Abstract
Background
Catheter-associated urinary tract infection is a global problem but it can be prevented with the appropriate implementation of evidence-based guidelines. This study was conducted to assess the level of compliance of healthcare workers with the catheter-associated urinary tract infection prevention guidelines during the insertion of a urinary catheter.
Methods
An observational study using a descriptive cross-sectional design was conducted at Sana’a City hospitals, Yemen. All the nurses and physicians from the governmental, teaching, and private hospitals were eligible to participate in the study. The data collection was performed through convenience sampling from March 2020 to December 2020, using a structured observational checklist prepared specifically for this study.
Results
The majority of the urinary catheter insertions were performed by nurses. There were no written policy or procedures for an urinary catheter insertion and no in-service education or training departments in the majority of the hospitals. The overall mean score of compliance was 7.31 of 10. About 71% of the healthcare workers had a high or acceptable level of compliance and 29% had an unsafe level of compliance. Compliance was low for maintaining aseptic technique throughout the insertion procedure, using a single use packet of lubricant jelly, performing hand hygiene immediately before insertion, and securing the urinary catheter once inserted. Factors affecting the healthcare workers compliance were gender, the working ward/unit of the healthcare workers, the availability of a written policy/procedure and a department or unit for in-service education.
Conclusion
Yemeni healthcare workers’ overall compliance was acceptable but it was unsafe in several critical measures. There is an urgent need for developing, implementing, and monitoring national guidelines and institutional policy and procedures for catheter-associated urinary tract infection prevention. Periodical in-service education and training programs and adequate access to the necessary materials and supplies are paramount.
Similar content being viewed by others
Background
Globally, healthcare associated infections (HAIs) are a persistent danger to patient safety. In 2011, HAIs affected 3.2 million patients in European hospitals with an estimated prevalence of 5.7% [1]. A major risk factor of HAIs is the use of invasive devices (e.g., vascular catheter, artificial airway, and urinary catheter) [1, 2]. Urinary catheterization occurs frequently and an indwelling urinary catheter (IUC) is the most prevalent indwelling device used in healthcare facilities [2, 3]. It is an important and necessary procedure for patient management in clinical settings. Approximately 100 million IUCs are used annually in the world and 16–33% of all [2, 4] hospitalized patients undergo urinary catheterization at least once during their hospitalization [5]. A IUC has many infectious and non-infectious complications, including catheter associated urinary tract infection (CAUTI), mechanical trauma, nonbacterial urethral inflammation, purulent urethritis, urethral strictures, prostatitis, and bladder urolithiasis [3].
CAUTI represents the most prevalent and costly complication associated with the use of IUC [6]. According to the National Healthcare Safety Network (NHSN), CAUTI is defined as the presence of an IUC for at least 2 days with fever and bacteriuria [2]. The source of microorganisms causing CAUTI can be endogenous, from patient’s meatal, vaginal, or rectal colonization, or exogenous, such as contaminated equipment or the hands of the healthcare workers (HCWs) [7]. The microorganisms can enter the urinary tract either by the catheter intraluminal route (internal ascension) from a contaminated urine collection bag or junction between the catheter and drainage tube, or by the catheter extraluminal route (external ascension), through movement along the external surfaces of the IUC in the periurethral mucous sheath, such as during catheter insertion without using aseptic technique [8, 9].
CAUTI is the most prevalent type of HAIs globally [9, 10], and accounts for 30-40% of all HAIs [5, 10]. Internationally, the mean CAUTI incidence is 5.07 per 1,000 catheter days in 703 ICUs in 50 countries [11]. Regionally, the CAUTI incidence was 3.2 per 1,000 catheter days [12]. In Yemen, as in the other low-income countries, the true impact of the CAUTI and the magnitude of the problem remains unidentified due to the weakness or absence of surveillance systems [13]. CAUTI represents a challenge to patient safety and the quality of the healthcare [14]. CAUTI is the largest cause of bacteremia in hospitalized patients [5, 12]. CAUTI increases bacterial resistance [12], length of hospital stay, morbidity, mortality, and healthcare costs [15]. Annually, an estimated 500,000 CAUTI events occur in the United States (US), with 13,000 deaths and $424 to $451 million direct healthcare cost [5, 13, 16]. CAUTI has significant clinical and economic consequences for patients, families, community, HCWs, and the healthcare services [17, 18].
