Abstract
The present study evaluated the potential of carrot (Daucus carota L.) leaf, a non-edible part of carrots, which are among the most consumed vegetables worldwide. The antioxidant activities of 70% ethanol extract (EEC) and hot water extract (HEC) of carrot leaves were compared. The results revealed that the total polyphenol content, total flavonoid content, and DPPH and ABTS radical scavenging activities were higher in EEC than in HEC. Both extracts protected the cells against H2O2-induced toxicity and markedly reduced the levels of reactive oxygen species in RAW 264.7 cells. Moreover, pretreatment of RAW 264.7 cells with EEC and HEC prior to H2O2 (500 μM) exposure increased superoxide dismutase and glutathione peroxidase activities in these cells. Notably, EEC and HEC increased intracellular catalase activity by 36.77 and 6.39 times, respectively. Compared to HEC, EEC remarkably inhibited the production of lipopolysaccharide-induced nitric oxide and reduced the gene expression of IL-6, IL-1β, iNOS, COX-2, and TNF-α. Comparative analysis of the composition of the extracts using HPLC–UV suggested notably higher contents of catechin, chlorogenic acid, caffeic acid, rutin, quercetin, and cynaroside in EEC than in HEC. Collectively, these results imply that carrot leaves are a potentially beneficial natural source of antioxidants and anti-inflammatory compounds in functional foods.
Similar content being viewed by others
Explore related subjects
Find the latest articles, discoveries, and news in related topics.Introduction
As a substantial relationship exists between diet and chronic diseases, the propensity to pursue a healthy diet is steadily increasing [1, 2]. Fruits and vegetables are a source of bioactive substances that are beneficial to health and lead to protection against various chronic diseases [2]. Previous studies have shown that increased fruit and vegetable intake is associated with reduced mortality [3, 4]. Furthermore, aging, resulting from oxidation and inflammation, progressively increases the risk of death from chronic diseases. Vegetables are well-known natural medicines that prevent aging [5, 6]. Particularly, root vegetables such as radishes, carrots, sweet potatoes, burdocks, onions, and ginger are rich in vitamin C, vitamin A, and carotenoids, which contribute to their potential bioactive effects that reduce mortality rates [7]. Importantly, root vegetables can supply and accumulate water and nutrients from the leaves to the roots in the ground [8]. Additionally, several benefits of the aerial parts of root vegetables have been previously reported. The leaves and stems of discarded radishes contain various phenolic constituents with high radical scavenging activity [9], and the leaves of sweet potato, a root vegetable, have high protein and polyphenol content [10]. Moreover, the iron chelate content, which acts as an antioxidant by scavenging reactive oxygen species (ROS), is higher in ginger leaves than in ginger roots [11].
Carrot (Daucus carota L.) is a popular root vegetable cultivated worldwide and an economically important vegetable crop in terms of production area and market size. [12, 13]. Several studies have revealed that carrots, owing to their bioactive compounds, have a variety of antioxidant, anticancer, and anti-inflammatory properties that prevent adverse health effects [14,15,16,17]. The roots of commonly eaten carrots contain large amounts of carotenoids and various other bioactive components [18, 19]. Moreover, similar to other root vegetables, the less useful aerial parts of carrots contain as many bioactive substances as the roots [20,21,22,23,24]. Carrot leaves contain the polyunsaturated fatty acid α-linolenic acid, which has anti-inflammatory effects [21, 22, 25]. Furthermore, the essential oil obtained from carrot leaves is remarkably rich in α-pinene, sabinene, and germacrene, which are known to have antimicrobial effects [23, 26, 27]. Luteolin is also present in subcritically extracted carrot leaves and can contribute to various effects such as antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and anticancer effects [24, 28, 29]. As research on carrot leaves has increased, carrot leaves and stems, which are relatively discarded compared to the roots, can become a potential source of nutrients.
Jeju Island, Korea, which is made of volcanic soil with good drainage, is suitable for producing high-quality carrots; 60% of the carrots grown in Korea are grown on Jeju Island [30]. If the above-ground parts of the carrots, such as the leaves and stems, which are discarded after harvesting on Jeju Island, can be used in proportion to the number of carrots cultivated, the production value of carrots can be improved. In this context, an investigation was conducted to evaluate the antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects of the above-ground parts of carrots grown on Jeju Island, Korea, using ethanol and water, which are the most accessible solvents for extracting natural products and identifying a wide range of compounds [31, 32].
Results and discussion
The extraction yields, total polyphenol and flavonoid content
The yield of carrot (Daucus carota L.) leaves treated with 70% ethanol and hot water is shown in Table 1. The yields of 70% ethanol extract (EEC) and hot water extract (HEC) of carrot leaves were calculated to be 25.80% and 29.48%, respectively, and the yield of the HEC was slightly higher. Previous studies have shown that water, which is polar, has a dielectric constant similar to that of organic solvents when heated, resulting in higher extraction yields than ethanol [33].
