data analysis
The Statistical Package for Social Sciences (SPSS) software version 23 and the Analysis of Moment Structures (AMOS) software version 24 were used for all statistical analyses. The continuous data were summarized as means +/- standard deviations (SD), and the categorical data were expressed as percentages. Spearman’s correlation analysis was used to test the correlation between the 4 variables.
The hypothesized mediation model was analysed using AMOS software (version 26). and AMOS 26.0 software was adopted to construct the mediating effect path analysis graph. In this study, well-established scales were used. Total scores of scales were used as observed variables, which simplified the analysis and interpretation of the data and mitigated the risk of model identification problems in the study with a small sample size. The level of significance was set at 0.05, care and over-protection are two dimensions of the PBI to measure parental attachment, that are negatively correlated and therefore analyze these two dimensions separately. Care and over-protection were two domains of the scale and were tested separately.
Ethical consideration
The study was approved by the University Research Ethics Committee(BME-2021-1-10). Written informed consent was obtained from all participants in the study. Before completing the survey, the participants were informed that their participation in this study would not pose any harm and that all the provided information would be kept confidential.
Results
Characteristics of the participants
A summary of the characteristics of the participants is provided in Table 1. The mean age of the participants was 30.19 years, and most of the women (56.4) had an undergraduate degree or higher. 95% of participants reported symptoms of depression, and 25.2% reported anxiety symptoms. 70% of the participants had complications postpartum. With regards to sleep quality during pregnancy, 55.1% reported either good or very good sleep quality, and 80.5% were satisfied with their couple’s relationship. Depression (p = 0.01), anxiety (p < 0.01), complication (p < 0.01), couple relationship satisfaction (p < 0.01), and sleep quality(p < 0.01) had a significant impact on the PBQ score (Table 1).
Association between attachment, resilience,PTSD, and maternal-infant bonding
Table 2 shows the mean ± SD score for each of the 5 variables and the Spearman’s correlation coefficient between each variable. The CD-RISC was positively correlated with the PBI care and negatively correlated with the PBI overprotection, PBQ, and PCL-C. The PBI care was negatively correlated with all other 3 variables. The PBI overprotection was moderately negatively correlated with the PBI care and CD-RISC. The PBQ was negatively correlated with CD-RIS and positively correlated with the PBI overprotection and care. The PCL-C was positively correlated with the PBQ and the PBI overprotection and negatively correlated with the PBI care and CD-RISC (Table 2). All correlations were statistically significant (p < 0.01).
Mediation analyses with resilience and PTSD as a mediator
After controlling all the confounders, there was a significant sequential indirect effect of attachment on PBQ through CD-RISC and PCL-C. Figures 2 and 3 show all the possible pathways for the process model. All individual paths between the variables in the model were statistically significant.
Note: a1: direct effect of care on CD-RISC, a2: direct effect of care on PCL-C, b1: direct effect of CD-RISC on PBQ, b2: direct effect of PCL-C on PBQ, c: direct effect of care on PBQ, d: direct effect of CD-RISC on PCL-C. *:p < 0.01. Mediation model of the effect of care dimension of attachment on maternal-infant bonding by resilience and PTSD
Note: a1: direct effect of Over-protection on CD-RISC, a2: direct effect of Over-protection on PCL-C, b1: direct effect of CD-RISC on PBQ, b2: direct effect of PCL-C on PBQ, c: direct effect of Over-protection on PBQ, d: direct effect of CD-RISC on PCL-C. *: p < 0.01. Mediation model of the effect of Over-protection dimension of attachment on maternal-infant bonding by resilience and PTSD
In our study, the four variables of interest (independent variable, two mediators and dependent variable) were observed variables using corresponding total score. No latent variable is involved, so the model fit showed perfect performance with CFI=1, RMSEA=0, SRMR=0 and Chi-Square/df=0.
Discussion
The present study investigated the relationship between attachment styles and maternal-infant bonding, in addition to exploring the mediating effects of resilience and PTSD. To our knowledge, this is the study to investigate the mediating role of resilience and PTSD in the relationship between parental attachment and maternal-infant bonding firstly. Our results show that the two dimensions of attachment (i.e., care and overprotection) relate to maternal-infant bonding at 1 to 3 months after birth. In addition, the relationship between attachment and bonding was mediated by resilience and PTSD.