CAUTI is an avoidable iatrogenic healthcare problem [13, 19] and its prevention should be an important goal of the infection prevention initiatives and programs at healthcare facilities. CAUTI preventive strategies are known and recommended in several evidence-based clinical guidelines [3, 6]. The strategies include inserting the UC only when appropriate, aseptic insertion technique, proper maintenance, and timely removal of the IUC [17, 20, 21]. Implementation of the recommendations results in a significant reduction in CAUTI rates [4, 16]. Poor adherence to the evidence-based CAUTI prevention measures contributes to the development of CAUTI and deters the great effort to mitigate iatrogenic infections.
Knowing which recommended CAUTI preventive measures are currently used and to what extent supports the identification of gaps in clinical practice and should be the first step for planning interventions and improving infection prevention efforts and patient safety. However, there is a shortage of studies regarding whether or not the preventive practices recommended by the guidelines are being applied in the healthcare facilities [22]. Due to a lack of similar studies locally and regionally, this study was conducted to assess the level of Yemeni HCWs compliance with the CAUTI prevention guidelines during the insertion of the urinary catheter (UC).
Methods
Study design
A quantitative observational (non-active approach) research was performed using a descriptive cross-sectional design.
Population and settings
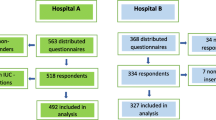
All the HCWs (nurses and physicians) in the hospitals of Sana’a city (Capital of Yemen) were eligible to participate in the study. Based on an estimated population size of 20,000 HCWs, a power level of 0.95, a response rate of 50%, and a margin of error of 0.05, a sample size of 377 HCWs was considered sufficient. A convenient sample of 403 nurses and physicians were approached, of whom 375 agreed to participate, resulting in a response rate of 93.1%. The HCWs were from all the governmental and teaching hospitals and from 3 large private hospitals in Sana’a city, Yemen.
Inclusion and exclusion criteria
HCWs who work in adult inpatient medical or surgical wards, intensive care units (ICUs), and emergency departments (EDs) and perform urinary catheterization and who agreed to participate were included in the study. The HCWs who worked in the pediatric or neonatal units, labor and operating rooms or who refused to participate in the study were excluded.
Data collection tool
The observation of the UC insertion was conducted using a structured observational checklist prepared specifically for this study. The instrument (checklist) contained two parts. The first part contained 13 items related to the characteristics of the HCWs, patients, UC, and workplace. The second part of the instrument contained 10 items (Table 3) related to the best evidence-based practices for CAUTI prevention during the insertion of the UC. The 10 items were in the form of checklist and rated from 0 to 1 point (Not Done = 0, Done = 1), and the total score of compliance range from 0 to 10 points. This score is converted to percentage of the score relative to the total score. The 10-item checklist was developed by the researchers based on the practices identified in the guidelines or recommendations from agencies and professional associations [5, 7, 23,24,25,26]. A panel of 2 infection control specialists, 2 bed side nurses, and 2 physicians assessed the validity of the checklist. The tool was not translated into Arabic as all the observers could speak English.
Data collection
The data collection was performed through convenience sampling from March 2020 to December 2020, by observers who received educational sessions about the best evidence-based practices for CAUTI prevention and how to use the observation checklist. The observers were intern nurses (collected data during their internship rotations in each department) or staff nurses. Data collection was performed during the three shifts by direct observation of the catheter inserters’ compliance to the CAUTI prevention guidelines. The patient same-sex observers used the structured observational checklist to observe and document the UC insertion without participation. During the observation, for each item in the checklist if the inserter performed an action consistent with the CAUTI prevention guidelines, the observer documented “done”; if the inserter demonstrated an action inconsistent with CAUTI prevention guidelines, missed it, or failed to apply it the observer documented “not done”. One observational sheet was filled out for each inserter, regardless of the number of UC insertions they performed. Once a HCW had been initially observed and agreed to participate in the study, he was included in the study sample. Subsequent UC insertions by the same HCW were not observed or counted as new participations within the study sample. This practice was adopted to mitigate potential observation bias, as HCWs were already aware of being under observation. Furthermore, if an inserter was counted multiple times, the data would be skewed depending on the inserter’s performance level.