The various phytochemicals found in plants and fruits are related to their antioxidant capacities. In particular, phenolic compounds, including flavonoids, are known to exhibit many physiological activities along with antioxidant effects [34]. As result of measuring the total polyphenol content (TPC), the EEC value was 3.26 ± 0.20 mg GAE/g, which was higher than HEC with 1.20 ± 0.01 mg GAE/g (Table 1). Also, HEC (0.80 ± 0.06 mg RE/g) showed a lower total flavonoid content (TFC) than EEC (1.80 ± 0.17 mg RE/g). These results indicate that ethanol extraction of carrot leaves can ensure a higher of phenol content than hot water extraction.
DPPH and ABTS radical scavenging activity
In vitro assays, such as DPPH and ABTS scavenging, are antioxidant experiments used to evaluate free radical scavenging activities [35]. As presented in Fig. 1A, the DPPH radical scavenging activity of both carrot leaf extracts increased in a concentration-dependent manner; however, the DPPH radical scavenging activity of EEC was the highest. The EEC also showed greater antioxidant ability than HEC in ABTS radical scavenging activity (Fig. 1B). EC50 values obtained for each assay are listed in Table 2. Through the EC50 values of EEC (1.35 ± 0.13 mg/mL for DPPH, 0.80 ± 0.10 mg/mL for ABTS), it can be seen that EEC has stronger radical scavenging effect than HEC (7.39 ± 0.93 mg/mL for DPPH, 1.98 ± 0.01 mg/mL for ABTS).
Cytotoxicity protection and reactive oxygen species inhibition effect of carrot leaves in H2O2-induced RAW 264.7 Cells
As a reactive oxygen species (ROS), H2O2 is one of the major cause of oxidative damage as well as causing various pathological processes [36]. H2O2 has high soluble in lipid and aqueous environments, therefore it is free to diffuse into cells and can regulate cell functions or induce cell death [37]. Exposure of RAW 264.7 cells to H2O2 resulted in decreased cell viability in a dose-dependent and time-dependent manner (Additional file 1: Fig. S1). However, the cytotoxicity induced by H2O2 was restored by carrot leaf extract (Fig. 2A). In particular, EEC exerted a greater protective effect on protecting RAW 264.7 cells than HEC. As cell death can be caused by oxidative stress accumulated due to H2O2 [38], we examined whether the two carrot leaf extracts that restored cell viability could affect intracellular ROS levels. As shown in Fig. 2B, H2O2 treatment alone increased intracellular ROS production by 4.60 times compared to that in the control group, whereas in the experimental group pretreated with carrot leaf extract, H2O2-induced ROS production was remarkably reduced in a concentration-dependent manner. In addition, when the intracellular ROS production inhibition or ROS scavenging ability of the carrot leaf extract itself was measured, it significantly decreased rapidly from an extract concentration of 62.5 μg/mL treatment group (Additional file 1: Fig. S2). These observations suggest that carrot leaf extract exhibits a protective effect against H2O2-induced cytotoxicity and an excellent inhibitory effect on intracellular ROS, and that the antioxidant capacity of EEC is superior to that of HEC.
Cytotoxic effects and intracellular reactive oxygen species (ROS) production levels in H2O2-induced RAW 264.7 cells. The cells were pretreated with carrot leaf extract at each concentration prior to exposure to 500 μM H2O2. A Cytotoxicity was assessed by MTT assay. B Intracellular ROS levels were measured using FACS. Values are presented as mean ± SD (n = 3). *p < 0.05, ***p < 0.001 vs. untreated control group; #p < 0.05 vs. H2O2 only treated group
Effect of carrot leaf extract on cellular antioxidant enzyme activity
Catalase, superoxide dismutase (SOD) and glutathione peroxidase (GPx) are the most important enzymes in the cellular oxidative stress defense system and are antioxidants that protect against oxidative damage caused by free radicals [39]. Catalase relieves oxidative stress by degrading H2O2 into oxygen and water molecules [40]. SOD is a front-line antioxidant enzyme that catalyzes the dismutation of superoxide anion free radical (O2−) into molecular oxygen (O2) and H2O2, preventing the production of more reactive compounds, such as peroxynitrite (ONOO−) or hydroxyl radicals (·OH) [41, 42]. GPxs are a family of oxidoreductases that convert H2O2 to water and catalyze the reduction of peroxide radicals to alcohols and oxygen [43]. Catalase, SOD, and Gpx enzyme activities were measured to confirm the effect of ROS-reducing carrot leaf extract on antioxidant enzyme activity. EEC exponentially increased catalase activity by more than 36.77 times in RAW 264.7 cells treated with 500 μM H2O2 (Fig. 3A). HEC also increased catalase activity 6.39 times in a dose-dependent manner in the same concentration range as EEC. In contrast, SOD activity after carrot leaf extract treatment did not increase as much as catalase activity. EEC increased SOD activity in H2O2-induced RAW 264.7 cells up to a concentration of 125 μg/mL, but slightly decreased at higher concentrations, and HEC induced an increase in SOD activity in a dose-dependent manner (Fig. 3B). The increase in GPx activity in cells pretreated with the extract was not remarkable, probably because intracellular GPx activity was not significantly reduced by H2O2 treatment (Fig. 3C). Among the antioxidant enzymes, catalase activity was most markedly increased by carrot leaf extract treatment, suggesting that leaf metabolites may act as catalase activators or affect enzyme protein levels [44]. These data provide strong evidence of antioxidant efficacy and support the antioxidant potential of carrot leaves reported in previous studies [45].