Our findings also confirmed that parental attachment had both a direct and indirect effect on maternal-infant bonding. The direct effect can be explained by the feature of attachment and maternal-infant bonding, which are intergenerational in nature. [13]. Previous studies have shown that the dual-disorganized and anxious-ambivalent romantic attachment patterns had more bonding impairments [11, 12]. In our study, we observed that the care and overprotection dimensions can accurately predict maternal-infant bonding. Poor infantile care means a lack of emotional response in childhood, resulting in depression and other negative behaviors, which can be transformed into hostility, aggression, and other negative behaviors, which is not conducive to the development of positive psychology in children, and an overprotective maternal attachment also can increase the child's vulnerability risk factor and may prevent children from spontaneously developing their own potential [39, 40].
We also demonstrated that attachment results in maternal-infant bonding through resilience and PTSD indirectly. Resilience is viewed as the individual's capability to cope with stress, anxiety, depression, and major adversity. As a result, resilience may mediate the development of secure attachments. Secure attachments affect a person's emotional and psychological well-being. Stable emotions can lead to stable resilience when coping with traumatic events, making it less likely to develop PTSD and maternal-infant bonding [41]. As for the mediation of PTSD, it was shown that insecure attachment would compromise the mentalization of trauma and, therefore, children with insecure attachments are more likely to develop PTSD [42]. It is important to note that the main treatment for general PTSD is to avoid recalling the traumatic event. However, in cases of PTSD postpartum, it is not possible to remove the traumatic event. As a result, women may fail to develop a bond with their infant since the presence of the newborn can cause the mother to constantly recall the traumatic event of childbirth [43].
The findings of this study have a number of implications for clinical practice. In order to develop resilience, mindful-based stress reduction exercises could be used to enable the mother to focus on enhancing her ability to cope with stress [44] and improve their ability to cope with the life-changing impact of a newborn. A systematic review recommended several interventions to improve resilience, including enough rest and sleep, peer support, individual consultations, professional counseling, and information sessions [45]. However, the applicability of these interventions in addressing the targets identified in our study requires further research.
The standard treatment for women suffering from PTSD involves the use of psychotherapy and medications. However, the use of medications for the management of PTSD postpartum is generally avoided due to the low rate of adherence and the potential harm that these medications might pose to the child as a result of breastfeeding [46]. A meta-analysis concluded that psychotherapy in the form of cognitive behavioral therapy, reprocessing desensitization, and exposure therapy could reduce PTSD symptoms in the early postnatal period [47]. However, despite the potential benefits of psychotherapy in the management of PTSD symptoms, it is time-consuming and not widely available.
Nurses can provide psychological support to mothers by raising their own awareness on maternal-infant bonding disorders and the psychosocial interventions that could be used to support mothers. A nursing-led community postnatal follow-up service could also be used to identify women suffering from PTSD symptoms and bonding disorders at an early stage and hence provide timely interventions.
Limitations
There are some limitations in this study. The maternal-infant bonding can change over time. However, since the questionnaires were administered only once, we could not capture the changes in maternal-infant bonding over time. Further longitudinal studies are therefore recommended. In this study, we only evaluated the impact of only 2 of the dimensions of attachment on the variables of interest. Future research could explore the impact of other attachment dimensions. In our study, we included all mothers irrespective of the health condition of their infant. Additional subgroup analysis could be performed to evaluate the impact of various conditions, such as premature birth and life-threatening health conditions, on the maternal-infant bond, resilience, and parental attachment.
Conclusion
The present study suggests that resilience and PTSD can mediate parental attachment and maternal-infant bonding among women at 1 to 3 months after delivery. Therefore healthcare professionals should focus on developing psychosocial interventions aimed at addressing PTSD symptoms and improving resilience might increase parental attachment and maternal-infant bonding after birth. However, The effectiveness of interventions for mother-child relationships needs to be explored in the future.
Availability of data and materials
The datasets generated and/or analysed during the current study are not publicly available due [The work of this manuscript is a part of a research project which is currently not finished.] but are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Gholampour F, Riem MME, van den Heuvel MI. Maternal brain in the process of maternal-infant bonding: review of the literature[J]. Soc Neurosci. 2020;15(4):380–4.
Chandra PS, Desai G, Reddy D, et al. The establishment of a mother-baby inpatient psychiatry unit in India: adaptation of a western model to meet local cultural and resource needs[J]. Indian J Psychiatry. 2015;57(3):290–4.
Brockington I, Fraser C, Wilson D. The Postpartum Bonding Questionnaire: a validation. Arch Womens Ment Health. 2006;9(5):233–42.
Kruijff Id, Choenni V, Groeneweg J, et al. Gastrointestinal symptoms in infants of mothers with a psychiatric history and the role of depression and bonding. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2019;69(6):662–7.