Ethical considerations
Ethical approval was obtained from the Research Ethical committee of Al-Razi University (022/FORMS/2020). Permission was obtained from the hospitals’ administrations and units’ managers where the study was conducted. Informed consent was obtained from all the participants (inserters). The covert observation was performed in a way that the catheter inserter did not note the presence of the observer to decrease the Hawthorne effect [27, 28]. After the completion of each observation, the inserter was approached in complete secrecy and was informed of the truth and the objectives of study. Inserters were informed that their participation were voluntarily, and they could withdraw from the study without any consequences. They were assured that their anonymity and confidentiality will be maintained throughout the study. If the catheter inserter agreed to participate in the study, he/she was considered a participant in the study. If the catheter inserter did not agree to participate in the study, the observation checklist was excluded from the study (28 participants were excluded). Participants were identified by code to preserve their anonymity. No names or other identification data were collected.
Statistical analysis
Data analysis was done using the Statistical Package for Social Sciences (SPSS) version 25. Compliance with individual items in the checklist is presented as frequency and percentage. The compliance score was calculated for each participant. A test of normality indicated a normal distribution of the score. The compliance score was converted to a dichotomous variable as follows: a score < 50th percentile (< 7.0) was classified as unsafe compliance, a score between the 50th and 75th percentiles (7.0–8.0) was as classified acceptable compliance, and a compliance score > 75th percentile (> 8.0) was classified as high compliance. This scoring was used based on previous observational studies conducted for similar purposes [29]. The relationships between the study variables and the compliance score were measured by using the independent t-test, and the one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA). The factors that were significant in the univariate analysis were entered in the multiple linear regression analysis (enter technique) to determine the factors affecting the HCWs compliance. The accepted level of significance was below 0.05 (p < 0.05).
Results
A total of 403 urinary catheterization procedures of 403 patients were recorded during a period of 9 months. In total, 375 UC insertion observations were analyzed and 28 observations were excluded from data analysis because the catheter inserter did not agree to participate in the study. The majority of the observed urinary catheterization procedures were performed by the nurses (76.8%). Male HCWs performed the majority of the observed catheterization procedures (59.2%). Less than half (41%) of the observed urinary catheterization procedures were in governmental hospitals, 35.5% in private hospitals, and 24% in teaching hospitals. More than a third (36%) of the observed catheterizations were in the medical wards, 32% in ICUs, 23.7% in surgical wards, and 8.8% in EDs. The majority of the wards (82.7%) where the catheterization procedure was performed do not have any written policy or procedure for the UC insertion and the majority (63.5%) did not have a department or unit for continuous education (Table 1).
Table 2 displays that 63.7% of the patients who received the UCs were male, with a mean age of 44.8 years old. The most frequent patient disorder was cardiac disorders (17.9%), followed by neurological and renal disorders (14.9% for each). The most frequent indication for urinary catheterization was the need for urine output monitoring (36%), followed by an unconscious state (27.5%), and perioperative (16.8%). Of note, a retention UC (IUC with a double lumen and balloon) was the most frequent (95.7%) type used in Sana’a hospitals. Silicon catheters were the most frequently used (49.3%), followed by Latex catheters (39.2%). The catheter sizes from 16 to 18 fr were mostly used (55.3%), followed by sizes from 12 to 14 fr (32.3%).
Table 3 reveals the HCWs’ compliance level was high (≥ 85%) in four items of the CAUTI prevention guidelines, including maintaining the urine bag below the level of the patient and off the floor, cleaning the urethral meatus with antiseptic solution before catheter insertion, maintaining an unobstructed urine flow, and using sterile gloves, drapes and sponges. The HCWs’ compliance level with using a small size catheter and performing hand hygiene immediately after insertion was acceptable. However, it is disturbing that the compliance was below the acceptable level (< 70%) in the remaining four items, including the performing of hand hygiene immediately before UC insertion, using a single use packet of lubricant jelly, securing the UC to a leg with tape once inserted, and maintaining the aseptic technique throughout the UC insertion procedure. It is alarming that the lowest compliance level (41%) was observed for an important item related to maintaining aseptic technique throughout the UC insertion procedure.