Antioxidant enzyme activity in H2O2-induced RAW 264.7 cells. The cells were pretreated with extracts of carrot leaves at each concentration prior to exposure to 500 μM H2O2. A Catalase, B superoxide dismutase, and C glutathione peroxidase. Values are presented as mean ± SD (n = 3). *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001 vs. untreated control group; #p < 0.05 vs. H2O2 only treated group
Restoration of NRF2 and HO-1 by extract of carrot leaves
Nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 (Nrf2) is a transcription factor responsible for regulating cellular redox balance by inducing the expression of heme oxygenase-1 (HO-1), SOD, and GPx in mammals [46]. HO-1, a gene regulated by Nrf2, participates in heme degradation to produce biliverdin and free iron as metabolites that can neutralize its pro-oxidative effects [47]. In many studies, increased Nrf2 and HO-1 expression is used to verify antioxidant activity [48,49,50], so to evaluate the antioxidant pathway by carrot leaf extract, the expression levels of Nrf2 and HO-1 were confirmed by Western blot. As shown in Fig. 4 and Additional file 1: Fig. S3, Western blot analysis revealed that treatment with carrot leaf extract increased the expression of Nrf2 in total and cytosolic fractions despite H2O2 pretreatment. In the nuclear fraction, induced oxidative stress caused by H2O2 promoted Nrf2 translocation, and EEC and HEC treatment showed that Nrf2 expression was maintained. Moreover, HO-1 expression significantly increased in EEC and HEC. Taken together, these results demonstrated that carrot leaves induce potent antioxidant effects by upregulating the Nrf2/HO-1 pathway.
Effect of carrot leaf extract on Nrf2/HO-1 pathways in H2O2-induced RAW 264.7 cells. The cells were pretreated with extracts of carrot leaves at each concentration prior to exposure to 500 μM H2O2. All protein levels were normalized compared to β-actin as the control using image J. Values are presented as mean ± SD (n = 3). *p < 0.05 vs. untreated control group; #p < 0.05 vs. H2O2 only treated group
Anti-inflammatory effect of carrot leaves in LPS-induced RAW 264.7 cells
Nitric oxide (NO) is an inflammatory mediator that causes inflammation owing to its overproduction under abnormal circumstances, causing cell damage along with ROS, resulting in various diseases [51]. Lipopolysaccharide (LPS) is an activator that mediates the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines, and its efficacy in inhibiting NO production in LPS-induced RAW 264.7 cells is generally a criterion for its anti-inflammatory effect [52]. When NO production was induced by exposing RAW 264.7 cells to 1 μg/mL LPS, the NO production was significantly decreased in a concentration-dependent manner by EEC (Fig. 5A). However, NO production in RAW 264.7, cells treated with HEC, was marginally reduced compared to EEC. A previous study comparing ethanol and water extracts demonstrated that NO production was further inhibited by ethanol extracts [53]. Similarly, it can be assumed that EEC contains more components than HEC, which can maximize the anti-inflammatory efficacy. Additionally, Fig. 5B showed that EEC significantly reduced the expression of several marker genes involved in anti-inflammatory. However, at the same concentration range, HEC did not affect the expression levels of these marker genes (Data not shown).