LE B. Maternal bonding, negative affect, and infant social-emotional development: a prospective cohort study[J]. J Affect Disord. 2021;281:926–34.
Van den Bergh BRH, van den Heuvel MI, Lahti M, et al. Prenatal developmental origins of behavior and mental health: the influence of maternal stress in pregnancy[J]. Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2020;117:26–64.
Dearman L, Musonda P, Roberts F, et al. Bonding in women with postnatal anaemia: a pilot case control study looking at postnatal bonding in women who have been diagnosed with anaemia at a University Hospital in the East of England. Arch Gynecol Obstet. 2012;285(5):1243–8.
Edhborg M, Nasreen H, Kabir Z. Impact of postpartum depressive and anxiety symptoms on mothers’ emotional tie to their infants 2–3 months postpartum: a population-based study from rural Bangladesh. Arch Women Ment Health. 2011;14(4):307–16.
Takacs L, Smolik F, Kazmierczak M, et al. Early infant temperament shapes the nature of mother-infant bonding in the first postpartum year[J]. Infant Behav Dev. 2020;58:101428.
Ertmann R, Bang C, Kriegbaum M, et al. What factors are most important for the development of the maternal-fetal relationship? A prospective study among pregnant women in danish general practice[J]. BMC Psychol. 2021;9(1):2.
Nonnenmacher N, Noe D, Ehrenthal JC, et al. Postpartum bonding: the impact of maternal depression and adult attachment style. Arch Womens Ment Health. 2016;19(5):927–35.
Chrzan-Dętkoś M, Łockiewicz M. Maternal romantic attachment, and antenatal and postnatal mother–infant attachment in a sample of polish women[J]. Eur J Dev Psychol. 2015;12(4):429–42.
MH vI. Adult attachment representations, parental responsiveness, and infant attachment: a meta-analysis on the predictive validity of the adult attachment Interview[J]. Psychol Bull. 1995;117(3):387–403.
Bowlby J, Attachment. Attachment and Loss Volume One. Basic Books[J]. Basic Books Classics,1969,1.
Hairston S, Assis IEHJ, Kovo CM. Postpartum Bonding Difficulities and Adultattachment Styles: the mediating role of Postpatum Depression and Childbirth-Related PTSD. Infant Mental Health J. 2018;39(2):198–208.
Mercer R, Ferketich S. Predictors of parental attachment during early parenthood. J Adv Nurs. 1990;15(3):268–80.
Zdolska-Wawrzkiewicz A, Bidzan M, Chrzan-Dętkoś M, et al. The Dynamics of becoming a mother during pregnancy and after Childbirth[J]. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2019;17(1):57.
Macdonald J, Youssef G, Phillips L, et al. The parental bonds of adolescent girls and next-generation maternal-infant bonding: findings from the victorian intergenerational Health Cohort Study. Arch Women Ment Health. 2018;21(2):171–80.
VanBussel J, Spitz B, Demyttenaere K. Three self-report questionnaires of the early mother-to-infant bond: reliability and validity of the dutch version of the MPAS, PBQ and MIBS. Arch Women Ment Health. 2010;13(5):373–84.
Bailey HN, Tarabulsy GM, Moran G, et al. New insight on intergenerational attachment from a relationship-based analysis. Development and psychopathology. 2017;29(2):433–48.
Ballard C, Stanley A, Brockington I. Post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) after childbirth[J]. Br J Psychiatry. 1995;166(4):525–8.
Yildiz PD, Ayers S, Phillips L. The prevalence of posttraumatic stress disorder in pregnancy and after birth: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Affect Disord. 2017;208:634–45.
MacKinnon A, Houazene S, Robins S, et al. Maternal attachment style, interpersonal trauma history, and Childbirth-Related post-traumatic Stress. Front Psych. 2018;9:2379.
Radoš S, Matijaš M, Anđelinović M, et al. The role of posttraumatic stress and depression symptoms in mother-infant bonding. J Affect Disord. 2020;268:134–40.
Ayers S, Eagle A, Waring H. The effects of childbirth-related post-traumatic stress disorder on women and their relationships: a qualitative study[J]. Psychol Health Med. 2006;11(4):389–98.
Handelzalts J, Levy S, Molmen-Lichter M, et al. The association of attachment style, postpartum PTSD and depression with bonding- A longitudinal path analysis model, from childbirth to six months[J]. J Affect Disord. 2021;280(Pt A):17–25.
Connor KM, Davidson JR. Development of a new resilience scale: the Connor-Davidson Resilience Scale (CD-RISC). Depress Anxiety. 2003;18(2):76–82.