The overall mean score of compliance was 7.31 out of 10. Less than quarter of the observed HCWs (22.7%) were categorized in the high level of compliance (> 8 out of 10) and 48.5% categorized in the acceptable level (7 to 8 out of 10). Of note, 29% of the observed HCWs were categorized in the unsafe level of compliance (< 7 out of 10). As shown in Table 4, the female HCWs had significantly higher compliance with the CAUTI prevention guidelines compared to the male HCWs (p = 0.011). The HCWs working in the ICUs demonstrated significantly higher level of compliance than the HCWs in the other wards (p = 0.021). HCWs working in the wards that have a written policy for UC insertion and maintenance, and the HCWs working in the hospitals with an in-service education department had significantly higher compliance than the HCWs working in the wards without a written policy or a continuous in-service education department (p = < 0.001).
In the multivariate analysis (Table 5), the females had a significantly higher level of compliance compared to the males (p = 0.019), and the HCWs in the ICUs compared to the group working in the EDs (p = 0.006), compliance was significantly higher in wards with a written policy for catheter insertion and maintenance (p = 0.005) and in the group with a continuous education department in their hospitals (p < 0.001). The total model was significant (p = 0.001) and the data fit the model. The model explains 15% of the variance of the compliance score. There was no multicollinearity.
Discussion
This study is to our knowledge, the first national and regional observational study of CAUTI prevention practices of physicians and nurses. This study provides novel insight into CAUTI prevention area and identifies the gap between the evidence-based recommendations and the current HCWs practices for CAUTI prevention. The overall mean score of compliance of Yemeni HCWs barely reached the acceptable level (7.31 out of 10). The compliance to several critical CAUTI prevention guideline measures was low, which decreased the general compliance of Yemeni HCWs. This level of Yemeni HCWs compliance may be linked, as the study results indicated, to the lack of a written policy or procedure for the UC insertion and the absence of a department/unit for the in-service education in the majority of the hospitals. We hypothesize that the Yemeni HCWs compliance level with CAUTI prevention guidelines can also be explained by the current state of healthcare services in the Yemen, including understaffing, inadequate working conditions, frequent shortages of necessary supplies, and overcrowded hospitals. However, these factors were not examined in this study. This deterioration in healthcare services reflects the difficult living conditions, as well as stress and frustrations in the daily life of Yemeni people. The dominant political violence, instability, and deteriorating economic conditions of the country are the primary causes underlying all the above deterioration.
Of note, 29% of the observed Yemeni HCWs were in the unsafe level of compliance (scored < 7 out of 10). Interestingly, this finding is lower than reported in a self-reported study by Algarni et al. (2019) who found that 83.94% of Saudi nurses have a poor level of practice with CAUTI prevention [30]. Similarly, Mong et al. (2022) [10], Conway et al. (2012) [22], Opina and Oducado (2014) [31], and Methu et al. (2019) [32] found that the implementation of guidelines for CAUTI prevention is inadequate and insufficient.
The finding of this study that the ward in which the HCW was working affect their level of compliance with the CAUTI prevention practices was in line with literature [30, 33]. The lower compliance level of the HCWs in the EDs could be attributed to the nature of the ED environment and certain prevalent ED practices. The infection prevention practices are usually overlooked in the fast-paced environment where life-threatening conditions take priority [34]. The findings of our study that the female HCWs had a significantly higher compliance level with the CAUTI prevention practices than their male colleagues was in contrast to an earlier study, concluding that the gender of the HCW who inserted the UC does not affect the compliance level [10, 33].
This study found that, in line with Oman et al. (2012), the presence of a policy positively impacted the HCWs’ compliance [35]. Policies and procedures in healthcare are aimed to standardize practice, to incorporate evidence-based practices, and to attain regulatory compliance. Our finding that the presence of an in-service education department/unit in the hospital positively affect the HCWs’ compliance was supported by Saint et al. (2016), who concluded that hospitals with a residency training program were > 4 times as likely to adopt a policy than hospitals without residency training programs [20]. Similarly, Oman et al. (2012) reported that training positively impact nurses’ compliance and CAUTI rates [35]. Medical and nursing education and healthcare services suffered extensively from a lack of essential resources due to the conflict in Yemen. A significant proportion of the HCWs studied, graduated, and worked during the internal conflict. In most Yemeni hospitals, quality projects and in-service education programs have been suspended or terminated. Infection prevention becomes a low priority in a conflict setting.