Anti-inflammatory effects of carrot leaves on LPS-induced RAW 264.7 cells. Cells were pretreated with carrot leaf extract at each concentration prior to exposure to 1 μg/mL LPS. A Nitric oxide (NO) production levels were measured using the NO assay. B qRT-PCR was used to determine gene expression of anti-inflammatory markers after EEC treatment. Values are presented as the mean ± SD (n = 3). ***p < 0.001 vs. untreated control group; #p < 0.05 vs. LPS only treated group
HPLC analysis of extracts from carrot leaves
According to previous studies on carrot leaves, the quercetin content was very abundant in methanol extraction, and the chlorogenic acid content was overwhelming in the 50% ethanol extract [45, 54]. As the content of biological compounds can vary depending on the extraction conditions as well as the environment, such as soil and climate [55, 56], the content of representative phytochemicals contained in Jeju carrot leaf extract grown in volcanic soil was analyzed, and the components of EEC and HEC were compared. HPLC analysis using ten phenolic and flavonoid compounds, catechin, rutin, quercetin, and cymaroside, were found in both extracts (Table 3). Especially, the rutin content in EEC (3738.50 ± 74.90 μg/g DW) was remarkably higher than that in HEC (301.56 ± 42.22 μg/g DW). The quercetin content of EEC (236.53 ± 34.33 μg/g DW) was very high compared to HEC (56.01 ± 7.96 μg/g DW). Rutin and quercetin are commonly found in many fruits and vegetables, including broccoli, apples, and tomatoes [57]. The abundant content of the compounds found in EEC is likely to contribute to its superior antioxidant effect compared to that of HEC. Actually, a Pearson product-moment correlation analysis indicated a strong positive relationship rutin and quercetin with the TPC (R2 = 0.990 and R2 = 0.949), TFC (R2 = 0.979 and R2 = 0.966), DPPH∙ (R2 = 0.990 and R2 = 0.978), ABTS∙ radical scavenging activity (R2 = 0.993 and R2 = 0.977), Catalase activity (R2 = 0.930 and R2 = 0.906) and NO production (R2 = 0.998 and R2 = 0.973) (Additional file 1: Table S1). Chlorogenic acid was only detected in EEC, whereas caffeic acid was detected only in HEC. Chlorogenic acid is known to exhibit anti-inflammatory and antioxidants [58]. The anti-inflammatory effect of carrot leaves may have been exerted by the chlorogenic acid uniquely present in the EEC.
Previous studies have shown that cynaroside, a compound isolated from the ethyl acetate extract of carrot leaves, exhibits anti-inflammatory activity [59]. Cynaroside was analyzed for extracts of carrot leaves, and these compounds were detected at a higher level in EEC than HEC (1150.13 ± 46.86 μg/g DW and 135.22 ± 13.64 μg/g DW, respectively), which had excellent anti-inflammatory efficacy (Table 3 and Additional file 1: Fig. S4). Also, as shown in the Additional file 1: Table S1, there was a significant correlation between cynaroside and NO production (R2 = 0.996). These results suggest that the compounds of carrot leaves from Jeju are different from those of previously reported carrot leaves, and may differ depending on the extraction solvent and conditions. The compounds identified through HPLC analysis provided a solid basis for supporting the antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects of Jeju carrot leaves.
Materials and methods
Sample preparation and extraction
Aerial parts of carrots (Daucus carota L.) harvested in February–March 2022 were obtained from Gujwa-eup, Jeju Island, South Korea. Carrot leaves were used after being freeze-dried. Ground carrot leaf powder (20 g) was extracted with 1 L of 70% ethanol and sonicated thrice for 30 min. In another experiment, ground carrot leaf powder (20 g) was mixed with 1 L distilled water (DW) and heated for 10 min at 121 °C in an autoclave. Then, both mixtures were filtered using Whatman No.2 filter paper, evaporated in a vacuum rotary evaporator at 40 °C, and lyophilized to obtain 70% ethanol extract of carrot leaves (EEC) and hot water extract of carrot leaves (HEC), respectively.
Determination of total polyphenol content
The samples (125 μL) were added to 1.375 mL of DW, and 500 μL of Folin-Ciocalteu’s reagent was added. After incubation for 3 min in the dark, 1 mL of 10% Na2Co3 was added and the mixture was allowed to react for 30 min in the dark. Absorbance was measured at 700 nm using a microplate reader. The results are presented as gallic acid equivalents (mg GAE/g).
Determination of total flavonoid content
The samples (40 μL) were added to 80 μL of DW and 6 μL of 5% NaNO2 was added. After incubation for 5 min, 12 μL of 10% AlCl3 was added and the mixture was allowed to react for 6 min. Then, 40 μL of 1N NaOH and 42 μL of DW were added to the reaction mixture, and the absorbance was measured at 510 nm using a microplate reader. The results are expressed as rutin equivalents (mg RE/g).
DPPH radical scavenging assay
Prior to the assay, a DPPH solution was prepared using 3 mM DPPH in 100% ethanol. Samples (40 μL) were added to 160 μL of 200 μM DPPH solution and incubated at 37 °C for 30 min. The absorbance was measured at 510 nm using a microplate reader. Catechin was used as a positive control. EC50 values were calculated using the GraphPad Prism 7.0 software (GraphPad Software, Inc., La Jolla, CA, USA).
ABTS radical scavenging assay
Before the assay, 7 mM ABTS solution in potassium persulfate was prepared and shaken in the dark for 20 h. Samples (100 μL) were added to 900 μL ABTS solution and allowed to react for 2 min. Absorbance was measured at 734 nm using a UV-1800 spectrophotometer (Shimadzu Co., Kyoto, Japan). α-tocopherol was used as the positive control. EC50 values were calculated using GraphPad Prism 7.0 software (GraphPad Software, Inc., La Jolla, CA, USA).