Wendy J, Combs-Orme TaT. Resilient parenting: overcoming poor parental Bonding[J]. Soc Work Res. 2007;31(3):135–49.
Holmes J. Roots and routes to resilience and its role in psychotherapy: a selective, attachment-informed review[J]. Attach Hum Dev. 2017;19(4):364–81.
Atzl V, Grande L, Davis E, et al. Perinatal promotive and protective factors for women with histories of childhood abuse and neglect. Child Abuse Neglect. 2019;91:63–77.
Wang MF, W XR, L XM. A Study on Relationships between Post‐traumatic Stress Prevalence and Psychological Resilience. Nurs J Chin People's Liberation Army. 2018;35(16):1–7. Chinese.
Yu X, Zhang J. Factors analysis and psychometric evaluation of the Connor-Davidson ResilienceScale (CD-RISC) with chinese people. Soc Behav Personality. 2007;35(1):19–30.
Brown SJ, Mensah F, Giallo R, et al. Intimate partner violence and maternal mental health ten years after a first birth: an australian prospective cohort study of first-time mothers[J]. J Affect Disord. 2020;262:247–57.
Xu BQ, W L, F L. Reliability and validity of the Chinese version of the Parental Bonding Instrument. Nurs Res. 1999;7:479–89. Chinese.
Cox JL, Holden JM, Sagovsky R. Detection of postnatal depression. Development of the 10-item Edinburgh postnatal depression Scale[J]. Br J Psychiatry. 1987;150:782–6.
Clark R, Tluczek A, Wenzel A. Psychotherapy for postpartum depression: a preliminary report[J]. Am J Orthopsychiatry. 2003;73(4):441–54.
Dunstan DA, Scott N. Norms for Zung’s self-rating anxiety Scale[J]. BMC Psychiatry. 2020;20(1):90.
Grace J. Structural equation modeling and natural systems. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press; 2006.
Plexousakis S, Kourkoutas E, Giovazolias T, et al. School bullying and post-traumatic stress disorder symptoms: the role of parental Bonding[J]. Front Public Health. 2019;7:75.
Schmoeger M, Deckert M, Wagner P, et al. Maternal bonding behavior, adult intimate relationship, and quality of life. Neuro-psychiatrie. 2018;32(1):26–32.
Citak C, Erten E. Impact of Childhood Trauma and attachment on resilience in remitted patients with bipolar Disorder. J Affect Disord. 2021;280(Pt A):219–27.
Woodhouse S, Ayers S, Field A. The relationship between adult attachment style and post-traumatic stress symptoms: a meta-analysis. J Anxiety Disord. 2015;35:103–17.
Kjerulff KH, Attanasio LB, Sznajder KK, et al. A prospective cohort study of post-traumatic stress disorder and maternal-infant bonding after first childbirth[J]. J Psychosom Res. 2021;144:110424.
Lu QR. Moderating effect of psychological resilience between prenatal perceived stress and postnatal depres -sion among perinatal women. Chin Nurs Res. 2019;33(11):1906–10. Chinese.
Pollock A, Campbell P, Cheyne J, et al. Interventions to support the resilience and mental health of frontline health and social care professionals during and after a disease outbreak, epidemic or pandemic: a mixed methods systematic review. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020;11:CD013779.
Thomson M, Sharma V. Pharmacotherapeutic considerations for the treatment of posttraumatic stress disorder during and after pregnancy[J]. Expert Opin Pharmacother. 2021;22(6):705–14.
Furuta M, Horsch A, Ng ESW, et al. Effectiveness of trauma-focused psychological therapies for treating post-traumatic stress disorder symptoms in women following childbirth: a systematic review and Meta-Analysis. Front Psychiatry. 2018;9:591.
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank TopEdit (www.topeditsci.com) for the English language editing of this manuscript.
Funding
This research was supporteded by Wuhan Polytechnic University Academic Scholarship.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
The research design was R N and MX P. Data collection and analysis were R N, MX P. and XW L, the paper was written and reviewed by R N and MX P. R N, MX P. and XW L agreed to be responsible for all aspects of the work and to ensure that issues related to the accuracy or completeness of any part of the study are properly investigated and resolved.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
The study was approved by the Wuhan polytechnic University’s Research Ethics Committee(BME-2021-1-10). Written informed consent was obtained from all participants in the study. All methods were performed in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/. The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver (http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
About this article
Cite this article
Nie, R., Pan, M. & Liu, X. The mediation role of resilience and postpartum traumatic stress disorder on parental attachment and the maternal-infant bonding. BMC Psychol 11, 359 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1186/s40359-023-01370-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s40359-023-01370-5