Although many CAUTI preventive measures had a good compliance rate, no item had 100% compliance. About one third (32.8%) and one fifth (20.3%) of the observed HCWs did not perform hand hygiene before and after catheter insertion, respectively. This finding is consistent with the other studies reported that from 10 to 40% of the nurses did not perform hand washing prior to UC insertion [30,31,32,33, 36, 37]. While the Yemeni HCWs compliance was acceptable in using a small size catheter (77.9%), an unsafe level of compliance was observed with the use of single pack lubricant jelly (50.4%) and securing the UC once inserted (67.7%). This finding contradicted the finding of other studies that reported 84% of nurses used a single pack lubricant jelly [36] and 30% secured the UC once inserted [32].
Although maintenance of aseptic technique throughout the UC insertion procedure is a critical item in the CAUTI prevention guidelines, the lowest compliance level (41.1%) was observed for this important item. This finding contradicted the finding of several studies that reported 74–95% compliance rate with aseptic technique during the UC insertion [1, 37, 38].
Of note, 87.5% of Yemeni HCWs clean the urethral meatus with an antiseptic before UC insertion and 84.8% use sterile gloves in UC insertion. This compliance level is lower than that reported in previous study that 97% of nurses always use sterile gloves [37]. The majority of the Yemeni HCWs (> 85%) followed good practices in terms of keeping the tubing and collecting bag free from kinking and below the level of the patient’ bladder. Studies reported that these items were complied with at all times, which is congruent with our study [14, 33, 39].
The low adherence of Yemeni HCWs to some preventive measures could be attributed to the inconsistent or inconvenient locations of hand sanitizers, limited resources and lack of supplies, such as the hand hygiene preparations, sterile gloves, different sizes of UC, single-use lubricant gel and a catheter-securing device in most hospitals [33, 34, 38]. This is one of the catastrophic consequences of the internal armed conflict during the last eight years in Yemen.
Compliance with isolated CAUTI preventive measures is not effective, prevention of CAUTI requires that all the HCWs are fully compliant to all the recommended preventive measures collectively and simultaneously. This study suggests that there is definite room for improvement in Yemeni HCWs practices. There is urgent need for developing, implementing, and monitoring national guidelines and an institutional policy and procedures for CAUTI prevention to reduce the gap between the evidence-based recommendations and the HCWs practices. To comply fully with the CAUTI preventive measures requires the provision of the necessary materials and supplies; however, the availability of the materials and supplies is not sufficient if they are not used correctly. There must be periodical in-service education and training programs for HCWs and adequate access to the necessary materials and supplies.
Limitations
Firstly, we focused on the HCWs compliance with the CAUTI prevention guidelines during UC insertion procedure only. The other UC care procedures were beyond the scope of the study. Secondly, the sample of hospitals represent Sana’a city (capital of Yemen). The situation in the hospitals outside Sana’a city may be worse. Additional studies integrating the assessment of the actual practice and auditing the impact on the CAUTI incidence are recommended.
Conclusions
Yemeni HCWs’ overall compliance was acceptable but it was unsafe in several critical measures, such as aseptic technique, using a single use packet of lubricant jelly, performing hand hygiene before insertion, and securing the UC once inserted. Several factors significantly affect the HCWs compliance with the CAUTI prevention guidelines, including gender and the working ward/unit of the HCWs, and the availability of a written policy or procedure and a department or unit for continuous in-service education.
Data Availability
The raw data are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Abbreviations
- ANOVA:
-
One-Way Analysis of Variance
- CAUTI:
-
Catheter Associated Urinary Tract Infection
- EDs:
-
Emergency departments
- HAIs:
-
Healthcare Associated Infections
- HCWs:
-
Healthcare Workers
- IUC:
-
Indwelling Urinary Catheter
- ICUs:
-
Intensive Care Units
- NHSN:
-
National Healthcare Safety Network
- SPSS:
-
Statistical Packages for Social Sciences
- UC:
-
Urinary Catheter
- US:
-
United States
References
Huis A, Schouten J, Lescure D, Krein S, Ratz D, Saint S, et al. Infection prevention practices in the Netherlands: results from a national survey. Antimicrob Resist Infect Control. 2020;9:7. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13756-019-0667-3.