MTT assay
An MTT assay was performed to measure cell viability. Raw 264.7 cells, which are macrophages, were seeded (1 × 104 cell/well) in 96 well plate and incubated for 24 h. The cells were pre-treated with the samples for 6 h and exposed to 500 μM H2O2 for 3 h. The supernatant was removed, 100 μL of 1 mg/mL MTT solution was added to each well, and the cells were incubated at 37 °C for 3 h. After incubation, the MTT solution was discarded and 150 μL of dimethyl sulfoxide was added to each well for 1 h at room temperature in the dark. Absorbance was measured at 570 nm using a microplate reader.
Flow cytometry
Intracellular reactive oxygen species (ROS) levels were determined using H2DCFDA. Raw 264.7 cells were seeded (20 × 104 cells/dish) in a 60 mm dish and incubated for 24 h. The cells were pre-treated with the samples for 6 h and exposed to 500 μM H2O2 for 1 h. Then, 10 μM H2DCFDA was added to each dish for 20 min, and the collected cells were analyzed using a flow cytometer (BD Biosciences Co., Franklin, NJ, USA) in Bio-Health Materials Core-Facility, Jeju National University.
Catalase, superoxide dismutase and glutathione peroxidase activity
RAW 264.7 cells were seeded (20 × 104 cells/dish) in a 60 mm dish and incubated for 24 h. The cells were pre-treated with the samples for 6 h and exposed to 500 μM H2O2 for 1 h. Cells were collected using a buffer solution, and Catalase, Superoxide dismutase (SOD), and glutathione peroxidase (GPx) activity kits (Cayman Chemical Co., Ann Arbor, MI, USA) were used according to the manufacturer’s instructions.
Nitric oxide assay
RAW 264.7 cells were seeded (10 × 104 cells/well) in 24 well plate and incubated for 18 h. Following incubation, cells were pre-treated with samples for 1 h, and 1 μg/mL LPS was added to each well, except for the control well, and incubated at 37 °C for 24 h. Next, 100 μL of the supernatant was transferred to a new 96 well plate, and 100 μL of Griess reagent was added. The mixture was incubated for 10 min in the dark and the absorbance was measured at 545 nm using a microplate reader.
Western blot
Following exposure to EEC and HEC for 24 h, RAW 264.7 cells were collected with RIPA buffer before sonication, and centrifuged for 25 min at 4 °C. Protein concentration was quantified using a BCA Protein Assay Kit (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA), and the lysates were subjected to 10% sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS) polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Following that, the resolved proteins were transferred to polyvinylidene diffuoride (PVD) membranes. After blocking with skim milk in Tris-buffered salin containing 0.1% Tween (TBST), the membranes were treated with the primary antibody for 24 h at 4 °C and then with a secondary antibody after washing with TBST. Protein bands were visualized using a ChemiDoc (Bio-Rad, Inc., Hercules, CA, USA) and quantified with β-actin as a control using an Image J software (National Institutes of Health, Bethesda, MD, USA). Primary antibodies were used at 1:1,000 dilutions (Nrf2 and HO-1 Cell Signaling Technology, Danvers, MA, USA), except β-actin (1:10,000, Cell Signaling Technology, Danvers, MA, USA), and secondary antibodies were used at 1:5,000 dilutions.
Quantitative real time PCR
RNA from RAW 264.7 cells treated with EEC and HEC was extracted using TRIzol reagent and used for complementary DNA synthesis. Real time PCR was performed using a thermal cycler (Takara Inc., Shiga, Japan). The results were quantified using the 2 − ΔΔCq method [60] and GAPDH used as control. Primer sequences used were as follows: F-5′ATTCACCTCTTCAGAACGAATTG3′R-5′CCATCTTTGGAAGGTTCAGCTTG3′ for IL-6, F-5′AAGATGGCTTATTACAGTGGCAA3′R-5′GTCGGAGATTCGTAGCTCGA3′ for IL-β, F-5′TGATCTACCCTCCCCACGTC3′R-5′ACACACTCTGTTGTGCTCCC3′ for COX2, F-5′AGCAACTACTGCTGGTGGTG3′R-5′TCTTCAGAGTCTGCCCATTG3′ for iNOS, F-5′CTCGAGTGACAAGCCCGTAG3′R-5′ATCTGCTGGTACCACCAGTT3′ for TNF-α.