Dehghanrad F, Nobakht-e-Ghalati Z, Zand F, Gholamzadeh S, Ghorbani M, Rosenthal V. Effect of instruction and implementation of a preventive urinary ract Infection bundle on the incidence of catheter associated urinary tract Infection in intensive care unit patients. Electron J Gen Med. 2019;16(2):em131. https://doi.org/10.29333/ejgm/94099.
Nicolle LE. Catheter associated urinary tract Infections. Antimicrob Resist Infect Control. 2014;3:23. https://doi.org/10.1186/2047-2994-3-23.
Al-Hameed FM, Ahmed GR, AlSaedi AA, Bhutta MJ, Al-Hameed FF, AlShamrani MM. Applying preventive measures leading to significant reduction of catheter associated urinary tract Infections in adult intensive care unit. Saudi Med J. 2018;39(1):97–102. https://doi.org/10.15537/smj.2018.1.20999.
Halm MA, O’Connor N. Do system-based interventions affect catheter-associated urinary tract Infection? Am J Crit Care. 2014;23(6):505–9. https://doi.org/10.4037/ajcc2014689.
Magill SS, Edwards JR, Bamberg W, Beldaus ZG, Dumyati G, Kainer MA, et al. Multistate point-prevalence survey of health care-associated Infections. N Engl J Med. 2014;370:1198–208. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa1306801.
Gould CV, Umscheid CA, Agarwal RK, Kuntz G, Pegues DA, Healthcare infection Control Practices Advisory Committee (HICPAC). Guideline for Prevention of Catheter-Associated Urinary Tract Infections 2009. US: Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, last Update: June 6, 2019 [cited 2021 June 10]. Available from: https://www.cdc.gov/infectioncontrol/guidelines/cauti/.
Trautner BW, Darouiche RO. Catheter-associated Infections: pathogenesis affects prevention. Arch Intern Med. 2004;164(8):842–50. https://doi.org/10.1001/archinte.164.8.842.
Rebmann T, Greene LR. Preventing catheter-associated urinary tract Infections: an executive summary of the Association for Professionals in Infection Control and Epidemiology, Inc, Elimination Guide. Am J Infect Control. 2010;38(8):644–6.
Mong I, Ramoo V, Ponnampalavanar S, Chong MC, Wan Nawawi WN. Knowledge, attitude and practice in relation to catheter-associated urinary tract Infection (CAUTI) prevention: a cross‐sectional study. J Clin Nurs. 2022;31(1–2):209–19. https://doi.org/10.1111/jocn.15899.
Rosenthal VD, Al-Abdely HM, El-Kholy AA, AlKhawaja SAA, Leblebicioglu H, Mehta Y, et al. International Nosocomial Infection Control Consortium report, data summary of 50 countries for 2010–2015: device-associated module. Am J Infect Control. 2016;44(12):1495–504. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ajic.2016.08.007.
Al Nasser W, El-Saed A, Al-Jardani A, Althaqafi A, Alansari H, Alsalman J, et al. Rates of catheter-associated urinary tract Infection in tertiary care hospitals in 3 Arabian Gulf countries: a 6-year surveillance study. Am J Infect Control. 2016;44(12):1589–94. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ajic.2016.06.030.
Menegueti MG, Ciol MA, Bellissimo-Rodrigues F, Auxiliadora-Martins M, Gaspar GG, Canini SRMDS, et al. Long-term prevention of catheter-associated urinary tract Infections among critically ill patients through the implementation of an educational program and a daily checklist for maintenance of indwelling urinary catheters: a quasi-experimental study. Med (Baltim). 2019;98(8):e14417. https://doi.org/10.1097/MD.0000000000014417.
Mota EC, Oliveira AC. Prevention of catheter-associated urinary tract Infection: what is the gap in clinical practice? Texto & Contexto Enfermagem. 2019;28:e20180050. https://doi.org/10.1590/1980-265X-TCE-2018-0050.
Liang C, Huang T, Yang S, Su JY, Mu P, Curia M. Prevention of catheter associated urinary tract Infection in neurological post- operation patients: a best practice implementation project. JBI Database of Systematic Reviews and Implementation Reports. 2019;17(6):1256–67. https://doi.org/10.11124/JBISRIR-2017-003945.
Davis KF, Colebaugh AM, Eithun BL, Klieger SB, Meredith DJ, Plachter N, et al. Reducing catheter-associated urinary tract Infections: a quality-improvement initiative. Pediatrics. 2014;134(3):e857–64. https://doi.org/10.1542/peds.2013-3470.
Sampathkumar P. Reducing catheter-associated urinary tract Infections in the ICU. Curr Opin Crit Care. 2017;23(5):372–7. https://doi.org/10.1097/MCC.0000000000000441.
Chenoweth C, Saint S. Preventing catheter-associated urinary tract Infections in the intensive care unit. Crit Care Clin. 2013;29:19–32. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ccc.2012.10.005.
Rosenthal VD, Todi SK, Álvarez-Moreno C, Pawar M, Karlekar A, et al. Impact of a multidimensional Infection control strategy on catheter-associated urinary tract Infection rates in the adult intensive care units of 15 developing countries: findings of the International Nosocomial Infection Control Consortium (INICC). Infection. 2012;40(5):517–26. https://doi.org/10.1007/s15010-012-0278-x.
Saint S, Greene MT, Krein SL, Rogers MA, Ratz D, Fowler KE, et al. A program to prevent catheter-associated urinary tract Infection in acute care. N Engl J Med. 2016;374(22):2111–9. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa1504906.
Henry M. Evaluation of evidence-based practice of catheter associated urinary tract Infections prevention in a critical care setting: an integrative review. J Nurs Educ Pract. 2018;8(7):22–30. https://doi.org/10.5430/jnep.v8n7p22.
Conway LJ, Pogorzelska M, Larson E, Stone PW. Adoption of policies to prevent catheter-associated urinary tract Infections in United States intensive care units. Am J Infect Control. 2012;40(8):705–10. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ajic.2011.09.020.
Lo E, Nicolle LE, Coffin SE, Gould C, Maragakis LL, Meddings J, Society for Healthcare Epidemiology of America (SHEA), et al. Infectious Diseases Society of America (IDSA). Strategies to Prevent Catheter-Associated urinary tract Infections in Acute Care hospitals: 2014 update. Infect Control Hosp Epidemiol. 2014;35(8):464–79. https://doi.org/10.1086/675718.
Geng V, Cobussen-Boekhorst H, Farrell J, Gea-Sánchez M, Pearce I, Schwennesen T et al. European Association of Urology Nurses (EAUN). Evidence-based guidelines for best practice in urological health care. Catheterization indwelling catheters in adults urethral and suprapubic. (February 2012). Available from: https://www.nursing.nl/PageFiles/11870/001_1391694991387.pdf.
Institute for Healthcare Improvement. How-to Guide: Prevent Catheter- Associated Urinary Tract Infection. 2011 [updated December 2011; cited March 2019]. Available from: https://www.urotoday.com/images/catheters/pdf/IHIHowtoGuidePreventCAUTI.pdf.
Meddings J, Saint S, Fowler KE, Gaies E, Hickner A, Krein SL, et al. The Ann Arbor criteria for appropriate urinary catheter use in hospitalized medical patients: results obtained by using the RAND/UCLA appropriateness method. Ann Intern Med. 2015;162(9 Suppl):1–34. https://doi.org/10.7326/M14-1304.
Aloush SM, Alsaraireh FA. Nurses’ compliance with central line associated blood stream Infection prevention guidelines. Saudi Med J. 2018;39(3):273–9. https://doi.org/10.15537/smj.2018.3.21497.
Aloush SM. Nurses’ implementation of ventilator-associated Pneumonia prevention guidelines: an observational study in Jordan. Nurs Crit Care. 2017;23(3):147–51. https://doi.org/10.1111/nicc.12323.
Al-Sayaghi KM. Critical care nurses’ compliance and barriers toward ventilator associated Pneumonia prevention guidelines: cross-sectional survey. J Taibah Univ Med Sci. 2021;16(2):274–82. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtumed.2020.12.001.