High performance liquid chromatography analysis
The high performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) was determined using a HPLC-ultraviolet detector (Shimadzu co., Kyoto, Japan) as previously described [61, 62]. EEC and HEC was diluted in 70% ethanol and DW, respectively. Phenolic compounds (gallic acid, 4-hydroxybenzoic aicd, catechin, chlorogenic acid, caffeic acid, p-coumaric acid, ferulic acid, rutin and quercetin) and cynaroside were diluted in methanol. (A) Acetic acid: methanol: water (2.5%: 2.5%: 95%, v/v/v) and (B) acetic acid: water: methanol (2.5%: 5%: 92.5%, v/v/v) used as mobile phase for phenolic compound analysis. The binary gradient elution mode was as follows: 0–10 min, 0–10% B; 10–48 min, 10–80% B, 48–58 min, 80–0% B. The column temperature and flow rate was maintained at 30 °C and 1.0 mL/min, respectively. The 20 μL of samples were injected, and detection wavelength was set to 280 nm. The analysis condition for cynaroside was indicated in Table 4.
Statistical analysis
All experiments were performed in triplicate and analyzed using the GraphPad Prism software (version 7.0). Differences among groups were compared by one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) using Tukey’s method, or multiple t-tests using the Holm-Sidak method. Data are expressed as means ± standard deviation (SD) and statistical significance at p < 0.05.
Availability of data and materials
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article.
Abbreviations
- ABTS:
-
2,2′-Azino-bis(3-ethylbenzothiazoline-6-sulfonic-acid
- DPPH:
-
2,2-Diphenyl-1-picryhydrazyl
- EEC:
-
70% Ethanol extract of carrot leaves
- EC50 :
-
The effective concentration of drug that causes 50% of the maximum response
- GPx:
-
Glutathione peroxidase
- HEC:
-
Hot water extract of carrot leaves
- HPLC:
-
High performance liquid chromatography
- ROS:
-
Reactive oxygen species
- LPS:
-
Lipopolysaccharide
- NO:
-
Nitric oxide
- MTT:
-
3-(4,5-Dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide
- TFC:
-
Total flavonoid content
- TPC:
-
Total polyphenol content
- SOD:
-
Superoxide dismutase
References
Blekkenhorst LC et al (2018) Cardiovascular health benefits of specific vegetable types: a narrative review. Nutrients 10(5):595
Yahia EM, García-Solís P, Celis MEM (2019) Contribution of fruits and vegetables to human nutrition and health. Postharvest physiology and biochemistry of fruits and vegetables. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 19–45
Steffen LM et al (2003) Associations of whole-grain, refined-grain, and fruit and vegetable consumption with risks of all-cause mortality and incident coronary artery disease and ischemic stroke: the Atherosclerosis risk in communities (ARIC) study. Am J Clin Nutr 78(3):383–390
Trichopoulou A et al (2003) Adherence to a Mediterranean diet and survival in a Greek population. N Engl J Med 348(26):2599–2608
Fedichev PO (2018) Hacking aging: a strategy to use big data from medical studies to extend human life. Front Genet 9:483
Mechchate H et al (2022) Vegetables and their bioactive compounds as anti-aging drugs. Molecules 27(7):2316
Agudo A et al (2007) Fruit and vegetable intakes, dietary antioxidant nutrients, and total mortality in Spanish adults: findings from the Spanish cohort of the European prospective investigation into cancer and nutrition (EPIC-Spain). Am J Clin Nutr 85(6):1634–1642
County N (2006) Influence of cadmium on growth of root vegetable and accumulation of cadmium in the edible root. Int J Appl Sci Eng 3:243–252
Beevi SS, Narasu ML, Gowda BB (2010) Polyphenolics profile, antioxidant and radical scavenging activity of leaves and stem of Raphanus sativus L. Plant Foods Hum Nutr 65(1):8–17
Ishida H et al (2000) Nutritive evaluation on chemical components of leaves, stalks and stems of sweet potatoes (Ipomoea batatas poir). Food Chem 68(3):359–367
Chan EWC et al (2008) Antioxidant and tyrosinase inhibition properties of leaves and rhizomes of ginger species. Food Chem 109(3):477–483
Simon PW et al (2008) Carrot. In: Prohens J, Nuez F (eds) Vegetables II. Springer, New York, pp 327–357
Sharma KD et al (2012) Chemical composition, functional properties and processing of carrot—a review. J Food Sci Technol 49(1):22–32
Sun T, Simon PW, Tanumihardjo SA (2009) Antioxidant phytochemicals and antioxidant capacity of biofortified carrots (Daucus carota L.) of various colors. J Agric Food Chem 57(10):4142–4147
Shebaby WN et al (2013) The antioxidant and anticancer effects of wild carrot oil extract. Phytother Res 27(5):737–744
Boivin D et al (2009) Antiproliferative and antioxidant activities of common vegetables: a comparative study. Food Chem 112(2):374–380
Mizgier P et al (2016) Characterization of phenolic compounds and antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties of red cabbage and purple carrot extracts. J Funct Foods 21:133–146
Hart DJ, Scott KJ (1995) Development and evaluation of an HPLC method for the analysis of carotenoids in foods, and the measurement of the carotenoid content of vegetables and fruits commonly consumed in the UK. Food Chem 54(1):101–111
da Silva Dias JC (2014) Nutritional and health benefits of carrots and their seed extracts. Food Nutr Sci 5(22):2147
Kähkönen MP et al (1999) Antioxidant activity of plant extracts containing phenolic compounds. J Agric Food Chem 47(10):3954–3962
Almeida VV et al (2009) Optimization of the carrot leaf dehydration aiming at the preservation of omega-3 fatty acids. Quim Nova 32:1334–1337
Leite CW et al (2011) Chemical characterization of leaves of organically grown carrot Dacus carota L.) in various stages of development for use as food. Food Sci Technol 31:735–738
Ksouri A et al (2015) Chemical composition and antioxidant activity of the essential oil and the methanol extract of Algerian wild carrot Daucus carota L. ssp. carota. (L.) Thell. J Mater Environ Sci. 6(3):784–791
Song R et al (2018) Effect of subcritical water on the extraction of bioactive compounds from carrot leaves. Food Bioprocess Technol 11(10):1895–1903
Ren J, Chung SH (2007) Anti-inflammatory effect of α-linolenic acid and its mode of action through the inhibition of nitric oxide production and inducible nitric oxide synthase gene expression via NF-κB and mitogen-activated protein kinase pathways. J Agric Food Chem 55(13):5073–5080
da Silva Rivas AC et al (2012) Biological activities of α-pinene and β-pinene enantiomers. Molecules 17(6):6305–6316
Park B-I et al (2019) Sabinene suppresses growth, biofilm formation, and adhesion of Streptococcus mutans by inhibiting cariogenic virulence factors. J Oral Microbiol 11(1):1632101
Kang KA et al (2017) Luteolin induces apoptotic cell death via antioxidant activity in human colon cancer cells. Int J Oncol 51(4):1169–1178
Aziz N, Kim M-Y, Cho JY (2018) Anti-inflammatory effects of luteolin: a review of in vitro, in vivo, and in silico studies. J Ethnopharmacol 225:342–358
Park YB, Kim YD, Moon JS (2002) Evaluation of commercial varieties of carrot in Jeju island. J Bio Environ Control 11:144–148
Jacotet-Navarro M et al (2018) What is the best ethanol-water ratio for the extraction of antioxidants from rosemary? Impact of the solvent on yield, composition, and activity of the extracts. Electrophoresis 39(15):1946–1956
Hwang E-S, Do Thi N (2014) Effects of extraction and processing methods on antioxidant compound contents and radical scavenging activities of laver (Porphyra tenera). Prev Nutr Food Sci 19(1):40
Dhanani T et al (2017) Effect of extraction methods on yield, phytochemical constituents and antioxidant activity of Withania somnifera. Arab J Chem 10:S1193–S1199
Zheng W, Wang SY (2001) Antioxidant activity and phenolic compounds in selected herbs. J Agric Food Chem 49(11):5165–5170
Mukherjee S et al (2011) Evaluation of free-radical quenching properties of standard Ayurvedic formulation Vayasthapana Rasayana. BMC Complement Altern Med 11(1):1–6
Scherz-Shouval R, Elazar Z (2011) Regulation of autophagy by ROS: physiology and pathology. Trends Biochem Sci 36(1):30–38
PARk, W.H. (2013) The effects of exogenous H2O2 on cell death, reactive oxygen species and glutathione levels in calf pulmonary artery and human umbilical vein endothelial cells. Int J Mol Med 31(2):471–476
Ryter SW et al (2007) Mechanisms of cell death in oxidative stress. Antioxid Redox Signal 9(1):49–89
Ighodaro O, Akinloye O (2018) First line defence antioxidants-superoxide dismutase (SOD), catalase (CAT) and glutathione peroxidase (GPX): Their fundamental role in the entire antioxidant defence grid. Alex J Med 54(4):287–293
Deisseroth A, Dounce AL (1970) Catalase: Physical and chemical properties, mechanism of catalysis, and physiological role. Physiol Rev 50(3):319–375
Younus H (2018) Therapeutic potentials of superoxide dismutase. Int J Health Sci 12(3):88
Afonso V et al (2007) Reactive oxygen species and superoxide dismutases: role in joint diseases. Joint Bone Spine 74(4):324–329
Li S et al (2000) The role of cellular glutathione peroxidase redox regulation in the suppression of tumor cell growth by manganese superoxide dismutase. Can Res 60(14):3927–3939
Friso G, van Wijk KJ (2015) Posttranslational protein modifications in plant metabolism. Plant Physiol 169(3):1469–1487
Goneim GA, Ibrahim FY, El-Shehawy SM (2011) Carrot leaves: antioxidative and nutritive values. J Food Dairy Sci 2(4):201–211
Loboda A et al (2016) Role of Nrf2/HO-1 system in development, oxidative stress response and diseases: an evolutionarily conserved mechanism. Cell Mol Life Sci 73(17):3221–3247