Algarni SS, Sofar SM, Wazqar DY. Nurses’ knowledge and practices toward prevention of catheter-associated urinary tract Infection at King Abdulaziz University hospital. J Health Med Nurs. 2019;4(1):50–73.
Opina ML, Oducado RM. Infection control in the use of urethral catheters: knowledge and practices of nurses in a private hospital in Iloilo City. Asia Pac J Educ Art Sci. 2014;1(5):93–100.
Methu CW, Mwenda CM, Mbugua RG. Nurse factors influencing compliance with CDC guidelines for catheter associated urinary tract Infection prevention in a referral hospital in Kenya. Int J Nurs Sci. 2019;9(3):70–6. https://doi.org/10.5923/j.nursing.20190903.03.
Taleschian-Tabrizi N, Farhadi F, Madani N, Mokhtarkhani M, Kolahdouzan K, Hajebrahimi S. Compliance with guideline statements for urethral catheterization in an Iranian teaching hospital. Int J Health Policy Manag. 2015;4(12):805–11. https://doi.org/10.15171/ijhpm.2015.128.
Manojlovich M, Saint S, Meddings J, Ratz D, Havey R, Bickmann J, et al. Indwelling urinary catheter insertion practices in the emergency department: an observational study. Infect Control Hosp Epidemiol. 2016;37(1):117–9. https://doi.org/10.1017/ice.2015.238.
Oman KS, Makic MBF, Fink R, Schraeder N, Hulett T, Keech T, et al. Nurse-directed interventions to reduce catheter-associated urinary tract Infections. Am J Infect Control. 2012;40(6):548–53. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ajic.2011.07.018.
McNulty CA, Bowen J, Foy C, Gunn K, Freeman E, Tompkins D, et al. Urinary catheterization in care homes for older people: self-reported questionnaire audit of catheter management by care home staff. J Hosp Infect. 2006;62(1):29–36. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhin.2005.03.008.
Fink R, Gilmartin H, RichardA, Capezuti E, Boltz M, Wald H. Indwelling urinary catheter management and catheter-associated urinary tract Infection prevention practices in nurses improving care for Healthsystem elders hospitals. Am J Infect Control. 2012;40(8):715–20. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ajic.2011.09.017.
Apisarnthanarak A, Ratz D, Greene MT, Khawcharoenporn T, Weber DJ, Saint S. National survey of practices to prevent health care-associated Infections in Thailand - the role of prevention bundles. Am J Infect Control. 2017;45(7):805–10. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ajic.2017.01.014.
Snyder MD, Priestley MA, Weiss M, Hoegg CL, Plachter N, Ardire S, Thompson A. Preventing catheter- associated urinary tract Infections in the pediatric intensive care unit. Crit Care Nurse. 2020;40(1):e12–7.
Acknowledgements
The authors thank the nursing staff and internship nurses for their assistance with data collection for this observational study. The authors also thank all HCWs at each hospital who assisted with conducting the study in their hospital, including the nurses and physicians inserting the UC during the study.
Funding
This research did not receive any type of grant from funding agencies.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conception and design, K.M.A., A.K.A., M.A., A.M.S., and H.R.A.; Data collection, T.A.H.A., S.A.A., and G.G.A.; Data analysis, K.M.A., and A.K.A.; writing and reviewing the initial draft, K.M.A., A.K.A., T.A.H.A., S.A.A., S,A.A., M.A.A., K.A.S., G.G.A., M.A., R.A.E., and Z.T.S.; All authors have critically reviewed and approved the final draft and are responsible for the content of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
The research was performed in accordance with the ethical practice outlined in the declaration of Helsinki. Ethical approval was obtained from the Research Ethical Committee of Alrazi University. Permission was taken from the hospitals’ administrations and units’ managers where the study was conducted. Informed consent was obtained from all the participants (inserters).
Consent for publication
Non applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/. The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver (http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
About this article
Cite this article
Al-Sayaghi, K.M., Alqalah, T.A.H., Alkubati, S.A. et al. Healthcare workers’ compliance with the catheter associated urinary tract infection prevention guidelines: an observational study in Yemen. Antimicrob Resist Infect Control 12, 144 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1186/s13756-023-01352-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s13756-023-01352-7