Chiang S-K, Chen S-E, Chang L-C (2018) A dual role of heme oxygenase-1 in cancer cells. Int J Mol Sci 20(1):39
Ci X et al (2015) The antioxidative potential of farrerol occurs via the activation of Nrf2 mediated HO-1 signaling in RAW 264.7 cells. Chem Biol Interact 239:192–199
Jayawardena TU et al (2018) Sargassum horneri (Turner) C. Agardh ethanol extract inhibits the fine dust inflammation response via activating Nrf2/HO-1 signaling in RAW 264.7 cells. BMC Complementary Altern Med 18(1):1–10
Xiao Q et al (2018) Orientin-mediated Nrf2/HO-1 signal alleviates H2O2-induced oxidative damage via induction of JNK and PI3K/AKT activation. Int J Biol Macromol 118:747–755
Sharma J, Al-Omran A, Parvathy S (2007) Role of nitric oxide in inflammatory diseases. Inflammopharmacology 15(6):252–259
Yoon W-J, Lee NH, Hyun C-G (2010) Limonene suppresses lipopolysaccharide-induced production of nitric oxide, prostaglandin E2, and pro-inflammatory cytokines in RAW 264.7 macrophages. J Oleo Sci 59(8):415–421
Bae J-Y et al (2012) A comparison between water and ethanol extracts of Rumex acetosa for protective effects on gastric ulcers in mice. Biomol Ther 20(4):425
Burri SCM et al (2017) Antioxidant capacity and major phenol compounds of horticultural plant materials not usually used. J Funct Foods 38(Pt A):119–127
Chavan U, Shahidi F, Naczk M (2001) Extraction of condensed tannins from beach pea (Lathyrus maritimus L.) as affected by different solvents. Food Chem 75(4):509–512
Min K et al (2015) The regulation by phenolic compounds of soil organic matter dynamics under a changing environment. Biomed Res Int 2015
Appleton J (2010) Evaluating the bioavailability of isoquercetin. Nat Med J 2(1):1–6
Hwang SJ et al (2014) Anti-inflammatory effects of chlorogenic acid in lipopolysaccharide-stimulated RAW 264.7 cells. Inflamm Res 63(1):81–90
Kim JE, Jo YJ, Lee NH (2018) Anti-inflammatory and anti-bacterial constituents from the extracts of Daucus carota var. sativa aerial parts. J Soc Cosmet Sci Korea. 44(4):427–436
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD (2001) Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2− ΔΔCT method. Methods. 25(4):402–408
Kim JS et al (2022) Antioxidant and antiproliferative activities of solvent fractions of broccoli (Brassica oleracea L.) sprout. Appl Biol Chem 65(1):1–11
Hong JH et al (2021) Analytical method validation of cynaroside in domestic Anthriscus sylvestris (L.) Hoffm. leaves extract for standardization as a functional ingredient using RP-HPLC. J Korean Soc Food Sci Nutr. https://doi.org/10.3746/jkfn.2021.50.4.395
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank Editage (www.editage.co.kr) for English language editing.
Funding
This research was financially supported by the Ministry of Small and Medium-sized Enterprises(SMEs) and Startups(MSS), Korea, under the “Regional Specialized Industry Development Plus Program(R&D, S3260761)” supervised by the Korea Technology and Information Promotion Agency for SMEs(TIPA).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
JSK: formal analysis; investigation; methodology; software; writing—original draft; writing—review and editing. JHL: investigation; funding acquisition. SKC: conceptualization; data curation; funding acquisition; project administration; resources; supervision; validation; visualization; writing—review and editing. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
There are no competing interests to declare.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
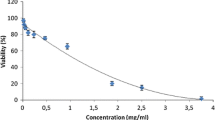
Additional file 1: Figure S1.
Cytotoxicity of H2O2 induced Raw 264.7 cells. Cell viability was measured by MTT assay. Values are mean ± SD (n = 3). Figure S2. Levels of reactive oxygen species (ROS) production in Raw 264.7 cells. Intracellular ROS levels were measured using FACS. Values are mean ± SD (n = 3). *p < 0.05 vs. untreated control group. Figure S3. Cell fractionation of Nrf2 in H2O2-induced RAW 264.7 cells. The cells were pretreated with extracts of carrot leaves at each concentration prior to exposure to 500 μM H2O2. α-tubulin and Histone H3 were used as controls for the protein in cytoplasmic and nuclear fractions, respectively. Values are mean ± SD (n = 3). Figure S4. HPLC-UVD chromatogram of cynaroside composition. (A) cynaroside, (B) EEC and (C) HEC. Table S1. Correlations between the compounds and activities of carrot leaf extract.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
About this article
Cite this article
Kim, J.S., Lim, J.H. & Cho, S.K. Effect of antioxidant and anti-inflammatory on bioactive components of carrot (Daucus carota L.) leaves from Jeju Island. Appl Biol Chem 66, 34 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1186/s13765-023-00786-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s13765-023-00786-2